目录
一、单链表
二、双向循环链表
三、判断链表是否带环
四、链表的回文结构判断
五、复制带随机指针的链表
一、单链表
优点:头部增删效率高,动态存储无空间浪费
缺点:尾部增删、遍历效率低,不支持随机访问节点
头结点:单链表头结点可有可无,带头结点更方便进行初始化
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int NodeData;
typedef struct List
{
NodeData data;
struct List* next;
}List;
void Init(List* list)
{
assert(list);
list->next = (List*)malloc(sizeof(List)); // 空头结点
list->next->next = NULL;
}
bool Empty(List* list)
{
assert(list);
return list->next->next == NULL;
}
void Push(List* list, NodeData x)
{
assert(list);
List* node = (List*)malloc(sizeof(List));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
return;
}
node->data = x;
node->next = list->next->next;
list->next->next = node;
}
void Pop(List* list)
{
assert(list);
if (!Empty(list))
{
List* cur = list->next->next;
list->next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = NULL;
}
}
size_t Size(List* list)
{
assert(list);
size_t size = 0;
List* cur = list->next->next;
while (cur)
{
++size;
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("the list size = %d\n", size);
return size;
}
void PrintList(List* list)
{
assert(list);
if (!Empty(list))
{
List* cur = list->next->next;
printf("%d ", cur->data);
while (cur->next)
{
printf("-> %d ", cur->next->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
List list;
Init(&list);
Push(&list, 1);
Push(&list, 3);
Push(&list, 5);
Push(&list, 7);
Size(&list);
PrintList(&list);
Pop(&list);
Pop(&list);
Pop(&list);
Pop(&list);
Pop(&list);
Size(&list);
PrintList(&list);
return 0;
}二、双向循环链表
特征:
- 每个Node都有一个data值,一个prev前驱指针和一个next后置指针
- C++的STL中封装的就是双向循环链表
- 头部增删和尾部增删效率一样高,但依然不支持随机访问
- 链表循环且带头结点,最后一个Node指向头结点,头结点也指向最后一个Node
- 空链表的前驱和后置指针都指向头结点,头结点不存放数据
代码分析:
Push和Pop函数通过调用Insert和Erase函数对Node进行按址增删,减少了代码的复用
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int NodeData;
typedef struct List
{
NodeData data;
struct List* prev;
struct List* next;
}List;
void Init(List* list)
{
assert(list);
list->prev = list;
list->next = list;
}
bool Empty(List* list)
{
assert(list);
return list->next == list;
}
void Insert(List* list, NodeData x, List* pos)
{
assert(list && pos);
List* prev = pos->prev;
List* node = (List*)malloc(sizeof(List));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
node->data = x;
node->next = pos;
pos->prev = node;
node->prev = prev;
prev->next = node;
}
void Erase(List* list, List* pos)
{
assert(list && pos);
List* prev = pos->prev;
List* next = pos->next;
prev->next = next;
next->prev = prev;
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
void PushFront(List* list, NodeData x)
{
assert(list);
Insert(list, x, list->next);
}
void PushBack(List* list, NodeData x)
{
assert(list);
Insert(list, x, list);
}
void PopFront(List* list)
{
assert(list);
Erase(list, list->next);
}
void PopBack(List* list)
{
assert(list);
Erase(list, list->prev);
}
size_t Size(List* list)
{
assert(list);
size_t size = 0;
List* cur = list->next;
while (cur != list)
{
++size;
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("the list size is %d\n", size);
return size;
}
void PrintList(List* list)
{
assert(list);
if (!Empty(list))
{
List* cur = list->next;
printf("%d ", cur->data);
while (cur->next != list)
{
printf("-> %d ", cur->next->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
List list;
Init(&list);
PushFront(&list, 1);
PushFront(&list, 3);
PushFront(&list, 5);
PushBack(&list, 2);
PushBack(&list, 4);
PushBack(&list, 6);
Size(&list);
PrintList(&list); //5 -> 3 -> 1 -> 2 -> 4 -> 6
PopFront(&list);
PopBack(&list);
PopBack(&list);
PushFront(&list, 10);
PushBack(&list, 20);
Size(&list);
PrintList(&list); //10 -> 3 -> 1 -> 2 -> 20
return 0;
}三、判断链表是否带环
链表带环:尾结点指向链表的某个节点
函数设计:设置快慢指针,根据链表头结点head,判断链表是否带环,返回bool值
bool IsCircle(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if (fast == slow)
return true;
}
return false;
}四、链表的回文结构判断
函数要求:时间复杂度为O(n), 额外空间复杂度为O(1), 返回bool值
函数设计:
- 用快慢指针找到链表中间节点
- 将中间节点之后的链表逆置
- 设置头指针和中间节点指针进行回文判断
- 将中间节点之后的链表再次逆置, 还原链表结构
struct ListNode* MidNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
struct ListNode* ReverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* p1 = NULL;
struct ListNode* p2 = head;
struct ListNode* p3 = NULL;
if (p2 != NULL)
p3 = head->next;
while (p3)
{
p2->next = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = p3;
p3 = p3->next;
}
p2->next = p1;
p1 = p2;
p2 = p3;
return p1;
}
bool ChkPalindrome(struct ListNode* A)
{
struct ListNode* mid = MidNode(A);
mid = ReverseList(mid);
struct ListNode* front = A;
struct ListNode* back = mid;
struct ListNode* cur = back;
int flag = 1;
while (back && front != cur)
{
if (front->val != back->val)
{
flag = 0;
break;
}
front = front->next;
back = back->next;
}
mid = ReverseList(mid); //再次逆置,防止链表结构被破坏
if (flag == 0)
return false;
return true;
}五、复制带随机指针的链表
函数要求:
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。
每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码只接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。

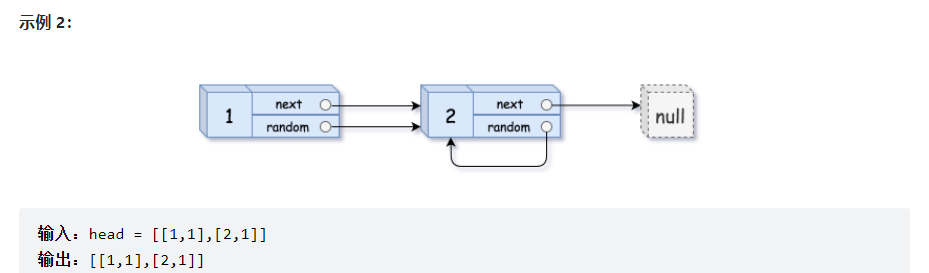
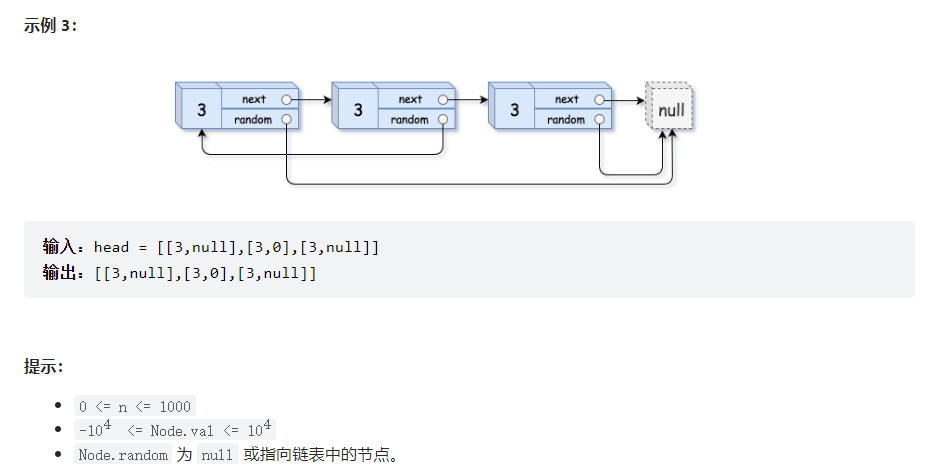
函数设计:
- 在每个节点后面复制一个一模一样的copy节点
- copy->random = cur->random->next
- 将copy部分和原节点断开
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head)
{
//1. 在每个节点后面复制一个相同的节点
struct Node* cur = head;
if (cur == NULL)
return NULL;
while (cur)
{
struct Node* copy = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
copy->val = cur->val;
copy->next = cur->next;
cur->next = copy;
cur = copy->next;
}
//2. copy->random = cur->random->next
cur = head;
while (cur)
{
struct Node* copy = cur->next;
if (cur->random == NULL)
copy->random = NULL;
else
copy->random = cur->random->next;
cur = copy->next;
}
//3. 将copy部分和原链表断开
cur = head;
struct Node* copy = cur->next;
struct Node* copytail = copy;
while (cur)
{
struct Node* next = copytail->next;
cur->next = next;
if (next)
copytail->next = next->next;
cur = next;
copytail = copytail->next;
}
return copy;
}
![[补充]托福口语21天——day2 课堂内容](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9e5d18b5b2854a9b91a7d38655da988a.png)







![【玩转Linux操作】详细讲解expr,read,echo,printf,test,[]等命令](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/435ac06145bc478ba4e7a7fa70623766.png)