线程优先级翻转
前面讲到信号量和互斥量,二者有些区别:
信号量,可以在任何线程(以及中断)释放,用于同步,线程只在获得许可时才可以运行,强调的是运行步骤;
互斥量,只能由持有它的线程释放,即在同一个线程中,获取和释放成对出现,只有获得锁的钥匙的线程才可以运行,强调的是许可和权限;
注意:使用信号量可能导致线程的优先级翻转,而互斥量可以通过优先级继承的方法解决优先级翻转问题。
优先级翻转,当一个高优先级线程试图通过某种互斥IPC对象机制访问共享资源时,如果该IPC对象已被一低优先级的线程所持有,而在低优先级线程运行过程中可能又被其他中等优先级的线程占用,因此造成高优先级被较低优先级的线程阻塞的情况。
优先级翻转会造成高优先级线程的实时性得不到保证。
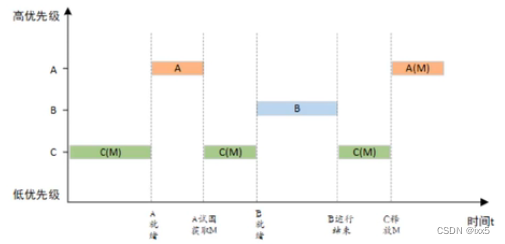
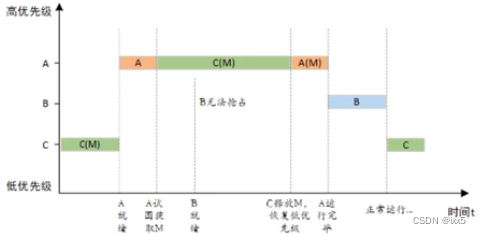
RT-Thread中,可通过互斥量的优先级继承算法,有效解决优先级翻转问题:
提高占用共享资源的低优先级线程的优先级到与所以等待该共享资源的线程中优先级最高的那个线程的优先级,这样可以更快地执行然后释放共享资源,当原占有共享资源的低优先级释放该资源后,优先级恢复到原来的优先级。
官方示例代码:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2006-2018, RT-Thread Development Team
*
* SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
*
* Change Logs:
* Date Author Notes
* 2018-08-24 yangjie the first version
*/
/*
* 程序清单:互斥量使用例程
*
* 这个例子将创建 3 个动态线程以检查持有互斥量时,持有的线程优先级是否
* 被调整到等待线程优先级中的最高优先级。
*
* 线程 1,2,3 的优先级从高到低分别被创建,
* 线程 3 先持有互斥量,而后线程 2 试图持有互斥量,此时线程 3 的优先级应该
* 被提升为和线程 2 的优先级相同。线程 1 用于检查线程 3 的优先级是否被提升
* 为与线程 2的优先级相同。
*/
#include <rtthread.h>
/* 指向线程控制块的指针 */
static rt_thread_t tid1 = RT_NULL;
static rt_thread_t tid2 = RT_NULL;
static rt_thread_t tid3 = RT_NULL;
static rt_mutex_t mutex = RT_NULL;
#define THREAD_PRIORITY 10
#define THREAD_STACK_SIZE 512
#define THREAD_TIMESLICE 5
/* 线程 1 入口 */
static void thread1_entry(void *parameter)
{
/* 先让低优先级线程运行 */
rt_thread_mdelay(100);
/* 此时 thread3 持有 mutex,并且 thread2 等待持有 mutex */
/* 检查 rt_kprintf("the producer generates a number: %d\n", array[set%MAXSEM]); 与 thread3 的优先级情况 */
if (tid2->current_priority != tid3->current_priority)
{
/* 优先级不相同,测试失败 */
rt_kprintf("the priority of thread2 is: %d\n", tid2->current_priority);
rt_kprintf("the priority of thread3 is: %d\n", tid3->current_priority);
rt_kprintf("test failed.\n");
return;
}
else
{
rt_kprintf("the priority of thread2 is: %d\n", tid2->current_priority);
rt_kprintf("the priority of thread3 is: %d\n", tid3->current_priority);
rt_kprintf("test OK.\n");
}
}
/* 线程 2 入口 */
static void thread2_entry(void *parameter)
{
rt_err_t result;
rt_kprintf("the priority of thread2 is: %d\n", tid2->current_priority);
/* 先让低优先级线程运行 */
rt_thread_mdelay(50);
/*
* 试图持有互斥锁,此时 thread3 持有,应把 thread3 的优先级提升
* 到 thread2 相同的优先级
*/
result = rt_mutex_take(mutex, RT_WAITING_FOREVER);
if (result == RT_EOK)
{
/* 释放互斥锁 */
rt_mutex_release(mutex);
}
}
/* 线程 3 入口 */
static void thread3_entry(void *parameter)
{
rt_tick_t tick;
rt_err_t result;
rt_kprintf("the priority of thread3 is: %d\n", tid3->current_priority);
result = rt_mutex_take(mutex, RT_WAITING_FOREVER);
if (result != RT_EOK)
{
rt_kprintf("thread3 take a mutex, failed.\n");
}
/* 做一个长时间的循环,500ms */
tick = rt_tick_get();
while (rt_tick_get() - tick < (RT_TICK_PER_SECOND / 2)) ;
rt_mutex_release(mutex);
}
int pri_inversion(void)
{
/* 创建互斥锁 */
mutex = rt_mutex_create("mutex", RT_IPC_FLAG_FIFO);
if (mutex == RT_NULL)
{
rt_kprintf("create dynamic mutex failed.\n");
return -1;
}
/* 创建线程 1 */
tid1 = rt_thread_create("thread1",
thread1_entry,
RT_NULL,
THREAD_STACK_SIZE,
THREAD_PRIORITY - 1, THREAD_TIMESLICE);
if (tid1 != RT_NULL)
rt_thread_startup(tid1);
/* 创建线程 2 */
tid2 = rt_thread_create("thread2",
thread2_entry,
RT_NULL,
THREAD_STACK_SIZE,
THREAD_PRIORITY, THREAD_TIMESLICE);
if (tid2 != RT_NULL)
rt_thread_startup(tid2);
/* 创建线程 3 */
tid3 = rt_thread_create("thread3",
thread3_entry,
RT_NULL,
THREAD_STACK_SIZE,
THREAD_PRIORITY + 1, THREAD_TIMESLICE);
if (tid3 != RT_NULL)
rt_thread_startup(tid3);
return 0;
}
/* 导出到 msh 命令列表中 */
MSH_CMD_EXPORT(pri_inversion, pri_inversion sample);
运行结果: