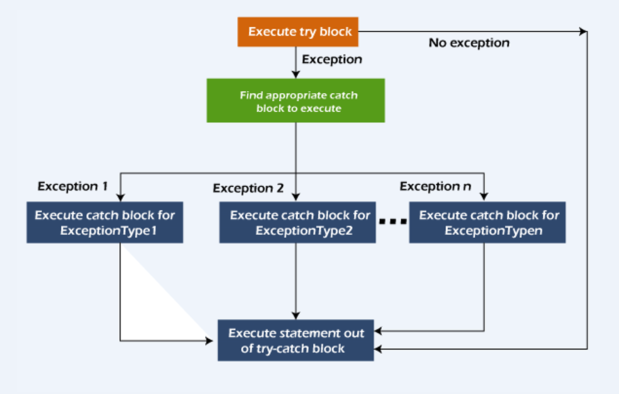
try块后面可以跟随一个或多个catch块。每个catch块必须包含一个不同的异常处理程序。因此,如果您在不同的异常发生时需要执行不同的任务,请使用Java多重捕获块。
需要记住的要点
-
一次只会发生一个异常,同时只有一个catch块被执行。
-
所有的catch块必须按照从最具体到最一般的顺序排列,即对于ArithmeticException的catch块必须放在Exception的catch块之前。
多重捕获块的流程图
示例1
让我们看一个简单的Java多重捕获块的示例。
MultipleCatchBlock1.java
public class MultipleCatchBlock1 {public static void main(String[] args) {try{int a[]=new int[5];a[5]=30/0;}catch(ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("Arithmetic Exception occurs");}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){System.out.println("ArrayIndexOutOfBounds Exception occurs");}catch(Exception e){System.out.println("Parent Exception occurs");}System.out.println("rest of the code");}}
输出:
Arithmetic Exception occursrest of the code
示例2
MultipleCatchBlock2.java
public class MultipleCatchBlock2 {public static void main(String[] args) {try{int a[]=new int[5];System.out.println(a[10]);}catch(ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("Arithmetic Exception occurs");}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){System.out.println("ArrayIndexOutOfBounds Exception occurs");}catch(Exception e){System.out.println("Parent Exception occurs");}System.out.println("rest of the code");}}
输出:
ArrayIndexOutOfBounds Exception occursrest of the code
在这个示例中,try块包含两个异常。但是一次只会发生一个异常,并且只会执行其对应的catch块。
MultipleCatchBlock3.java
public class MultipleCatchBlock3 {public static void main(String[] args) {try{int a[]=new int[5];a[5]=30/0;System.out.println(a[10]);}catch(ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("Arithmetic Exception occurs");}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){System.out.println("ArrayIndexOutOfBounds Exception occurs");}catch(Exception e){System.out.println("Parent Exception occurs");}System.out.println("rest of the code");}}
输出:
Arithmetic Exception occursrest of the code
示例4
在这个示例中,我们生成了NullPointerException,但没有提供相应的异常类型。在这种情况下,将调用包含父异常类Exception的catch块
MultipleCatchBlock4.java
public class MultipleCatchBlock4 {public static void main(String[] args) {try{String s=null;System.out.println(s.length());}catch(ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("Arithmetic Exception occurs");}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){System.out.println("ArrayIndexOutOfBounds Exception occurs");}catch(Exception e){System.out.println("Parent Exception occurs");}System.out.println("rest of the code");}}
输出:
Parent Exception occursrest of the code
示例5
让我们看一个不维护异常顺序(即从最具体到最一般)的异常处理的示例
MultipleCatchBlock5.java
class MultipleCatchBlock5{public static void main(String args[]){try{int a[]=new int[5];a[5]=30/0;}catch(Exception e){System.out.println("common task completed");}catch(ArithmeticException e){System.out.println("task1 is completed");}catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e){System.out.println("task 2 completed");}System.out.println("rest of the code...");}}
输出:
Compile-time error