以下内容均整理来自deeplearning.ai的同名课程
Location 课程访问地址
DLAI - Learning Platform Beta (deeplearning.ai)
一、什么是LangChain
1、LangChain介绍
LangChain是一个框架,用于开发由大语言模型驱动的应用程序。开发者相信,最强大的、差异化的应用不仅会调用语言模型,而且还会具备以下原则:
数据感知:将语言模型与其他数据源连接起来。
代理性:允许语言模型与环境互动
LangChain支持python和javascript两种语言。专注于组合和模块化。
官方文档:https://python.langchain.com/en/latest/
中文文档:https://www.langchain.com.cn/
2、LangChain的模块化能力
包括大量的整合对话模型、聊天模型;提示词模板,输出分析器,示例选择器。
支持检索和调用其他数据源,包括不限于文本、数组,支持多个数据检索工具。
支持搭建对话链模板,按输入信息,自动生成标准化加工后的输出结果。
可调用多个预设或者自定义的算法和小工具。
二、模型、提示词和输出解析器Models, Prompts and Output Parsers
1、Prompt template提示词模板
通常来说,我们通过以下方式调用gpt
def get_completion(prompt, model="gpt-3.5-turbo"):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
temperature=0,
)
return response.choices[0].message["content"]
# 创建一个调用函数
prompt = f"""Translate the text \
that is delimited by triple backticks
into a style that is {style}.
text: ```{customer_email}```
"""
# 编写提示语
response = get_completion(prompt)
#调用生成结果现在看下langchain怎么基于模型进行调用
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
chat = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.0)
# 加载langchain对话模型,并设置对话随机性为0
template_string = """Translate the text \
that is delimited by triple backticks \
into a style that is {style}. \
text: ```{text}```
"""
# 设计模板信息
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template_string)
# 加载提示语模板,载入模板信息
customer_style = """American English \
in a calm and respectful tone
"""
customer_email = """
Arrr, I be fuming that me blender lid \
flew off and splattered me kitchen walls \
with smoothie! And to make matters worse, \
the warranty don't cover the cost of \
cleaning up me kitchen. I need yer help \
right now, matey!
"""
# 定义模板中可变字段的变量信息
customer_messages = prompt_template.format_messages(
style=customer_style,
text=customer_email)
# 调用模板,对模板中的变量进行赋值,并生成最终提示语
customer_response = chat(customer_messages)
# 调用提示语,生成对话结果
通过“创建包含变量信息的提示词模板”,可以按照需求场景,灵活的通过改变变量信息,生成新的提示词。实现了模板的复用。
2、Output Parsers输出解析器
将大语言模型生成的结果,转换为特定结构的输出,如字典,数组等
from langchain.output_parsers import ResponseSchema
from langchain.output_parsers import StructuredOutputParser
# 加载输出解析器
gift_schema = ResponseSchema(name="gift",
description="Was the item purchased\
as a gift for someone else? \
Answer True if yes,\
False if not or unknown.")
delivery_days_schema = ResponseSchema(name="delivery_days",
description="How many days\
did it take for the product\
to arrive? If this \
information is not found,\
output -1.")
price_value_schema = ResponseSchema(name="price_value",
description="Extract any\
sentences about the value or \
price, and output them as a \
comma separated Python list.")
response_schemas = [gift_schema,
delivery_days_schema,
price_value_schema]
# 创建一组解析规则
output_parser = StructuredOutputParser.from_response_schemas(response_schemas)
format_instructions = output_parser.get_format_instructions()
#编译解析规则
review_template_2 = """\
For the following text, extract the following information:
gift: Was the item purchased as a gift for someone else? \
Answer True if yes, False if not or unknown.
delivery_days: How many days did it take for the product\
to arrive? If this information is not found, output -1.
price_value: Extract any sentences about the value or price,\
and output them as a comma separated Python list.
text: {text}
{format_instructions}
"""
# 创建一个提示词模板,将编译好的解析规则添加到模板中
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template=review_template_2)
messages = prompt.format_messages(text=customer_review,
format_instructions=format_instructions)
# 通过模板生成提示词信息
response = chat(messages)
# 生成结果
output_dict = output_parser.parse(response.content)
# 将生成结果存入字典中三、Memory内存组件
大语言模型在通过接口调用过程中,并不会自动记忆历史问答/上下文(来进行回答)。而通过调用memory组件。langchain提供了多种记忆历史问答/上下文的方式。
Outline概要
- ConversationBufferMemory
- ConversationBufferWindowMemory
- ConversationTokenBufferMemory
- ConversationSummaryMemory
ConversationBufferMemory对话内存
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.chains import ConversationChain
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
# 加载所需包
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.0)
memory = ConversationBufferMemory()
conversation = ConversationChain(
llm=llm,
memory = memory,
verbose=True
)
# 船创建一个对话,创建一个上下文储存区,创建一个链式沟通会话。
conversation.predict(input="Hi, my name is Andrew")
conversation.predict(input="What is 1+1?")
conversation.predict(input="What is my name?")
#在会话中添加会话内容,程序会自动将提问和回答一起保存到上下文储存区
print(memory.buffer)
memory.load_memory_variables({})
#显示上下文储存区内保存的会话内容
memory.save_context({"input": "Hi"},
{"output": "What's up"})
#直接对上下文储存区内的会话内容进行赋值(赋值内容为问答对)ConversationBufferWindowMemory有限对话内存
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferWindowMemory
# 加载组件
memory = ConversationBufferWindowMemory(k=1)
# 添加一个只有1空间的记忆内存
memory.save_context({"input": "Hi"},
{"output": "What's up"})
memory.save_context({"input": "Not much, just hanging"},
{"output": "Cool"})
# 此时,上下文储存区里面,只有第二个对话的记忆,即在1空间情况下,程序只会记忆最新的1空间的问答记忆。ConversationTokenBufferMemory有限词汇内存
from langchain.memory import ConversationTokenBufferMemory
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.0)
# 加载组件
memory = ConversationTokenBufferMemory(llm=llm, max_token_limit=30)
# 创建一个只有30词汇大小的记忆空间(因为有限空间的判断也会用到大预言模型,所以需要加载llm)
memory.save_context({"input": "AI is what?!"},
{"output": "Amazing!"})
memory.save_context({"input": "Backpropagation is what?"},
{"output": "Beautiful!"})
memory.save_context({"input": "Chatbots are what?"},
{"output": "Charming!"})
# 在这种情况下,程序只会保存不大于30个词汇的最新的问答,此时并不会强行保证问答都存在,仅包含答案也行。
memory.load_memory_variables({})
# 显示结果:{'history': 'AI: Beautiful!\nHuman: Chatbots are what?\nAI: Charming!'}ConversationSummaryMemory总结式记忆内存
from langchain.memory import ConversationSummaryBufferMemory
# 加载包
schedule = "There is a meeting at 8am with your product team. \
You will need your powerpoint presentation prepared. \
9am-12pm have time to work on your LangChain \
project which will go quickly because Langchain is such a powerful tool. \
At Noon, lunch at the italian resturant with a customer who is driving \
from over an hour away to meet you to understand the latest in AI. \
Be sure to bring your laptop to show the latest LLM demo."
# 一个长内容
memory = ConversationSummaryBufferMemory(llm=llm, max_token_limit=100)
# 创建一个最大词汇量为100的上下文总结式记忆空间(需要大预言模型进行总结,所以加载模型)
memory.save_context({"input": "Hello"}, {"output": "What's up"})
memory.save_context({"input": "Not much, just hanging"},
{"output": "Cool"})
memory.save_context({"input": "What is on the schedule today?"},
{"output": f"{schedule}"})
# 添加对话
memory.load_memory_variables({})
# 显示结果为总结后的内容,通过总结将记忆内容缩短到100个词汇以内:{'history': "System: The human and AI engage in small talk before discussing the day's schedule. The AI informs the human of a morning meeting with the product team, time to work on the LangChain project, and a lunch meeting with a customer interested in the latest AI developments."}
conversation = ConversationChain(
llm=llm,
memory = memory,
verbose=True
)
conversation.predict(input="What would be a good demo to show?")
# 特别的,在对话中调用总结式记忆空间。会自动保存最新一段AI答的原文(不总结归纳)
# 并把其他对话内容进行总结。这样做可能是为了更好的获取回答,最后一段AI答价值很大,不宜信息缩减。三、Chains对话链
Outline
- LLMChain
- Sequential Chains
- SimpleSequentialChain
- SequentialChain
- Router Chain
LLMChain基础链
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.9)
# 加载包
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"What is the best name to describe \
a company that makes {product}?"
)
# 创建一个待变量product的提示词
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
# 创建一个基础对话链
product = "Queen Size Sheet Set"
chain.run(product)
# 提示词变量赋值,并获得回答SimpleSequentialChain一般序列链
一般序列链可以将前一个链的输出结果,作为后一个链的输入。一般序列链有唯一输入和输出变量。
from langchain.chains import SimpleSequentialChain
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.9)
# 加载包
first_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"What is the best name to describe \
a company that makes {product}?"
)
# 提示词模板1,变量为product
chain_one = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=first_prompt)
# 链1
second_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Write a 20 words description for the following \
company:{company_name}"
)
# 提示词模板2,变量为company_name
chain_two = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=second_prompt)
# 链2
overall_simple_chain = SimpleSequentialChain(chains=[chain_one, chain_two],
verbose=True)
overall_simple_chain.run(product)
# 组合链1、链2,获取结果SequentialChain序列链
序列链中包含多个链,其中一些链的结果可以作为另一个链的输入。序列链可以支持多个输入和输出变量。

from langchain.chains import SequentialChain
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0.9)
# 加载
first_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Translate the following review to english:"
"\n\n{Review}"
chain_one = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=first_prompt,
output_key="English_Review"
)
# 链1:输入Review,输出English_Review
second_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Can you summarize the following review in 1 sentence:"
"\n\n{English_Review}"
)
chain_two = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=second_prompt,
output_key="summary"
)
# 链2:输入English_Review,输出summary
third_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"What language is the following review:\n\n{Review}"
)
chain_three = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=third_prompt,
output_key="language"
)
# 链3:输入Review,输出language
fourth_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"Write a follow up response to the following "
"summary in the specified language:"
"\n\nSummary: {summary}\n\nLanguage: {language}"
)
chain_four = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=fourth_prompt,
output_key="followup_message"
)
# 链4:输入summary、language,输出followup_message
overall_chain = SequentialChain(
chains=[chain_one, chain_two, chain_three, chain_four],
input_variables=["Review"],
output_variables=["English_Review", "summary","followup_message"],
verbose=True
)
# 构建完整链,输入Review,输出"English_Review", "summary","followup_message"
overall_chain(review)Router Chain路由链
路由链类似一个while else的函数,根据输入值,选择对应的路由(路径)进行后续的链路。整个路由链一般一个输入,一个输出。
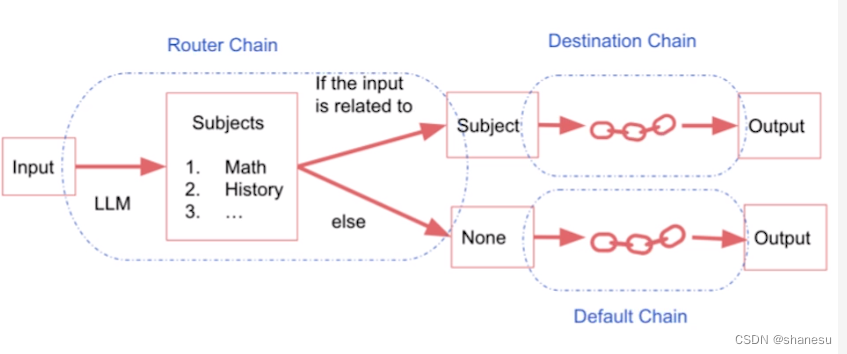
physics_template = """You are a very smart physics professor. \
You are great at answering questions about physics in a concise\
and easy to understand manner. \
When you don't know the answer to a question you admit\
that you don't know.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
math_template = """You are a very good mathematician. \
You are great at answering math questions. \
You are so good because you are able to break down \
hard problems into their component parts,
answer the component parts, and then put them together\
to answer the broader question.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
history_template = """You are a very good historian. \
You have an excellent knowledge of and understanding of people,\
events and contexts from a range of historical periods. \
You have the ability to think, reflect, debate, discuss and \
evaluate the past. You have a respect for historical evidence\
and the ability to make use of it to support your explanations \
and judgements.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
computerscience_template = """ You are a successful computer scientist.\
You have a passion for creativity, collaboration,\
forward-thinking, confidence, strong problem-solving capabilities,\
understanding of theories and algorithms, and excellent communication \
skills. You are great at answering coding questions. \
You are so good because you know how to solve a problem by \
describing the solution in imperative steps \
that a machine can easily interpret and you know how to \
choose a solution that has a good balance between \
time complexity and space complexity.
Here is a question:
{input}"""
# 创建4种提示词模板
prompt_infos = [
{
"name": "physics",
"description": "Good for answering questions about physics",
"prompt_template": physics_template
},
{
"name": "math",
"description": "Good for answering math questions",
"prompt_template": math_template
},
{
"name": "History",
"description": "Good for answering history questions",
"prompt_template": history_template
},
{
"name": "computer science",
"description": "Good for answering computer science questions",
"prompt_template": computerscience_template
}
]
# 提示词要点信息
from langchain.chains.router import MultiPromptChain
from langchain.chains.router.llm_router import LLMRouterChain,RouterOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0)
# 加载
destination_chains = {}
for p_info in prompt_infos:
name = p_info["name"]
prompt_template = p_info["prompt_template"]
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(template=prompt_template)
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt)
destination_chains[name] = chain
destinations = [f"{p['name']}: {p['description']}" for p in prompt_infos]
destinations_str = "\n".join(destinations)
# 根据提示词要点信息,生成4个链,存入destination中
default_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("{input}")
default_chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=default_prompt)
# 创建默认提示词和链
MULTI_PROMPT_ROUTER_TEMPLATE = """Given a raw text input to a \
language model select the model prompt best suited for the input. \
You will be given the names of the available prompts and a \
description of what the prompt is best suited for. \
You may also revise the original input if you think that revising\
it will ultimately lead to a better response from the language model.
<< FORMATTING >>
Return a markdown code snippet with a JSON object formatted to look like:
```json
{{{{
"destination": string \ name of the prompt to use or "DEFAULT"
"next_inputs": string \ a potentially modified version of the original input
}}}}
```
REMEMBER: "destination" MUST be one of the candidate prompt \
names specified below OR it can be "DEFAULT" if the input is not\
well suited for any of the candidate prompts.
REMEMBER: "next_inputs" can just be the original input \
if you don't think any modifications are needed.
<< CANDIDATE PROMPTS >>
{destinations}
<< INPUT >>
{{input}}
<< OUTPUT (remember to include the ```json)>>"""
# 创建一个提示词模板,包含destination和input两个变量
router_template = MULTI_PROMPT_ROUTER_TEMPLATE.format(
destinations=destinations_str
)
# 提示词模板赋值destination
router_prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=router_template,
input_variables=["input"],
output_parser=RouterOutputParser(),
)
# 提示词模板赋值
router_chain = LLMRouterChain.from_llm(llm, router_prompt)
chain = MultiPromptChain(router_chain=router_chain,
destination_chains=destination_chains,
default_chain=default_chain, verbose=True)
# 生成路由链
chain.run("xxx")

![[python][yolov8][深度学习]将yolov8实例分割成一个类几句代码完成实例分割任务](https://i1.hdslb.com/bfs/archive/901f587718f84878626aadaab7d6fa3e7176379c.jpg@100w_100h_1c.png@57w_57h_1c.png)








![[皮尔逊相关系数corrwith]使用案例:电影推荐系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/172e8d0d7b314338b76f1e64f7b32bec.png)