实验一
一、实验内容或题目:
随机产生页面访问序列,并实现LRU, FIFO, OPT三种算法进行缺页比较
二、实验目的与要求:
1、编写程序,随机产生页面访问序列,并实现LRU, FIFO, OPT三种算法进行缺页比较。
2、理解三种算法的机制及优劣点。
3、理解belady现象
三、实验步骤:
1、在pagefault.c基础上实现三种算法。
2、运行并比较三种算法的缺页次数
3、通过固定srand函数的种子,并调节MEMORY_SIZE大小以及随机实验,尝试让FIFO算法出现belady现象
四、实验结果:

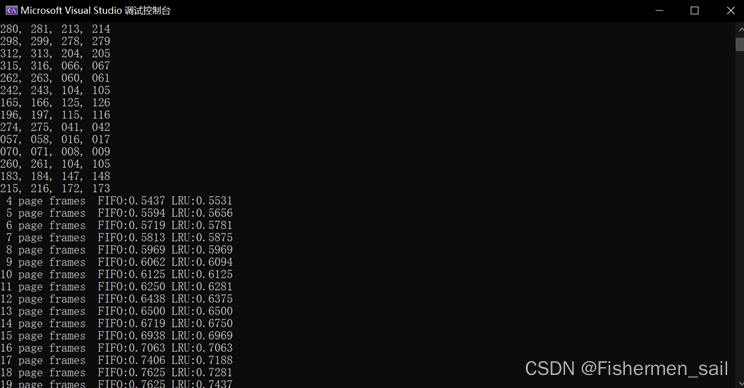
五、总结:
由于期末临近,实在是没有时间来完成这个实验,在GitHub上找了一个作者的代码进行了阅读,LRU, FIFO, OPT三个算法思路还是比较清晰的,当然OPT是无法跑的,作者用了数据结构的方式来实现这三个方式,读起来有些复杂的,但思路还是很清晰的。如果自己写还是比较难写出来的,这个需要考虑的东西会很多,很容易出错。
| 算法 | 规则 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| OPT | 优先淘汰最长时间内不会被访问的页面 | 缺页率最小,性能最好,但无法实现 |
| FIFO | 优先淘汰最先进入内存的页面 | 实现简单,但性能很差,可能出现Belady异常 |
| LRU | 优先淘汰最近最久没访问的页面 | 性能很好,但需要硬件支持,算法开销大 |
Belady现象是指当进程分配的物理块数增大时,缺页次数不减反增的异常现象。
六、源码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <process.h>
#include <time.h>
#define total_instruction 320 //指令流长(指令数量)
#define total_vp 32 //虚页长(虚拟空间大小)
#define INVALID -1
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define clear_period 50 //清零周期(NUR)
typedef struct
{
int pn; //page number
int pfn; //page_frame number
int counter; //访问记录(LFU、NUR)
int time; //访问时间(LRU)
}pl_type;//页面结构体(进程)
pl_type pl[32];//32个虚存页面
typedef struct pfc_struct
{
int pn, pfn;
struct pfc_struct* next;
}pfc_type;//页框结构体(内存)
pfc_type pfc[32], * freepf_head, * busypf_head, * busypf_tail;
int diseffect; //缺页次数
int a[total_instruction]; //地址序列
int page[total_instruction]; //页号
int offset[total_instruction]; //页内偏移
void generate_inst_addr_sq() { //生成地址序列
int s, i;
srand(time(NULL)); //设置随机数种子
s = (float)319 * rand() / RAND_MAX + 1; //0-319随机数
for (i = 0; i < total_instruction; i += 4)
{
if (s < 0 || s>319)
{
printf("When i==%d, Error, s==%d\n", i, s);
exit(0);
}
a[i] = s; //任意一指令访问点
a[i + 1] = a[i] + 1; //顺序执行一条指令
a[i + 2] = (float)a[i] * rand() / RAND_MAX; //执行前指令m
a[i + 3] = a[i + 2] + 1; //顺序执行一条指令
s = (float)(318 - a[i + 2]) * rand() / RAND_MAX + a[i + 2] + 2;
if ((a[i + 2] > 318) || (s > 319))
printf("a[%d+2], a number which is: %d and s==%d", i, a[i + 2], s);
}
for (i = 0; i < total_instruction; i += 4)
printf("%03d, %03d, %03d, %03d\n", a[i], a[i + 1], a[i + 2], a[i + 3]);
for (i = 0; i < total_instruction; i++)
{//将地址转换为页号、页内偏移,每个页面大小为10
page[i] = a[i] / 10;
offset[i] = a[i] % 10;
}
}
void initialize(int total_pf)
{
int i;
diseffect = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 32; i++)
{
pl[i].pn = i;
pl[i].pfn = INVALID;
pl[i].counter = 0;
pl[i].time = -1;
}
for (i = 0; i < total_pf - 1; i++)
{
pfc[i].next = &pfc[i + 1];
pfc[i].pfn = i;
}
pfc[total_pf - 1].next = NULL;
pfc[total_pf - 1].pfn = total_pf - 1;
freepf_head = &pfc[0]; //freepf_head总是指向可用页框
}
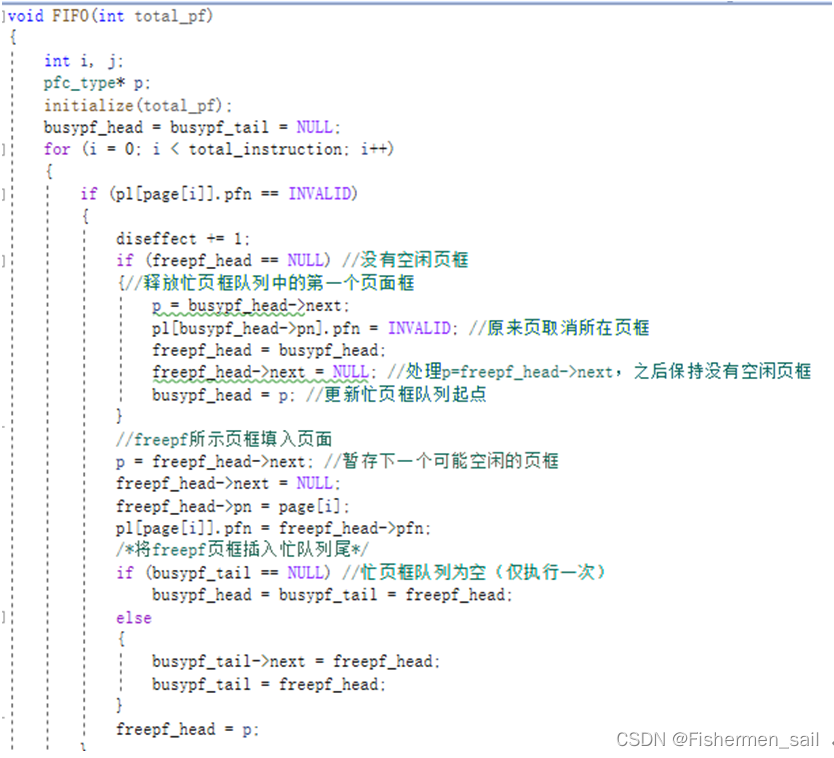
void FIFO(int total_pf)
{
int i, j;
pfc_type* p;
initialize(total_pf);
busypf_head = busypf_tail = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < total_instruction; i++)
{
if (pl[page[i]].pfn == INVALID)
{
diseffect += 1;
if (freepf_head == NULL) //没有空闲页框
{//释放忙页框队列中的第一个页面框
p = busypf_head->next;
pl[busypf_head->pn].pfn = INVALID; //原来页取消所在页框
freepf_head = busypf_head;
freepf_head->next = NULL; //处理p=freepf_head->next,之后保持没有空闲页框
busypf_head = p; //更新忙页框队列起点
}
//freepf所示页框填入页面
p = freepf_head->next; //暂存下一个可能空闲的页框
freepf_head->next = NULL;
freepf_head->pn = page[i];
pl[page[i]].pfn = freepf_head->pfn;
/*将freepf页框插入忙队列尾*/
if (busypf_tail == NULL) //忙页框队列为空(仅执行一次)
busypf_head = busypf_tail = freepf_head;
else
{
busypf_tail->next = freepf_head;
busypf_tail = freepf_head;
}
freepf_head = p;
}
}
printf("FIFO:%6.4f ", 1 - (float)diseffect / 320);
}
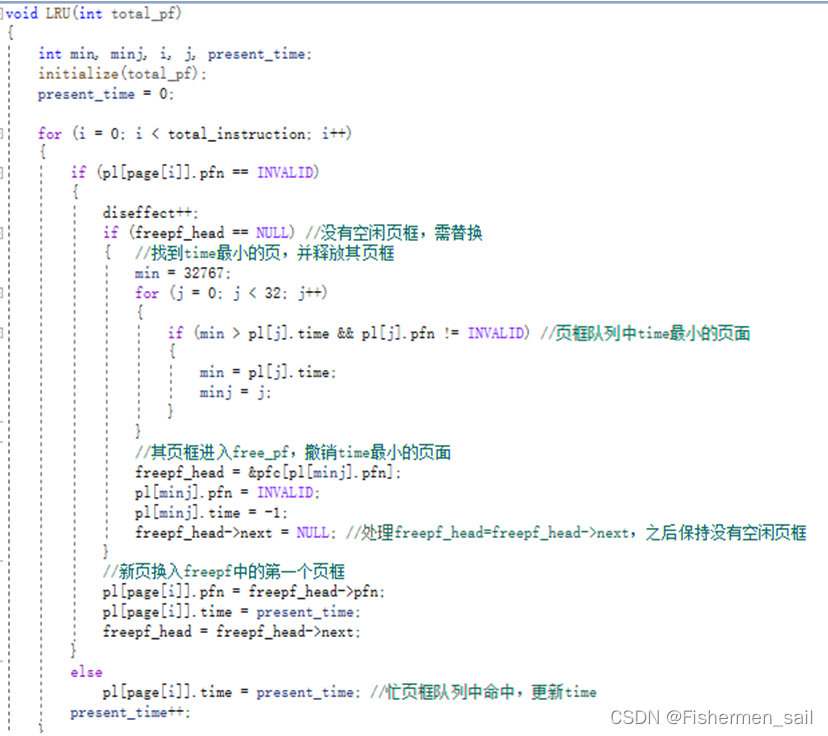
void LRU(int total_pf)
{
int min, minj, i, j, present_time;
initialize(total_pf);
present_time = 0;
for (i = 0; i < total_instruction; i++)
{
if (pl[page[i]].pfn == INVALID)
{
diseffect++;
if (freepf_head == NULL) //没有空闲页框,需替换
{ //找到time最小的页,并释放其页框
min = 32767;
for (j = 0; j < 32; j++)
{
if (min > pl[j].time && pl[j].pfn != INVALID) //页框队列中time最小的页面
{
min = pl[j].time;
minj = j;
}
}
//其页框进入free_pf,撤销time最小的页面
freepf_head = &pfc[pl[minj].pfn];
pl[minj].pfn = INVALID;
pl[minj].time = -1;
freepf_head->next = NULL; //处理freepf_head=freepf_head->next,之后保持没有空闲页框
}
//新页换入freepf中的第一个页框
pl[page[i]].pfn = freepf_head->pfn;
pl[page[i]].time = present_time;
freepf_head = freepf_head->next;
}
else
pl[page[i]].time = present_time; //忙页框队列中命中,更新time
present_time++;
}
printf("LRU:%6.4f ", 1 - (float)diseffect / 320);
}
void OPT(int total_pf)
{
int i,j , max, maxpage, d, dist[total_vp];
pfc_type *t;
initialize(total_pf);
for(i=0;i<total_instruction;i++)
{
if(pl[page[i]].pfn==INVALID)
{
diseffect++;
if(freepf_head==NULL)
{
for(j=0;j<total_vp;j++)
if(pl[j].pfn!=INVALID)
dist[j]=32767;
else
dist[j]=0;
d=1;
for(j=i+1;j<total_instruction;j++)
{
if(pl[page[j]].pfn!=INVALID)
dist[page[j]]=d;
d++;
}
max=-1;
for(j=0;j<total_vp;j++)
if(max<dist[j])
{
max=dist[j];
maxpage=j;
}
freepf_head=&pfc[pl[maxpage].pfn];
freepf_head->next=NULL;
pl[maxpage].pfn=INVALID;
}
pl[page[i]].pfn=freepf_head->pfn;
freepf_head=freepf_head->next;
}
}
printf("OPT:%6.4f ",1-(float)diseffect/320);
}
int main()
{
int i;
generate_inst_addr_sq();
for (i = 4; i <= 32; i++) //物理内存容量:4-32个页框
{
printf("%2d page frames\t", i);
FIFO(i);
LRU(i);
//OPT(i);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
实验二
一、实验内容或题目:
通用调用操作系统API,实现对文件的创建和异步读取操作。
二、实验目的与要求:
1、通用调用操作系统API,实现对文件的创建和异步读取操作
2、了调文件系统中的一些常用参数应用
3、编写程序实现并理解I/O设备的异步访问
三、实验步骤:
1、编写createAndExpandFile函数,在指定位置创建文件并扩展到1M长度
2、编写getFileContentAsync函数,异步读取文件内容。内容并无意义,读到缓冲区中即可,但要求使用异步读取,主函数在发起异步请求后等待在事件上,等异步完成后回调再唤醒。
需要使用的api:
CreateFile, SetEndOfFile, SetFilePointer, ReadFile, WaitEvent
四、实验结果:
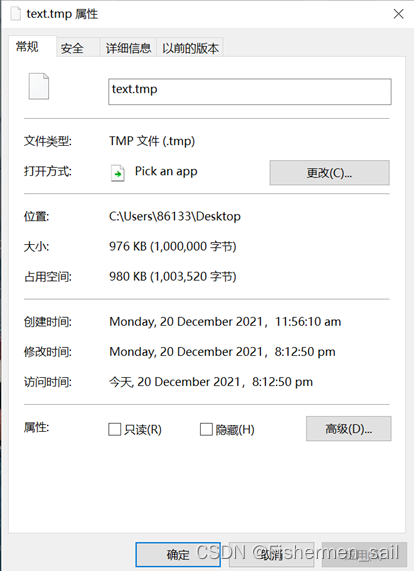
五、总结
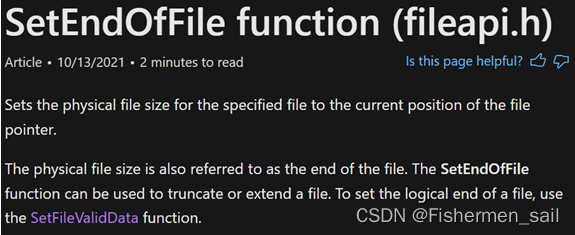
根据官网的指示,要使用SetEndOfFile才能实现文件的扩展。由于官网并没有给实例代码,查了很多资料才知道怎么写。通过将SetFilePointer调用到所需位置,然后通过SetEndOfFile截断到所需位置,就可以实现文件长度的扩展。

在第二个实验上,通过事件内核对象,可以支持多个异步io。每个read或者write里面的overlapped的结构,可以设置一个事件内核对象,这样每次io的事件内核对象是不一样的,就可以支持多个异步io了。
六、源码
#include <Windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <winerror.h>
#define FILE_NAMEA TEXT(FILE_NAME)
HANDLE hEvent;
/**
在此函数中创建FILE_NAME并将之扩展到1MB大小
注意:
1)创建文件时使用TRUNCATE_EXSITING标识
2)传参时使用FILE_NAMEA
**/
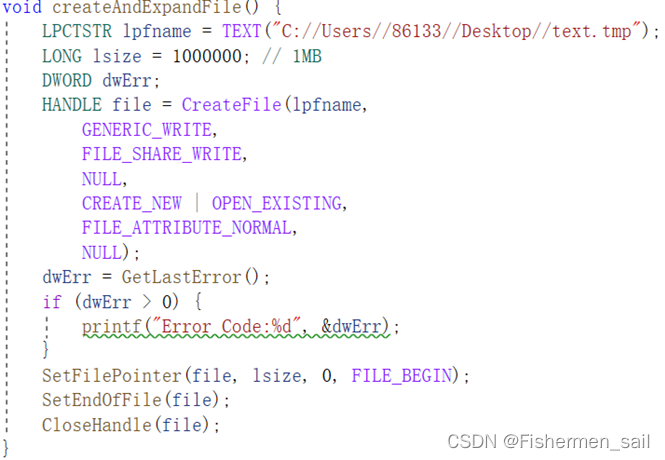
void createAndExpandFile() {
LPCTSTR lpfname = TEXT("C://Users//86133//Desktop//text.tmp");
LONG lsize = 1000000; // 1MB
DWORD dwErr;
HANDLE file = CreateFile(lpfname,
GENERIC_WRITE,
FILE_SHARE_WRITE,
NULL,
CREATE_NEW | OPEN_EXISTING,
FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL,
NULL);
dwErr = GetLastError();
if (dwErr > 0) {
printf("Error Code:%d", &dwErr);
}
SetFilePointer(file, lsize, 0, FILE_BEGIN);
SetEndOfFile(file);
CloseHandle(file);
}
/**
在此函数中打开创建的文件,读出其所有内容到一个缓冲区中
使用异步读,在读回调函数里使用hEvent通知主函数继续运行
**/
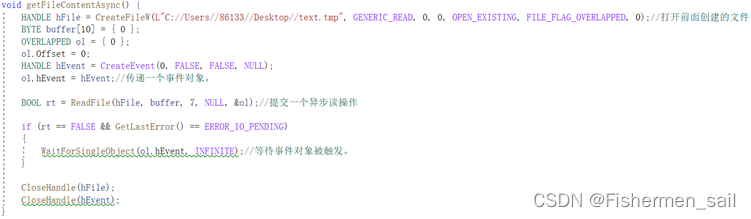
void getFileContentAsync() {
HANDLE hFile = CreateFileW(L"C://Users//86133//Desktop//text.tmp", GENERIC_READ, 0, 0, OPEN_EXISTING, FILE_FLAG_OVERLAPPED, 0);//打开前面创建的文件
BYTE buffer[10] = { 0 };
OVERLAPPED ol = { 0 };
ol.Offset = 0;
HANDLE hEvent = CreateEvent(0, FALSE, FALSE, NULL);
ol.hEvent = hEvent;//传递一个事件对象。
BOOL rt = ReadFile(hFile, buffer, 7, NULL, &ol);//提交一个异步读操作
if (rt == FALSE && GetLastError() == ERROR_IO_PENDING)
{
WaitForSingleObject(ol.hEvent, INFINITE);//等待事件对象被触发。
}
CloseHandle(hFile);
CloseHandle(hEvent);
}
int main() {
hEvent = CreateEvent(
NULL, // default security attributes
TRUE, // manual-reset event
FALSE, // initial state is nonsignaled
NULL // object name
);
createAndExpandFile();
getFileContentAsync();
}