👨🎓个人主页:研学社的博客
💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
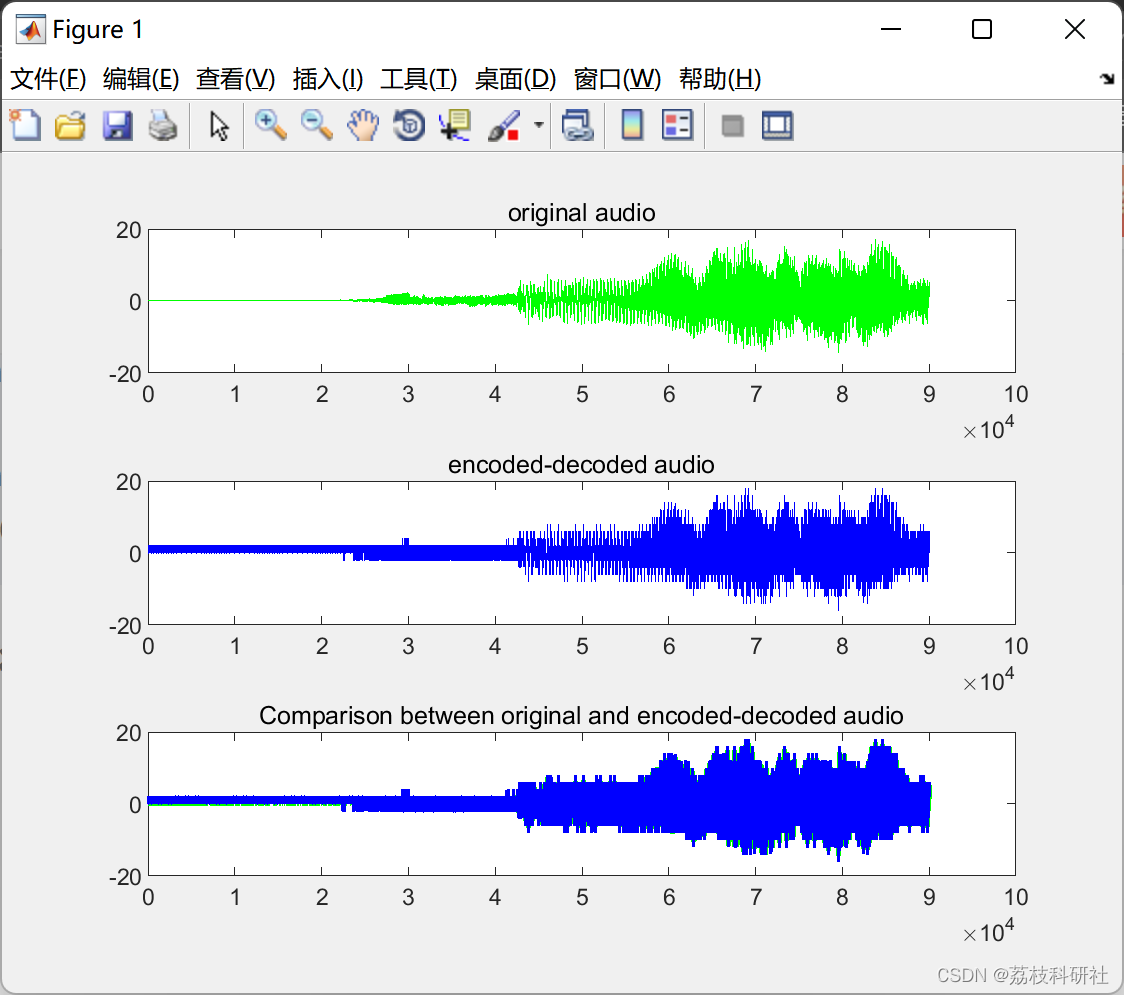
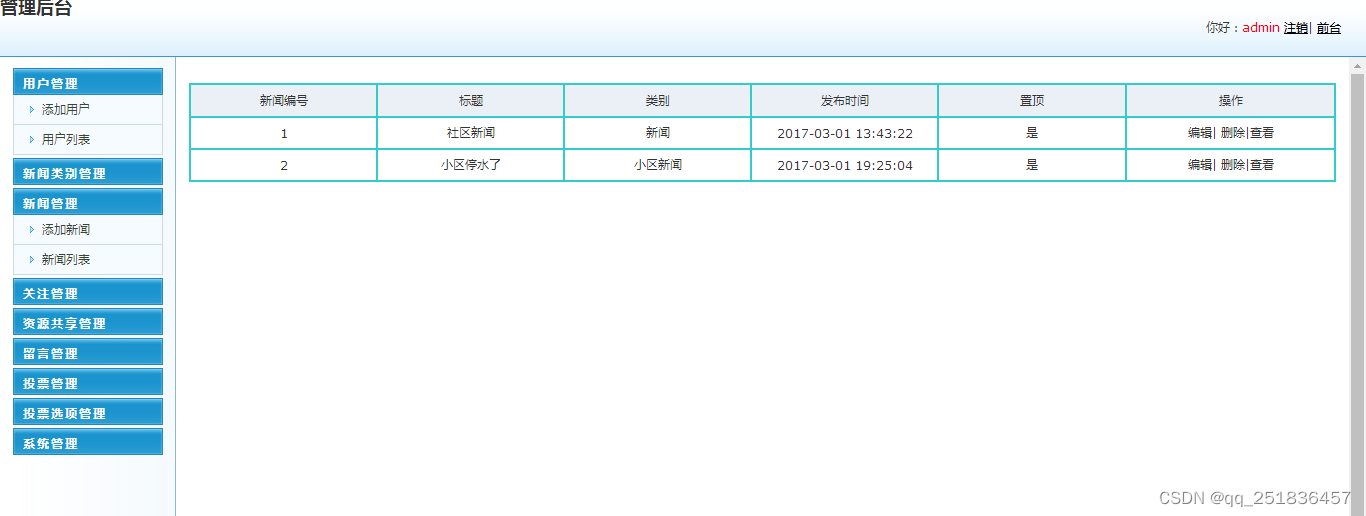
📚2 运行结果
🌈3 Matlab代码+语音+详细文章讲解
🎉4 参考文献
💥1 概述
本应讲解在对话语音处理应用中使用的自适应差分脉冲编码调制(ADPCM)的实现
包括以下内容:
•语音数据文件的文件格式
•ADPCM编码算法
•ADPCM解码算法
•步长确定
•初始和重置条件。
图1显示了ADPCM编码过程的框图。将线性输入样本X(n)与该输入X(n-l)的先前估计进行比较。差值d(n)以及当前步长ss(n)被提供给编码器逻辑。如下所述,该逻辑产生ADPCM输出样本。该输出样本还用于更新步长计算ss(n+l),并提供给解码器以计算输入样本的线性估计。
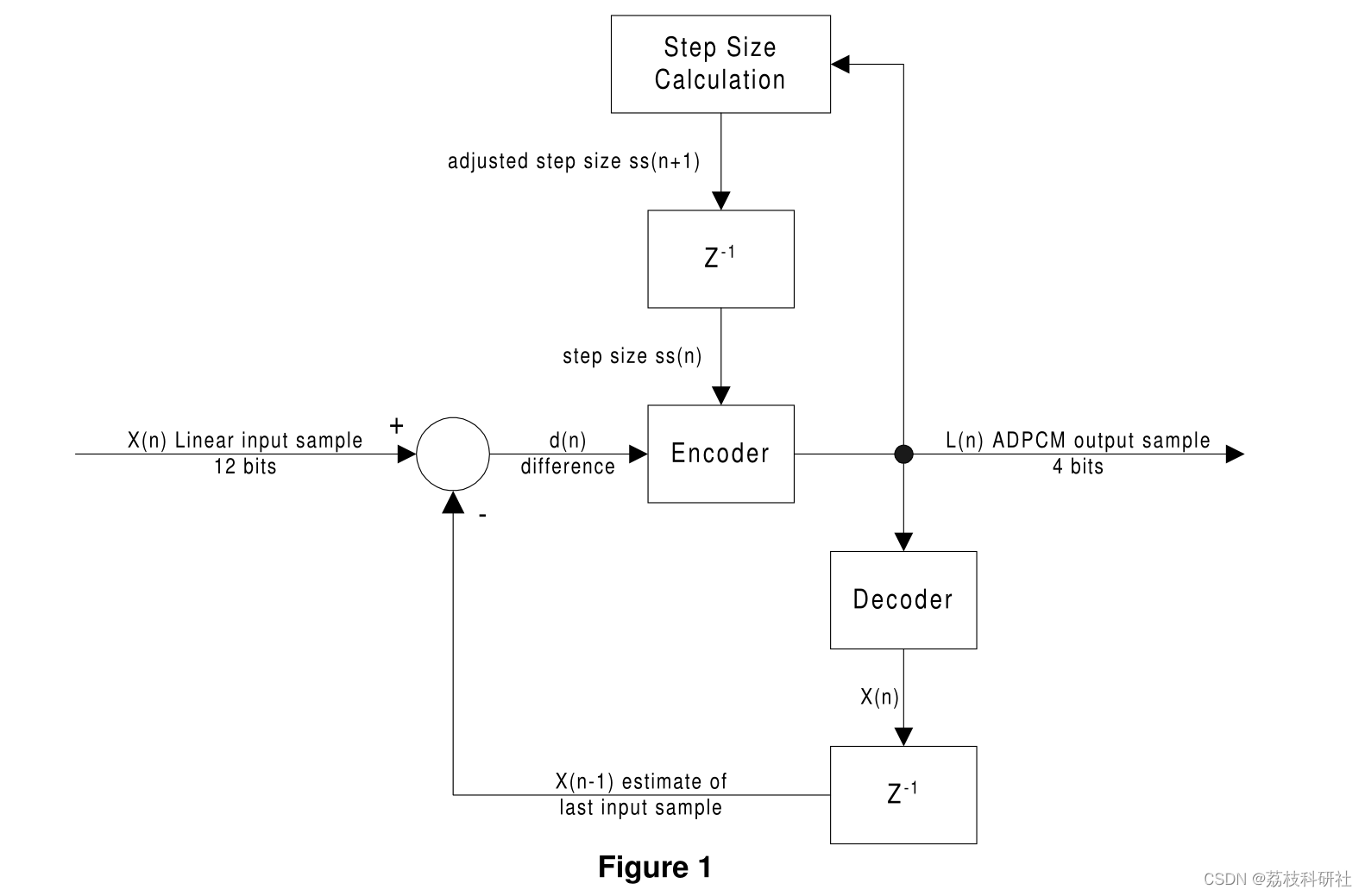
编码器接受来自比较器的差值d(n)和步长,并计算4位ADPCM码。以下是此计算的伪代码表示:
let B3 = B2 = B1 = B0 = 0
if (d(n) < 0)
then B3 = 1
d(n) = ABS(d(n))
if (d(n) >= ss(n))
then B2 = 1 and d(n) = d(n) - ss(n)
if (d(n) >= ss(n) / 2)
then B1 = 1 and d(n) = d(n) - ss(n) / 2
if (d(n) >= ss(n) / 4)
then B0 = 1
L(n) = (10002 * B3) + (1002 * B2) + (102 * B1) + B0
📚2 运行结果
🌈3 Matlab代码+语音+详细文章讲解
部分代码:
function [out,B0,B1,B2,B3] = encoder(x)
%ADPCM Encoder.
% Args:
% x: An audio file with the format as Microsoft WAVE ".wav".
%
% Returns:
% out: A row matrix containing the quantified and encoded decimal stream transformed from the
% encoded binary bit stream, with the ADPCM encoded.
% B0: A row matrix containing the lowest order of each output(out) in binary format.
% B1: A row matrix containing the second low order of each output(out) in binary format.
% B2: A row matrix containing the second high order of each output(out) in binary format.
% B3: A row matrix containing the highest order of each output(out) in binary format.
%
%
%Finished by Qiushi Yang, 6/12/2018.
Ml_values_table = [-1,-1,-1,-1,2,4,6,8];
step_sizes_table = [16,17,19,21,23,25,28,31,34,37,41,45,50,55,60,66,73,80,88,97,107,118,130,143,157,173,190,209,230,253,279,307,337,371,408,449,494,544,598,658,724,796,876,963,1060,1166,1282,1411,1552];
ss = step_sizes_table;
% Initialization
index = 0;
pre_data = 0;
B0=zeros(size(x));
B1=zeros(size(x));
B2=zeros(size(x));
B3=zeros(size(x));
% L=0;
out = zeros(size(x));
for i = 1:length(x),
current_data = x(i); % input current data
diff = current_data - pre_data; % calculate data-increment
% Calculate the B3,B2,B1,B0 step by step following the References-1 as
% follows:
% let B3 = B2 = B1 = B0 = 0
% if (d(n) < 0)
% then B3 = 1
% d(n) = ABS(d(n))
% if (d(n) >= ss(n))
% then B2 = 1 and d(n) = d(n) - ss(n)
% if (d(n) >= ss(n) / 2)
% then B1 = 1 and d(n) = d(n) - ss(n) / 2
% if (d(n) >= ss(n) / 4)
% then B0 = 1 L(n) = (10002 * B3) + (1002 * B2) + (102 * B1) + B0
if diff<0,
diff = abs(diff);
B3(i) = 1;
end
if diff < ss(index+1)/4,
B2(i) = 0; B1(i) = 0; B0(i) = 0;
elseif diff > ss(index+1)/4 && diff < ss(index+1)/2,
B2(i) = 0; B1(i) = 0; B0(i) = 1;
elseif diff > ss(index+1)/2 && diff < ss(index+1)*3/4,
B2(i) = 0; B1(i) = 1; B0(i) = 0;
elseif diff > ss(index+1)*3/4 && diff < ss(index+1),
B2(i) = 0; B1(i) = 1; B0(i) = 1;
elseif diff > ss(index+1) && diff < ss(index+1)*5/4,
B2(i) = 1; B1(i) = 0; B0(i) = 0;
elseif diff > ss(index+1)*5/4 && diff < ss(index+1)*3/2,
B2(i) = 1; B1(i) = 0; B0(i) = 1;
elseif diff > ss(index+1)*3/2 && diff < ss(index+1)*7/4,
B2(i) = 1; B1(i) = 1; B0(i) = 0;
elseif diff > ss(index+1)*7/4,
B2(i) = 1; B1(i) = 1; B0(i) = 1;
end
L = 8*B3(i) + 4*B2(i) + 2*B1(i) + B0(i); % Convert the binary number "(B3B2B1B0)_2" to decimal number L as output
out(i) = L;
% Get the data-increment based on step_sizes_table and index
diff = fix(ss(index+1)/8) + fix(B0(i)*ss(index+1)/4) + fix(B1(i)*ss(index+1)/2) + fix(B2(i)*ss(index+1));
diff = (-1)^B3(i)*diff;
pre_data = pre_data + diff; % Get the predicted data according to the data-increment
index = index + Ml_values_table(4*B2(i) + 2*B1(i) + 1*B0(i) + 1); % Convert the binary number "(B2B1B0)_2" to decimal number
if (index<0),
index=0;
elseif (index>48),
index=48; % Limit the index in the range of step_sizes_table:(0,49)
end
end
end
🎉4 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。
Copyright 1988, Dialogic Corporation All Rights Reserved. 00-1366-001


![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM家教管理系统(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9ef9a5b769a54b79abc24ea36f92bb50.png)

![[矩阵论] Unit 4. 矩阵的广义逆 - 知识点整理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c812555e1a4f4b848672e979c427dda3.png)