文章目录
- //模拟实现string类,并完成测试
- • string类的基本结构
- • Destructor
- • Construct
- 〔构造函数〕
- ‹ 无参构造 ›
- ‹ 单参数构造 ›
- ‹ 全缺省参数构造 ›
- 〔拷贝构造〕
- • operator= 赋值重载
- • Element access(operator[])
- 补充:const 变量的场景
- • Iterator
- • Relational Operators(比较大小)
- • Capacity
- 〔size〕&〔capacity〕&〔empty〕
- 〔reserve〕
- 〔resize〕
- • Modify
- 〔push_back〕&〔append〕
- 〔+=〕
- 〔swap〕
- 〔clear〕& 〔c_str〕
- • 「insert」在 pos 位置插入字符或字符串
- • 「erase」从 pos 位置删除 len 个字符
- 注:npos的声明和定义
- • 「find」
- • 「流插入<<、流提取>>」
- ‹ 流插入 ›
- ‹ 流提取 ›
//模拟实现string类,并完成测试
头文件声明:
//anolog_string.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
namespace RoundBottle//与库里面的string类做区分
{
class string
{
public:
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
//全缺省构造
string(const char* str = "");
//拷贝构造
string(const string& s);
//赋值重载是关于两个已经存在的对象
string& operator=(const string& s);
~string();
/
// access
char& operator[](size_t index);
const char& operator[](size_t index)const;
//
// iterator
iterator begin();
iterator end();
const_iterator begin()const;
const_iterator end()const;
/
// modify
void push_back(char c);
string& operator+=(char c);
void append(const char* str);
string& operator+=(const char* str);
void clear();
void swap(string& s);
const char* c_str()const;
/
// capacity
size_t size()const;
size_t capacity()const;
bool empty()const;
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0');
void reserve(size_t n);
/
//relational operators
bool operator<(const string& s);
bool operator<=(const string& s);
bool operator>(const string& s);
bool operator>=(const string& s);
bool operator==(const string& s);
bool operator!=(const string& s);
// 返回c在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
// 返回子串s在string中第一次出现的位置
size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
// 在pos位置上插入字符c/字符串str,并返回该字符的位置
string& insert(size_t pos, char c);
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str);
// 删除pos位置上的元素,并返回该元素的下一个位置
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos);
private:
char* _str;
size_t _capacity;
size_t _size;
static size_t npos;
};
size_t string::npos = -1;
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& _cout, const RoundBottle::string& s);
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& _cin, RoundBottle::string& s);
//测试
void string_test()
{}
};
//test.cpp
#include "analog_string.h"
int main()
{
try
{
RoundBottle::string_test();
}
catch (const std::exception& e)
{
cout << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
• string类的基本结构
private:
char* _str;
size_t _capacity;
size_t _size;

• Destructor
~string()
{
delete[]_str;
_str = nullptr;
_size = _capacity = 0;
}
• Construct
〔构造函数〕
‹ 无参构造 ›
- 方式一:
_str 置空指针
//全缺省构造
string()
: _str(nullptr)
, _size(0)
, _capacity(0)
{}
//cout 自动识别类型,对于指针,会进行解引用!
cout << s.c_str() <<endl; 👉 s.c_str()成员函数 会返回对象 s 中的成员变量 _str,若 _str==nullptr 则 cout 会对空指针进行解引用!
- 方式二:给_str所指向的空间开新空间——
new char
//全缺省构造
string()
: _str(new char)
, _size(0)
, _capacity(0)
{}
//析构函数执行的语句是:delete [] _str; 与 new 不匹配(关于new和delete详见文章C++ -5- 内存管理)
- 方式三:
_str = new char [1]
//全缺省构造
string()
: _str(new char [1])
, _size(0)
, _capacity(0)
{
_str[size] = '\0';
}
‹ 单参数构造 ›
- 方式一:直接赋值
//全缺省构造
string(const char* str)
: _str(str)//权限放大
, _size(strlen(str))
, _capacity(strlen(str))
{}
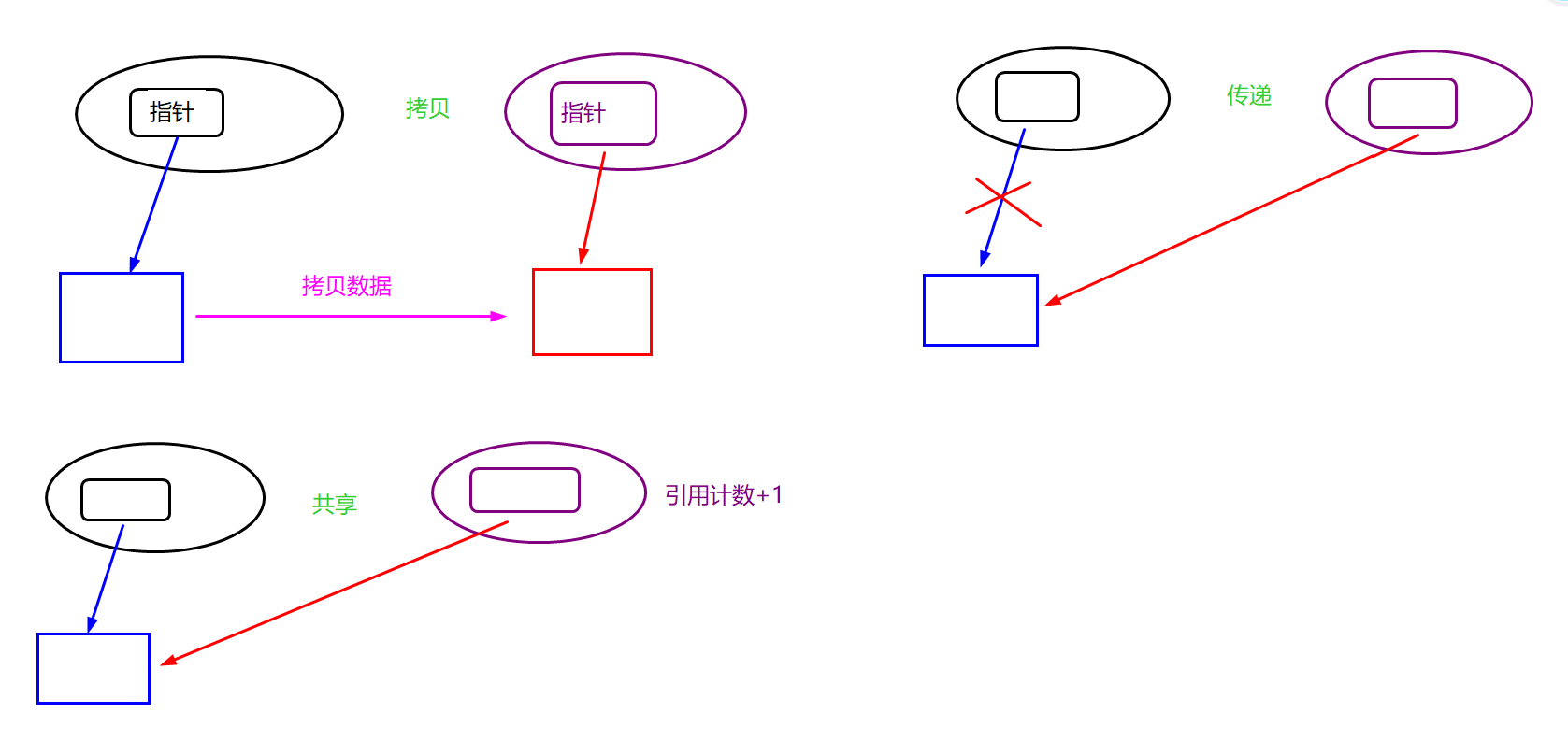
将 str 中的地址赋值给 _str 很明显是权限放大,如下图:

- 方式二:
//全缺省构造
string(const char* str)
: _size(strlen(str))
{
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
- 关于 capacity:
- 能存多少个有效数据(不包括’\0’)→ 所以开空间要多开一个留给’\0’
- 尽量不要再初始化列表里面用 size 来初始化 capacity,因为初始化的顺序是变量声明的顺序,变量声明顺序更改会影响初始化的结果。
‹ 全缺省参数构造 ›
无参构造和单参数构造可以合成一个全缺省参数构造
//全缺省构造
string(const char* str = "")
: _size(strlen(str))
{
_capacity = _size;
_str = new char[_capacity + 1];
strcpy(_str, str);
}
""常量字符串默认以 ‘\0’ 结束 (字符串为不为空都是如此)const char* str = '\0'不可以! ‘\0’ 只是一个 char 类型的字符,将 char 类型的数据赋值给 const char* 类型不匹配,会发生类型转换,char 类型转化为 int 类型,类型仍然不匹配,则 str 会被赋值为空指针。“\0”才是一个常量字符串const char* str = ""==const char* str = "\0"
〔拷贝构造〕
开新空间 + 拷贝数据
string(const string& s)
{
_str = new char[s._capacity + 1];
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
strcpy(_str, s._str);
}
• operator= 赋值重载
delete原空间- 自己赋值给自己( s = s )?自己给自己 delete 之后就什么都没了~,所以如果是自己给自己赋值,这里需要判断一下,什么也不执行就行了。
new新空间- 为了防止开空间失败,这个可以先创建临时变量
strcpy内容到新空间- 修改
size和capacity
❗❗赋值重载是关于两个已经存在的对象
string& operator=(const string& s)
{
if (this != &s)
{
//防止开空间失败
char* tmp = new char[s._capacity + 1];
strcpy(tmp, s._str);
//
delete[]_str;//销毁原空间
_str = tmp;//拷贝数据
_size = s._size;
_capacity = s._capacity;
}
return *this;
}
• Element access(operator[])
char& operator[](size_t index)
{
assert(index < _size);
return _str[index];
}
const char& operator[](size_t index)const
{
assert(index < _size);
return _str[index];
}
补充:const 变量的场景
const 变量不可以调用非 const 成员函数,不修改成员函数变量数据的函数最好都加 const
例如如下代码:参数为 const string 类型
const char& operator[](size_t index)const
{
assert(index < _size);
return _str[index];
}
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
void Print(const string& s)
{
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)//size()
{
cout << s[i] << " ";//[]操作符重载
}
cout << endl;
}
• Iterator
这里用指针来模拟实现迭代器,但库中的迭代器不一定都是用指针实现的。
另外,begin() 和 end() 遵循 “左闭右开” 的原则。
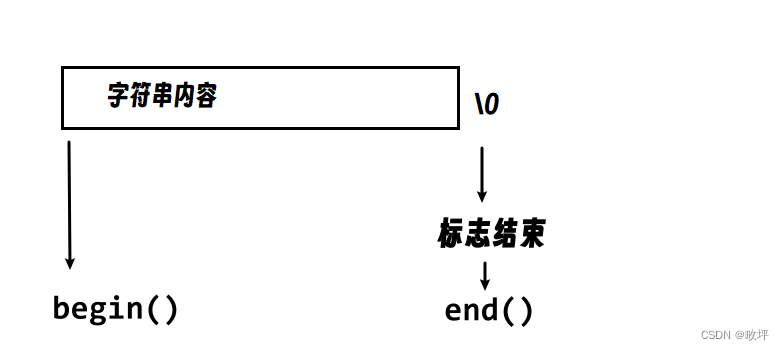
typedef char* iterator;
typedef const char* const_iterator;
// iterator
iterator begin()
{
return _str;
}
iterator end()
{
return (_str + _size);
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _str;
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return (_str + _size);
}
实现了迭代器之后,范围for也可以用。
应用示例:
void string_test6()
{
string s("abcdefghijklm");
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for(auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
• Relational Operators(比较大小)
比较ASCII码值的大小,复用 strcmp
bool operator<(const string& s)
{
return strcmp(_str, s._str) < 0;
}
bool operator<=(const string& s)
{
return strcmp(_str, s._str) <= 0;
}
bool operator>(const string& s)
{
return !(*this <= s);
}
bool operator>=(const string& s)
{
return !(*this < s);
}
bool operator==(const string& s)
{
return strcmp(_str, s._str) == 0;
}
bool operator!=(const string& s)
{
return !(*this == s);
}
• Capacity
〔size〕&〔capacity〕&〔empty〕
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
size_t capacity()const
{
return _capacity;
}
bool empty()const
{
return _size == 0;
}
〔reserve〕
- reverse 是管理容量的函数
- 不缩容原则,如果要更改的容量大小小于原容量大小则不执行操作
- 实现思路:
- 按指定容量大小开新空间(永远多开一个位置给’\0’)
- 拷贝数据到新空间
- 释放原空间
- 新空间地址赋值给 _str
- 修改容量大小
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
char* tmp = new char[n + 1];
strcpy(tmp, _str);
delete[]_str;
_str = tmp;
_capacity = n;
}
}
〔resize〕
- resize :开空间(size_t n) + 初始化(char c)
if (n <= _size)容量不缩,只保留前 n 个数据if (n > _capacity)扩容- ps. size >= capacity
void resize(size_t n, char c = '\0')
{
if (n <= _size)
{
_str[n] = '\0';
_size = n;
}
else
{
if (n > _capacity)
{
reserve(n);
}
int cout = n - _size;
while (cout--)
{
_str[_size] = c;
++_size;
}
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
}
• Modify
〔push_back〕&〔append〕
插入数据就要考虑容量问题,势必要进行扩容,由于原本的空间就是 new 出来的,扩容肯定不能用 realloc 直接扩容,所以最终我们选择手动扩容 → 调用 reserve 函数

整体思路:
- 检查容量
- 插入数据
- 修改 _size
void push_back(char c)
{
if (_size == _capacity)
{
//扩容
int new_capacity = _capacity == 0 ? 7 : _capacity * 2;
reserve(new_capacity);
}
_str[_size] = c;
++_size;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
void append(const char* str)
{
int len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)
{
reserve(_size + len);
}
strcpy(_str + _size, str);
_size += len;
}
〔+=〕
复用 push_back 和 append
string& operator+=(char c)
{
push_back(c);
return *this;
}
string& operator+=(const char* str)
{
append(str);
return *this;
}
〔swap〕
可以复用 std 库里的 swap 函数
void swap(string& s)
{
/*char* ptmp = _str;
_str = s._str;
s._str = _str;
char size = _size;
_size = s._size;
s._size = _size;
char capacity = _capacity;
_capacity = s._capacity;
s._capacity = _capacity;*/
std::swap(_str, s._str);
std::swap(_size, s._size);
std::swap(_capacity, s._capacity);
}
〔clear〕& 〔c_str〕
clear :清空数据
void clear()
{
_size = 0;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
const char* c_str()const
{
return _str;
}
• 「insert」在 pos 位置插入字符或字符串
插入字符就相当于插入只有单个字符的字符串,所以这里详细分析插入字符串时的情况,插入字符的思路与之类似。
基本思路:①检查容量;②挪动数据(strncpy);③插入数据。(注意检查 pos 位置的有效性)
如下图,在 pos 位置插入长度为 len 的字符串:则我们需要把 红色区域 的数据往后挪动 len个单位长度,再将要插入的数据从原 pos 位置往后依此插入。
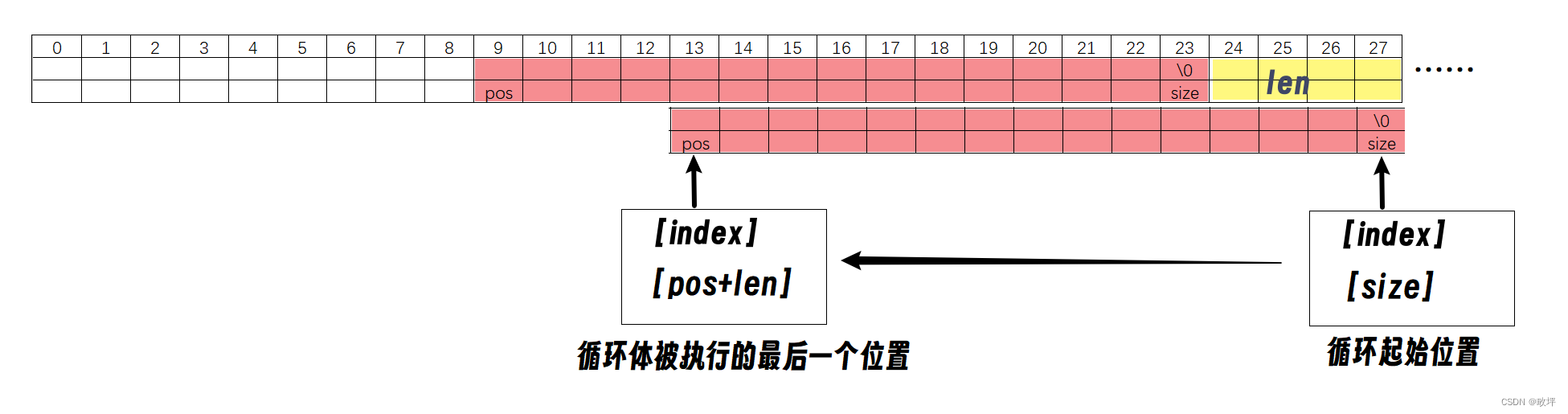
- 可以选择 index 从 size 位置开始吗??👉不可以
当 pos == 0 时情况如下:
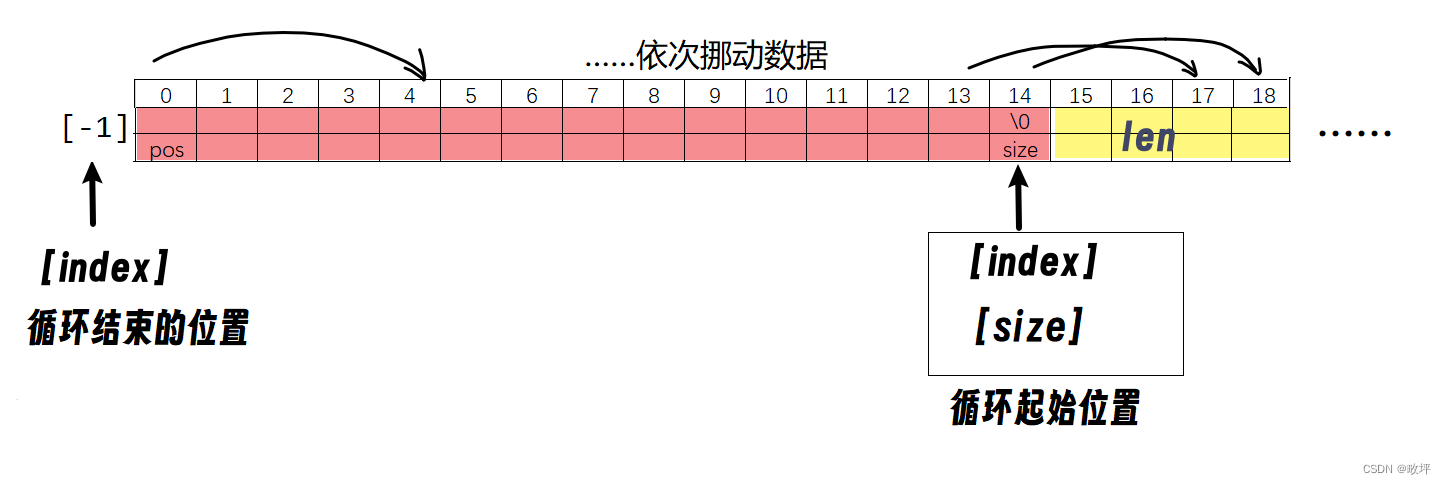
①size_t index是无符号整型,-1即为整型的最大值,以 index >= pos 作为循环判断条件,在 pos ==0 的情况下将进入死循环;
②若声明int index,仍以 index >= pos 作为循环判断条件,>=操作符左右变量的类型不同,会发生类型转换,通常是比较范围小的向范围大的转换,即在该情况下,有符号整型一般转化为无符号整型。
简单说明一下strnpy函数:strncpy( dst-copy到哪 , scr-从哪copy , 从scr copy 多少个)
string& insert(size_t pos, char c)
{
assert((pos <= _size) && (pos >= 0));
if (_size + 1 > _capacity)//扩容
{
int new_capacity = _capacity == 0 ? 7 : _capacity * 2;
reserve(new_capacity);
}
for (size_t index = _size + 1; index >= pos + 1; --index)//挪动数据
{
_str[index] = _str[index - 1];
}
_str[pos] = c;
++_size;
return *this;
}
string& insert(size_t pos, const char* str)
{
assert((pos <= _size) && (pos >= 0));
int len = strlen(str);
if (_size + len > _capacity)//扩容
{
int new_capacity = _size + len;
reserve(new_capacity);
}
for (int index = _size + len; index >= pos + len; --index)//挪动数据
{
_str[index] = _str[index - len];
}
strncpy(_str + pos, str, len);
_size += len;
return *this;
}
• 「erase」从 pos 位置删除 len 个字符
- pos 往后还有 >= len 个长度的字符:挪动覆盖数据(memmove/strcpy)
- pos 往后不足 len 个长度的字符:从 pos 往后全部删除(包括 pos 位置的数据)
注意:pos + len >= _size || len == npos len == npos必须单独判断,npos 已经是整型的最大值。
string& erase(size_t pos, size_t len = npos)
{
assert((pos < _size) && pos);
if (pos + len >= _size || len == npos)
{
_size = pos;
_str[_size] = '\0';
}
else
{
for (size_t index = pos + len; index <= _size; ++index)
{
_str[index - len] = _str[index];
}
//strcpy(_str+pos,_str+pos+len)
_size -= len;
}
return *this;
}
注:npos的声明和定义
class string
{
private:
char* _str;
size_t _capacity;
size_t _size;
static size_t npos;
//static size_t npos = -1;error
};
size_t string::npos = -1;
静态成员变量:类内声明,类外定义。
(ps. C++中加 const 的静态成员变量可以给缺省值,但是只针对整型变量)(最好不要这么用)
class string
{
private:
const static size_t npos = -1;
};
• 「find」
- 找字符:找到就返回该字符下标,没有找到返回 npos
- 找字串:strstr函数暴力匹配
- 为 nullptr 即没找到
- 找到返回子串第一个字符的地址 👉 地址 - 地址 = 下标
//找字符c
size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const
{
for (int i = 0; i < _size; ++i)
{
if (_str[i] == c)
return i;
}
return npos;
}
//找字串s
size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const
{
char* p = strstr(_str, s);
if (p == nullptr)
{
return npos;
}
else
{
return (p - _str);
}
}
• 「流插入<<、流提取>>」
肯定不能写成成员函数,可以用友元函数,但也不一定要写成友元函数。
‹ 流插入 ›
- 流插入重载要根据 size 打印,即使字符串间夹杂着 ‘\0’
- 不能直接访问成员变量,可以通过成员函数间接访问。( iterator / 范围for / [下标] )
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& _cout, const RoundBottle::string& s)
{
for (auto e : s)
{
_cout << e;
}
return _cout;
}
‹ 流提取 ›
cin 和 scanf 对于空格和换行不识别 👉 采用 istream 的成员函数 get()
优化:不断输入字符会导致频繁的扩容,这里可以用一个临时数组储存输入字符,临时数组每满一次就追加到 string s 中,知道输入结束后,将临时数组里剩下的字符再追加到 string s 中。
std::istream& operator>>(std::istream& _cin, RoundBottle::string& s)
{
s.clear();
char tmp[128];
char c = _cin.get();
int index = 0;
while (c != '\0' && c != '\n')
{
tmp[index] = c;
++index;
if (index == 127)
{
tmp[index] = '\0';
s += tmp;
index = 0;
}
c = _cin.get();
}
if (index != 0)
{
tmp[index] = '\0';
s += tmp;
}
return _cin;
}
END