项目背景
紧接上文,我们已经完成了 SpringBoot中集成Spring Security,并且用户名帐号和密码都是从数据库中获取。但是这种方式还是不能满足现在的开发需求。
使用JWT的好处:
- 无状态认证:JWT本身包含了认证信息和声明,服务器不需要在会话中保存任何状态。这样使得应用程序可以更加容易的扩展,并且更适合分布式部署和微服务架构。
- 跨域支持:由于JWT在HTTP头部中进行传输,因此它可以轻松的支持跨域请求。
- 灵活性:JWT可以包含任意数量的声明,这些声明可以用来传递用户、角色、或者其他相关的元数据。这些数据可以在服务器端和客户端之间共享,从而简化了授权和访问控制管理。
- 安全性:JWT使用数字签名或者加密算法来验证其完整性和真实性。这确保了JWT在传输过程中不会被篡改或伪造。
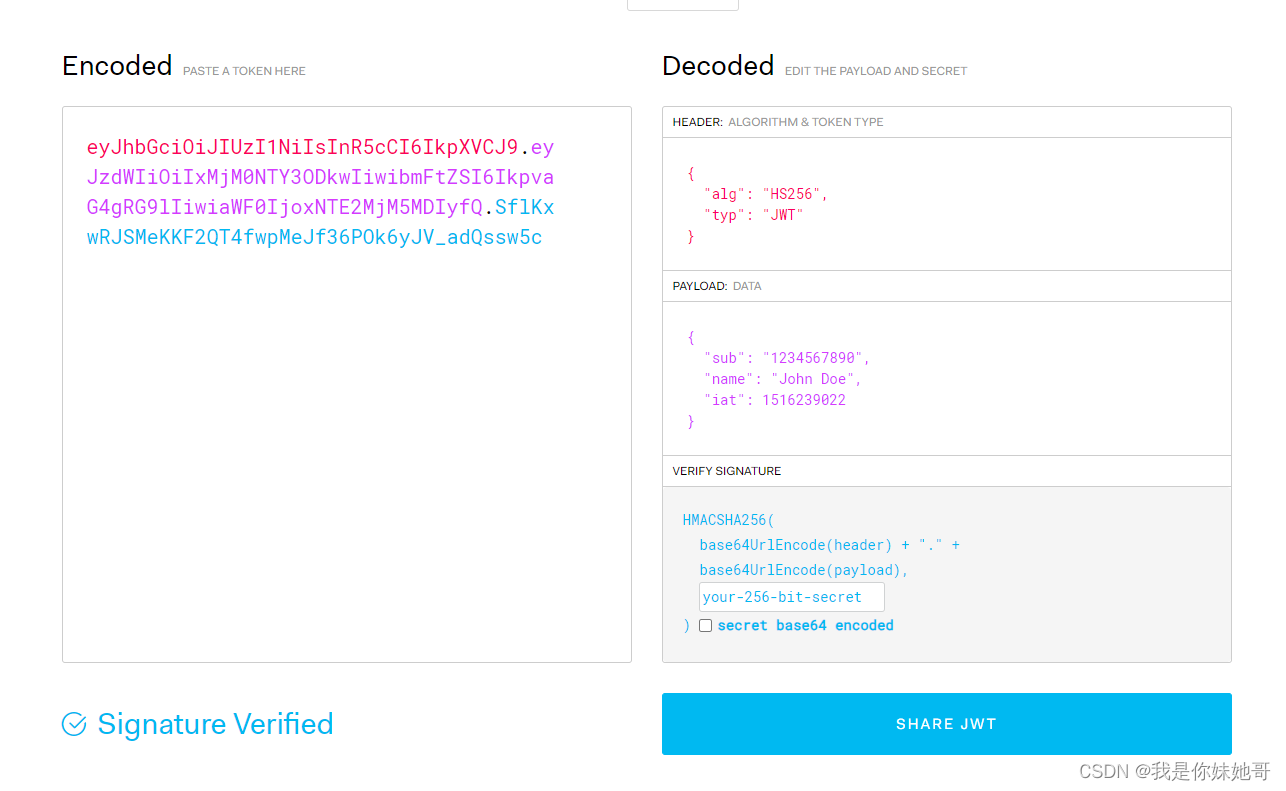
JWT(Json Web Tokens)
JSON Web Token (JWT) is an open standard (RFC 7519) that defines a compact and self-contained way for securely transmitting information between parties as a JSON object. This information can be verified and trusted because it is digitally signed. JWTs can be signed using a secret (with the HMAC algorithm) or a public/private key pair using RSA or ECDS
翻译:JSON Web Token (JWT) 是一个开放标准 (RFC 7519),它定义了一种紧凑且自包含的方式,用于在各方之间安全地传输信息作为 JSON 对象。 此信息可以验证和信任,因为它是数字签名的。 JWT 可以使用密钥(使用 HMAC 算法)或使用 RSA 或 ECDSA 的公钥/私钥对进行签名。
JWT组成
- header: 存放签名的生成算法。
- payload:存放用户名、token的生成时间和过期时间。
- signature:以header和payload生成的签名,一旦header和payload被篡改,验证将失败。
可以在该网站上进行解析:https://jwt.io/
Spring Security集成JWT
maven引入
<dependency>
<groupId>io.jsonwebtoken</groupId>
<artifactId>jjwt</artifactId>
<version>0.9.0</version>
</dependency>
首先不论是不是Spring Security中集成JWT,我们得先有个工具类。这个工具类的主要内容是什么呢?
创建JWT、验证JWT、 解析JWT
步骤一:
JwtUtils工具类
/**
* jwt工具类
*
* @author caojing
* @since 2023/6/14
*/
public class JwtUtils {
/**
* token过期时间
*/
public static final long EXPIRE = 1000 * 60 * 60 * 24;
/**
* 秘钥
*/
public static final String APP_SECRET = "ukc8BDbRigUDaY6pZFfWus2jZWLPHO";
/**
* 生成token字符串的方法
*
* @param id
* @param nickname
* @return
*/
public static String getJwtToken(String id, String nickname) {
String jwtToken = Jwts.builder().setHeaderParam("typ", "JWT").setHeaderParam("alg", "HS256")
.setSubject("guli-user").setIssuedAt(new Date()).setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis() + EXPIRE))
//设置token主体部分 ,存储用户信息
.claim("id", id)
.claim("nickname", nickname)
.signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS256, APP_SECRET).compact();
return jwtToken;
}
/**
* 判断token是否存在与有效
*
* @param jwtToken
* @return
*/
public static boolean checkToken(String jwtToken) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(jwtToken)) {
return false;
}
try {
Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(APP_SECRET).parseClaimsJws(jwtToken);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 判断token是否存在与有效
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
public static boolean checkToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
String jwtToken = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(jwtToken)) {
return false;
}
Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(APP_SECRET).parseClaimsJws(jwtToken);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* 根据token字符串获取会员id
*
* @param request
* @return
*/
public static String getUserIdByJwtToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
String jwtToken = request.getHeader("Authorization");
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(jwtToken)) {
return "";
}
Jws<Claims> claimsJws = Jwts.parser().setSigningKey(APP_SECRET).parseClaimsJws(jwtToken);
Claims claims = claimsJws.getBody();
return (String) claims.get("id");
}
/**
* 验证jwt
*/
public static Claims verifyJwt(String token) {
Claims claims;
try {
//得到DefaultJwtParser
claims = Jwts.parser()
//设置签名的秘钥
.setSigningKey(APP_SECRET)
.parseClaimsJws(token).getBody();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
claims = null;
}//设置需要解析的jwt
return claims;
}
}
我们可以设想下这么一个流程:
前端在请求头中设置 Authorization参数,后台再进入到controller之前,会走一个过滤器对header中的Authorization参数进行校验,也就是利用JWTUtils对token进行解析。
1.通过校验:模拟 spring Security 登录成功,把token值塞到一个变量里面。
2.未通过校验:继续走spring Security的验证流程(理论上会抛出异常)
注意以上我们分析的关键字:过滤器
因此,我们新建一个JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter 类继承OncePerRequestFilter 。
继承 OncePerRequestFilter 的原因:
- 确保在一次请求中只执行一次过滤操作。OncePerRequestFilter是Spring框架提供的一个过滤器基类,它确保每个请求只通过一次,而不会重复执行过滤逻辑。
- 当客户端发送请求时,过滤器链会按照配置的顺序对请求进行过滤。如果一个过滤器没有继承OncePerRequestFilter,它可能会在请求链中的多个位置执行,导致重复处理请求的问题。
- 继承OncePerRequestFilter可以确保JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter在整个过滤器链中的每个请求中只执行一次,避免了多次处理同一个请求的问题。这对于执行基于JWT的身份验证和授权逻辑非常重要,因为它确保只有在一次请求中进行一次JWT的验证和解析,避免了不必要的性能开销和潜在的安全问题。
总结来说,JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter继承OncePerRequestFilter是为了保证它在过滤器链中的每个请求中只执行一次,避免了重复处理请求的问题,确保了JWT身份验证和授权逻辑的准确性和性能。
步骤二
将jwtFilter添加到Spring Security 过滤器中
JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter 类
/**
* token过滤器 验证token有效性
* 判断用户是否有效走 MyUserDetailService的 loadUserByUsername 方法
*
* @author caojing
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
@Autowired
private RedisUtils redisUtils;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 从请求头中获取token
String authToken = request.getHeader("Authorization");
// 截取token
if (authToken != null) {
//验证token,获取token中的username
Claims claims = JwtUtils.verifyJwt(authToken);
if (claims == null) {
throw new ServletException("token异常,请重新登录");
}
//从redis 获取缓存
String redisKey = JwtUtils.getUserIdByJwtToken(request);
UserBean userBean = redisUtils.getCacheObject(redisKey);
//重新设置token的失效时间
redisUtils.setCacheObject(redisKey, userBean, 30, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
if (userBean != null && SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
//获取到值,相当于手动把session值设置到此次request中,后续就会认为已经登录,不做登录校验
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authenticationToken =
new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(userBean, null, userBean.getAuthorities());
authenticationToken.setDetails(new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(request));
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authenticationToken);
}
}
//继续下一个过滤器
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter添加到ScurityConfig类中
/**
* Spring Security 配置类
*
* @author caojing
* @since 2023/6/14
*/
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private MyUserDetailService userDetailService;
@Autowired
private JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http// 基于token,所以不需要session
.sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS).and()
.addFilterBefore(JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
// auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
// .passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
// .withUser("user").password(encoder.encode("123456")).roles("USER");
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailService).passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder());
}
}
说明:利用addFilterBefore方法,把jwt认证放到UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter过滤器之前。为什么要放到这里,我们下一篇文章会说。
步骤三
怎么把验证交给Spring Security
基本工作已经做完。我们还剩下一个获取token的controller。
想一想这个controller应该有什么功能?
没有使用spring Security之前,我们是不是在login获取用户输入的帐号名和密码,然后根据帐号名从数据库查询出来对应的用户信息。然后对比密码(加密后)是否正确。
使用了Spring Security之后,思考一下,哪些能用,哪些需要替换。
- 帐号名密码的获取肯定是要继续用的。
- 认证移动到了MyUserDetailService中认证,也就是使用Spring Security的
DaoAuthenticationProvider进行认证。所以原先的认证需要删除替换成DaoAuthenticationProvider认证。
上面第一个问题好解决,那么第二个问题该如何实现呢?
先说结果:
使用AuthenticationManager的authenticate方法进行认证。
如何找到这个入口?
我们现在已知的类是DaoAuthenticationProvider,所以先从这个类开始。先看下这个类是实现AuthenticationProvider接口。先说一下这个接口的2个方法构成:
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
/**
* Performs authentication with the same contract as
* {@link org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager#authenticate(Authentication)}
* .
*
* @param authentication the authentication request object.
*
* @return a fully authenticated object including credentials. May return
* <code>null</code> if the <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> is unable to support
* authentication of the passed <code>Authentication</code> object. In such a case,
* the next <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> that supports the presented
* <code>Authentication</code> class will be tried.
*
* @throws AuthenticationException if authentication fails.
*/
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
/**
* Returns <code>true</code> if this <Code>AuthenticationProvider</code> supports the
* indicated <Code>Authentication</code> object.
* <p>
* Returning <code>true</code> does not guarantee an
* <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> will be able to authenticate the presented
* instance of the <code>Authentication</code> class. It simply indicates it can
* support closer evaluation of it. An <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> can still
* return <code>null</code> from the {@link #authenticate(Authentication)} method to
* indicate another <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> should be tried.
* </p>
* <p>
* Selection of an <code>AuthenticationProvider</code> capable of performing
* authentication is conducted at runtime the <code>ProviderManager</code>.
* </p>
*
* @param authentication
*
* @return <code>true</code> if the implementation can more closely evaluate the
* <code>Authentication</code> class presented
*/
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
这边重点注意2句话:
Performs authentication with the same contract as * {@link org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationManager#authenticate(Authentication)}
翻译:
执行的身份认证和AuthenticationManager#authenticate这个方法具有相同的合同?
黑人问号脸?换个说人话的:
合同 = 契约。
软件开发中 contract一般都翻译成契约的意思。而且契约在软件开发中特制:定义了功能、接口或方法应该具有的行为和特征的规范。当两个功能或组件具有相同的契约时,它们在执行特定操作时遵循相同的规则和约定。也就是俗称约定。
人话:
这个方法和AuthenticationManager#authenticate(Authentication) 具有相同的认证规则和约定Selection of an AuthenticationProvider capable of performing authentication is conducted at runtime the ProviderManager.
翻译:
选择一个AuthenticationProvider能够执行身份校验是在ProviderManager运行执行期间?
人话:
在ProviderManager运行执行期间来使用该方法判断AuthenticationProvider是否能执行身份校验
这2个方法都提到了一个类:ProviderManager。所以下一步我们看看这个类。
有点长。。。。。。。。
直接看AuthenticationManager这个接口吧:
/**
* Processes an {@link Authentication} request.
*
* @author Ben Alex
*/
public interface AuthenticationManager {
// ~ Methods
// ========================================================================================================
/**
* Attempts to authenticate the passed {@link Authentication} object, returning a
* fully populated <code>Authentication</code> object (including granted authorities)
* if successful.
* <p>
* An <code>AuthenticationManager</code> must honour the following contract concerning
* exceptions:
* <ul>
* <li>A {@link DisabledException} must be thrown if an account is disabled and the
* <code>AuthenticationManager</code> can test for this state.</li>
* <li>A {@link LockedException} must be thrown if an account is locked and the
* <code>AuthenticationManager</code> can test for account locking.</li>
* <li>A {@link BadCredentialsException} must be thrown if incorrect credentials are
* presented. Whilst the above exceptions are optional, an
* <code>AuthenticationManager</code> must <B>always</B> test credentials.</li>
* </ul>
* Exceptions should be tested for and if applicable thrown in the order expressed
* above (i.e. if an account is disabled or locked, the authentication request is
* immediately rejected and the credentials testing process is not performed). This
* prevents credentials being tested against disabled or locked accounts.
*
* @param authentication the authentication request object
*
* @return a fully authenticated object including credentials
*
* @throws AuthenticationException if authentication fails
*/
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}
该类只有一个方法:authenticate。
解释:
尝试对传递的 Authentication 对象进行身份验证,如果成功则返回一个完全填充的 Authentication 对象(包括授予的权限)。。。。。。。。。
人话:
对我们传入的Authentication对象进行身份认证,通过以后会返回Authentication 对象。
简而言之。这个类AuthenticationManager 就是我们具体身份认证的入口了,但这是一个接口,具体的实现类是通过默认的ProviderManager实现。
继续看ProviderManager中的authenticate方法:
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException {
Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass();
AuthenticationException lastException = null;
AuthenticationException parentException = null;
Authentication result = null;
Authentication parentResult = null;
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) {
if (!provider.supports(toTest)) {
continue;
}
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Authentication attempt using "
+ provider.getClass().getName());
}
try {
result = provider.authenticate(authentication);
if (result != null) {
copyDetails(authentication, result);
break;
}
}
catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException e) {
prepareException(e, authentication);
// SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to
// invalid account status
throw e;
} catch (AuthenticationException e) {
lastException = e;
}
}
......
}
我这里只贴出来部分代码:我们可以看到代码的主要结构是一个for循环。循环的内容是啥呢?是AuthenticationProvider的实现类。循环干什么呢?
- 根据
AuthenticationProvider中的provider方法判断是否支持验证当前的authentication,具体行:189行。 - 判断具体的身份权限交给
AuthenticationProvider的authenticate方法,具体行:199行
解释一下第一句话:
AuthenticationProvider和authentication 都是接口,并不是具体的实现类,所以看来比较抽象。因此,我就拿用户名密码登录方式举例。
在用户名和密码登录模式中 AuthenticationProvider的具体实现类AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider
authentication 的具体实现类是UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken。那么验证身份流程就变成了
ProviderManager#authentication -> AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider#supports->AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider#authenticate->return UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
具体时序图如下所示:

基于以上的流程,我们不难知道在login中需要调用authenticationManager#authenticate方法进行认证了
如何引入AuthenticationManager?
看下配置类中继承的类WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter
其中有个方法:
/**
* Override this method to expose the {@link AuthenticationManager} from
* {@link #configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder)} to be exposed as a Bean. For
* example:
*
* <pre>
* @Bean(name name="myAuthenticationManager")
* @Override
* public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
* return super.authenticationManagerBean();
* }
* </pre>
*
* @return the {@link AuthenticationManager}
* @throws Exception
*/
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return new AuthenticationManagerDelegator(authenticationBuilder, context);
}
这很好理解吧,不需要翻译了。
Logservice 代码如下:
/**
* 登录接口
*
* @author caojing
* @since 2023/6/15
*/
@Slf4j
@Service
public class LoginService {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Autowired
private RedisUtils redisUtils;
public ResponseBean<String> login(String username, String password) {
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password);
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(usernamePasswordAuthenticationToken);
//这边可以获取用户信息.这里getPrincipal和 JwtAuthenticationTokenFilter类中 完成token验证之后
//new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 塞进去的值
UserBean userBean = (UserBean) authentication.getPrincipal();
log.info("用户信息:{}", JSON.toJSONString(userBean));
String token = JwtUtils.getJwtToken(String.valueOf(userBean.getId()), username);
//每次登录都获取最新的值,
redisUtils.setCacheObject(String.valueOf(userBean.getId()), userBean, 30, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
return new ResponseBean<>(HttpStatus.OK.value(), "获取成功", token);
}
}
SecurityConfig配置类增加
/**
* Spring Security 配置类
*
* @author caojing
* @since 2023/6/14
*/
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
//......................
@Override
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
}
启动项目
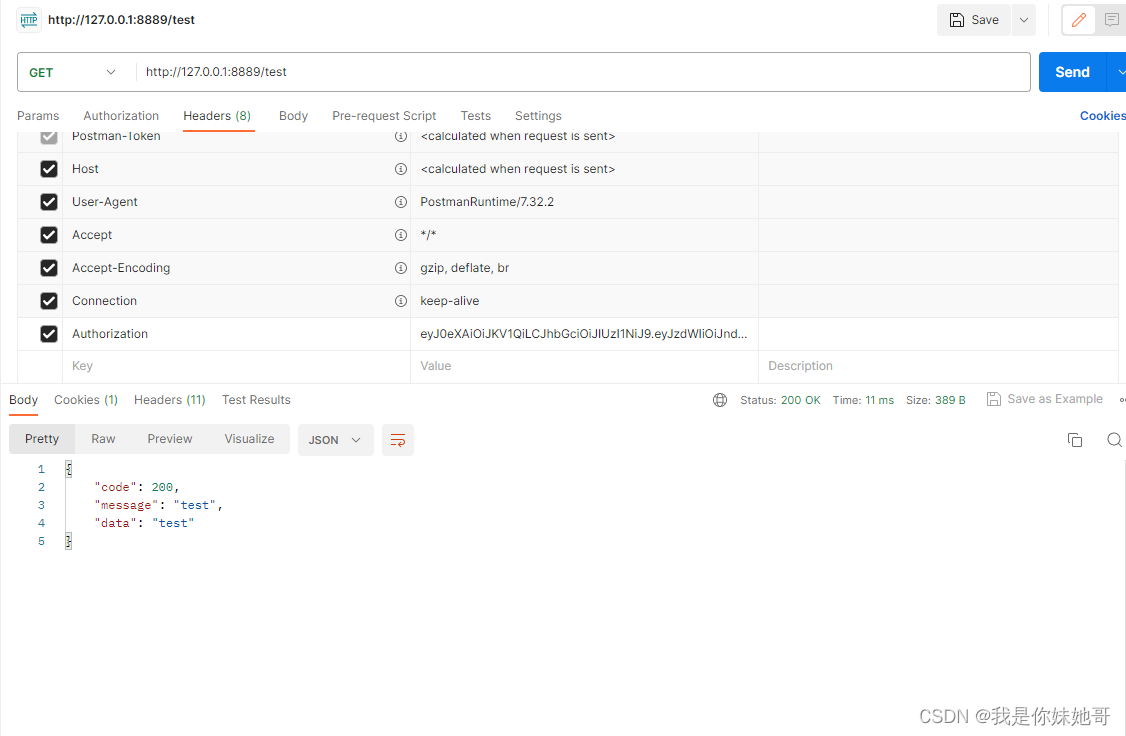
访问地址:http://127.0.0.1:8889/token

测试一下token值是否有效。
先测试不带Authorization的请求:http://127.0.0.1:8889/test

带Authorization的请求:http://127.0.0.1:8889/test
总结
思路:
整体思路分2个部分:
-
登录认证获取token
提供一个controller,将controller的地址加到spring Security 的config中不做权限控制,访问该controller,将用户名和密码的判断交给spring Security 的userDetailService处理,根据处理的返回结果决定是否生成对应的token值。- 如何交给Spring Security 处理认证过程:
authenticationManager.authenticate()。具体是怎么找到这个入口的,详情可以看步骤三。
- 如何交给Spring Security 处理认证过程:
-
接口认证token值
- 加入JWT生成的工具类
- Spring Security 提供多种认证方式,但我们需要熟悉的是
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter。剩下的认证方式了解即可。 - 在了解了Spring Security的几种认证方式之后,我们需要考虑将自定义的jwtFilter加入到Srping Security的过滤器中。对应上面的步骤二。
- 步骤二完成以后,当token值存在的时候,会把用户信息转化成
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken,其实也不是非要这个类,任何一个实现Authentication即接口的类都可以。然后通过SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication()方法,将用户信息设置到SecurityContextHolder中
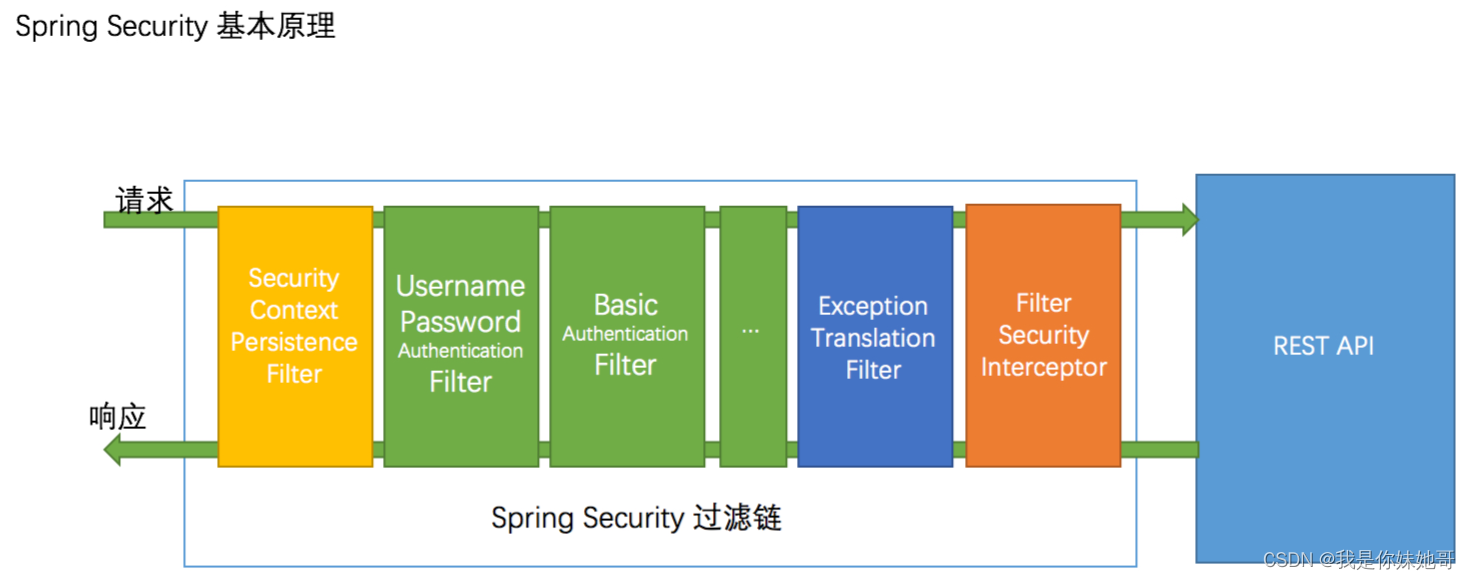
下面是一张Spring Security的过滤器的链路图,基本上Spring Security 都是围绕着这几个过滤器进行一些功能。比如后续的异常、权限控制(选举策略)都是在过滤器中实现。具体内容咱们下个章节继续聊。
习题:
- 为什么通过
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication()方法就可以实现登录了。或者说SecurityContextHolder到底有什么用。 - Spring Security中主要分为权限和认证,认证已经讲过了,那么权限是如何控制的?(提示:也是过滤器,涉及的几个类
SecurityMetadataSource、GrantedAuthority、AccessDecisionManager) - 能否找到Spring Security中的大部分的过滤器?
下一篇主要内容是稍微介绍下Spring Security的源码,顺带解决习题中的几个问题。
上一篇文章地址:SpringBoot2.3集成Spring Security(一)