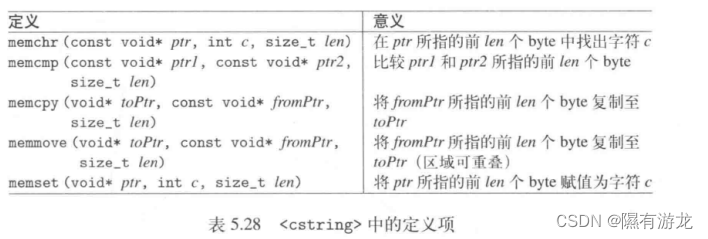
一 代码实现
理论依据:
管道中无数据时,读阻塞。
写数据时,长度小于PIPE_BUF时,写数据是原子操作,这样不会出现写一半的情况。在我的虚拟机上PIPE_BUF的值是4096,在标准中linux系统中该值都是4096.
测试代码:编写源码如下所示:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define DEBUG_INFO(format, ...) printf("%s - %d - %s :: "format"\n",__FILE__,__LINE__,__func__ ,##__VA_ARGS__)
struct mq_data{
int len;
int cmd;
int seq;
char data[128];
};
//写线程
void *pthread_write(void *arg){
int fd = (int)arg;
struct mq_data data;
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(data));
data.len = sizeof("456");
memcpy(data.data,"456",sizeof("456"));
write(fd,&data,sizeof(data));
return NULL;
}
//读线程
void *pthread_read(void *arg){
int fd = (int)arg;
struct mq_data data;
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(data));
int len = read(fd,&data,sizeof(data));
DEBUG_INFO("read %d,data = %s",len,data.data);
exit(0);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int res = 0;
int fds[2];
res = pipe(fds);
if(res < 0){
perror("pipe");
return -1;
}
pthread_t p1,p2;
res = pthread_create(&p1,NULL,pthread_write,(void*)fds[1]);
if(res == -1){
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(p1);
res = pthread_create(&p2,NULL,pthread_read,(void*)fds[0]);
if(res == -1){
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(p2);
while(1){
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}CMakeLists
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.8)
project(myapp)
SET(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -std=c99 -pthread")
add_executable(pipe_thread_com pipe_thread_com.c)编译脚本
rm -rf _build_
mkdir _build_ -p
cmake -S ./ -B _build_
make -C _build_
./_build_/pipe_thread_com测试结果:
二 time命令
time命令最常用的使用方式就是在其后面直接跟上命令和参数:
1
time [options]command [arguments...]在命令执行完成之后就会打印出CPU的使用情况:
real 0m5.064s <== 实际使用时间(real time)
user 0m0.020s <== 用户态使用时间(the process spent in user mode)
sys 0m0.040s <== 内核态使用时间(the process spent in kernel mode)
time命令跟上-p参数可以只打印时间数值(秒数),不打印单位。
实例,这是测试sleep 1命令执行花费的时间,这不是废话吗,肯定是一秒啊?结果如下所示,结果是1.002秒。2毫秒有必要计较吗?当然有必要。
$ time sleep 1
real 0m1.002s
user 0m0.001s
sys 0m0.000s这个测试至少还说明了,sleep命令完全是在用户态实现的。
三 性能测试
测试一 测试上面代码的花费时间,总计1毫秒,系统调用时间为0.应该是太短忽略不计了吧。
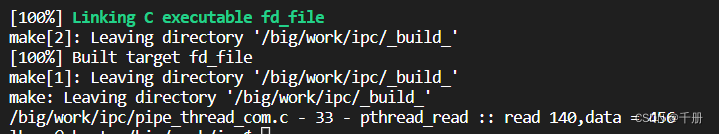
$ time ./pipe_thread_com
/big/work/ipc/pipe_thread_com.c - 33 - pthread_read :: read 140,data = 456
real 0m0.001s
user 0m0.001s
sys 0m0.000s修改代码,写1000次,在读线程中读1000次,然后使用time观察时间。发现时间和一次一样。
嗯,修改测试次数为10万次。
下面是优化后的代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define DEBUG_INFO(format, ...) printf("%s - %d - %s :: "format"\n",__FILE__,__LINE__,__func__ ,##__VA_ARGS__)
#define TEST_MAX_COUNT 100000
struct mq_data{
int len;
int cmd;
int seq;
char data[128];
};
//写线程
void *pthread_write(void *arg){
int fd = (int)arg;
int res = 0;
struct mq_data data;
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(data));
data.len = sizeof("456");
memcpy(data.data,"456",sizeof("456"));
for(int i=0; i<TEST_MAX_COUNT;i++){
res = write(fd,&data,sizeof(data));
if(res < 0){
DEBUG_INFO("write:");
break;
}
}
close(fd);
return NULL;
}
//读线程
void *pthread_read(void *arg){
int fd = (int)arg;
int res = 0;
struct mq_data data;
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(data));
int count = 0;
do{
res = read(fd,&data,sizeof(data));
if(res == 0){
DEBUG_INFO("pipe close");
break;
}
if(res < 0){
perror("read");
break;
}
if(res != sizeof(data)){
DEBUG_INFO("length error");
exit(1);
}
count++;
}while(1);
close(fd);
if(count != TEST_MAX_COUNT){
DEBUG_INFO("recv count error");
}
DEBUG_INFO("count = %d",count);
exit(0);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int res = 0;
int fds[2];
res = pipe(fds);
if(res < 0){
perror("pipe");
return -1;
}
pthread_t p1,p2;
res = pthread_create(&p1,NULL,pthread_write,(void*)fds[1]);
if(res == -1){
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(p1);
res = pthread_create(&p2,NULL,pthread_read,(void*)fds[0]);
if(res == -1){
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(p2);
while(1){
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}测试结果:
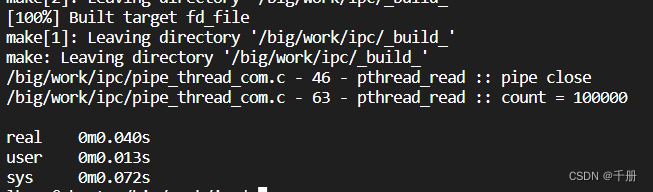
使用select操作读管道:
在此需要将管道读端设置为非阻塞模式
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define DEBUG_INFO(format, ...) printf("%s - %d - %s :: "format"\n",__FILE__,__LINE__,__func__ ,##__VA_ARGS__)
#define TEST_MAX_COUNT 100000
struct mq_data{
int len;
int cmd;
int seq;
char data[128];
};
//写线程
void *pthread_write(void *arg){
int fd = (int)arg;
int res = 0;
struct mq_data data;
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(data));
data.len = sizeof("456");
memcpy(data.data,"456",sizeof("456"));
for(int i=0; i<TEST_MAX_COUNT;i++){
res = write(fd,&data,sizeof(data));
if(res < 0){
DEBUG_INFO("write:");
break;
}
}
close(fd);
return NULL;
}
//读线程
void *pthread_read(void *arg){
int fd = (int)arg;
int res = 0;
struct mq_data data;
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(data));
int count = 0;
fd_set rset;
FD_ZERO(&rset);
FD_SET(fd,&rset);
int flag = fcntl(fd,F_GETFL);
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,flag);
while(1){
res = select(fd + 1,&rset,NULL,NULL,NULL);
if(res == -1){
perror("selct");
exit(-1);
}
if(FD_ISSET(fd,&rset)){
int read_res = read(fd,&data,sizeof(data));
if(read_res == 0){
DEBUG_INFO("pipe close");
break;
}
if(read_res < 0){
perror("read");
break;
}
if(read_res != sizeof(data)){
DEBUG_INFO("length error");
exit(1);
}
//DEBUG_INFO("%s",data.data);
count++;
}
}
close(fd);
if(count != TEST_MAX_COUNT){
DEBUG_INFO("recv count error");
}
DEBUG_INFO("count = %d",count);
exit(0);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int res = 0;
int fds[2];
res = pipe(fds);
if(res < 0){
perror("pipe");
return -1;
}
pthread_t p1,p2;
res = pthread_create(&p1,NULL,pthread_write,(void*)fds[1]);
if(res == -1){
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(p1);
res = pthread_create(&p2,NULL,pthread_read,(void*)fds[0]);
if(res == -1){
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(p2);
while(1){
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}执行结果:

使用select同时操作读写管道
这个还可以验证写入长度是否是原子操作。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/select.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define DEBUG_INFO(format, ...) printf("%s - %d - %s :: "format"\n",__FILE__,__LINE__,__func__ ,##__VA_ARGS__)
#define TEST_MAX_COUNT 100000
struct mq_data{
int len;
int cmd;
int seq;
char data[128];
};
//写线程
void *pthread_write(void *arg){
int fd = (int)arg;
int res = 0;
struct mq_data data;
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(data));
data.len = sizeof("456");
memcpy(data.data,"456",sizeof("456"));
int flag = fcntl(fd,F_GETFL);
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,flag);
fd_set wset;
FD_ZERO(&wset);
FD_SET(fd,&wset);
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i<TEST_MAX_COUNT;i++){
res = select(fd + 1,NULL,&wset,NULL,NULL);
if(res == -1){
perror("selct");
exit(-1);
}
if(FD_ISSET(fd,&wset)){
int write_res = write(fd,&data,sizeof(data));
if(write_res < 0){
DEBUG_INFO("write:");
break;
}
}
}
close(fd);
return NULL;
}
//读线程
void *pthread_read(void *arg){
int fd = (int)arg;
int res = 0;
struct mq_data data;
memset(&data, 0, sizeof(data));
int count = 0;
fd_set rset;
FD_ZERO(&rset);
FD_SET(fd,&rset);
int flag = fcntl(fd,F_GETFL);
flag |= O_NONBLOCK;
fcntl(fd,F_SETFL,flag);
while(1){
res = select(fd + 1,&rset,NULL,NULL,NULL);
if(res == -1){
perror("selct");
exit(-1);
}
if(FD_ISSET(fd,&rset)){
int read_res = read(fd,&data,sizeof(data));
if(read_res == 0){
DEBUG_INFO("pipe close");
break;
}
if(read_res < 0){
perror("read");
break;
}
if(read_res != sizeof(data)){
DEBUG_INFO("length error");
exit(1);
}
// DEBUG_INFO("%s",data.data);
count++;
}
}
close(fd);
if(count != TEST_MAX_COUNT){
DEBUG_INFO("recv count error");
}
DEBUG_INFO("count = %d",count);
exit(0);
return NULL;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int res = 0;
int fds[2];
res = pipe(fds);
if(res < 0){
perror("pipe");
return -1;
}
pthread_t p1,p2;
res = pthread_create(&p1,NULL,pthread_write,(void*)fds[1]);
if(res == -1){
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(p1);
res = pthread_create(&p2,NULL,pthread_read,(void*)fds[0]);
if(res == -1){
perror("pthread_create");
return -1;
}
pthread_detach(p2);
while(1){
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}执行结果:
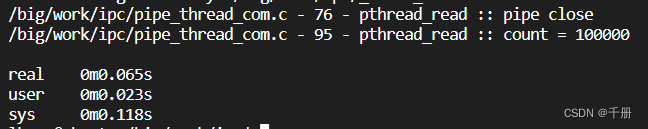
第一次对比

虽然有点牵强,也算是一种严谨性的体现吧。