文章目录
- 引言
- 主要流程
- 启动类剖析
- 启动类示例
- SpringApplication.run()方法
- 创建SpringApplication对象过程
- 创建对象源码流程整体分析
- 不服就debug
- 创建对象核心过程分解
- 流程1:deduceFromClasspath()获取主程序类和应用类型
- 流程2: setInitializers()设置初始化器
- 流程3: setListeners()设置监听器
- 流程4:deduceMainApplicationClass()获取主程序类Class
- getSpringFactoriesInstances()方法分析
- spring.factories文件
- getSpringFactoriesInstances()核心源码
- 创建对象主流程总结
- 执行SpringApplication.run()方法过程
- 执行run()方法源码过程整体分析
- 不服就debug
- run()方法核心过程分解
- 流程1:获取并启动运行过程监听器
- 流程2:准备并构建环境
- 流程3:IoC容器创建,即创建应用程序上下文
- 流程4:IoC容器的前置处理
- 流程5: IoC容器的刷新,即刷新应用程序上下文
- 流程6: IoC容器的后置处理
- 流程7: 监听器启动完成
- 流程8:执行Runners
- 执行run()方法主流程总结
引言
用了这么久Spring Boot框架,这次决定对Spring Boot的启动过程一探究竟!卷一波源码!
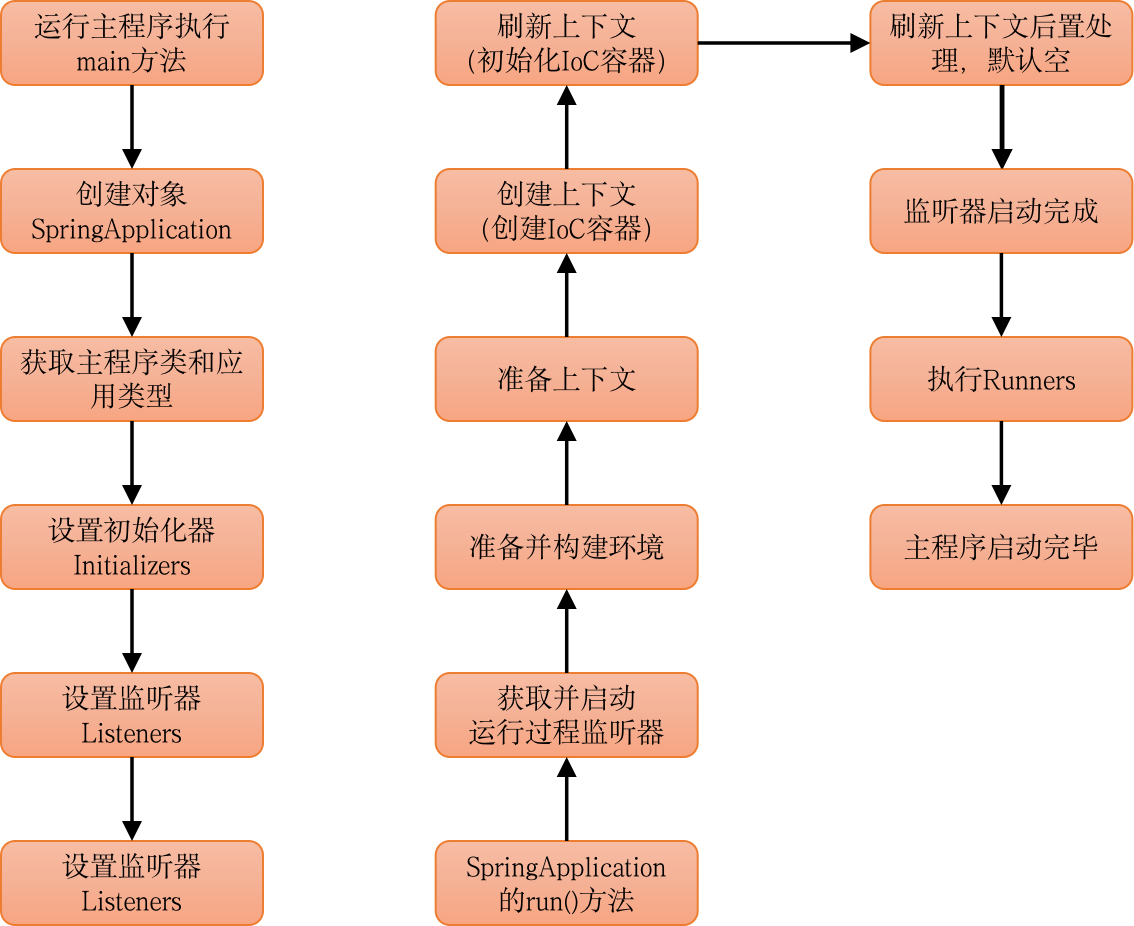
主要流程
话不多说,直接上主流程总结!
一、创建SpringApplication对象
- 获取主程序类和应用类型
- 设置初始化器Initializers
- 设置监听器Listeners
- 获取主程序类Class
二、执行run()方法 - 初始化环境配置
- 创建容器,即创建上下文
- 容器前置处理
- 刷新容器,即刷新上下文(springboot启动核心)
- 容器后置处理
- 通知监听者,执行Runners,程序启动完成
启动类剖析
启动类示例
首先,我们先要有一个正确的打开姿势:启动类入口
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SelfCodingApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SelfCodingApplication.class, args);
}
}
启动类在运行静态run()方法时,是先创建一个SpringApplication对象,再运行对象的run方法,工厂初始配置在构造函数中完成,而run方法定义程序启动总流程。
SpringApplication.run()方法
从启动类中的main()静态方法中点入SpringApplication.run()源码中,可以看到
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class[]{primarySource}, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
//1. new SpringApplication
//2. 执行run()方法
return (new SpringApplication(primarySources)).run(args);
}
主要涉及到创建SpringApplication对象以及执行run()方法两个过程。
创建SpringApplication对象过程
创建对象源码流程整体分析
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this((ResourceLoader)null, primarySources);
}
//构造对象
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.sources = new LinkedHashSet();
//打印springboot启动时的图标
this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE;
//true的话,打印jvm的启动和运行信息,如启动类、java版本、pid等
this.logStartupInfo = true;
//允许通过命令行参数向application.properties中添加属性配置,如--spring.profiles.active=dev
this.addCommandLineProperties = true;
//加载默认的类型转换和格式化类 (ApplicationConversionService)
this.addConversionService = true;
//开启java的headless模式,此模式允许java服务器可能缺少显示设备、键盘、鼠标等外设的情况下可以使用这种模式
this.headless = true;
//注册一个Shutdown Hook,创建线程,该线程用来在java程序关闭后释放资源
this.registerShutdownHook = true;
//默认空,读取“dev”、“test”等不同环境的配置
this.additionalProfiles = Collections.emptySet();
//会实例化一个环境转换器
this.isCustomEnvironment = false;
//是否懒初始化
this.lazyInitialization = false;
//默认的ApplicationContextFactory实现,它将为WebApplicationType创建一个适当的上下文。
this.applicationContextFactory = ApplicationContextFactory.DEFAULT;
//默认的ApplicationStartup实现,设置DefaultApplicationStartup
this.applicationStartup = ApplicationStartup.DEFAULT;
//设置resourceLoader,获取资源,默认null
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
//primarySources主启动类判空
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//将主启动类设置到LinkedHashSet集合中存储起来
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//设置web应用类型为:NONE/SERVLET/REACTIVE
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//从 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中得到 key 为 org.springframework.boot.BootstrapRegistryInitializer 的全类名集合,进行实例化,然后注入 bootstrapRegistryInitializers 属性
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
//配置应用程序启动前的初始化对象,从 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中得到初始化器集合,并注入
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//配置应用程序启动前的监听器,从 META-INF/spring.factories 文件中得到监听器实例的集合,并注入
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
//获取当前运行的 main 方法所在的类,即主类
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
不服就debug
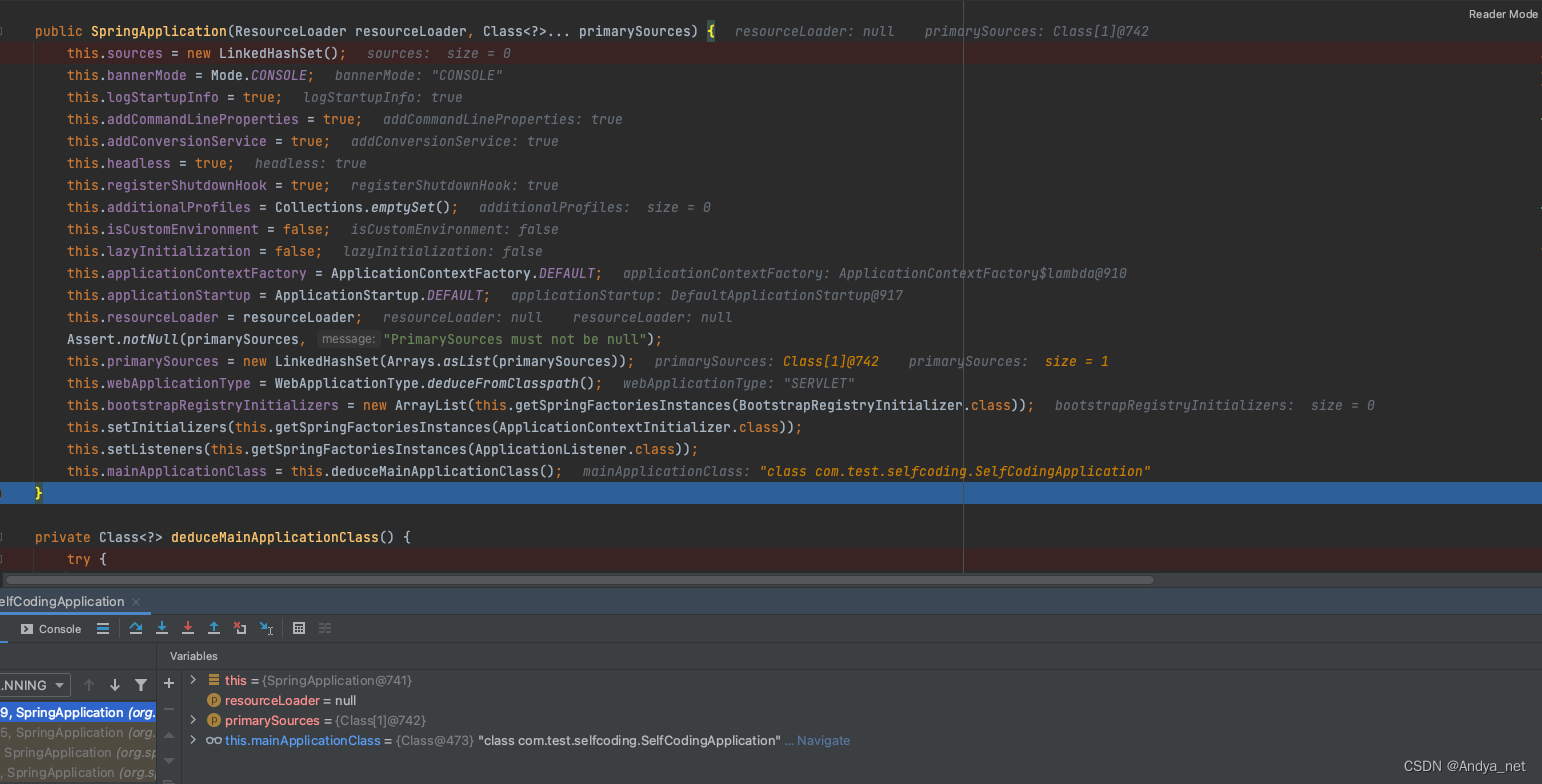
创建对象核心过程分解
流程1:deduceFromClasspath()获取主程序类和应用类型
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent("org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler", (ClassLoader)null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent("org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet", (ClassLoader)null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent("org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer", (ClassLoader)null)) {
return REACTIVE;
} else {
String[] var0 = SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES;
int var1 = var0.length;
for(int var2 = 0; var2 < var1; ++var2) {
String className = var0[var2];
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, (ClassLoader)null)) {
return NONE;
}
}
return SERVLET;
}
}
其中,WebApplicationType枚举类
public enum WebApplicationType {
NONE,
SERVLET,
REACTIVE;
... ...
- NONE:啥也没有,即程序不额外的启动web容器。
- SERVLET:基于servlet的web程序,需启动内嵌的servlet web容器,如Tomcat。
- REACTIVE:基于reactive的web程序,需启动内嵌reactive web容器,如webflux。
流程2: setInitializers()设置初始化器
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
主要设置初始化器ApplicationContextInitializer
public void setInitializers(Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers) {
this.initializers = new ArrayList(initializers);
}
流程3: setListeners()设置监听器
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
主要设置监听器ApplicationListener
public void setListeners(Collection<? extends ApplicationListener<?>> listeners) {
this.listeners = new ArrayList(listeners);
}
流程4:deduceMainApplicationClass()获取主程序类Class
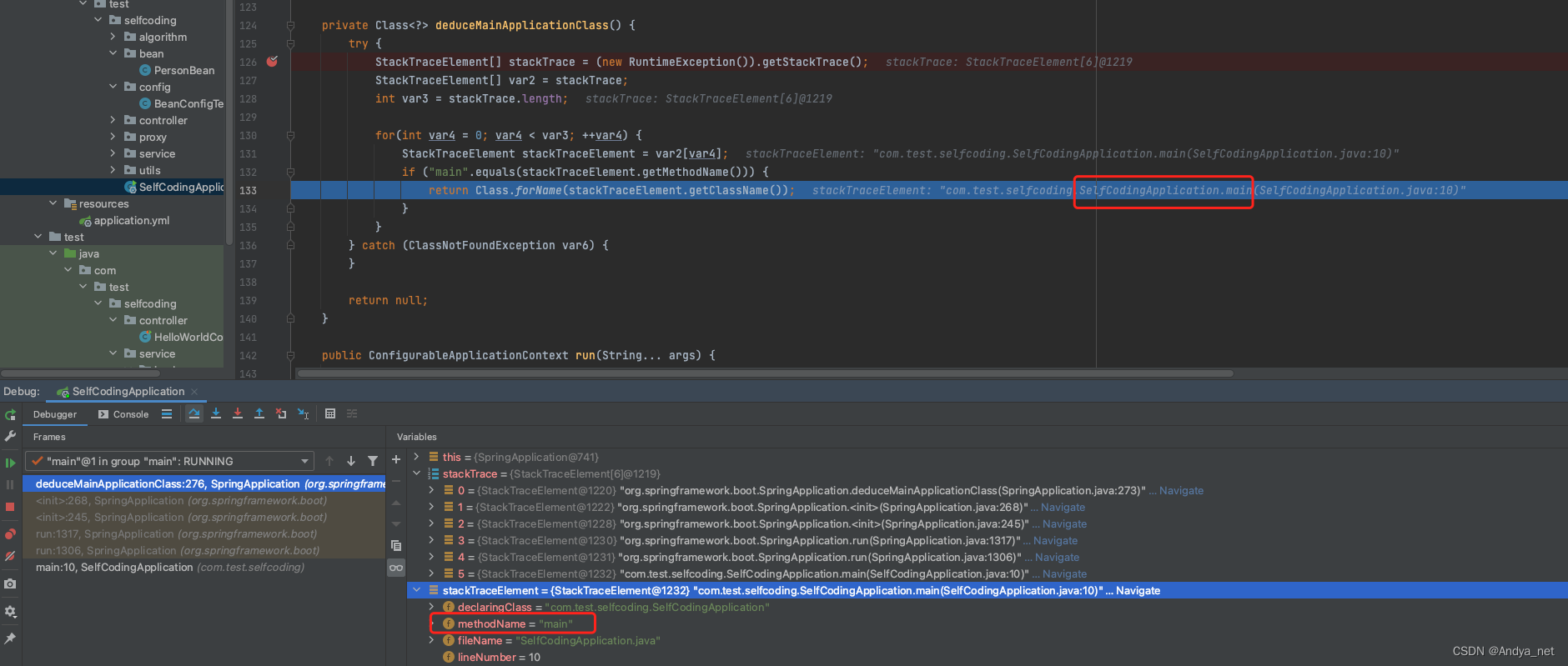
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = (new RuntimeException()).getStackTrace();
StackTraceElement[] var2 = stackTrace;
int var3 = stackTrace.length;
for(int var4 = 0; var4 < var3; ++var4) {
StackTraceElement stackTraceElement = var2[var4];
//找到主类的main方法
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var6) {
}
return null;
}
getSpringFactoriesInstances()方法分析
spring.factories文件
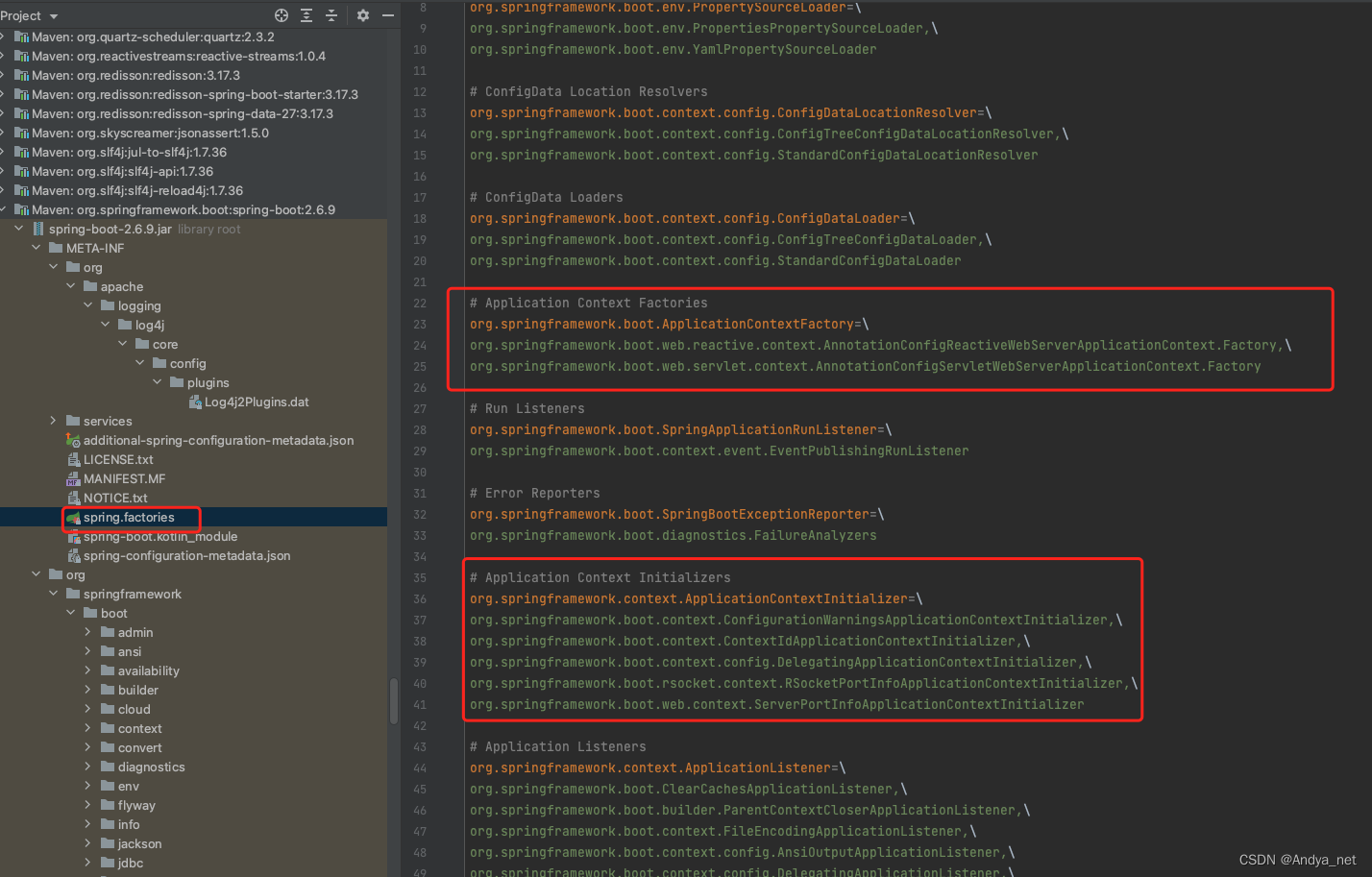
getSpringFactoriesInstances()核心源码
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
//获取spring 工厂实例
return this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class[0]);
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClassLoader();
// 获取初始化类的类名
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 在通过类名实例化对象
List<T> instances = this.createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoader == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
//加载spring工厂,读取运行环境中所有META-INF/spring.factories配置
return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = (Map)cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
} else {
HashMap result = new HashMap();
try {
//从META-INF/spring.factories中加载资源
Enumeration urls = classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories");
while(urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator();
while(var6.hasNext()) {
Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next();
String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue());
String[] var10 = factoryImplementationNames;
int var11 = factoryImplementationNames.length;
for(int var12 = 0; var12 < var11; ++var12) {
String factoryImplementationName = var10[var12];
((List)result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, (key) -> {
return new ArrayList();
})).add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> {
return (List)implementations.stream().distinct().collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList));
});
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
} catch (IOException var14) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var14);
}
}
}
创建对象主流程总结
- 获取主程序类和应用类型
- 设置初始化器Initializers
- 设置监听器Listeners
- 获取主程序类Class

执行SpringApplication.run()方法过程
执行run()方法源码过程整体分析
//run方法 开始启动程序
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//记录开始时间戳
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
//添加默认的Bootstrap上下文DefaultBootstrapContext实例
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = this.createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
//配置headless属性
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
//获取RunListeners监听器集合,得到EventPublishingRunListener监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
//循环启动监听器,通知监听者启动开始
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
//封装参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//创建并配置环境,读取配置文件,如application.properties、application.yml
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
//配置忽略bean信息
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印 Banner
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
//创建IoC容器,即实例化上下文对象
context = this.createApplicationContext();
//设置上下文启动
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
//前置处理IoC容器,即准备上下文
this.prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新IoC容器刷新,即刷新上下文
this.refreshContext(context);
//后置处理IoC容器
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//计算启动时长
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
//监听器执行 started 方法,表示启动成功
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
//执行Runners:CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var12) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var12, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var12);
}
try {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
//监听器执行 ready 方法
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var11) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var11, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var11);
}
}
不服就debug
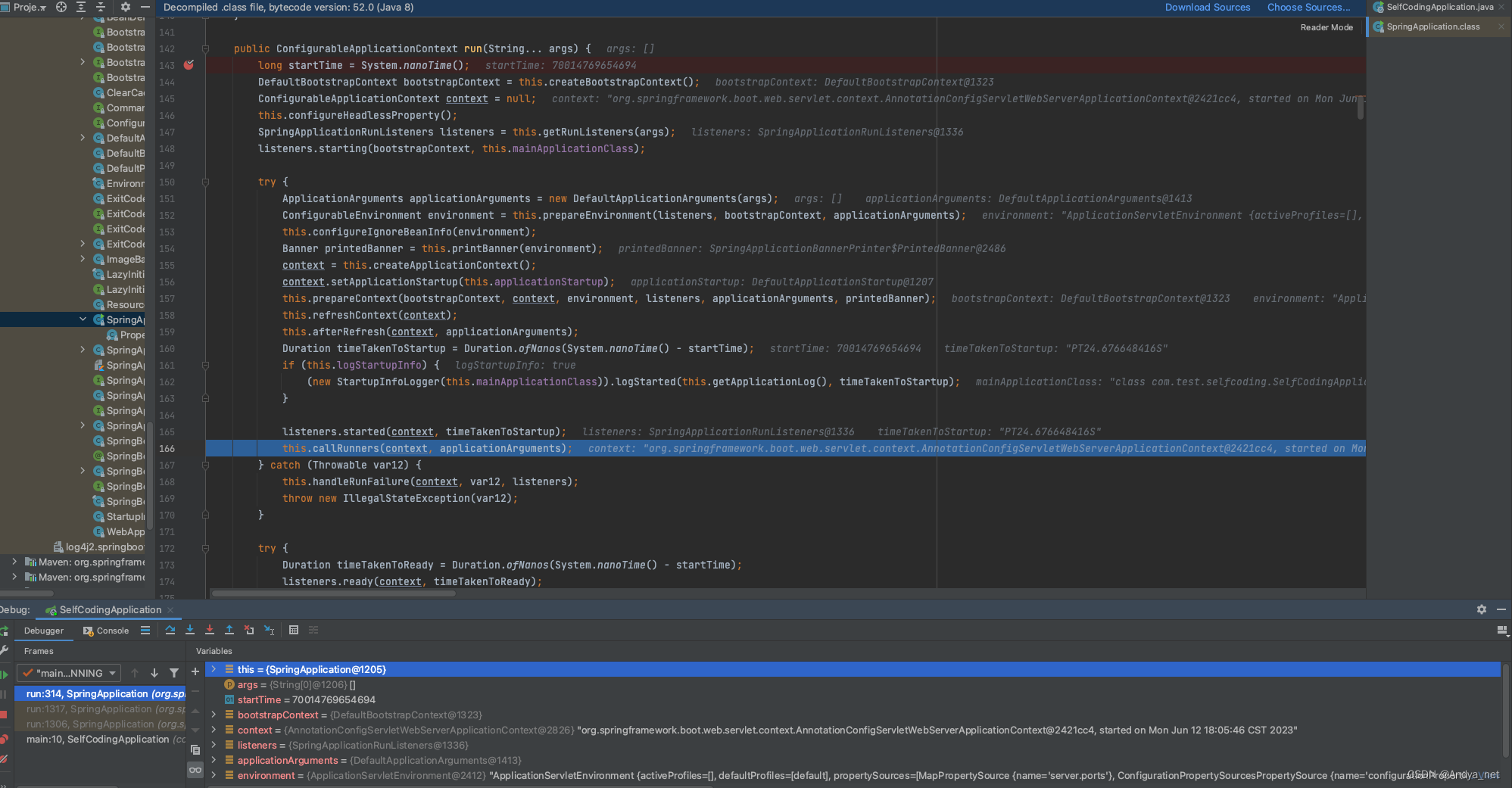
run()方法核心过程分解
流程1:获取并启动运行过程监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
- 获取监听器
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class[]{SpringApplication.class, String[].class};
//调用getSpringFactoriesInstances()方法
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger, this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args), this.applicationStartup);
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = this.getClassLoader();
//调用loadFactoryNames从spring.factories文件中获取类全名
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
//创建实例
List<T> instances = this.createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
- 启动监听器
void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, Class<?> mainApplicationClass) {
//启动监听器,通知所有的监听器
this.doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.starting", (listener) -> {
listener.starting(bootstrapContext);
}, (step) -> {
if (mainApplicationClass != null) {
step.tag("mainApplicationClass", mainApplicationClass.getName());
}
});
}
private void doWithListeners(String stepName, Consumer<SpringApplicationRunListener> listenerAction, Consumer<StartupStep> stepAction) {
//创建新步骤并标记其开始
StartupStep step = this.applicationStartup.start(stepName);
//通知所有的事件监听者
this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction);
//标识
if (stepAction != null) {
stepAction.accept(step);
}
//标记该步骤结束,且不能修改该步骤的状态
step.end();
}
流程2:准备并构建环境
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
构建环境流程prepareEnvironment()方法详解
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
//获取并创建对应的环境:SERVLET/REACTIVE或默认
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.getOrCreateEnvironment();
//加载系统属性配置
this.configureEnvironment((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach((Environment)environment);
//加载用户自定义application.yml或application.properties,触发监听器,装备好广播环境
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, (ConfigurableEnvironment)environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment);
Assert.state(!((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment).containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"), "Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
//为当前应用绑定环境
this.bindToSpringApplication((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = this.convertEnvironment((ConfigurableEnvironment)environment);
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach((Environment)environment);
return (ConfigurableEnvironment)environment;
}
//构建并返回对应环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
} else {
switch(this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
return new ApplicationServletEnvironment();
case REACTIVE:
return new ApplicationReactiveWebEnvironment();
default:
return new ApplicationEnvironment();
}
}
}
流程3:IoC容器创建,即创建应用程序上下文
context = this.createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
创建上下文createApplicationContext()方法调用链
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
return this.applicationContextFactory.create(this.webApplicationType);
}
... ...
//主要是ApplicationContextFactory接口
ApplicationContextFactory DEFAULT = (webApplicationType) -> {
try {
Iterator var1 = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(ApplicationContextFactory.class, ApplicationContextFactory.class.getClassLoader()).iterator();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context;
do {
if (!var1.hasNext()) {
return new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
}
ApplicationContextFactory candidate = (ApplicationContextFactory)var1.next();
context = candidate.create(webApplicationType);
} while(context == null);
return context;
} catch (Exception var4) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext instance, you may need a custom ApplicationContextFactory", var4);
}
};
//接口
ConfigurableApplicationContext create(WebApplicationType webApplicationType);
//SERVLET实现
static class Factory implements ApplicationContextFactory {
Factory() {
}
public ConfigurableApplicationContext create(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return webApplicationType != WebApplicationType.SERVLET ? null : new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
}
}
//REACTIVE实现
static class Factory implements ApplicationContextFactory {
Factory() {
}
public ConfigurableApplicationContext create(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) {
return webApplicationType != WebApplicationType.REACTIVE ? null : new AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext();
}
}
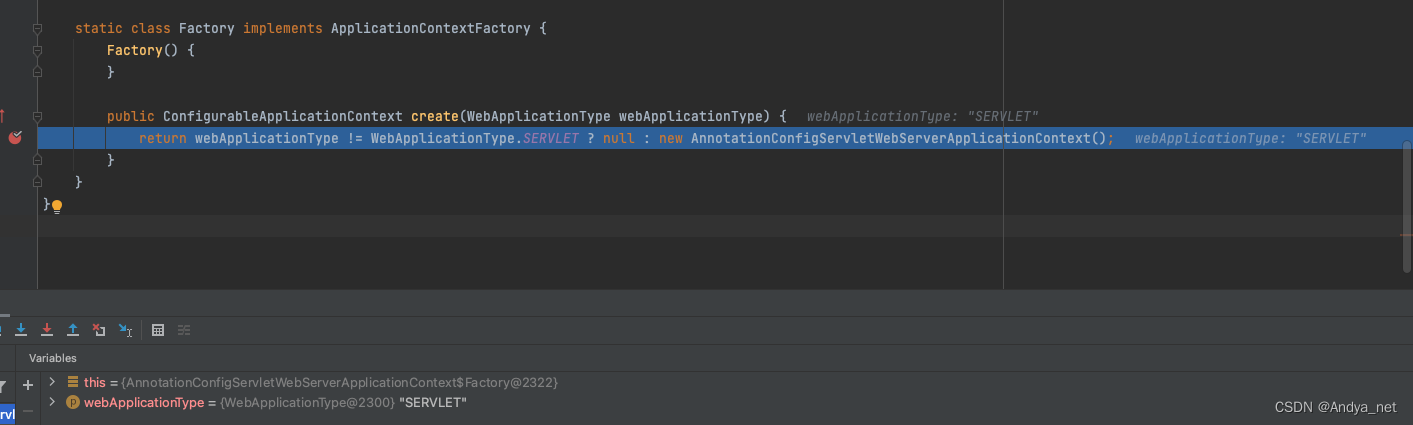
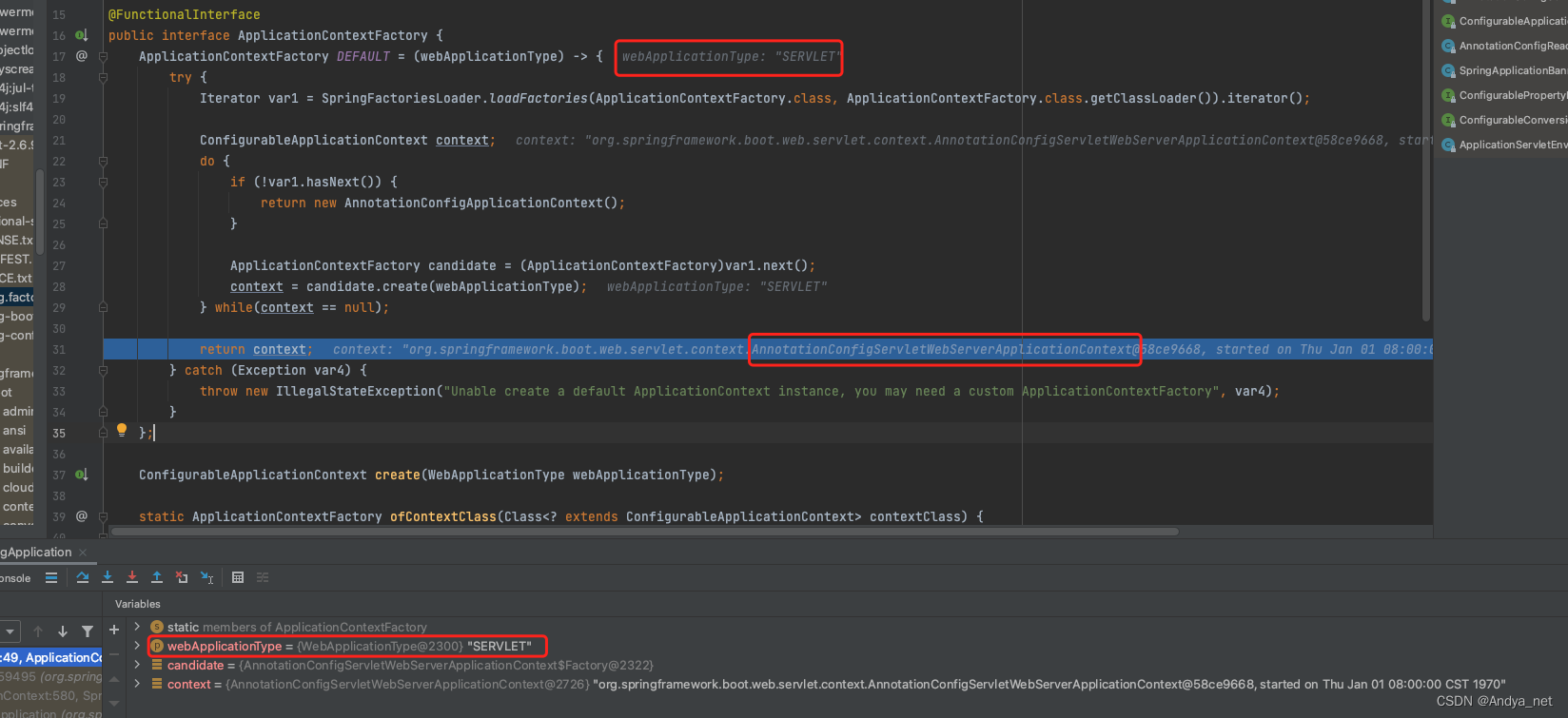
根据webApplicationType决定创建上下文的类型是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext还是AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext
流程4:IoC容器的前置处理
this.prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
prepareContext方法详解
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
//设置容器环境,如自定义配置、系统环境配置
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//执行后置处理
this.postProcessApplicationContext(context);
//执行初始化器
this.applyInitializers(context);
//广播容器准备完成事件,触发监听器
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
//打印启动信息
this.logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
//打印profile信息
this.logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
//注册启动参数Bean,将容器的参数封装成Bean,注入容器
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
//将springApplicationArguments注册到容器中
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
//注册springBootBanner
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
//不允许重复注册BeanDefinition
((AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory)beanFactory).setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory)beanFactory).setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
}
//若为懒加载,添加懒加载后置处理器
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new SpringApplication.PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context));
//获取启动类指定的参数
Set<Object> sources = this.getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
//加载启动类,并注入容器
this.load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
//发布容器已加载事件,触发监听器
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
//执行后置处理
protected void postProcessApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationBeanNameGenerator", this.beanNameGenerator);
}
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
if (context instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {
((GenericApplicationContext)context).setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (context instanceof DefaultResourceLoader) {
((DefaultResourceLoader)context).setClassLoader(this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
}
}
if (this.addConversionService) {
context.getBeanFactory().setConversionService(context.getEnvironment().getConversionService());
}
}
- postProcessApplicationContext()进行后置处理
protected void postProcessApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
//BeanFactory中注册BeanNameGenerator
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationBeanNameGenerator", this.beanNameGenerator);
}
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
if (context instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {
((GenericApplicationContext)context).setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (context instanceof DefaultResourceLoader) {
((DefaultResourceLoader)context).setClassLoader(this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
}
}
//BeanFactory中注册ConversionService
if (this.addConversionService) {
context.getBeanFactory().setConversionService(context.getEnvironment().getConversionService());
}
}
- applyInitializers()执行初始化器
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
Iterator var2 = this.getInitializers().iterator();
//SpringApplication构造器中初始化了各种ApplicationContextInitializer
while(var2.hasNext()) {
ApplicationContextInitializer initializer = (ApplicationContextInitializer)var2.next();
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(), ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
initializer.initialize(context);
}
}
- getAllSources()和load()加载启动类并注入容器
public Set<Object> getAllSources() {
Set<Object> allSources = new LinkedHashSet();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.primarySources)) {
//获取启动类
allSources.addAll(this.primarySources);
}
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.sources)) {
allSources.addAll(this.sources);
}
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(allSources);
}
//启动类加入IoC容器中
protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loading source " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(sources));
}
BeanDefinitionLoader loader = this.createBeanDefinitionLoader(this.getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources);
//设置BeanNameGenerator
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator);
}
//设置ResourceLoader
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
//设置Environment
if (this.environment != null) {
loader.setEnvironment(this.environment);
}
//加载
loader.load();
}
- contextLoaded()广播事件
void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
this.doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.context-loaded", (listener) -> {
listener.contextLoaded(context);
});
}
//触发监听者
private void doWithListeners(String stepName, Consumer<SpringApplicationRunListener> listenerAction) {
this.doWithListeners(stepName, listenerAction, (Consumer)null);
}
//触发监听者
private void doWithListeners(String stepName, Consumer<SpringApplicationRunListener> listenerAction, Consumer<StartupStep> stepAction) {
StartupStep step = this.applicationStartup.start(stepName);
this.listeners.forEach(listenerAction);
if (stepAction != null) {
stepAction.accept(step);
}
step.end();
}
//广播事件
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
ApplicationListener listener;
for(Iterator var2 = this.application.getListeners().iterator(); var2.hasNext(); context.addApplicationListener(listener)) {
listener = (ApplicationListener)var2.next();
if (listener instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware)listener).setApplicationContext(context);
}
}
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
}
流程5: IoC容器的刷新,即刷新应用程序上下文
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
shutdownHook.registerApplicationContext(context);
}
this.refresh(context);
}
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
//刷新上下文
this.prepareRefresh();
//初始化BeanFactory,解析XML
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//为上下文准备BeanFactory,即对BeanFactory的各种功能进行填充,如常用的注解@Autowired
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
//提供子类覆盖的额外处理,即子类处理自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcess
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
//激活各种BeanFactory处理器
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//注册拦截Bean创建的Bean处理器
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
//初始化上下文中的资源文件
this.initMessageSource();
//初始化上下文事件广播器
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//给子类扩展初始化其他Bean
this.onRefresh();
//注册到广播器
this.registerListeners();
//设置转换器setConversionService,注册默认解析器addEmbeddedValueResolver,初始化非延迟加载的bean
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//通过spring的事件发布机制发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var10) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var10);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var10);
throw var10;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
流程6: IoC容器的后置处理
//默认空,可以自定义
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
}
流程7: 监听器启动完成
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
流程8:执行Runners
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
Iterator var4 = (new LinkedHashSet(runners)).iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
Object runner = var4.next();
//ApplicationRunner
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
this.callRunner((ApplicationRunner)runner, args);
}
//CommandLineRunner
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
this.callRunner((CommandLineRunner)runner, args);
}
}
}
执行run()方法主流程总结
- 获取并启动运行过程监听器。
- 准备并构建环境。
- IoC容器的创建,即创建应用程序上下文。
- IoC容器的前置处理,即准备上下文。
- IoC容器的刷新,即刷新应用程序上下文。
- IoC容器的后置处理。
- 监听器启动完成。
- 执行Runners。