目录
- 一、MyBatis的各种查询功能
- 1.1 查询一个实体类对象
- 1.2 查询一个List集合
- 1.3 查询单个数据
- 1.4 查询一条数据为map集合
- 1.5 查询多条数据为map集合
- 1.5.1 方法一:
- 1.5.2 方法二:
- 二、特殊SQL的执行
- 2.1 模糊查询
- 2.2 批量删除
- 2.3 动态设置表名
- 2.4 添加功能获取自增的主键
- 三、自定义映射resultMap
- 3.1 多对一映射处理
- 3.2 一对多映射处理
- 3.3 延迟加载
- 四、动态SQL
- 4.1 if
- 4.2 where
- 4.3 trim
- 4.4 choose、when、otherwise
- 4.5 foreach
- 4.6 SQL片段
一、MyBatis的各种查询功能
- 如果查询出的数据只有一条,可以通过
- 实体类对象接收
- List集合接收
- Map集合接收,结果{password=123456, sex=男, id=1, age=23, username=admin}
- 如果查询出的数据有多条,一定不能用实体类对象接收,会抛异常TooManyResultsException,可以通过
- 实体类类型的LIst集合接收
- Map类型的LIst集合接收
- 在mapper接口的方法上添加@MapKey注解
1.1 查询一个实体类对象
/**
* 根据用户id查询用户信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
User getUserById(@Param("id") int id);
<!--User getUserById(@Param("id") int id);-->
<select id="getUserById" resultType="User">
select * from t_user where id = #{id}
</select>
1.2 查询一个List集合
/**
* 查询所有用户信息
* @return
*/
List<User> getUserList();
<!--List<User> getUserList();-->
<select id="getUserList" resultType="User">
select * from t_user
</select>
1.3 查询单个数据
/**
* 查询用户的总记录数
* @return
* 在MyBatis中,对于Java中常用的类型都设置了类型别名
* 例如:java.lang.Integer-->int|integer
* 例如:int-->_int|_integer
* 例如:Map-->map,List-->list
*/
int getCount();
<!--int getCount();-->
<select id="getCount" resultType="_integer">
select count(id) from t_user
</select>
1.4 查询一条数据为map集合
/**
* 根据用户id查询用户信息为map集合
* @param id
* @return
*/
Map<String, Object> getUserToMap(@Param("id") int id);
<!--Map<String, Object> getUserToMap(@Param("id") int id);-->
<select id="getUserToMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_user where id = #{id}
</select>
<!--结果:{password=123456, sex=男, id=1, age=23, username=admin}-->
1.5 查询多条数据为map集合
1.5.1 方法一:
/**
* 查询所有用户信息为map集合
* @return
* 将表中的数据以map集合的方式查询,一条数据对应一个map;若有多条数据,就会产生多个map集合,此时可以将这些map放在一个list集合中获取
*/
List<Map<String, Object>> getAllUserToMap();
<!--Map<String, Object> getAllUserToMap();-->
<select id="getAllUserToMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_user
</select>
<!--
结果:
[{password=123456, sex=男, id=1, age=23, username=admin},
{password=123456, sex=男, id=2, age=23, username=张三},
{password=123456, sex=男, id=3, age=23, username=张三}]
-->
1.5.2 方法二:
/**
* 查询所有用户信息为map集合
* @return
* 将表中的数据以map集合的方式查询,一条数据对应一个map;若有多条数据,就会产生多个map集合,并且最终要以一个map的方式返回数据,此时需要通过@MapKey注解设置map集合的键,值是每条数据所对应的map集合
*/
@MapKey("id")
Map<String, Object> getAllUserToMap();
<!--Map<String, Object> getAllUserToMap();-->
<select id="getAllUserToMap" resultType="map">
select * from t_user
</select>
<!--
结果:
{
1={password=123456, sex=男, id=1, age=23, username=admin},
2={password=123456, sex=男, id=2, age=23, username=张三},
3={password=123456, sex=男, id=3, age=23, username=张三}
}
-->
二、特殊SQL的执行
2.1 模糊查询
/**
* 根据用户名进行模糊查询
* @param username
* @date 2022/2/26 21:56
*/
List<User> getUserByLike(@Param("username") String username);
<!--List<User> getUserByLike(@Param("username") String username);-->
<select id="getUserByLike" resultType="User">
<!--select * from t_user where username like '%${mohu}%'-->
<!--select * from t_user where username like concat('%',#{mohu},'%')-->
select * from t_user where username like "%"#{mohu}"%"
</select>
其中select * from t_user where username like “%”#{mohu}"%"是最常用的
2.2 批量删除
只能使用${},如果使用#{},则解析后的sql语句为delete from t_user where id in (‘1,2,3’),这样是将1,2,3看做是一个整体,只有id为1,2,3的数据会被删除。正确的语句应该是delete from t_user where id in (1,2,3),或者delete from t_user where id in (‘1’,‘2’,‘3’)
/**
* 根据id批量删除
* @param ids
* @return int
* @date 2022/2/26 22:06
*/
int deleteMore(@Param("ids") String ids);
<delete id="deleteMore">
delete from t_user where id in (${ids})
</delete>
//测试类
@Test
public void deleteMore() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
SQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SQLMapper.class);
int result = mapper.deleteMore("1,2,3,8");
System.out.println(result);
}
2.3 动态设置表名
- 只能使用${},因为表名不能加单引号
/**
* 查询指定表中的数据
* @param tableName
*/
List<User> getUserByTable(@Param("tableName") String tableName);
<!--List<User> getUserByTable(@Param("tableName") String tableName);-->
<select id="getUserByTable" resultType="User">
select * from ${tableName}
</select>
2.4 添加功能获取自增的主键
- 使用场景
- t_clazz(clazz_id,clazz_name)
- t_student(student_id,student_name,clazz_id)
- 添加班级信息
- 获取新添加的班级的id
- 为班级分配学生,即将某学生班级id修改为新添加的班级的id
- 在mapper.xml中设置两个属性
- useGeneratedKeys:设置使用自增的主键
- keyProperty:因为增删改有统一的返回值是受影响的行数,因此只能将获取的自增的主键放在传输的参数user对象的某个属性中,指定实体类中的哪个变量接收自增id
/**
* 添加用户信息
* @param user
* @date 2022/2/27 15:04
*/
void insertUser(User user);
<!--void insertUser(User user);-->
<insert id="insertUser" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into t_user values (null,#{username},#{password},#{age},#{sex},#{email})
</insert>
//测试类
@Test
public void insertUser() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
SQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(SQLMapper.class);
User user = new User(null, "ton", "123", 23, "男", "123@321.com");
mapper.insertUser(user);
System.out.println(user);
//输出:user{id=10, username='ton', password='123', age=23, sex='男', email='123@321.com'},自增主键存放到了user的id属性中
}
三、自定义映射resultMap
resultMap处理字段和属性的映射关系
- resultMap:设置自定义映射
- 属性:
- id:表示自定义映射的唯一标识,不能重复
- type:查询的数据要映射的实体类的类型
- 子标签:
- id:设置主键的映射关系
- result:设置普通字段的映射关系
- 子标签属性:
- property:设置映射关系中实体类中的属性名
- column:设置映射关系中表中的字段名
- 属性:
- 若字段名和实体类中的属性名不一致,则可以通过resultMap设置自定义映射,即使字段名和属性名一致的属性也要映射,也就是全部属性都要列出来
<resultMap id="empResultMap" type="Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
</resultMap>
<!--List<Emp> getAllEmp();-->
<select id="getAllEmp" resultMap="empResultMap">
select * from t_emp
</select>
若字段名和实体类中的属性名不一致,但是字段名符合数据库的规则(使用_),实体类中的属性名符合Java的规则(使用驼峰)。此时也可通过以下两种方式处理字段名和实体类中的属性的映射关系 .
- 可以通过为字段起别名的方式,保证和实体类中的属性名保持一致
<!--List<Emp> getAllEmp();-->
<select id="getAllEmp" resultType="Emp">
select eid,emp_name empName,age,sex,email from t_emp
</select>
- 可以在MyBatis的核心配置文件中的setting标签中,设置一个全局配置信息mapUnderscoreToCamelCase,可以在查询表中数据时,自动将_类型的字段名转换为驼峰,例如:字段名user_name,设置了mapUnderscoreToCamelCase,此时字段名就会转换为userName。
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
3.1 多对一映射处理
查询员工信息以及员工所对应的部门信息
public class Emp {
private Integer eid;
private String empName;
private Integer age;
private String sex;
private String email;
private Dept dept;
//...构造器、get、set方法等
}
第一种方法:级联方式处理映射关系
<resultMap id="empAndDeptResultMapOne" type="Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
<result property="dept.did" column="did"></result>
<result property="dept.deptName" column="dept_name"></result>
</resultMap>
<!--Emp getEmpAndDept(@Param("eid")Integer eid);-->
<select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="empAndDeptResultMapOne">
select * from t_emp left join t_dept on t_emp.eid = t_dept.did where t_emp.eid = #{eid}
</select>
第二种方法:使用association处理映射关系
- association:处理多对一的映射关系
- property:需要处理多对的映射关系的属性名
- javaType:该属性的类型
<resultMap id="empAndDeptResultMapTwo" type="Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
<association property="dept" javaType="Dept">
<id property="did" column="did"></id>
<result property="deptName" column="dept_name"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
<!--Emp getEmpAndDept(@Param("eid")Integer eid);-->
<select id="getEmpAndDept" resultMap="empAndDeptResultMapTwo">
select * from t_emp left join t_dept on t_emp.eid = t_dept.did where t_emp.eid = #{eid}
</select>
第三种方法:分步查询
- 查询员工信息
select:设置分布查询的sql的唯一标识(namespace.SQLId或mapper接口的全类名.方法名)
column:设置分步查询的条件
//EmpMapper里的方法
/**
* 通过分步查询,员工及所对应的部门信息
* 分步查询第一步:查询员工信息
* @param
*/
Emp getEmpAndDeptByStepOne(@Param("eid") Integer eid);
<resultMap id="empAndDeptByStepResultMap" type="Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
<association property="dept"
select="com.lx.mybatis.mapper.DeptMapper.getEmpAndDeptByStepTwo"
column="did"></association>
</resultMap>
<!--Emp getEmpAndDeptByStepOne(@Param("eid") Integer eid);-->
<select id="getEmpAndDeptByStepOne" resultMap="empAndDeptByStepResultMap">
select * from t_emp where eid = #{eid}
</select>
2.查询部门信息
//DeptMapper里的方法
/**
* 通过分步查询,员工及所对应的部门信息
* 分步查询第二步:通过did查询员工对应的部门信息
* @param
*/
Dept getEmpAndDeptByStepTwo(@Param("did") Integer did);
<!--此处的resultMap仅是处理字段和属性的映射关系-->
<resultMap id="EmpAndDeptByStepTwoResultMap" type="Dept">
<id property="did" column="did"></id>
<result property="deptName" column="dept_name"></result>
</resultMap>
<!--Dept getEmpAndDeptByStepTwo(@Param("did") Integer did);-->
<select id="getEmpAndDeptByStepTwo" resultMap="EmpAndDeptByStepTwoResultMap">
select * from t_dept where did = #{did}
</select>
3.2 一对多映射处理
public class Dept {
private Integer did;
private String deptName;
private List<Emp> emps;
//...构造器、get、set方法等
}java
collection
- collection:用来处理一对多的映射关系
- ofType:表示该属性对应的集合中存储的数据的类型
<resultMap id="DeptAndEmpResultMap" type="Dept">
<id property="did" column="did"></id>
<result property="deptName" column="dept_name"></result>
<collection property="emps" ofType="Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!--Dept getDeptAndEmp(@Param("did") Integer did);-->
<select id="getDeptAndEmp" resultMap="DeptAndEmpResultMap">
select * from t_dept left join t_emp on t_dept.did = t_emp.did where t_dept.did = #{did}
</select>
分步查询
1.查询部门信息
/**
* 通过分步查询,查询部门及对应的所有员工信息
* 分步查询第一步:查询部门信息
* @param did
*/
Dept getDeptAndEmpByStepOne(@Param("did") Integer did);
<resultMap id="DeptAndEmpByStepOneResultMap" type="Dept">
<id property="did" column="did"></id>
<result property="deptName" column="dept_name"></result>
<collection property="emps"
select="com.lx.mybatis.mapper.EmpMapper.getDeptAndEmpByStepTwo"
column="did"></collection>
</resultMap>
<!--Dept getDeptAndEmpByStepOne(@Param("did") Integer did);-->
<select id="getDeptAndEmpByStepOne" resultMap="DeptAndEmpByStepOneResultMap">
select * from t_dept where did = #{did}
</select>
2.根据部门id查询部门中的所有员工
/**
* 通过分步查询,查询部门及对应的所有员工信息
* 分步查询第二步:根据部门id查询部门中的所有员工
* @param did
*/
List<Emp> getDeptAndEmpByStepTwo(@Param("did") Integer did);
<!--List<Emp> getDeptAndEmpByStepTwo(@Param("did") Integer did);-->
<select id="getDeptAndEmpByStepTwo" resultType="Emp">
select * from t_emp where did = #{did}
</select>
3.3 延迟加载
- 分步查询的优点:可以实现延迟加载,但是必须在核心配置文件中设置全局配置信息:
- lazyLoadingEnabled:延迟加载的全局开关。当开启时,所有关联对象都会延迟加载
- aggressiveLazyLoading:当开启时,任何方法的调用都会加载该对象的所有属性。 否则,每个属性会按需加载
- 此时就可以实现按需加载,获取的数据是什么,就只会执行相应的sql。此时可通过association和collection中的fetchType属性设置当前的分步查询是否使用延迟加载,fetchType=“lazy(延迟加载)|eager(立即加载)”
<settings>
<!--开启延迟加载-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
@Test
public void getEmpAndDeptByStepOne() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
EmpMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpMapper.class);
Emp emp = mapper.getEmpAndDeptByStepOne(1);
System.out.println(emp.getEmpName());
}
- 关闭延迟加载,两条SQL语句都运行了
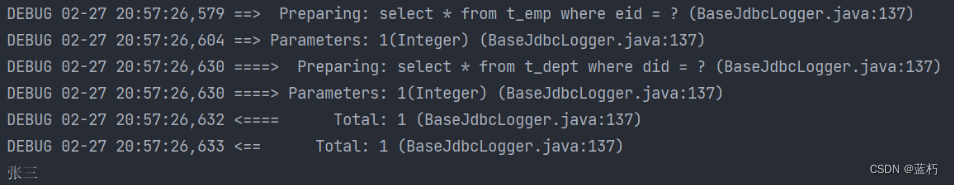
- 开启延迟加载,只运行获取emp的SQL语句
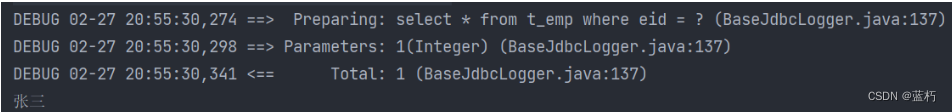
- fetchType:当开启了全局的延迟加载之后,可以通过该属性手动控制延迟加载的效果,fetchType=“lazy(延迟加载)|eager(立即加载)”
<resultMap id="empAndDeptByStepResultMap" type="Emp">
<id property="eid" column="eid"></id>
<result property="empName" column="emp_name"></result>
<result property="age" column="age"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="email" column="email"></result>
<association property="dept"
select="com.atguigu.mybatis.mapper.DeptMapper.getEmpAndDeptByStepTwo"
column="did"
fetchType="lazy"></association>
</resultMap>
四、动态SQL
Mybatis框架的动态SQL技术是一种根据特定条件动态拼装SQL语句的功能,它存在的意义是为了解决拼接SQL语句字符串时的痛点问题
4.1 if
- if标签可通过test属性(即传递过来的数据)的表达式进行判断,若表达式的结果为true,则标签中的内容会执行;反之标签中的内容不会执行
- 在where后面添加一个恒成立条件1=1
- 这个恒成立条件并不会影响查询的结果
- 这个1=1可以用来拼接and语句,例如:当empName为null时
- 如果不加上恒成立条件,则SQL语句为select * from t_emp where and age = ? and sex = ? and email = ?,此时where会与and连用,SQL语句会报错
- 如果加上一个恒成立条件,则SQL语句为select * from t_emp where 1= 1 and age = ? and sex = ? and email = ?,此时不报错
<!--List<Emp> getEmpByCondition(Emp emp);-->
<select id="getEmpByCondition" resultType="Emp">
select * from t_emp where 1=1
<if test="empName != null and empName !=''">
and emp_name = #{empName}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age !=''">
and age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex !=''">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="email != null and email !=''">
and email = #{email}
</if>
</select>
4.2 where
where和if一般结合使用:
- 若where标签中的if条件都不满足,则where标签没有任何功能,即不会添加where关键字
- 若where标签中的if条件满足,则where标签会自动添加where关键字,并将条件最前方多余的and/or去掉
<!--List<Emp> getEmpByCondition(Emp emp);-->
<select id="getEmpByCondition" resultType="Emp">
select * from t_emp
<where>
<if test="empName != null and empName !=''">
emp_name = #{empName}
</if>
<if test="age != null and age !=''">
and age = #{age}
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex !=''">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
<if test="email != null and email !=''">
and email = #{email}
</if>
</where>
</select>
注意:where标签不能去掉条件后多余的and/or
<!--这种用法是错误的,只能去掉条件前面的and/or,条件后面的不行-->
<if test="empName != null and empName !=''">
emp_name = #{empName} and
</if>
<if test="age != null and age !=''">
age = #{age}
</if>
4.3 trim
- trim用于去掉或添加标签中的内容
- 常用属性
- prefix:在trim标签中的内容的前面添加某些内容
- suffix:在trim标签中的内容的后面添加某些内容
- prefixOverrides:在trim标签中的内容的前面去掉某些内容
- suffixOverrides:在trim标签中的内容的后面去掉某些内容
- 若trim中的标签都不满足条件,则trim标签没有任何效果,也就是只剩下select * from t_emp
<!--List<Emp> getEmpByCondition(Emp emp);-->
<select id="getEmpByCondition" resultType="Emp">
select * from t_emp
<trim prefix="where" suffixOverrides="and|or">
<if test="empName != null and empName !=''">
emp_name = #{empName} and
</if>
<if test="age != null and age !=''">
age = #{age} and
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex !=''">
sex = #{sex} or
</if>
<if test="email != null and email !=''">
email = #{email}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
//测试类
@Test
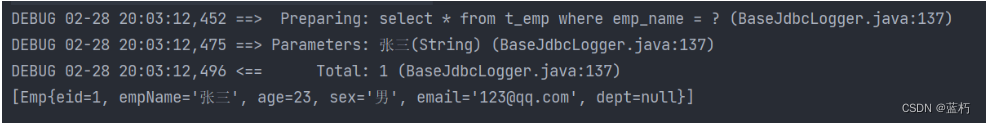
public void getEmpByCondition() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
DynamicSQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);
List<Emp> emps= mapper.getEmpByCondition(new Emp(null, "张三", null, null, null, null));
System.out.println(emps);
}
4.4 choose、when、otherwise
- choose、when、otherwise相当于if…else if…else
- when至少要有一个,otherwise至多只有一个
<select id="getEmpByChoose" resultType="Emp">
select * from t_emp
<where>
<choose>
<when test="empName != null and empName != ''">
emp_name = #{empName}
</when>
<when test="age != null and age != ''">
age = #{age}
</when>
<when test="sex != null and sex != ''">
sex = #{sex}
</when>
<when test="email != null and email != ''">
email = #{email}
</when>
<otherwise>
did = 1
</otherwise>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
@Test
public void getEmpByChoose() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
DynamicSQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);
List<Emp> emps = mapper.getEmpByChoose(new Emp(null, "张三", 23, "男", "123@qq.com", null));
System.out.println(emps);
}
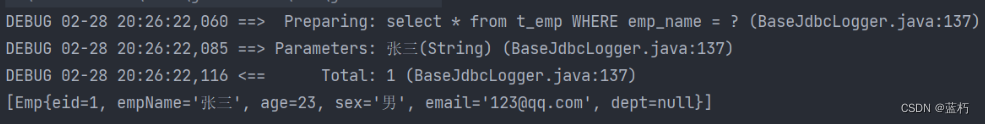
只要满足一个when条件,后面的when就不会再判断了。
4.5 foreach
- 属性:
- collection:设置要循环的数组或集合
- item:表示集合或数组中的每一个数据
- separator:设置循环体之间的分隔符,分隔符前后默认有一个空格,如,
- open:设置foreach标签中的内容的开始符
- close:设置foreach标签中的内容的结束符
- 批量删除
<!--int deleteMoreByArray(Integer[] eids);-->
<delete id="deleteMoreByArray">
delete from t_emp where eid in
<foreach collection="eids" item="eid" separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{eid}
</foreach>
</delete>
@Test
public void deleteMoreByArray() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
DynamicSQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);
int result = mapper.deleteMoreByArray(new Integer[]{6, 7, 8, 9});
System.out.println(result);
}

- 批量添加
<!--int insertMoreByList(@Param("emps") List<Emp> emps);-->
<insert id="insertMoreByList">
insert into t_emp values
<foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator=",">
(null,#{emp.empName},#{emp.age},#{emp.sex},#{emp.email},null)
</foreach>
</insert>
@Test
public void insertMoreByList() {
SqlSession sqlSession = SqlSessionUtils.getSqlSession();
DynamicSQLMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(DynamicSQLMapper.class);
Emp emp1 = new Emp(null,"a",1,"男","123@321.com",null);
Emp emp2 = new Emp(null,"b",1,"男","123@321.com",null);
Emp emp3 = new Emp(null,"c",1,"男","123@321.com",null);
List<Emp> emps = Arrays.asList(emp1, emp2, emp3);
int result = mapper.insertMoreByList(emps);
System.out.println(result);
}

4.6 SQL片段
- sql片段,可以记录一段公共sql片段,在使用的地方通过include标签进行引入
- 声明sql片段:
<sql>标签
<sql id="empColumns">eid,emp_name,age,sex,email</sql>
- 引用sql片段:
<include>标签
<!--List<Emp> getEmpByCondition(Emp emp);-->
<select id="getEmpByCondition" resultType="Emp">
select <include refid="empColumns"></include> from t_emp
</select>