来源:力扣(LeetCode)
描述:
给你一棵树,树上有 n 个节点,按从 0 到 n-1 编号。树以父节点数组的形式给出,其中 parent[i] 是节点 i 的父节点。树的根节点是编号为 0 的节点。
树节点的第 k 个祖先节点是从该节点到根节点路径上的第 k 个节点。
实现 TreeAncestor 类:
TreeAncestor(int n, int[] parent)对树和父数组中的节点数初始化对象。getKthAncestor(int node, int k)返回节点node的第k个祖先节点。如果不存在这样的祖先节点,返回-1。
示例 1:
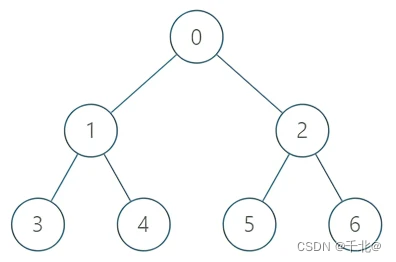
输入:
["TreeAncestor","getKthAncestor","getKthAncestor","getKthAncestor"]
[[7,[-1,0,0,1,1,2,2]],[3,1],[5,2],[6,3]]
输出:
[null,1,0,-1]
解释:
TreeAncestor treeAncestor = new TreeAncestor(7, [-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 2, 2]);
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(3, 1); // 返回 1 ,它是 3 的父节点
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(5, 2); // 返回 0 ,它是 5 的祖父节点
treeAncestor.getKthAncestor(6, 3); // 返回 -1 因为不存在满足要求的祖先节点
提示:
- 1 <= k <= n <= 5 * 104
- parent[0] == -1 表示编号为 0 的节点是根节点。
- 对于所有的 0 < i < n ,0 <= parent[i] < n 总成立
- 0 <= node < n
- 至多查询 5 * 104 次
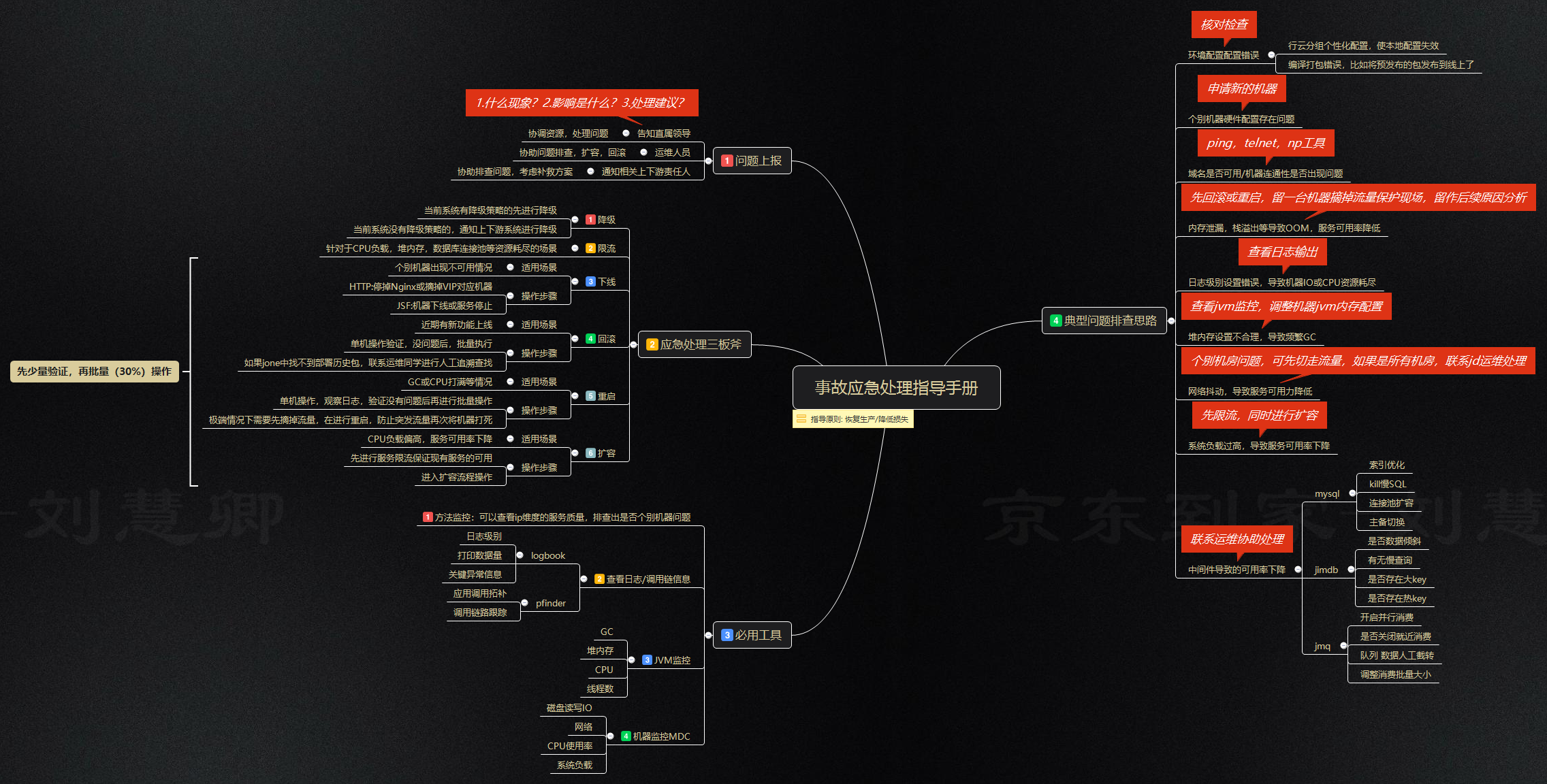
方法:倍增
思路
倍增的思路类似于动态规划,定义 ancestors[i][j] 表示节点 i 的第 2j 个祖先。此题中,树最多有 50000 个节点,因此 ancestors 的第二维度的最大值可以设为 16。根据定义,ancestors[i][0] = parent[i]。状态转移方程是 ancestors[i][j] = ancestors[ancestors[i][j−1]][j−1],即当前节点的第 2j 个祖先,是他的第 2j−1 个祖先的第 2j−1 个祖先。当第 2j 个祖先不存在时,记为 −1。
查询时,需要将 k 的二进制表示从最低位到最高位依次进行判断,如果第 j 位为 1,则节点 node 需要进行转移到 ancestors[node][j],表示 node 向祖先方向移动了 2j 次。直至遍历完 k 所有位或者 node 变为 −1。
代码:
class TreeAncestor {
public:
constexpr static int Log = 16;
vector<vector<int>> ancestors;
TreeAncestor(int n, vector<int>& parent) {
ancestors = vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(Log, -1));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ancestors[i][0] = parent[i];
}
for (int j = 1; j < Log; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (ancestors[i][j - 1] != -1) {
ancestors[i][j] = ancestors[ancestors[i][j - 1]][j - 1];
}
}
}
}
int getKthAncestor(int node, int k) {
for (int j = 0; j < Log; j++) {
if ((k >> j) & 1) {
node = ancestors[node][j];
if (node == -1) {
return -1;
}
}
}
return node;
}
};
执行用时:304 ms, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了68.35%的用户
内存消耗:113 MB, 在所有 C++ 提交中击败了77.85%的用户
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:初始化的时间复杂度是 O(n×logn),单次查询的时间复杂度是 O(logn)。
空间复杂度:初始化的空间复杂度是 O(n×logn),单次查询的空间复杂度是 O(1)。
author:LeetCode-Solution



![对数组的“reg [7:0] a_tmp[32:0]”理解](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/9f4db2f1c190cf9d43982793d1973f7b.png)