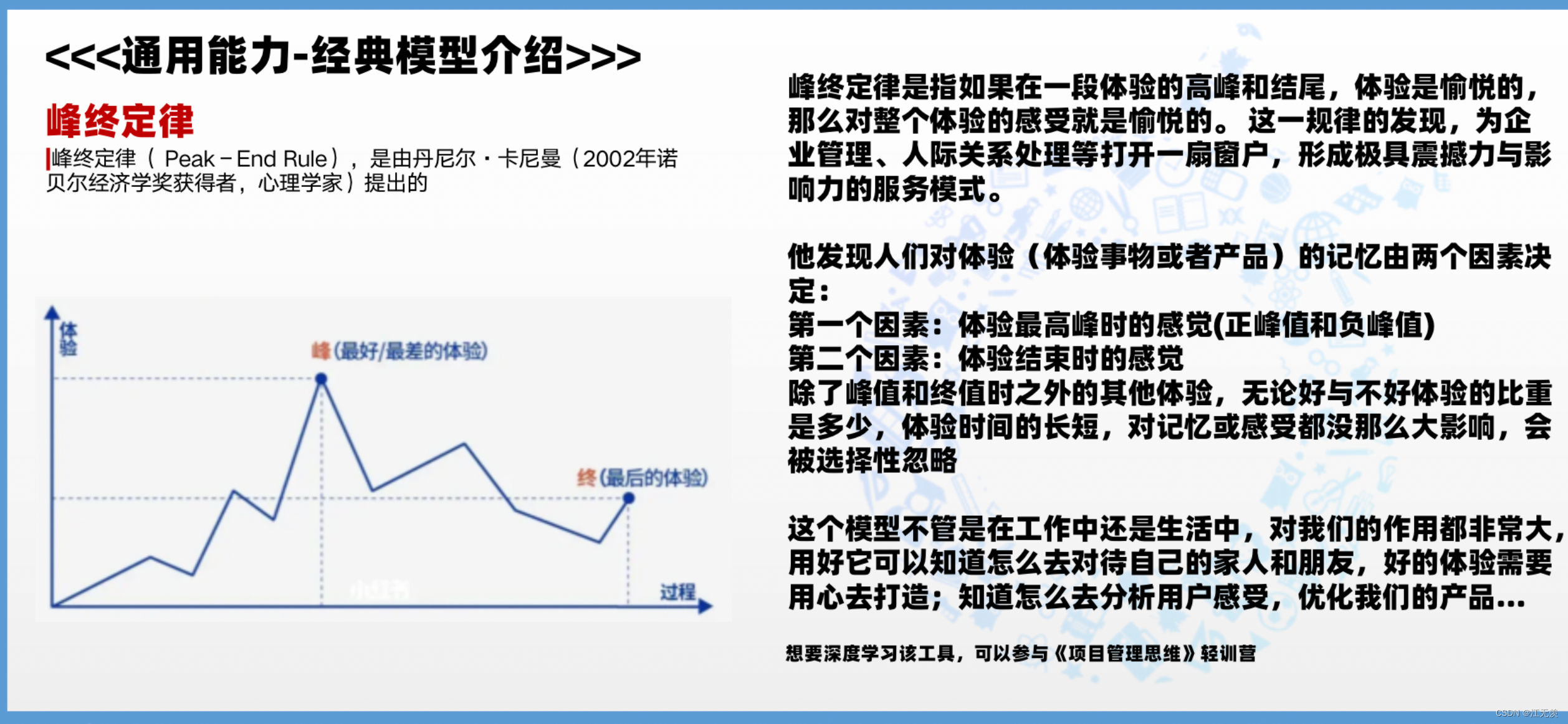
了解总线设备驱动模型之前,可以先了解常规驱动程序的编写:
LED驱动程序框架
驱动设计的思想:面向对象/分层/分离(以LED操作为例)
此次总线设备驱动模型程序的编写基于上述两种框架。
1. 总线设备驱动模型框架
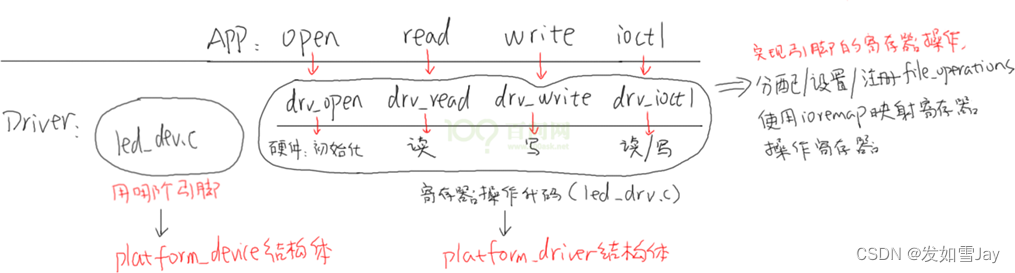
在led_dev.c中注册platform_device结构体,确定硬件信息。在led_drv.c中注册platform_driver结构体。
2. 总线设备驱动模型中两个最重要的结构体
platform维护的所有的驱动都必须要用该结构体定义:
2.1 platform_driver
struct platform_driver {
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *); //
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
bool prevent_deferred_probe;
};
该结构体,用于注册驱动到platform总线,
| 成员 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| probe | 当驱动和硬件信息匹配成功之后,就会调用probe函数,驱动所有的资源的注册和初始化全部放在probe函数中 |
| remove | 硬件信息被移除了,或者驱动被卸载了,全部要释放,释放资源的操作就放在该函数中 |
| struct device_driver driver | 内核维护的所有的驱动必须包含该成员,通常driver->name用于和设备进行匹配 |
| const struct platform_device_id *id_table | 往往一个驱动可能能同时支持多个硬件,这些硬件的名字都放在该结构体数组中 |
编写驱动的时候往往需要填充以上几个成员
2.2 platform_device
platform总线用于描述设备硬件信息的结构体,包括该硬件的所有资源(io,memory、中断、DMA等等)。
struct platform_device {
const char *name;
int id;
bool id_auto;
struct device dev;
u32 num_resources;
struct resource *resource;
const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;
char *driver_override; /* Driver name to force a match */
const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;
/* MFD cell pointer */
struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;
/* arch specific additions */
struct pdev_archdata archdata;
};
| 成员 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| const char *name | 设备的名字,用于和驱动进行匹配的 |
| struct device dev | 内核中维护的所有的设备必须包含该成员, |
| u32 num_resources | 资源个数 |
| struct resource *resource | 描述资源 |
2.3 硬件与驱动的匹配规则
platform_device 与 platform_driver 的匹配
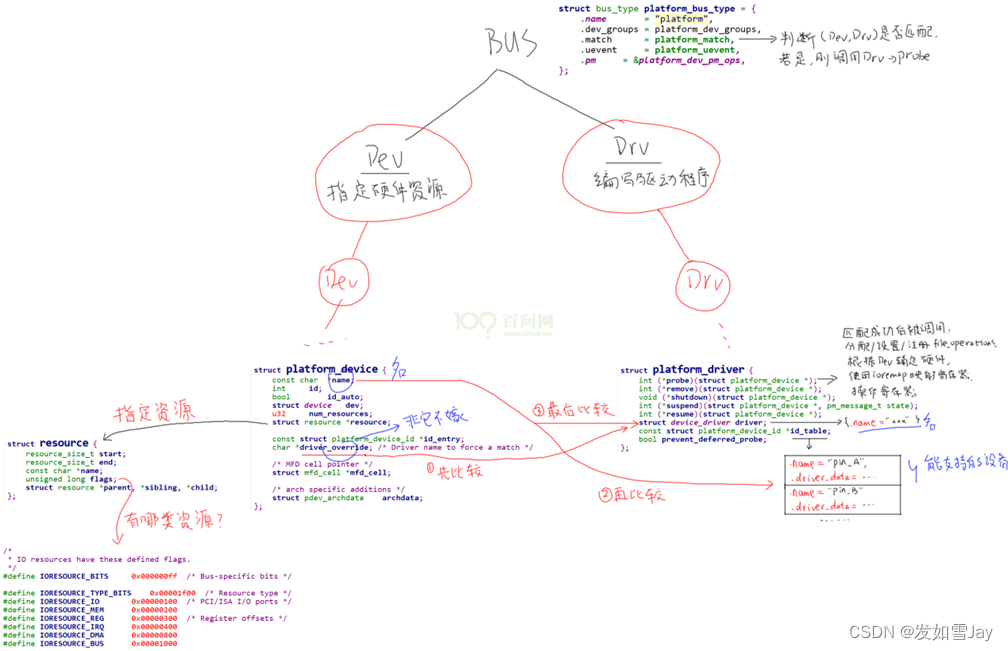
(1)最先比较:platform_device. driver_override和platform_driver.driver.name
可以设置platform_device的driver_override,强制选择某个platform_driver。
(2)然后比较:platform_device.name和platform_driver.id_table[i].name
platform_driver.id_table是“platform_device_id”指针,表示该drv支持若干个device,它里面列出了各个device的{.name, .driver_data},其中的“name”表示该drv支持的设备的名字,driver_data是些提供给该device的私有数据。
(3)最后比较:platform_device.name和platform_driver.driver.name
platform_driver.id_table可能为空,这时可以根据platform_driver.driver.name来寻找同名的platform_device。
3. 注册/反注册
(1)注册驱动:platform_device_register
/**
* platform_device_register - add a platform-level device
* @pdev: platform device we're adding
*/
int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *pdev){
device_initialize(&pdev->dev);
arch_setup_pdev_archdata(pdev);
return platform_device_add(pdev);
}
(2)注册设备:platform_driver_register
#define platform_driver_register(drv) \
__platform_driver_register(drv, THIS_MODULE)
4. platform_device 与platform_driver 的注册
4.1 platform_driver 定义和注册
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/ioport.h>
static int hello_probe(struct platform_device *pdev){
printk("match ok \n");
return 0;
}
static int hello_remove(struct platform_device *pdev){
printk("hello_remove \n");
return 0;
}
static struct platform_driver hello_driver ={
.probe = hello_probe,
.driver.name = "duang",
.remove = hello_remove,
};
static int hello_init(void){
printk("hello_init \n");
return platform_driver_register(&hello_driver);
}
static void hello_exit(void){
printk("hello_exit \n");
platform_driver_unregister(&hello_driver);
return;
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
4.2 platform_device定义和注册
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/ioport.h>
static void hello_release(struct device *dev){
return;
}
static struct platform_device hello_device ={
.name = "duang",
.id = -1,
.dev.release = hello_release,
};
static int hello_init(void){
printk("hello_init \n");
return platform_device_register(&hello_device);
}
static void hello_exit(void){
printk("hello_exit \n");
platform_device_unregister(&hello_device);
return;
}
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
该程序只用于测试platform框架是否可以成功匹配,struct platform_device hello_device 并没有设置任何硬件信息。
4.3 Makfile
ifneq ($(KERNELRELEASE),)
obj-m:=device.o driver.o
else
KDIR :=/lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build
PWD :=$(shell pwd)
all:
make -C $(KDIR) M=$(PWD) modules
clean:
rm -f *.ko *.o *.mod.o *.symvers *.cmd *.mod.c *.order
endif
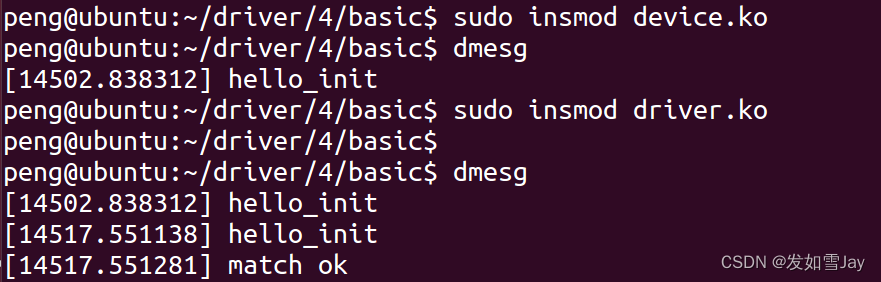
编译之后,加载模块
5. 实例
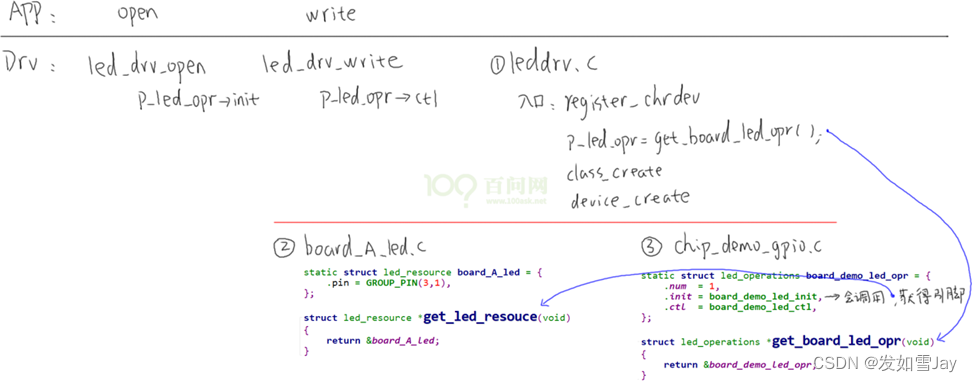
原来的框架:
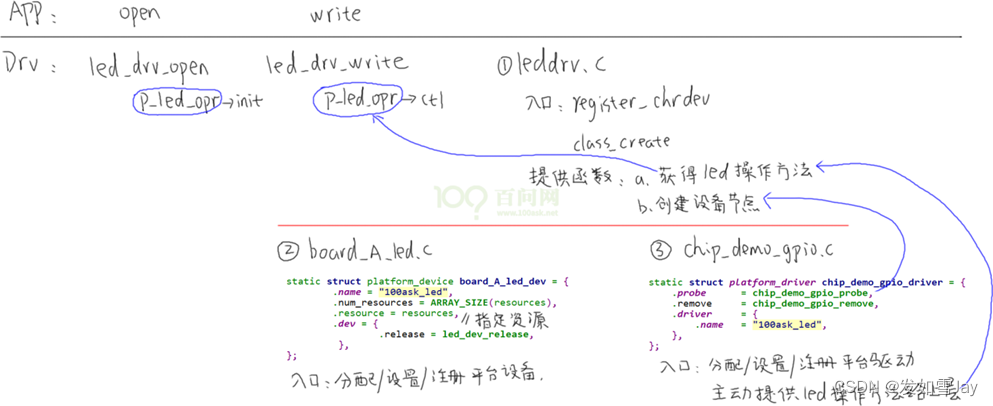
要实现的框架:
文件如下:
程序仍分为上下结构:上层leddrv.c向内核注册file_operations结构体;下层chip_demo_gpio.c提供led_operations结构体来操作硬件。
下层的代码分为2个:chip_demo_gpio.c实现通用的GPIO操作,在里面注册platform_driver 结构体,board_A_led.c指定使用哪个GPIO,即“资源”,在里面注册platform_device结构体,指定硬件资源。
chip_demo_gpio.c实现了单板A对应芯片的GPIO操作,适用于该芯片的所有GPIO引脚。
board_A_led.c则是指定使用哪一个引脚。在board_A_led.c中实现led_resouce结构体,它定义“资源”──要用哪一个引脚。
leddrv.h如下:
#ifndef _LED_RESOURCE_H
#define _LED_RESOURCE_H
/* GPIO3_0 */
/* bit[31:16] = group */
/* bit[15:0] = which pin */
#define GROUP(x) (x>>16)
#define PIN(x) (x&0xFFFF)
#define GROUP_PIN(g,p) ((g<<16) | (p))
#endif
board_A_led.c
board_A_led.c,leddrv.h的实现。
board_A_led.c作为一个可加载模块,里面也有入口函数、出口函数。在入口函数中注册platform_device结构体,在platform_device结构体中指定使用哪个GPIO引脚。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include "led_resource.h"
//空函数led_dev_release,它被赋给board_A_led_dev结构体,这个函数在卸载platform_device时会被调用,如果不提供的话内核会打印警告信息。
static void led_dev_release(struct device *dev)
{
}
//硬件资源
static struct resource resources[] = {
{
.start = GROUP_PIN(3,1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ,
.name = "100ask_led_pin",
},
{
.start = GROUP_PIN(5,8),
.flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ,
.name = "100ask_led_pin",
},
};
static struct platform_device board_A_led_dev = {
.name = "100ask_led",
.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(resources),
.resource = resources,
.dev = {
.release = led_dev_release,
},
};
static int __init led_dev_init(void){
int err;
err = platform_device_register(&board_A_led_dev);
return 0;
}
static void __exit led_dev_exit(void){
platform_device_unregister(&board_A_led_dev);
}
module_init(led_dev_init);
module_exit(led_dev_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
led_opr.h:
#ifndef _LED_OPR_H
#define _LED_OPR_H
struct led_operations {
int (*init) (int which); /* 初始化LED, which-哪个LED */
int (*ctl) (int which, char status); /* 控制LED, which-哪个LED, status:1-亮,0-灭 */
};
struct led_operations *get_board_led_opr(void);
#endif
chip_demo_gpio.c
chip_demo_gpio.c,led_opr.h的实现。
chip_demo_gpio.c中注册platform_driver结构体,它使用Bus/Dev/Drv模型,当有匹配的platform_device时,它的probe函数就会被调用。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include "led_opr.h"
#include "leddrv.h"
#include "led_resource.h"
static int g_ledpins[100];
static int g_ledcnt = 0;
static int board_demo_led_init (int which) /* 初始化LED, which-哪个LED */
{
//printk("%s %s line %d, led %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, which);
printk("init gpio: group %d, pin %d\n", GROUP(g_ledpins[which]), PIN(g_ledpins[which]));
//数组g_ledpins,里面的值来自platform_device,在probe函数中根据platform_device的资源确定了引脚
switch(GROUP(g_ledpins[which])){
case 0:
{
printk("init pin of group 0 ...\n");
break;
}
case 1:
{
printk("init pin of group 1 ...\n");
break;
}
case 2:
{
printk("init pin of group 2 ...\n");
break;
}
case 3:
{
printk("init pin of group 3 ...\n");
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
static int board_demo_led_ctl (int which, char status) /* 控制LED, which-哪个LED, status:1-亮,0-灭 */
{
//printk("%s %s line %d, led %d, %s\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, which, status ? "on" : "off");
printk("set led %s: group %d, pin %d\n", status ? "on" : "off", GROUP(g_ledpins[which]), PIN(g_ledpins[which]));
switch(GROUP(g_ledpins[which])){
case 0:
{
printk("set pin of group 0 ...\n");
break;
}
case 1:
{
printk("set pin of group 1 ...\n");
break;
}
case 2:
{
printk("set pin of group 2 ...\n");
break;
}
case 3:
{
printk("set pin of group 3 ...\n");
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
static struct led_operations board_demo_led_opr = {
.init = board_demo_led_init,
.ctl = board_demo_led_ctl,
};
struct led_operations *get_board_led_opr(void){
return &board_demo_led_opr;
}
static int chip_demo_gpio_probe(struct platform_device *pdev){
struct resource *res;
int i = 0;
while (1){
//从匹配的platform_device中获取资源,确定GPIO引脚。
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_IRQ, i++);
if (!res)
break;
//把引脚记录下来,在操作硬件时要用。
g_ledpins[g_ledcnt] = res->start;
//新发现了一个GPIO引脚,就调用上层驱动的代码创建设备节点。
led_class_create_device(g_ledcnt);
g_ledcnt++;
}
return 0;
}
static int chip_demo_gpio_remove(struct platform_device *pdev){
struct resource *res;
int i = 0;
while (1)
{
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_IRQ, i);
if (!res)
break;
led_class_destroy_device(i);
i++;
g_ledcnt--;
}
return 0;
}
static struct platform_driver chip_demo_gpio_driver = {
.probe = chip_demo_gpio_probe,
.remove = chip_demo_gpio_remove,
.driver = {
.name = "100ask_led",
},
};
static int __init chip_demo_gpio_drv_init(void){
int err;
err = platform_driver_register(&chip_demo_gpio_driver);
register_led_operations(&board_demo_led_opr);
return 0;
}
static void __exit lchip_demo_gpio_drv_exit(void){
platform_driver_unregister(&chip_demo_gpio_driver);
}
module_init(chip_demo_gpio_drv_init);
module_exit(lchip_demo_gpio_drv_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
leddrv.h:
#ifndef _LEDDRV_H
#define _LEDDRV_H
#include "led_opr.h"
void led_class_create_device(int minor);
void led_class_destroy_device(int minor);
void register_led_operations(struct led_operations *opr);
#endif /* _LEDDRV_H */
leddrv.c
leddrv.c,leddrv.h的实现。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/major.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/stat.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
#include <linux/gfp.h>
#include "led_opr.h"
/* 1. 确定主设备号 */
static int major = 0;
static struct class *led_class;
struct led_operations *p_led_opr;
#define MIN(a, b) (a < b ? a : b)
void led_class_create_device(int minor){
device_create(led_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, minor), NULL, "100ask_led%d", minor); /* /dev/100ask_led0,1,... */
}
void led_class_destroy_device(int minor){
device_destroy(led_class, MKDEV(major, minor));
}
void register_led_operations(struct led_operations *opr){
p_led_opr = opr;
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(led_class_create_device);
EXPORT_SYMBOL(led_class_destroy_device);
EXPORT_SYMBOL(register_led_operations);
/* 3. 实现对应的open/read/write等函数,填入file_operations结构体 */
static ssize_t led_drv_read (struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset){
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
/* write(fd, &val, 1); */
static ssize_t led_drv_write (struct file *file, const char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *offset){
int err;
char status;
struct inode *inode = file_inode(file);
int minor = iminor(inode);
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
err = copy_from_user(&status, buf, 1);
/* 根据次设备号和status控制LED */
p_led_opr->ctl(minor, status);
return 1;
}
static int led_drv_open (struct inode *node, struct file *file){
int minor = iminor(node);
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
/* 根据次设备号初始化LED */
p_led_opr->init(minor);
return 0;
}
static int led_drv_close (struct inode *node, struct file *file){
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
/* 2. 定义自己的file_operations结构体 */
static struct file_operations led_drv = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_drv_open,
.read = led_drv_read,
.write = led_drv_write,
.release = led_drv_close,
};
/* 4. 把file_operations结构体告诉内核:注册驱动程序 */
/* 5. 谁来注册驱动程序啊?得有一个入口函数:安装驱动程序时,就会去调用这个入口函数 */
static int __init led_init(void){
int err;
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
major = register_chrdev(0, "100ask_led", &led_drv); /* /dev/led */
led_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "100ask_led_class");
err = PTR_ERR(led_class);
if (IS_ERR(led_class)) {
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
unregister_chrdev(major, "led");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
/* 6. 有入口函数就应该有出口函数:卸载驱动程序时,就会去调用这个出口函数 */
static void __exit led_exit(void){
printk("%s %s line %d\n", __FILE__, __FUNCTION__, __LINE__);
class_destroy(led_class);
unregister_chrdev(major, "100ask_led");
}
/* 7. 其他完善:提供设备信息,自动创建设备节点 */
module_init(led_init);
module_exit(led_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
测试程序ledtest.c:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
/*
* ./ledtest /dev/100ask_led0 on
* ./ledtest /dev/100ask_led0 off
*/
int main(int argc, char **argv){
int fd;
char status;
/* 1. 判断参数 */
if (argc != 3) {
printf("Usage: %s <dev> <on | off>\n", argv[0]);
return -1;
}
/* 2. 打开文件 */
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd == -1){
printf("can not open file %s\n", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
/* 3. 写文件 */
if (0 == strcmp(argv[2], "on")){
status = 1;
write(fd, &status, 1);
}
else{
status = 0;
write(fd, &status, 1);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
makefile:
# 1. 使用不同的开发板内核时, 一定要修改KERN_DIR
# 2. KERN_DIR中的内核要事先配置、编译, 为了能编译内核, 要先设置下列环境变量:
# 2.1 ARCH, 比如: export ARCH=arm64
# 2.2 CROSS_COMPILE, 比如: export CROSS_COMPILE=aarch64-linux-gnu-
# 2.3 PATH, 比如: export PATH=$PATH:/home/book/100ask_roc-rk3399-pc/ToolChain-6.3.1/gcc-linaro-6.3.1-2017.05-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin
# 注意: 不同的开发板不同的编译器上述3个环境变量不一定相同,
# 请参考各开发板的高级用户使用手册
KERN_DIR = /home/book/100ask_roc-rk3399-pc/linux-4.4
all:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules
$(CROSS_COMPILE)gcc -o ledtest ledtest.c
clean:
make -C $(KERN_DIR) M=`pwd` modules clean
rm -rf modules.order
rm -f ledtest
# 参考内核源码drivers/char/ipmi/Makefile
# 要想把a.c, b.c编译成ab.ko, 可以这样指定:
# ab-y := a.o b.o
# obj-m += ab.o
obj-m += leddrv.o chip_demo_gpio.o board_A_led.o
注意事项
(1)如果platform_device中不提供release函数,如下图所示不提供红框部分的函数:
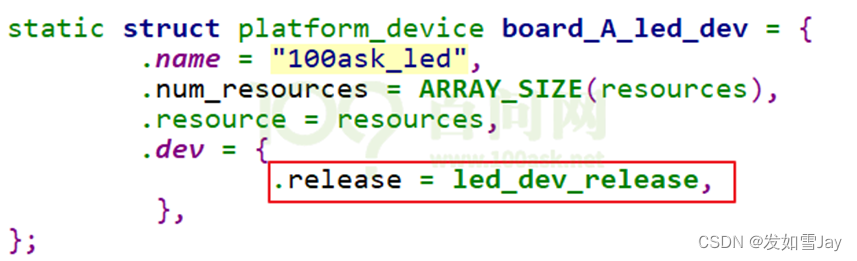
则在调用platform_device_unregister时会出现警告,如下图所示:

你可以提供一个release函数,如果实在无事可做,把这函数写为空。
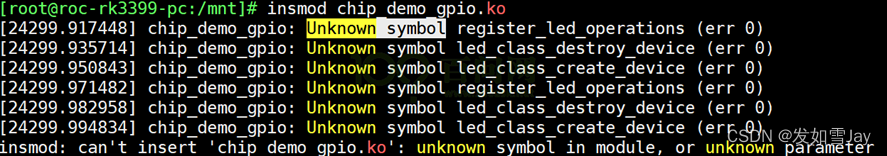
(2)EXPORT_SYMBOL
a.c编译为a.ko,里面定义了func_a;如果它想让b.ko使用该函数,那么a.c里需要导出此函数(如果a.c, b.c都编进内核,则无需导出):
EXPORT_SYMBOL(led_device_create);
并且,使用时要先加载a.ko。
如果先加载b.ko,会有类似如下“Unknown symbol”的提示:
(3)首先,程序是在windows系统编写,在Ubuntu系统上使用交叉工具链编译。编译之后,将生成的文件通过网络设备节点拷贝到开发板上,在开发板上执行驱动的加载。
参考:
手把手教Linux驱动10-platform总线详解