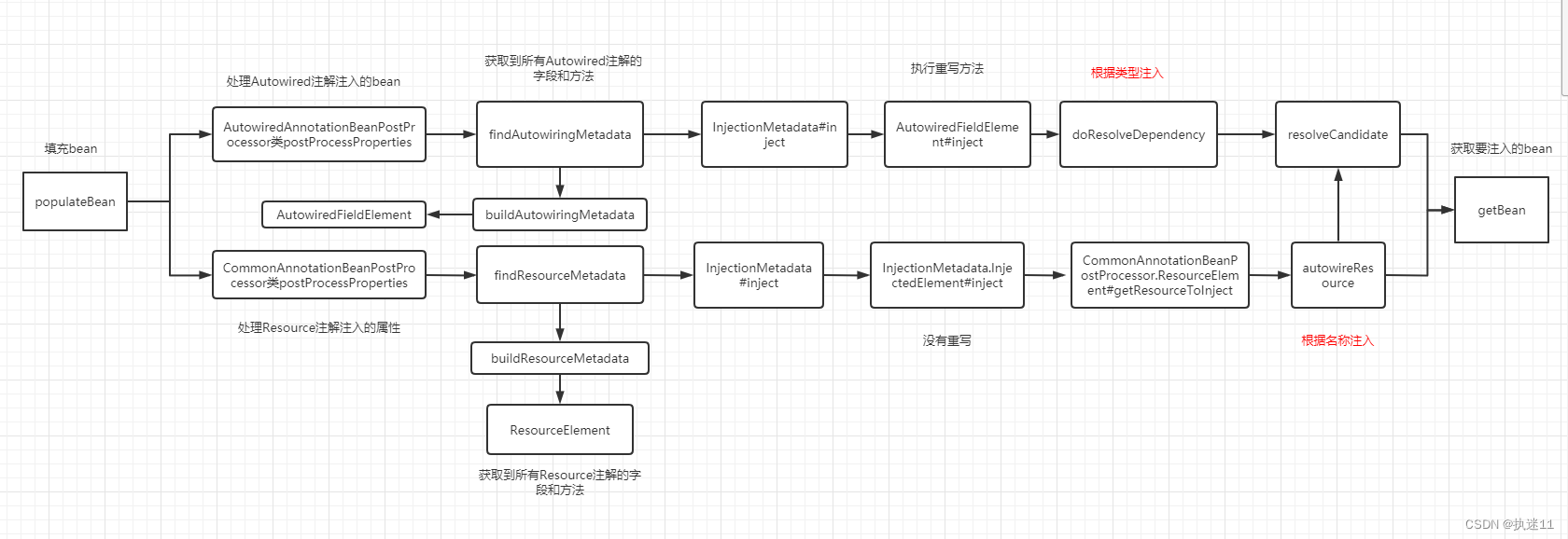
实例化bean之后要执行属性填充,也就是serviceA注入了servcieB,实例化servcieA时要通过populateBean先实例化serviceB.
也就是最终要执行serviceB的getBean
只是字段注入的流程
关键的两个Processor
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 处理Autowired注解
- CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 处理Resource注解
都是调用postProcessProperties方法
1.Autowired
1. AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
if (bw == null) {
if (mbd.hasPropertyValues()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
//终止属性填充 暂时不考虑
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
// @Bean(autowire = Autowire.BY_NAME) 这种暂时不考虑 从来没用过
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
//是否有相关的porcessor
//这里肯定有的
//AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 处理Autowired注解
//CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 处理Resource注解
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
//关键方法 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类postProcessProperties方法
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
if (pvs != null) {
//将实例化的bean填充的注入它的bean中 也就是将serviceA设置到serviceB的属性中
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
2. AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
//获取到Autowired注解的字段和方法
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
//执行注入bean的实例化
//重要2
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
获取到Autowired注解的字段和方法
2.1. AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#findAutowiringMetadata
获取到加了Autowired注解的字段和方法
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
//先从缓存拿
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
//缓存没有 构建metadata
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
2.2. AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildAutowiringMetadata
找到所有加了Autowired的字段和方法 放到elements中
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, this.autowiredAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
//找到加了Autowired的字段
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
//Autowired不能加到static字段
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
//这里的类型是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的内部类,也是
//InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement的子类
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
//找到加了Autowired的方法
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
MergedAnnotation<?> ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
//Autowired不能加到static字段
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
//Autowired必须加有参数的的方法
if (method.getParameterCount() == 0) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
//获取Autowired的Required属性 看用户有没有指定 唯一的一个属性
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
//这里的类型是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的内部类,也是
//InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement的子类
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
});
//currElements加到elements
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
//获取父类继续处理父类的Autowired
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
//构建新的InjectionMetadata 传入刚刚获取的elements
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
3. InjectionMetadata#inject
获取到Autowired注解的字段和方法后执行InjectionMetadata的inject方法
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
//遍历获取到的Autowired注解的字段和方法
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
//执行对应element的inject方法 这里的element是AutowiredFieldElement
//AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的内部类
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
4. AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredFieldElement#inject
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
//实例化需要注入的bean 并返回
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
this.cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
else {
this.cachedFieldValue = null;
}
this.cached = true;
}
}
}
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
}
5.DefaultListableBeanFactory#doResolveDependency
beanFactory.resolveDependency会调用doResolveDependency方法
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
Object shortcut = descriptor.resolveShortcut(this);
if (shortcut != null) {
return shortcut;
}
Class<?> type = descriptor.getDependencyType();
Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor);
if (value != null) {
if (value instanceof String) {
String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ?
getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null);
value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd);
}
TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter());
try {
return converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getTypeDescriptor());
}
catch (UnsupportedOperationException ex) {
// A custom TypeConverter which does not support TypeDescriptor resolution...
return (descriptor.getField() != null ?
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) :
converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter()));
}
}
Object multipleBeans = resolveMultipleBeans(descriptor, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
if (multipleBeans != null) {
return multipleBeans;
}
//获取到需要注入的类型 descriptor中有需要注入的类型
//比如原始字段类型service 及其实现类 serviceImpl
Map<String, Object> matchingBeans = findAutowireCandidates(beanName, type, descriptor);
if (matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
return null;
}
String autowiredBeanName;
Object instanceCandidate;
if (matchingBeans.size() > 1) {
autowiredBeanName = determineAutowireCandidate(matchingBeans, descriptor);
if (autowiredBeanName == null) {
if (isRequired(descriptor) || !indicatesMultipleBeans(type)) {
return descriptor.resolveNotUnique(descriptor.getResolvableType(), matchingBeans);
}
else {
// In case of an optional Collection/Map, silently ignore a non-unique case:
// possibly it was meant to be an empty collection of multiple regular beans
// (before 4.3 in particular when we didn't even look for collection beans).
return null;
}
}
instanceCandidate = matchingBeans.get(autowiredBeanName);
}
else {
// We have exactly one match.
Map.Entry<String, Object> entry = matchingBeans.entrySet().iterator().next();
//要注入的beanName
autowiredBeanName = entry.getKey();
//要注入的bean
instanceCandidate = entry.getValue();
}
if (autowiredBeanNames != null) {
autowiredBeanNames.add(autowiredBeanName);
}
if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {
//处理要注入的bean 也就是调用getBean方法 再执行一遍实例化bean的逻辑
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
}
Object result = instanceCandidate;
if (result instanceof NullBean) {
if (isRequired(descriptor)) {
raiseNoMatchingBeanFound(type, descriptor.getResolvableType(), descriptor);
}
result = null;
}
if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(type, result)) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(autowiredBeanName, type, instanceCandidate.getClass());
}
return result;
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
}
6. DependencyDescriptor#resolveCandidate
public Object resolveCandidate(String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, BeanFactory beanFactory)
throws BeansException {
return beanFactory.getBean(beanName);
}
整体逻辑就是获取到Autowired注解标注的字段(反射),然后调用getBean方法实例化,然后设置到引入它的bean中。
2.@Resource
1.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessProperties
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findResourceMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of resource dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
和autowired同样的逻辑,获取metadata,然后执行inject方法
1.1 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#findResourceMetadata
private InjectionMetadata findResourceMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
//从缓存获取
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
//构建
metadata = buildResourceMetadata(clazz);
//放到缓存
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
1.2 CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#buildResourceMetadata
private InjectionMetadata buildResourceMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
if (!AnnotationUtils.isCandidateClass(clazz, resourceAnnotationTypes)) {
return InjectionMetadata.EMPTY;
}
List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new ArrayList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final List<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new ArrayList<>();
//遍历当前类的所有字段 看有没有@Resource注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
if (webServiceRefClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(field, field, null));
}
else if (ejbClass != null && field.isAnnotationPresent(ejbClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(field, field, null));
}
//如果有@Resource注解 则会进入判断
else if (field.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {
//@Resource注解不能用在静态字段
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static fields");
}
//如果不是忽略的 就加入currElements
if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(field.getType().getName())) {
currElements.add(new ResourceElement(field, field, null));
}
}
});
//遍历当前类的所有方法 看有没有@Resource注解
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, method -> {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
if (method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (webServiceRefClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(webServiceRefClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@WebServiceRef annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new WebServiceRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
else if (ejbClass != null && bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(ejbClass)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
if (method.getParameterCount() != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@EJB annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new EjbRefElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
else if (bridgedMethod.isAnnotationPresent(Resource.class)) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation is not supported on static methods");
}
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
if (paramTypes.length != 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("@Resource annotation requires a single-arg method: " + method);
}
if (!this.ignoredResourceTypes.contains(paramTypes[0].getName())) {
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new ResourceElement(method, bridgedMethod, pd));
}
}
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
//elements放到InjectionMetadata的injectedElements属性中
return InjectionMetadata.forElements(elements, clazz);
}
1.3.ResourceElement构造方法
public ResourceElement(Member member, AnnotatedElement ae, @Nullable PropertyDescriptor pd) {
//父类也是CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的内部类LookupElement
//他们的父类都是InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement
super(member, pd);
//获取Resource注解
Resource resource = ae.getAnnotation(Resource.class);
//获取注解的name属性 不配置默认为""
String resourceName = resource.name();
//获取注解的type属性 默认是object
Class<?> resourceType = resource.type();
//如果不指定name resourceName就为"" isDefaultName就为true 反之isDefaultName为false
this.isDefaultName = !StringUtils.hasLength(resourceName);
//如果是默认name的话
if (this.isDefaultName) {
//直接获取到成员的名字 ClassA classA 获取到classA
resourceName = this.member.getName();
if (this.member instanceof Method && resourceName.startsWith("set") && resourceName.length() > 3) {
resourceName = Introspector.decapitalize(resourceName.substring(3));
}
}
//如果不是默认的名字 就处理指定的name
else if (embeddedValueResolver != null) {
resourceName = embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(resourceName);
}
//如果不是默认类型 也就是指定了resource的type属性(一般不用)
//因为resource主要是根据name注入 没有的话再根据type注入
if (Object.class != resourceType) {
checkResourceType(resourceType);
}
else {
// No resource type specified... check field/method.
//获取到object类型
resourceType = getResourceType();
}
//设置name的值 一般会有值 因为不设置的话会用字段的名字
this.name = (resourceName != null ? resourceName : "");
// type object类型
this.lookupType = resourceType;
//目前他为空""
String lookupValue = resource.lookup();
//他也为空""
this.mappedName = (StringUtils.hasLength(lookupValue) ? lookupValue : resource.mappedName());
Lazy lazy = ae.getAnnotation(Lazy.class);
this.lazyLookup = (lazy != null && lazy.value());
}
2.InjectionMetadata#inject
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
//执行对应的element的inject方法 这里应该执行ResourceElement的inject方法,
//但是他没有重写 所以执行父类的inject方法 也就是InjectionMetadata的内部类
//InjectedElement的inject方法
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
3.InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement#inject
protected void inject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs)
throws Throwable {
//如果是字段
if (this.isField) {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
//设置字段 调用getResourceToInject方法 这个方法ResourceElement重写了 所以可以执行
field.set(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
else {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
try {
Method method = (Method) this.member;
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(target, getResourceToInject(target, requestingBeanName));
}
catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw ex.getTargetException();
}
}
}
4.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.ResourceElement#getResourceToInject
@Override
protected Object getResourceToInject(Object target, @Nullable String requestingBeanName) {
//不是懒加载 所以执行getResource方法
return (this.lazyLookup ? buildLazyResourceProxy(this, requestingBeanName) :
getResource(this, requestingBeanName));
}
5.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#getResource
protected Object getResource(LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
// JNDI lookup to perform?
String jndiName = null;
if (StringUtils.hasLength(element.mappedName)) {
jndiName = element.mappedName;
}
else if (this.alwaysUseJndiLookup) {
jndiName = element.name;
}
if (jndiName != null) {
if (this.jndiFactory == null) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.lookupType,
"No JNDI factory configured - specify the 'jndiFactory' property");
}
return this.jndiFactory.getBean(jndiName, element.lookupType);
}
// Regular resource autowiring
if (this.resourceFactory == null) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.lookupType,
"No resource factory configured - specify the 'resourceFactory' property");
}
//上面都不是 走这个方法
return autowireResource(this.resourceFactory, element, requestingBeanName);
}
6.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#autowireResource
protected Object autowireResource(BeanFactory factory, LookupElement element, @Nullable String requestingBeanName)
throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException {
Object resource;
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames;
String name = element.name;
if (factory instanceof AutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
AutowireCapableBeanFactory beanFactory = (AutowireCapableBeanFactory) factory;
DependencyDescriptor descriptor = element.getDependencyDescriptor();
//如果没有指定name 并且factory中也没有要注入的这个bean
//这个判断一般不进 第三个条件是判断当前是否是factorybean 是的话第三个判断才为true
//使用resource时成员变量名字很关键,会根据变量名查找已注册的bean或者beanDefinition
// 要遵循驼峰命名 第一个字母小写
//会进入判断的定义 进入判断 意味着和autowired一样 根据类型注入bean
//Airservice aService(应该是airService)
// AServcie aService 这样也不行 第一个是单个字母的 spring生成的是AService,第一个
//字母不会变成小写 应该是 AService AService
if (this.fallbackToDefaultTypeMatch && element.isDefaultName && !factory.containsBean(name)) {
autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>();
//和autowired一样 根据类型注入bean
resource = beanFactory.resolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, null);
if (resource == null) {
throw new NoSuchBeanDefinitionException(element.getLookupType(), "No resolvable resource object");
}
}
//如果指定了名字 或者没指定名字 但不是factorybean 进入 大多数走这个方法
//这就是根据名字注入了 使用resource的目的就是根据名字注入
else {
//根据名字调用getBean方法
resource = beanFactory.resolveBeanByName(name, descriptor);
autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);
}
}
else {
resource = factory.getBean(name, element.lookupType);
autowiredBeanNames = Collections.singleton(name);
}
if (factory instanceof ConfigurableBeanFactory) {
ConfigurableBeanFactory beanFactory = (ConfigurableBeanFactory) factory;
for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {
if (requestingBeanName != null && beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) {
beanFactory.registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, requestingBeanName);
}
}
}
return resource;
}