目录
一. 选择排序的实现
1. 简单选择排序
2. 性能分析
二. 代码实现
1. 核心代码
三. 代码展示
四. 数据测试
五. 总结
一. 选择排序的实现
1. 简单选择排序
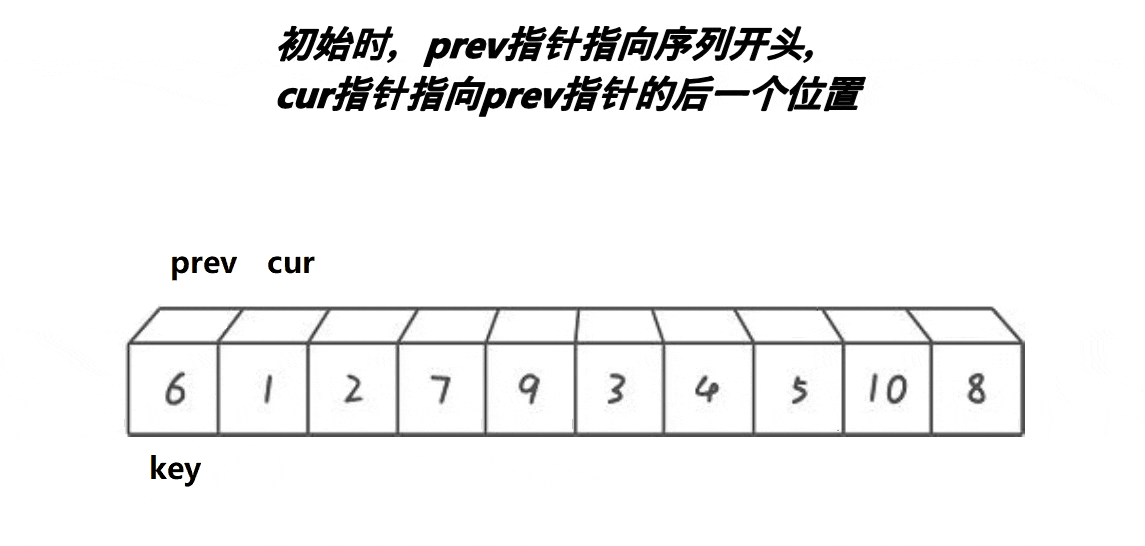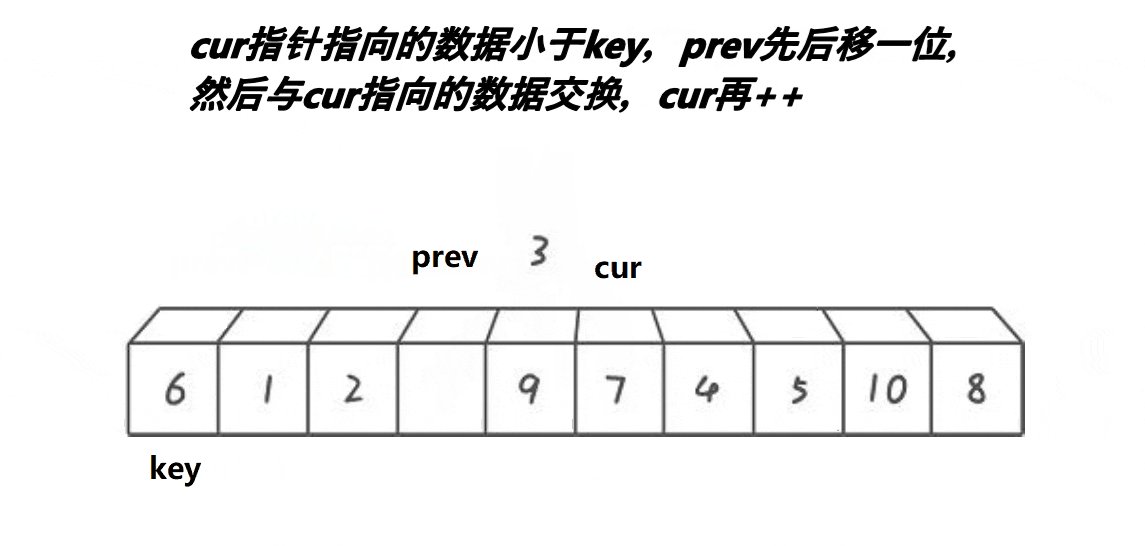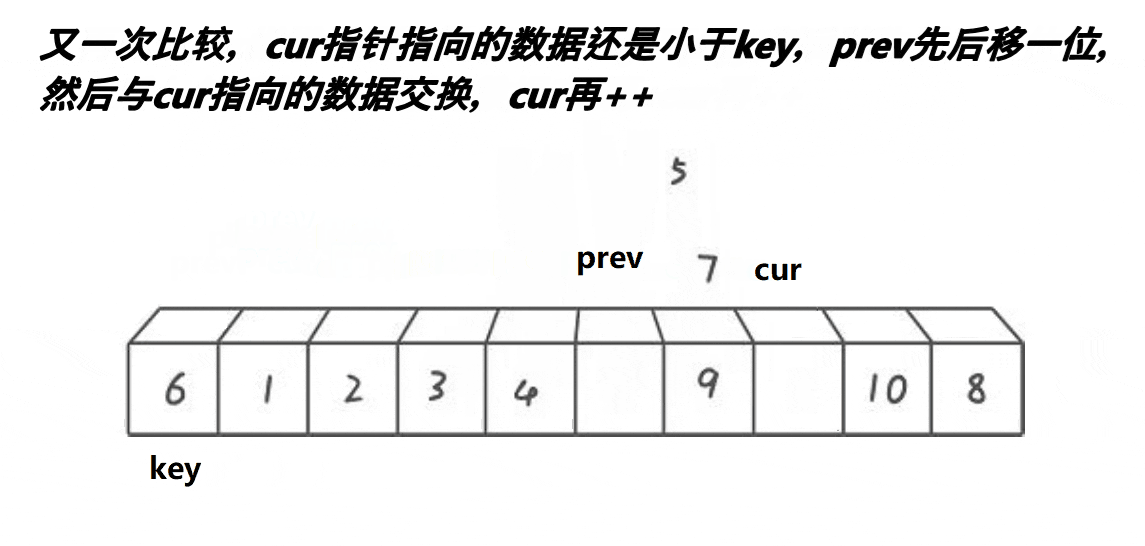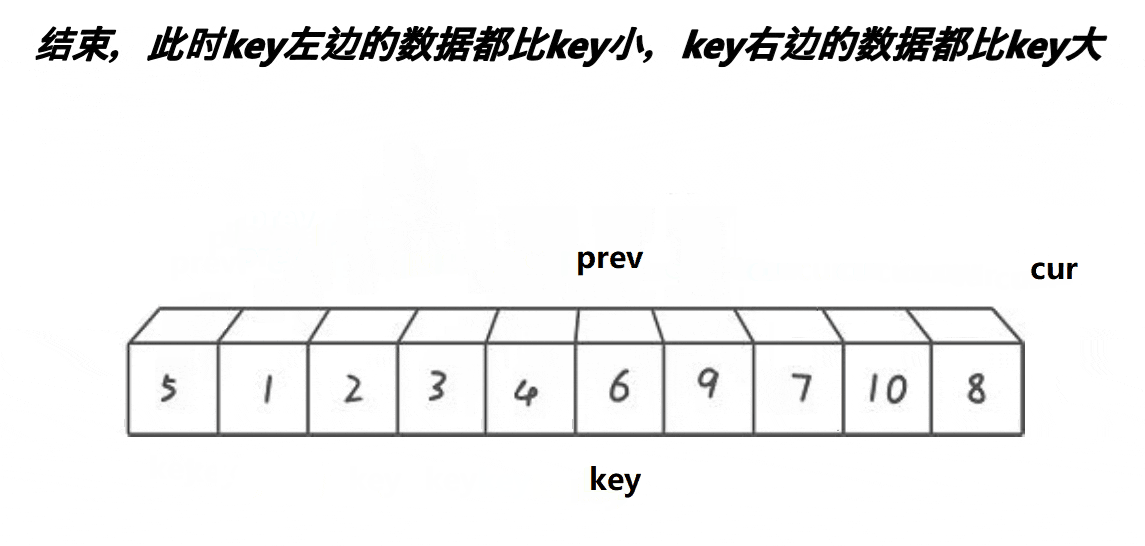
选择排序的基本思想是:每一趟(如第i趟)在后面n-i+1(i=1,2,3...n-1)个待排序元素中选取关键字最小的元素,作为有序子序列的第i个元素,直到第n-1趟做完,待排序元素只剩下1个,完成排序。
根据上面的思想可以很直观的得出简单选择排序算法的思想:假设排序表为L[1...n],第i趟排序即从L[i...n]中选择关键字最小的元素与L(i)交换,每一趟排序可以确定一个元素的最终位置,这样经过n-1趟排序就可使得整个排序表有序。
2. 性能分析
空间效率:仅使用常数个辅助单元,故空间效率为O(1)。
时间效率:在简单选择排序过程中,元素的比较次数与序列的初始状态无关,始终是n(n-1)/2次,故时间复杂度是。
稳定性:在第i趟找到最小的元素后,和第i个元素交换,可能会导致第i个元素与其含有相同关键字元素的相对位置发生改变。因此,简单选择排序是一种不稳定的排序方法。
二. 代码实现
1. 核心代码
相当easy的代码,两轮循环,第一轮循环控制最小数字的位置i,第二轮循环找到最小数字的位置min,最后将i和min互换位置即可得到最终排序结果。
/**
*********************
* Selection sort. All data are valid.
*********************
*/
public void selectionSort() {
DataNode tempNode;
int tempIndexForSmallest;
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
// Initialize.
tempNode = data[i];
tempIndexForSmallest = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < length; j++) {
if (data[j].key < tempNode.key) {
tempNode = data[j];
tempIndexForSmallest = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// Change the selected one with the current one.
data[tempIndexForSmallest] = data[i];
data[i] = tempNode;
} // Of for i
}// Of selectionSort三. 代码展示
主类:
package Day_47;
import Day_41.DataArray;
public class demo1 {
/**
*********************
* The entrance of the program.
*
* @param args Not used now.
*********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
// System.out.println("\r\n-------sequentialSearchTest-------");
int []paraKeyArray;
paraKeyArray=new int[]{11,2,3};
String[] paraContentArray = new String[]{"121","21","324"};
DataArray test=new DataArray(paraKeyArray,paraContentArray);
// test.insertionSort();
// System.out.println("Result\r\n" + test);
test.selectionSortTest();
}// Of main
}调用类:
/**
*********************
* Selection sort. All data are valid.
*********************
*/
public void selectionSort() {
DataNode tempNode;
int tempIndexForSmallest;
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++) {
// Initialize.
tempNode = data[i];
tempIndexForSmallest = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < length; j++) {
if (data[j].key < tempNode.key) {
tempNode = data[j];
tempIndexForSmallest = j;
} // Of if
} // Of for j
// Change the selected one with the current one.
data[tempIndexForSmallest] = data[i];
data[i] = tempNode;
} // Of for i
}// Of selectionSort
/**
*********************
* Test the method.
*********************
*/
public static void selectionSortTest() {
int[] tempUnsortedKeys = { 5, 3, 6, 10, 7, 1, 9 };
String[] tempContents = { "if", "then", "else", "switch", "case", "for", "while" };
DataArray tempDataArray = new DataArray(tempUnsortedKeys, tempContents);
System.out.println(tempDataArray);
tempDataArray.selectionSort();
System.out.println("Result\r\n" + tempDataArray);
}// Of selectionSortTest
四. 数据测试
运行结果

五. 总结
我个人感觉这个排序算法是最好理解的代码了(没有之一!),每一次从数字序列里面找到最小的数字,将它换到头部,一直进行n-1轮,故可以得到最终答案。