目录
1.指针的基本概念
2.定义指针,使用指针
3.指针所占的内存空间
4.空指针和野指针
4.1空指针
4.2野指针
5.const修饰指针
5.1常量指针
5.2指针常量
5.3const既修饰指针又修饰常量
6.指针和数组,利用指针访问数组
6.1概述
6.2使用数组名和下表访问
6.3使用数组名和指针
6.4使用指针变量访问数组
6.5总结
7.指针和函数
7.1指针当作函数的参数
7.2值传递和地址传递
8.指针、数组、函数案例练习
8.1函数传递数组
1.指针的基本概念

2.定义指针,使用指针
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1.定义指针
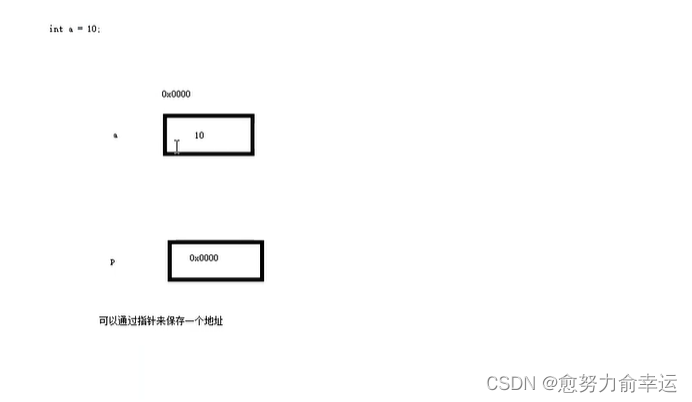
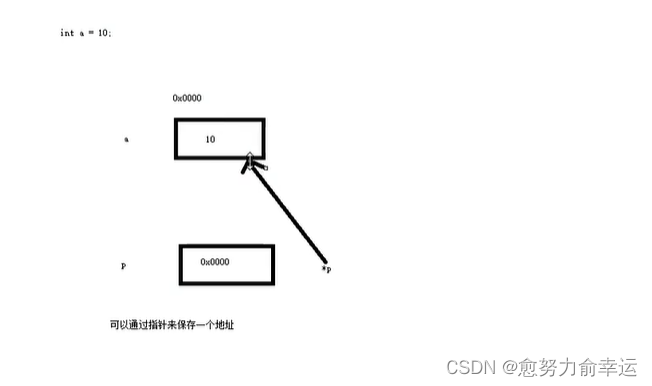
int a = 10;
//指针定义的语法:数据类型 *指针变量名
int* p;
//让指针记录变量a的地址,整型变量就定义整型指针
p = &a;//&取变量的地址
cout << "a的地址为:" << &a << endl;
cout << "指针p为:" << p << endl;//指针就是地址,保存地址
//2.使用指针
//可以通过解引用的方式找到指针指向的内存中的数据
//指针前加 * 代表解引用,找到指针指向的内存中的数据
*p = 1000;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "*p = " << *p << endl;
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
3.指针所占的内存空间


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//指针所占的内存空间大小
int a = 10;
int * p = &a;
//在32位操作系统下,指针都是占4个字节空间大小,不管是什么数据类型
//在64位操作系统下,指针都是占4个字节空间大小,不管是什么数据类型
cout << "sizeof(int *) = " << sizeof(int *) << endl;
//cout << "sizeof(int *) = " << sizeof(p) << endl;和上面等价
cout << "sizeof(int *) = " << sizeof(double *) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(int *) = " << sizeof(char *) << endl;
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
4.空指针和野指针
4.1空指针

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//空指针:指向编号为0的指针为空指针
//1.用于给指针变量进行初始化,如果指针一开始不知道指向哪合适,
//那就指向编号为0的内存处
//后期有地方指在重新更改指向就好
int * p = NULL;
int a = 100;
p = &a;
cout << p << endl;
//2.空指针是不可以进行访问的
//0~255之间的内存编号是系统占用的,因此不可以访问
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
4.2野指针

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//野指针
//在程序中,尽量避免使用野指针
int* p = (int*)0x1100;
//访问指针报错
cout<<*p<<endl;
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}

5.const修饰指针

5.1常量指针

5.2指针常量

5.3const既修饰指针又修饰常量
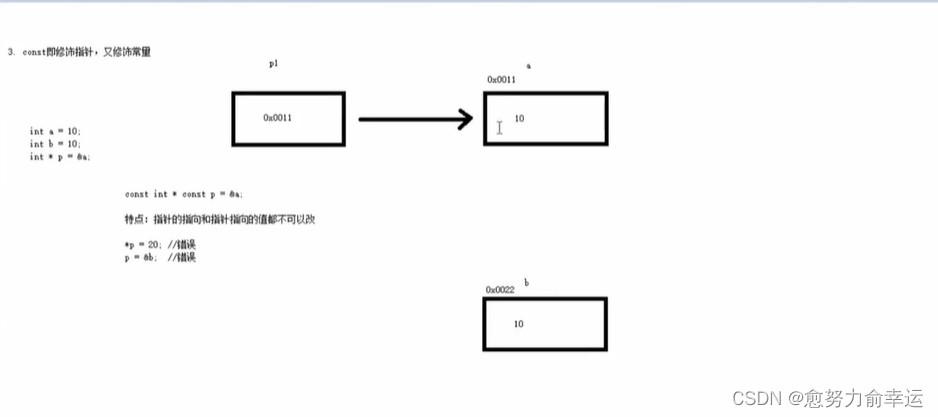

记忆技巧 :*:指针,const:常量,所以
const int *p:常量指针
int * const p:指针常量
可不可以修改的记忆技巧:
const后面是*p,对*p修改就是错误的,也就是,常量指针
指向可以改,指向的值不可以改。
const后面是p,对p的修改就是错误的,也就是,指针常量指向的值可以改,指向不可以改。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1.const修饰指针,常量指针
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
const int * p = &a;
//指针指向的值不可以改,指针的指向可以改
//*p=20错误
p = &b;//正确
//2.const修饰常量,指针常量
int * const p1 = &a;
//指针的指向不可以改,指针指向的值可以改
*p1 = 30;//正确
//p1=&b//错误
//
//3.const既修饰指针又修饰常量
const int* const p2 = &a;
//指针的指向和指针指向的值都不可以改
//*p2=200;//错误
//p2=&b//错误
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
6.指针和数组,利用指针访问数组

6.1概述
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//指针和数组
//利用指针访问数组中的元素
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int* p = arr;//数组名就是数组在内存中的首地址
cout << "利用指针访问第一个元素:" << *p << endl;
p++;//因为p本身是整型,加1后就主动往后面移4个字节
cout << "利用指针访问第二个元素:" << *p << endl;
cout << "利用指针输出数组元素" << endl;
int* p1 = arr;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << "利用指针访问第" << (i + 1) << "个元素:" << *p1 << endl;
p1++;
}
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
6.2使用数组名和下表访问
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//指针和数组
//利用指针访问数组中的元素
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << endl;
}
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
6.3使用数组名和指针
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//指针和数组
//利用指针访问数组中的元素
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << *(arr+i) << endl;
}
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
6.4使用指针变量访问数组
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//指针和数组
//利用指针访问数组中的元素
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int* p = arr;//等价于int* p = &arr[0]
int* p1 = &arr[0];
int* p2 = arr;
//第一种指针=1
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << *p <<" ";
p++;
}
cout << endl;
//第二种
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << *(p1 + i) <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
//第三种
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << p2[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
6.5总结
下面进行总结看是否掌握
1、arr[i], *(p+i), *(a+i), p[i]都是等效的。
2.指针p可以++,不能写 arr++,因为arr是数组首地址、是常量
7.指针和函数
7.1指针当作函数的参数

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//实现两个数字进行交换
void swap01(int a, int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
cout << "swap01 a = " << a << " " << "swap01 b = " << b << endl;
}
void swap02(int *p1, int *p2)
{
int temp = *p1;
*p1 = *p2;
*p2 = temp;
}
int main()
{
//指针和函数
//1.值传递
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
swap01(a, b);
cout << "a = " << a << " " << "b = " << b << endl;
int c = 100;
int d = 200;
//2.地址传递
//如果是地址传递,可以修改实参
swap02(&c, &d);//传入c变量的地址,传入d变量的地址
cout << "c= " << c << " " << "d = " << d << endl;
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}

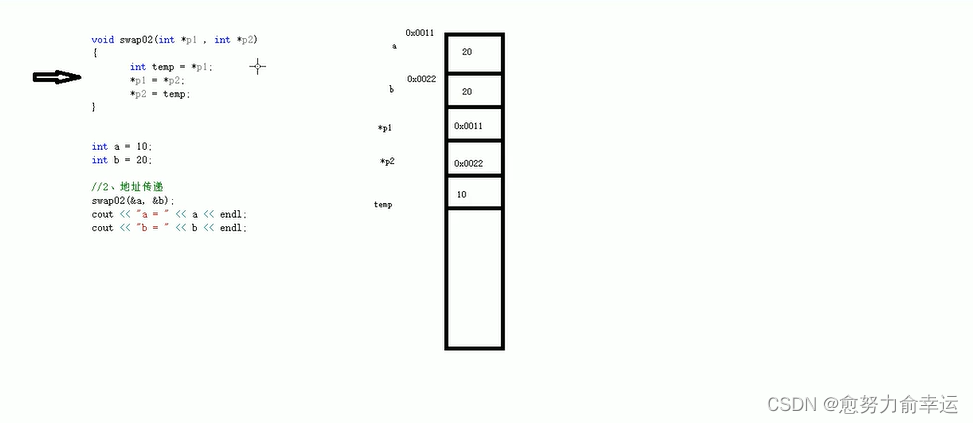
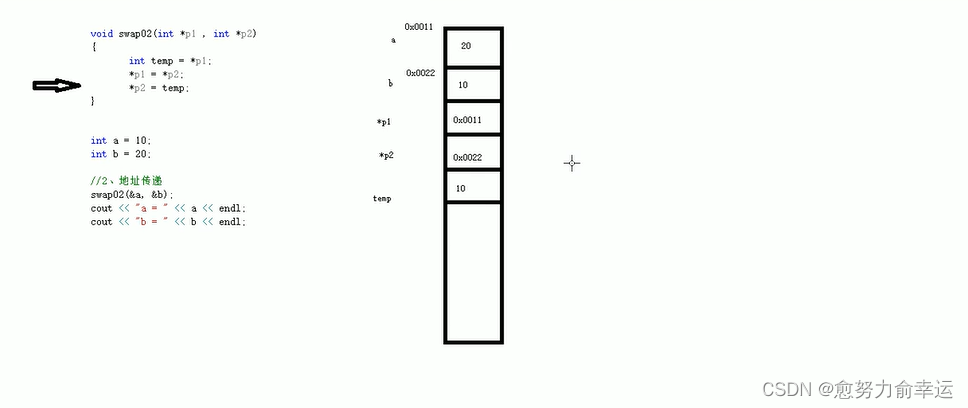
7.2值传递和地址传递

8.指针、数组、函数案例练习
8.1函数传递数组
第一种写法:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//冒泡排序,参数1数组的首地址,参数2数组的长度
void bubbleSort(int* p, int len)
{
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < len-1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < len-1-i; j++)
{
if (p[j] > p[j + 1])
{
temp = p[j];
p[j] = p[j + 1];
p[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 4,3,6,9,1,2,10,8,7,5 };
//数组的长度
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubbleSort(arr,len);//数组名就是数组的首地址
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
第二种写法
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//冒泡排序,参数1数组的首地址,参数2数组的长度
void bubbleSort(int p[], int len)
{
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < len - 1 - i; j++)
{
if (p[j] > p[j + 1])
{
temp = p[j];
p[j] = p[j + 1];
p[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 4,3,6,9,1,2,10,8,7,5 };
//数组的长度
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubbleSort(arr, len);//数组名就是数组的首地址
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}
第三种写法:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//冒泡排序,参数1数组的首地址,参数2数组的长度
void bubbleSort(int* p, int len)
{
int temp;
for (int i = 0; i < len-1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < len-1-i; j++)
{
if (*(p+j) > *(p+j + 1))
{
temp = *(p+j);
*(p+j) = *(p+j + 1);
*(p + j + 1) = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[10] = { 4,3,6,9,1,2,10,8,7,5 };
//数组的长度
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bubbleSort(arr,len);//数组名就是数组的首地址
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
system("pause");//按任意键继续
return 0;
}




![[go学习笔记.第十八章.数据结构] 1.基本介绍,稀疏数组,队列(数组实现),链表](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d7aea688b36e4a96b8e309eccec89c71.png)