前期准备
接上一篇,来实现事件中心的管理:使用定义好的事件中心管理器EventManager,实现鼠标拖拽、角色移动、发射子弹等几个功能。
1. InputSystem的准备:需要设置输入设备并关联事件,比如监听键盘输入"WASD"事件实现角色移动的回调,监听鼠标点击事件实现拖拽物体移动等。详见插件1--新版InputSystem;
2. 需要使用并修改之前的几个脚本:
(1)修改Rigidbody--移动控制当中控制角色移动的方法;
(2)在Ray/Raycast/Linecast/OverlapSphere中点击拖拽物体的方法不再需要了,更新为使用事件监听判断鼠标按键;
(3)开火的功能,也不需要if去判断按键,修改为监听开火Fire事件。
以下开始一个一个地实现:
控制移动
在Rigidbody--移动控制当中使用Input.GetAxis("Horizontal"), Input.GetAxis("Vertical")的方式获取键盘WASD的输入数据,在有了事件中心后,改为采用注册移动事件的方式,发送并回传一个位置的参数。写一个HeroMoveEvent.cs脚本:
//注册一个移动的事件
public class HeroMoveEvent : MonoBehaviour
{
private Rigidbody rb;
private Vector2 moveInput; //接收回传的参数
private Vector3 movement;//移动的坐标位置(将之前的二维坐标转成这里的三维)
private Quaternion targetRotation;
public float moveSpeed = 2;
public float rotateSpeed = 2;
GameObject Bullet;
void Start()
{
rb = GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
EventManager.Instance.AddEvent(EventType.OnPlayerMove, this, data =>
{ //注册一个移动的事件,监听者是HeroMoveEvent(本类),这个事件由
//InputManager中的OnMove()发送给场景中的PlayerInput
var eventData = data as EventDataPlayerMove;
//EventData参数转为EventDataPlayerMove类型
moveInput = eventData.position;
//移动的距离由EventDataPlayerMove中的position变量决定
});
}
void FixedUpdate()
{
//moveInput = new Vector2(Input.GetAxis("Horizontal"), Input.GetAxis("Vertical")); //之前使用Input拿到的水平、垂直方向数据
//使用事件后,通过回传的EventData数据赋值给moveInput变量
movement.Set(moveInput.x, 0, moveInput.y);//得到移动的坐标
movement.Normalize();
//检测是否有输入
bool hInput = !Mathf.Approximately(moveInput.x, 0);
bool vInput = !Mathf.Approximately(moveInput.y, 0);
if (hInput || vInput)
{
movement = Quaternion.Euler(0, Camera.main.transform.eulerAngles.y, 0) * movement;
}
Vector3 lookForward = Vector3.RotateTowards(transform.forward, movement, rotateSpeed * Time.fixedDeltaTime, 360);
targetRotation = Quaternion.LookRotation(lookForward);
rb.MovePosition(rb.position + movement * moveSpeed * Time.fixedDeltaTime);
rb.MoveRotation(targetRotation);
}注册事件后,需要发送事件,以及在PlayerInput中绑定它(详见插件1--新版InputSystem中的添加并绑定移动事件)在脚本中建立一个方法OnMove(),用于发送OnPlayerMove事件:
public void OnMove(InputAction.CallbackContext context)
{//绑定PlayerInput中的PlayerMap-Move事件
EventManager.Instance.SendEvent(EventType.OnPlayerMove, new EventDataPlayerMove()
{//发送事件
position=context.ReadValue<Vector2>() //返回context参数
});
}并且在场景中的PlayerInput->Event->PlayerMap->Move中绑定这个方法:

控制鼠标点击拖拽物体
拖拽的方式还是使用Ray/Raycast/Linecast/OverlapSphere中的方法应用2:实现鼠标点击拖拽物体,使用射线检测是否点击到物体,如果以及点击到了,就将鼠标输入的XY坐标位置转换为物体的XZ场景位置。不同的是,这里改为监听鼠标点击的事件,不再在update()中判断鼠标的输入状态。同样,也需要在InputSystem中设置鼠标按键。步骤如下:
1. 参照新版InputSystem的设置,在InputControl中添加LeftMouseClick、LeftMouseUp和MouseDrag三个Action,设置如下:

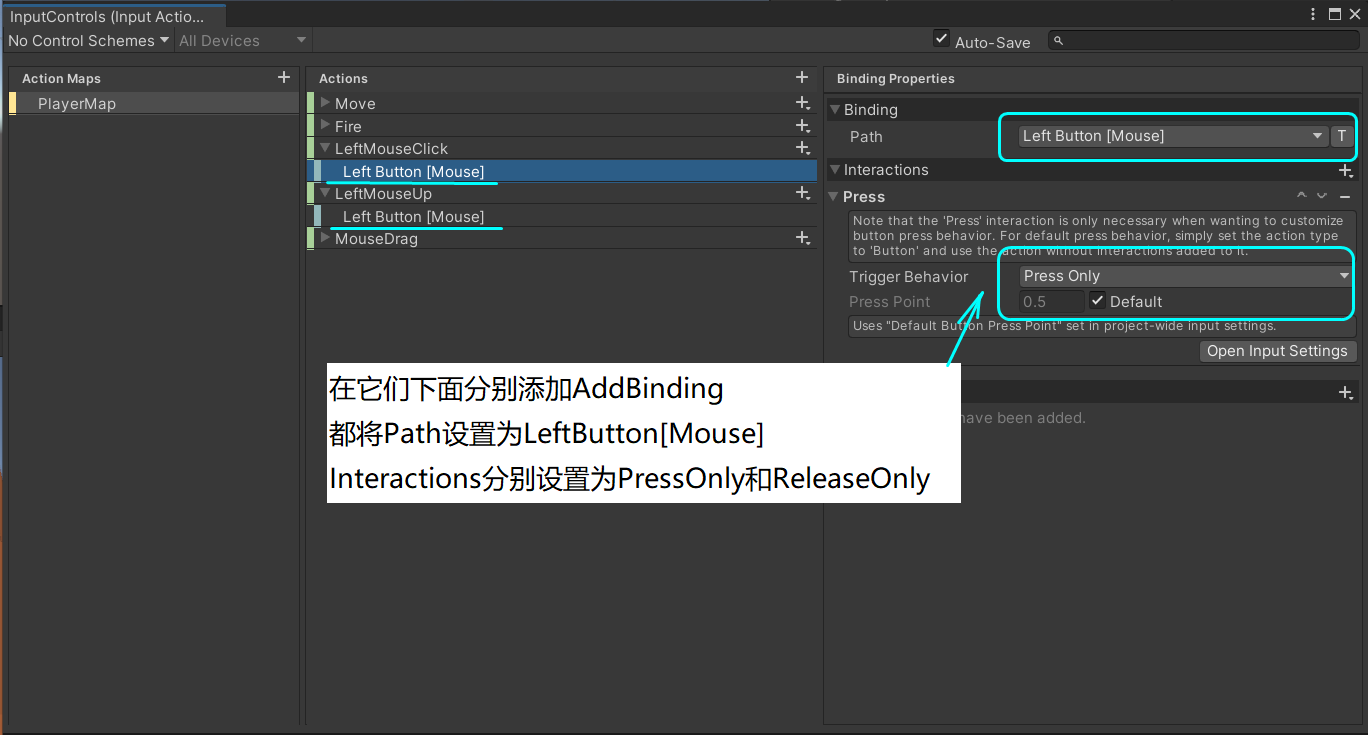

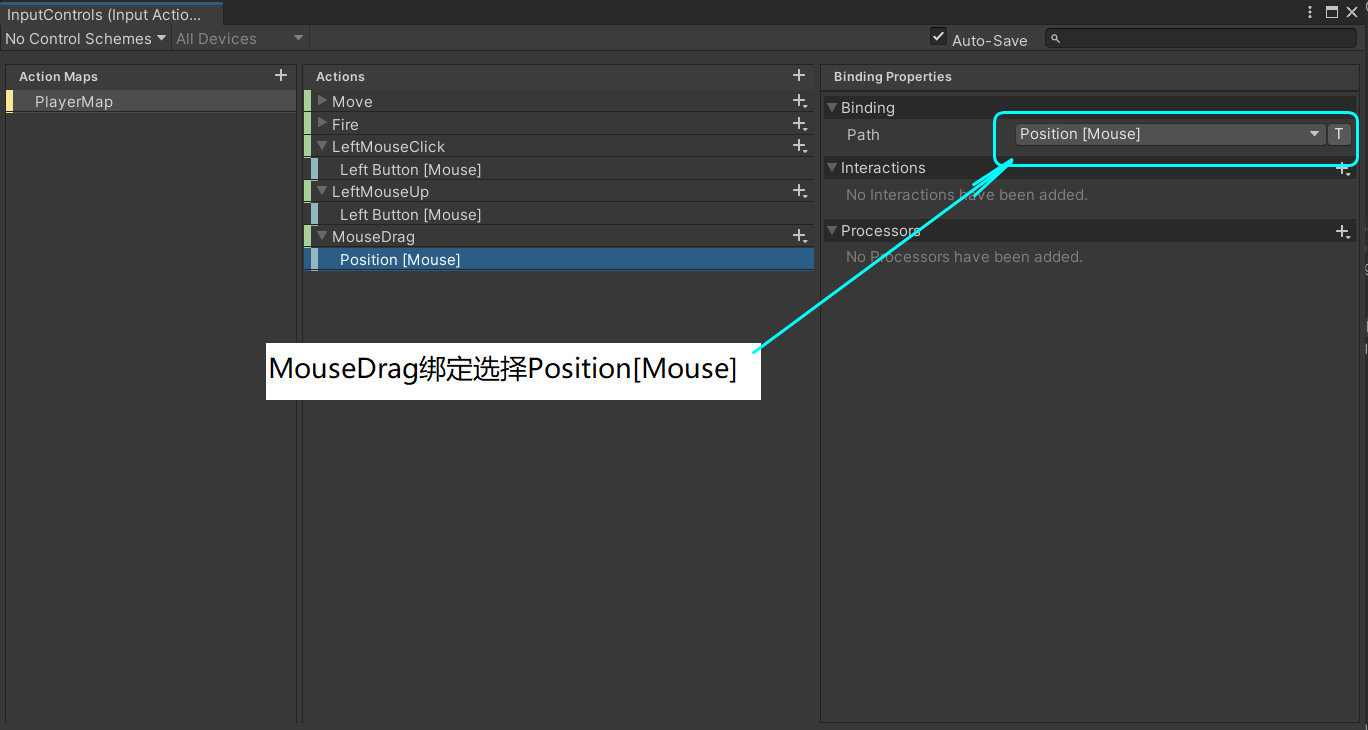
2. 注册添加鼠标拖拽事件,并且定义回调函数,回调函数的内容与Ray/Raycast/Linecast/OverlapSphere一文中的应用2:实现鼠标点击拖拽物体类似,主要就是利用从摄像机向鼠标位置射出的射线,判断是否点击到物体:
public class MouseClick : MonoBehaviour
{
private Ray ray; //定义射线
private Transform clicked; //被鼠标点击的物体
void Start()
{//注册鼠标输入事件
EventManager.Instance.AddEvent(EventType.OnMouseInput, this, MoveGameObject);
}
//定义回调函数
void MoveGameObject(EventDataBase data)
{
var eventData = data as EventDataMouseInput;
var state = eventData.State; //检测鼠标状态
var key= eventData.Key; //检测鼠标按键
if(key==EMouseInputKey.Left&&state==EMouseInputState.Down)
{//当检测到左键、按下
ray = Camera.main.ScreenPointToRay(eventData.MousePosition);
//使用事件数据库传入的二维向量参数,做一套从屏幕射向鼠标位置的射线
Physics.Raycast(ray, out RaycastHit hit, 100, LayerMask.GetMask("Enemy"));
if (hit.collider != null)
{//被点击中的物体,赋值给Click变量,准备之后被鼠标拖拽
clicked = hit.transform;
var wPos = Tools.MouseToWorld(clicked.position);
//使用工具集中的坐标转换,将鼠标坐标转为世界坐标
}
}
if(key == EMouseInputKey.Left && state == EMouseInputState.Stay)
{//鼠标左键停留持续按下的状态
if (clicked != null)
{
Vector3 pos = Tools.MouseToWorld(clicked.position);
clicked.position = new Vector3(pos.x , clicked.position.y,
pos.z);
}
}
if (key == EMouseInputKey.Left && state == EMouseInputState.Up)
{//鼠标抬起
clicked= null;
}
}
}3. 发送事件,建立一个新脚本,或者我直接放在InputManager.cs中,管理所有输入事件(详见InputManager),这个脚本挂在场景中的SingleMono上。这里写了三个发送事件方法,“左键点击”、“左键拖拽”、“左键释放”:
public class InputManager : SingleMono<InputManager>
{
public void OnLeftMouseClick(InputAction.CallbackContext context)
{
//Debug.LogError("发送鼠标左键单击世界事件");
//鼠标点击世界左键按下事件,可以在任何一个地方监听这个事件
EventDataMouseInput mouseInput= new EventDataMouseInput(EMouseInputKey.Left,
EMouseInputState.Down,Input.mousePosition);
EventManager.Instance.SendEvent(EventType.OnMouseInput, mouseInput);
}
public void OnMouseDrag(InputAction.CallbackContext context)
{
//Debug.LogError("鼠标左键持续点击世界事件");
EventManager.Instance.SendEvent(EventType.OnMouseInput, new EventDataMouseInput()
{
State = EMouseInputState.Stay,
Key = EMouseInputKey.Left,
MousePosition = context.ReadValue<Vector2>()
});
}
public void OnLeftMouseUp(InputAction.CallbackContext context)
{
//Debug.LogError("发送鼠标左键抬起事件");
EventManager.Instance.SendEvent(EventType.OnMouseInput, new EventDataMouseInput
(EMouseInputKey.Left, EMouseInputState.Up, Input.mousePosition));
}
}4. 上面3中定义的“左键点击”、“左键拖拽”、“左键释放”三个方法,在场内的PlayerInput组件中,绑定到上面1中添加的LeftMouseClick、LeftMouseUp和MouseDrag三个Action上,详见新版InputSystem中的方法,这里简单放一下设置结果:
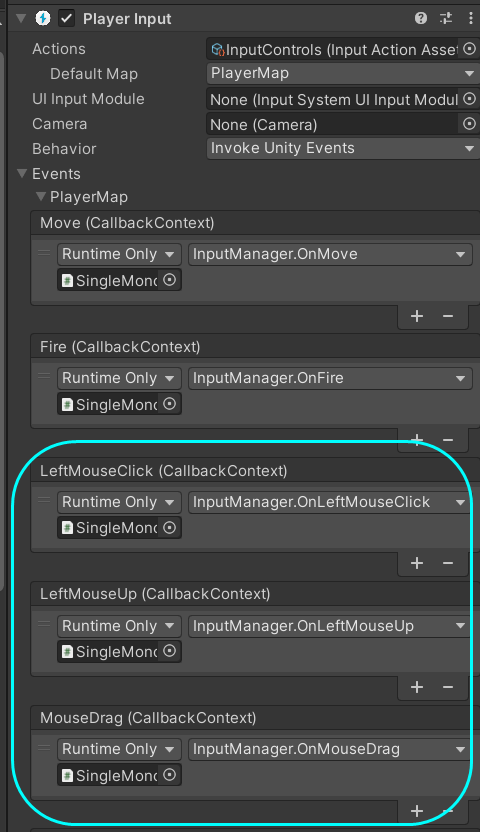
5. 运行结果,与Ray/Raycast/Linecast/OverlapSphere中应用2:实现鼠标点击拖拽物体相同
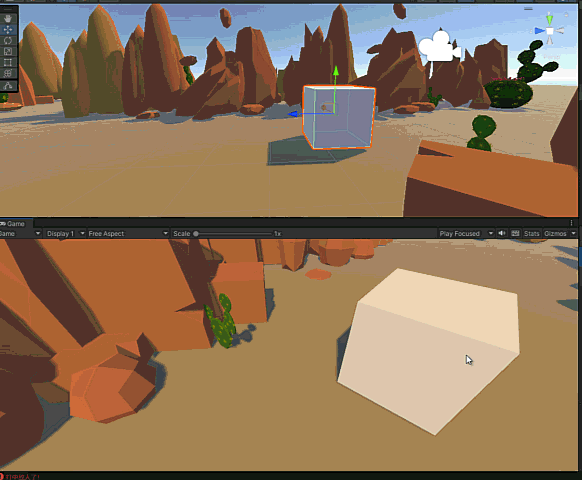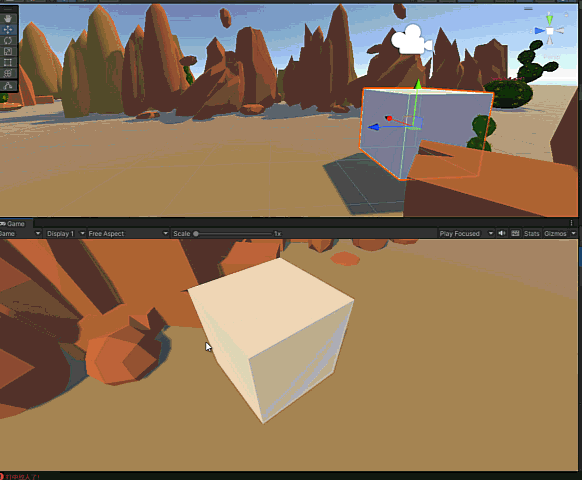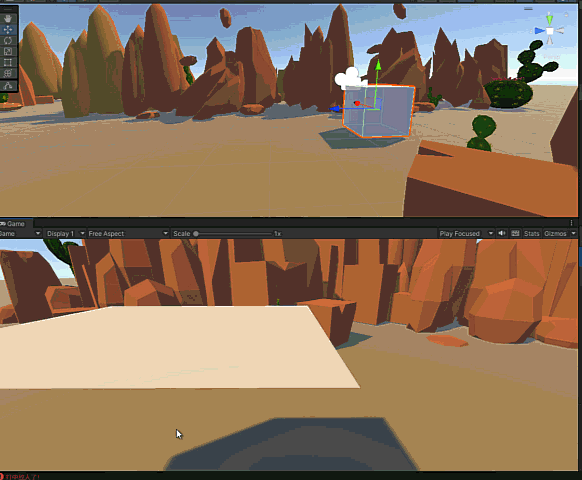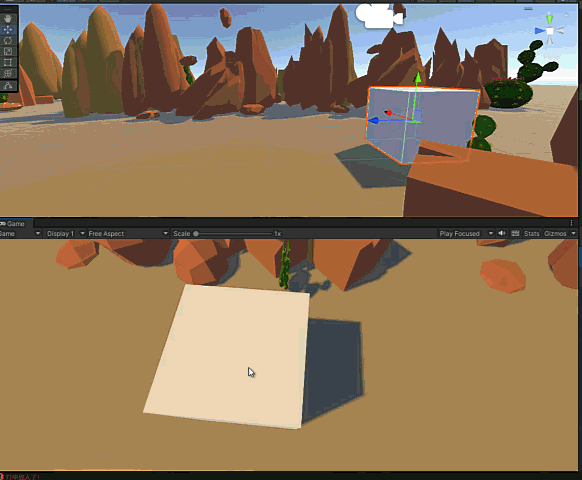
添加开火事件
在新版InputSystem中有详细的方法,这里放一下简单的步骤和脚本:
1. 注册事件:
public class BulletFireEvent : MonoBehaviour
{
public GameObject bullet;
void Start()
{
EventManager.Instance.AddEvent(EventType.OnPlayerFire, this, callback =>
{
bullet = Resload.Instance.LoadPrefab("Bullet");
bullet.SetActive(true);
bullet.transform.position = transform.position;
bullet.transform.rotation = transform.rotation;
Destroy(bullet, 2);
});
}
}2. 发送事件,这里写在上面的InputManager.cs中
public void OnFire(InputAction.CallbackContext context)
{//绑定新版InputSystem中的PlayerMap-Fire事件
EventManager.Instance.SendEvent(EventType.OnPlayerFire, null);
}3. 在场景中PlayerInput组件中绑定OnFire事件,详见新版InputSystem中的设置方法:
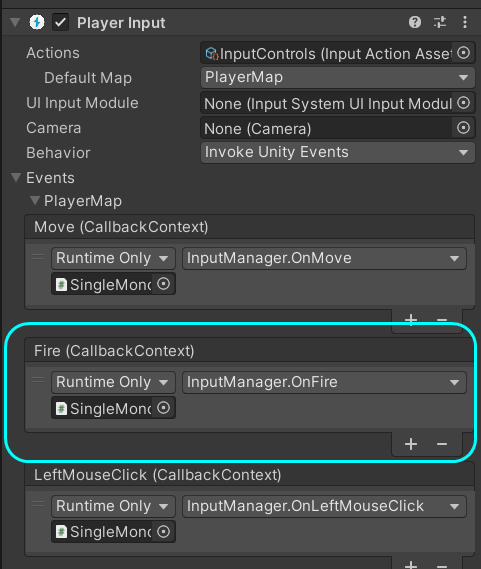
效果与之前的开火效果相同,就不放效果图了。
总结
可以比较一下使用“事件”和不使用“事件”的代码,比如在Ray/Raycast/Linecast/OverlapSphere一篇中的应用2:实现鼠标点击拖拽物体,和本篇的鼠标点击拖拽事件相比较,前者在update()中用了3个If判断鼠标的状态,而后者没有使用update(),因此在节约性能方面,事件中心的建立和使用更胜一筹。
更重要的是,如果在建立一个较大项目时,事件中心的优点就更能体现出来了,否则代码量会非常庞大。