忙活了大半个学期,终于学完了C++,虽然很基础,但是至少算是写完了实验,开心~~
实验一
实验二
实验三
实验四
实验五
实验六
题目一
一、分析下面的程序,写出其运行时的输出结果。上机运行该程序,观察运行结果是否与你的分析相同。如有不同,试分析原因。
(一)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{public:
A(){cout<<"A::A() called.\n";}
virtual ~A(){cout<<"A::~A() called.\n";}
};
class B:public A
{ public:
B(int i)
{ cout<<"B::B() called.\n";
buf=new char[i];
}
virtual ~B()
{ delete []buf;
cout<<"B::~B() called.\n";
}
private:
char *buf;
};
void fun(A *a)
{ cout<<"May you succeed!";
delete a;
}
int main()
{
A *a=new B(15);
fun(a);
return 0;
}
实验结果

(二)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
A(int a):x(a){ cout<<"A constructor..."<<x<<endl; }
int f(){return ++x;}
~A(){cout<<"destructor A..."<<endl;}
private:
int x;
};
class B:public virtual A{
private:
int y;
A Aobj;
public:
B(int a,int b,int c):A(a),y(c),Aobj(c){ cout<<"B constructor..."<<y<<endl;}
int f(){
A::f();
Aobj.f();
return ++y;
}
void display(){ cout<<A::f()<<"\t"<<Aobj.f()<<"\t"<<f()<<endl; }
~B(){cout<<"destructor B..."<<endl;}
};
class C:public B{
public:
C(int a,int b,int c):B(a,b,c),A(0){ cout<<"C constructor..."<<endl;}
};
class D:public C,public virtual A{
public:
D(int a,int b,int c):C(a,b,c),A(c){ cout<<"D constructor..."<<endl;}
~D(){cout<<"destructor D...."<<endl;}
};
int main()
{
D d(7,8,9);
d.f();
d.display();
return 0;
}
实验效果

(三)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
public:
A(int a,int b):x(a),y(b){ cout<<"A constructor..."<<endl; }
void Add(int a,int b){ x+=a;y+=b;}
void display(){ cout<<"("<<x<<","<<y<<")";}
~A(){cout<<"destructor A..."<<endl;}
private:
int x,y;
};
class B:private A{
private:
int i,j;
A Aobj;
public:
B(int a,int b,int c,int d):A(a,b),i(c),j(d) ,Aobj(1,1){ cout<<"B constructor..."<<endl;}
void Add(int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
{
A::Add(x1,y1);
i+=x2; j+=y2;
}
void display(){
A::display();
Aobj.display();
cout<<"("<<i<<","<<j<<")"<<endl;
}
~B(){cout<<"destructor B..."<<endl;}
};
int main()
{
B b(1,2,3,4);
b.display();
b.Add(1,3,5,7);
b.display();
return 0;
}
实验效果

(四)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base1
{
public:
Base1()
{
cout<<"class Base1!"<<endl;
}
};
class Base2
{
public:
Base2()
{
cout<<"class Base2!"<<endl;
}
};
class Level1:public Base2,virtual public Base1
{
public:
Level1()
{
cout<<"class Level1!"<<endl;
}
};
class Level2: public Base2,virtual public Base1
{
public:
Level2()
{
cout<<"class Level2!"<<endl;
}
};
class TopLevel:public Level1,virtual public Level2
{
public:
TopLevel()
{
cout<<"class TopLevel!"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
TopLevel obj;
return 0;
}
实验效果

题目二
某出版系统发行图书和磁带,利用继承设计管理出版物的类。要求如下:建立一个基类Publication存储出版物的标题title、出版物名称name、单价price及出版日期date。用Book类和Tape类分别管理图书和磁带,它们都从Publication类派生。Book类具有保存图书页数的数据成员page,Tape类具有保存播放时间的数据成员playtime。每个类都有构造函数、析构函数,且都有用于从键盘获取数据的成员函数inputData(),用于显示数据的成员函数display()。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
class Publication
{
public:
Publication(){};
~Publication(){};
virtual void inputData() {
string title_0;
string name_0;
int price_0;
int date_0;
cout << "请输入出版物的标题,出版商的名称,出版物的单价和出版物的出版日期(用空格隔开):";
cin >> title >> name >> price >> date;
};//从键盘获取数据的成员函数inputData(),
virtual void display() {
cout << "出版物的标题:" << title << endl;
cout << "出版物的名称:" << name << endl;
cout << "出版物的单价:" << price << endl;
cout << "出版物的出版日期:" << date << endl;
};//用于显示数据的成员函数display()。
protected:
string title;//出版物的标题title
string name;//出版物名称name
int price;//单价price
int date;//出版日期date
};
class Book: public Publication
{
public:
Book() {};
~Book() {};
void inputData() {
cout << "请输入保存的图书页数:";
cin >> pages;
};//从键盘获取数据的成员函数inputData(),
void display() {
cout << "该本书的图书页数是:" << pages << endl;
};//用于显示数据的成员函数display()。
private:
int pages;//保存图书页数
};
class Tape :public Publication
{
public:
Tape() {};
~Tape() {};
void inputData() {
cout << "请输入磁盘的播放时间:";
cin >> playtime;
};//从键盘获取数据的成员函数inputData(),
void display() {
cout << "该磁盘的播放时间是:" << playtime << endl;
};//用于显示数据的成员函数display()。
private:
int playtime;//保存播放时间playtime。
};
int main()
{
Publication P;
P.inputData();
P.display();
Book B;
B.inputData();
B.display();
Tape T;
T.inputData();
T.display();
return 0;
}
实验效果

题目三
(1)定义一个分数类Score。它有3个数据成员:
Chinese //语文课成绩
English //英语课成绩
Mathematics //数学课成绩
2个构造函数:无参的和带参数的
3个成员函数:是否带参数根据需要自定
sum() //计算三门课总成绩
print() //输出三门课成绩和总成绩
modify() //修改三门课成绩
(2)定义一个学生类Student。它有3个数据成员:
Num //学号
Name //姓名
MyScore //成绩
2个构造函数:无参的和带参数的
3个成员函数:是否带参数根据需要自定
sum() //计算某学生三门课总成绩
print() //输出某学生学号、姓名和成绩
modify() //修改某学生学号、姓名和成绩
(3)在主函数中,先定义一个学生类对象数组,再通过for循环给对象数组赋上实际值,最后输出对象数组个元素的值。
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Score//分数类,存语数外成绩
{
public:
int Chinese;
int English;
int Math;
int add;
Score();//构造函数
Score(int a, int b, int c);
void Sum();
void print();
void modify();
};
class Student//学生类
{
public:
int Num;
string name;
Score myScore;//以Score为类定义对象
Student();//构造函数
Student(int d, string e, int a, int b, int c);
void Sum();
void print();
void modify();
};
Score::Score()//Score初始赋值
{
Chinese = 0;
English = 0;
Math = 0;
add = 0;
}
Score::Score(int a, int b, int c)//Score再赋值
{
Chinese = a;
English = b;
Math = c;
Sum();
}
Student::Student()//Student初始赋值
{
name = " ";
Num = 0;
myScore.Chinese = 0;
myScore.English = 0;
myScore.Math = 0;
Sum();
}
Student::Student(int d, string e, int a, int b, int c)//Student再赋值
{
name = e;
Num = d;
myScore.Chinese = a;
myScore.English = b;
myScore.Math = c;
}
void Score::Sum(){
add = Chinese + English + Math;
}
void Student::Sum(){
myScore.add = myScore.Chinese + myScore.English + myScore.Math;
}
void Score::print(){
cout << "语文成绩:" << Chinese << endl;
cout << "英语成绩:" << English << endl;
cout << "数学成绩:" << Math << endl;
cout << "总成绩:" << add << endl;
}
void Student::print(){
cout << "姓名:" << name << endl;
cout << "学号:" << Num << endl;
cout << "语文成绩:" << myScore.Chinese << endl;
cout << "英语成绩:" << myScore.English << endl;
cout << "数学成绩:" << myScore.Math << endl;
cout << "总成绩:" << myScore.add << endl;
}
void Score::modify(){
int a;
int b;
int c;
cout << "请输入学生的语文成绩,英语成绩,数学成绩:" << endl;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
Chinese = a;
English = b;
Math = c;
Sum();
}
void Student::modify(){
int d;string e;
int a;int b;
int c;
cout << "请输入学生的姓名:" << endl;
cin >> e;
cout << "请输入学生的学号:" << endl;
cin >> d;
cout << "请输入学生的语文成绩:" << endl;
cin >> a;
cout << "请输入学生的英语成绩:" << endl;
cin >> b;
cout << "请输入学生的数学成绩:" << endl;
cin >> c;
name = e;Num = d;
myScore.Chinese = a;
myScore.English = b;
myScore.Math = c;
Sum();
}
int main()
{
Student a[10];//定义数组
int i, j;
cout << "请输入学生人数:";//得知循环数
cin >> i;
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)//循环赋值
{
a[j].modify();
}
for (j = 0; j < i; j++)//循环输出
{
a[j].print();
}
return 0;
}
实验效果


题目四
编写一个程序实现小型公司的人员信息管理系统。该公司雇员(employee)包括经理(manager),技术人员(technician)、销售员(salesman)和销售部经理(salesmanager)。要求存储这些人员的姓名、编号、级别、当月薪水,计算月薪并显示全部信息。
程序要对所有人员有提升级别的功能。为简单起见,所有人员的初始级别均为1,然后进行升级,经理升为4级,技术人员和销售部经理升为3级,销售员仍为1级。
月薪计算办法是:经理拿固定月薪8000元,技术人员按每小时100元领取月薪,销售员按该当月销售额4%提成,销售经理既拿固定月工资也领取销售提成,固定月工资为5000元,销售提成为所管辖部门当月销售额的5‰。
#include<string>
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<windows.h>
using namespace std;
class employee{
protected:
string name, id;
int grade; double salary;
public:
employee(){
grade = 1; salary = 0;
}
string GetName(){
return name;
}
string GetId(){
return id;
}
double GetSalary(){
return salary;
}
};
class manager :public employee{
public:
manager(){
cout << "请输入经理的姓名:"; cin >> name;
cout << "请输入经理的编号:"; cin >> id;
grade = 4; salary = 8000;
}
manager(string _name, string _id){
name = _name; id = _id; grade = 4; salary = 8000;
}
void DisInform(){
cout << "经理:" << name << endl;
cout << "编号:" << id << endl;
cout << "薪水:" << salary << endl;
}
};
class technician :public employee{
double worktime;
public:
technician(){
cout << "请输入技术人员的姓名:"; cin >> name;
cout << "请输入技术人员的编号:"; cin >> id;
cout << "请输入工作人员每月的工作时间:"; cin >> worktime;
grade = 3; salary = 100 * worktime;
}
technician(string _name, string _id, double t = 0){
name = _name; id = _id; worktime = t; salary = t * 100; grade = 3;
}
void SetTime(double t) { worktime = t; salary = 100 * t; }
void DisInform(){
cout << "技术人员:" << name << endl;
cout << "编号:" << id << endl;
cout << "薪水:" << salary << endl;
}
};
class salemanager :public employee{
double sale;
public:
vector<int> MSlist;//销售经理管理销售员的名单
int MSNum;
salemanager(){
cout << "请输入销售经理的姓名:"; cin >> name;
cout << "请输入销售经理的编号:"; cin >> id;
grade = 3; salary = 5000; sale = 0; MSNum = 0;
}
salemanager(string _name, string _id){
name = _name; id = _id;
grade = 3; salary = 5000; sale = 0; MSNum = 0;
}
salemanager(const salemanager& x){
name = x.name; grade = 3; id = x.id; salary = x.salary; sale = x.sale; MSNum = x.MSNum;
MSlist.assign(x.MSlist.begin(), x.MSlist.end());
}
void DisInform(){
cout << "销售经理:" << name << endl;
cout << "编号:" << id << endl;
cout << "薪水:" << salary << endl;
}
void SetSale(double t){
sale = t; salary += t * 0.005;
}
void AddSale(double t){
sale += t; salary += 0.005 * t;
}
};
class salesman :public employee{
double sale;
public:
int M;//该销售员受管辖的销售经理
salesman(){
cout << "请输入销售员的姓名:"; cin >> name;
cout << "请输入销售员的编号:"; cin >> id;
cout << "请输入销售员的销售额:"; cin >> sale;
grade = 1; salary = 0.04 * sale;
//cout << "薪水:" << salary << endl;
M = -1;
}
salesman(string _name, string _id, double _sale = 0){
name = _name; id = _id; sale = _sale; grade = 1; salary = 0.04 * sale; M = -1;
}
salesman(const salesman& x){
name = x.name; id = x.id; M = x.M; salary = x.salary; sale = x.sale; grade = 1;
}
void DisInform(){
cout << "销售员:" << name << endl;
cout << "编号:" << id << endl;
cout << "薪水:" << salary << endl;
}
void SetSale(double _sale){
sale = _sale; salary = 0.04 * sale;
}
double GetSale(){
return sale;
}
};
class depart{
depart(){
SNum = 0; MNum = 0; sale = 0;
}
depart(depart&) = delete;
depart& operator=(const depart&) = delete;
static depart* p;
public:
vector<salesman> Slist; //销售部门所有销售员的名单
int SNum;
vector<salemanager> Mlist; //销售部门所有销售经理的名单
int MNum;
double sale;//总的销售额
static depart* GetDepart(){
if (p == nullptr) p = new depart;
return p;
}
static void DelDepart(){
delete p; p = nullptr;
}
void AddSaleForManager(salemanager& x){
cout << "请输入该销售经理管理的销售员ID:[ESC退出输入]" << endl;
//cin.clear();
string _ID;
while (1){
cin >> _ID;
if (_ID == "ESC") break;
bool flag = false;//标记是否存在该销售员
for (int i = 0; i < SNum; i++) {
if (p->Slist[i].GetId() == _ID){
p->Mlist[MNum - 1].MSlist.push_back(i);//将该销售员加入到销售经理的名单中
p->Mlist[MNum - 1].MSNum++;
p->Mlist[MNum - 1].AddSale(p->Slist[i].GetSale());//改变销售经理当月的销售额
p->Slist[i].M = MNum - 1;//记录该销售员对应的销售经理
flag = true; break;//标记找到了并退出查找
}
}
if (!flag){
cout << "对不起,该销售员没有登记,请先到管理部门登记" << endl;
}
//cin.clear();
}
}
void CreatNewManager(){
p->Mlist.push_back(salemanager()); MNum++;
AddSaleForManager(p->Mlist[MNum - 1]); //为该销售经理添加销售员
}
void UpgradeManger(string _name, string _Id){
p->Mlist.push_back(salemanager(_name, _Id)); MNum++;
AddSaleForManager(p->Mlist[MNum - 1]); //为该销售经理添加销售员
}
void CreatNewManager(int x){
while (x--)
{
p->Mlist.push_back(salemanager()); MNum++;
AddSaleForManager(p->Mlist[MNum - 1]); //为该销售经理添加销售员
}
}
void CreatNewSales(){
p->Slist.push_back(salesman()); SNum++;
}
void CreatNewSales(int x){
while (x--)
{
p->Slist.push_back(salesman()); SNum++;
}
}
};
depart* depart::p = nullptr;
class company{
int num = 0;//公司人数
public:
vector<manager> MMList; int MMNum;
vector<technician> TList; int TNum;
int t;
company(){
//system("cls");
cout << "创建公司:" << endl;
cout << "请输入经理人数:"; cin >> MMNum; num += MMNum;
for (int i = 0; i < MMNum; i++){
MMList.push_back(manager());
}
//system("cls");
cout << "创建公司:" << endl;
cout << "请输入技术人员人数:"; cin >> TNum; num += TNum;
for (int i = 0; i < TNum; i++){
TList.push_back(technician());
}
cout << "创建公司:" << endl;
depart* Dp = depart::GetDepart(); //创建销售部门
cout << "请输入销售员人数:"; cin >> t; num += t; Dp->CreatNewSales(t);
//system("cls");
cout << "创建公司:" << endl;
cout << "请输入销售经理的人数:"; cin >> t; num += t; Dp->CreatNewManager(t);
}
void DisplayManager(){
//system("cls");
cout << "公司经理信息:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < MMNum; i++){
MMList[i].DisInform();
}
}
void DisplayTechnician(){
//system("cls");
cout << "公司技术人员信息:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < TNum; i++){
TList[i].DisInform();
}
//system("pause");
}
void DisplaySale(){
//system("cls");
cout << "公司销售员信息:" << endl;
depart* Dp = depart::GetDepart();
for (int i = 0; i < Dp->SNum; i++)
{
Dp->Slist[i].DisInform();
cout << "上司姓名:" << ((Dp->Slist[i].M == -1) ? "无" : Dp->Mlist[Dp->Slist[i].M].GetName()) << endl;
cout << "上司编号:" << ((Dp->Slist[i].M == -1) ? "无" : Dp->Mlist[Dp->Slist[i].M].GetId()) << endl;
}
}
void DisplaySaleManager(){
cout << "公司销售经理信息:" << endl;
depart* Dp = depart::GetDepart();
for (int i = 0; i < Dp->MNum; i++){
Dp->Mlist[i].DisInform();
cout << "管理销售员名单:" << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < Dp->Mlist[i].MSNum; j++){
cout << "销售员编号:" << Dp->Slist[Dp->Mlist[i].MSlist[j]].GetId() << "\t" << "销售员姓名:" << Dp->Slist[Dp->Mlist[i].MSlist[j]].GetName() << endl;
}
}
}
void SalesmanUpgrade(){
cout << "请输入需要升级的销售员ID:[ESC退出输入]" << endl;
cin.clear();
string _ID;
depart* Dp = depart::GetDepart();
while (1){
cin >> _ID;
if (_ID == "ESC") break;
//cout << "ok!!" << endl;
bool flag = false;
salesman* tmp = nullptr;
int index;
for (int i = 0; i < Dp->SNum; i++){
if (Dp->Slist[i].GetId() == _ID){
tmp = new salesman(Dp->Slist[i]);
index = i;
flag = true; break;
}
}
if (!flag){
cout << "不存在该销售员!" << endl;
continue;
}
if (tmp->M != -1){
int num = Dp->Mlist[tmp->M].MSNum;
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++){
if (Dp->Slist[Dp->Mlist[tmp->M].MSlist[i]].GetId() == tmp->GetId())
{
Dp->Mlist[tmp->M].MSlist.erase(Dp->Mlist[tmp->M].MSlist.begin() + i);
Dp->Mlist[tmp->M].MSNum--;
break;
}
}
}
Dp->Slist.erase(Dp->Slist.begin() + index); Dp->SNum--;
//printf("test\n");
//将销售员升级为销售经理
Dp->UpgradeManger(tmp->GetName(), tmp->GetId());
delete tmp;
}
}
~company()
{
depart::DelDepart();
}
};
int main()
{
company A;
A.DisplayManager();
A.DisplayTechnician();
A.DisplaySaleManager();
A.DisplaySale();
A.SalesmanUpgrade();
A.DisplaySaleManager();
A.DisplaySale();
}
实验效果



实验七
题目一
分析下面的程序,写出其运行时的输出结果。上机运行该程序,观察运行结果是否与你的分析相同。如有不同,试分析原因。
(一)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base{
protected:
int n;
public:
Base (int m){ n=m++; }
virtual void g1(){cout<<"Base::g1()..."<<n<<endl; g4();}
virtual void g2(){cout<<"Base::g2()..."<<++n<<endl;g3();}
void g3(){cout<<"Base::g3()..."<<++n<<endl; g4();}
void g4(){cout<<"Base::g4()..."<<++n<<endl;}
};
class Derive:public Base{
int j;
public:
Derive(int n1,int n2):Base(n1){ j=n2; }
void g1(){cout<<"Deri::g1()..."<<++n<<endl;g2();}
void g3(){cout<<"Deri::g2()..."<<++n<<endl;g4();}
};
int main(){
Derive Dobj(1,0);
Base Bobj=Dobj;
Bobj.g1();
cout<<"------------------"<<endl;
Base *bp=&Dobj;
bp->g1();
cout<<"------------------"<<endl;
Base &bobj2=Dobj;
bobj2.g1();
cout<<"------------------"<<endl;
Dobj.g1();
return 0;
}
效果如下

(二)
#include<iostream.h>
class ABC{
int a,b,c;
public:
ABC(int x,int y,int z):a(x),b(y),c(z){}
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,ABC& f);
};
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,ABC& f)
{
out<<"a="<<f.a<<endl<<"b="<<f.b<<endl<<"c="<<f.c<<endl;
return out;
}
int main(){
ABC obj(10,20,30);
cout<<obj;
return 0;
}
这个代码似乎有一点问题
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class ABC {
int a, b, c;
public:
ABC(int x, int y, int z) :a(x), b(y), c(z) {}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, ABC& f);
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, ABC& f)
{
out << "a=" << f.a << endl << "b=" << f.b << endl << "c=" << f.c << endl;
return out;
}
int main() {
ABC obj(10, 20, 30);
cout << obj;
return 0;
}
实验效果

(三)
#include<iostream.h>
class Number{
int n;
public:
Number(int x):n(x){}
Number& operator++(){ ++n; return *this; }
Number& operator++(int){ n++; return *this;}
friend Number &operator--(Number &o);
friend Number &operator--(Number o,int);
void display(){cout<<"This Number is: "<<n<<endl;}
};
Number &operator--(Number &o){--o.n; return o; }
Number &operator--(Number o,int){o.n--; return o; }
int main(){
Number N1(10);
++ ++ ++N1;
N1.display();
N1++;
N1.display();
--N1;
N1.display();
N1-- -- --;
N1.display();
return 0;
}
这个似乎也有一点问题
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Number {
int n;
public:
Number(int x) :n(x) {}
Number& operator++() { ++n; return *this; }
Number& operator++(int) { n++; return *this; }
friend Number& operator--(Number& o);
friend Number& operator--(Number o, int);
void display() { cout << "This Number is: " << n << endl; }
};
Number& operator--(Number& o) { --o.n; return o; }
Number& operator--(Number o, int) { o.n--; return o; }
int main() {
Number N1(10);
++ ++ ++N1;
N1.display();
N1++;
N1.display();
--N1;
N1.display();
N1-- -- --;
N1.display();
return 0;
}
实验效果

题目二
先建立一个点类Point,包含数据成员x,y(坐标点)。以它为基类,派生出圆类Circle,增加数据成员radius(半径),再以Cirlcle类为直接基类,派生出圆柱体类Cylinder,再增加数据成员height(高)。要求:
(1)每个类都有构造函数、用于从键盘获取数据的成员函数set(),用于显示数据的成员函数display()。
(2)用虚函数输出各类对象信息。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
int x;
int y;
Point() {
x = 0;
y = 0;
};
void set() {
cout << "点的位置,输入X和Y:";
cin >> x >> y;
}
virtual void display()
{
cout << "点的位置是:" << x << " " << y << endl;
}
};
class Circle:public Point
{
public:
int radius;
Circle() { radius = 0; };
void set()
{
cout << "半径的大小,输入radius:";
cin >> radius;
}
void display()override
{
cout << "圆的半径是:" << radius << endl;
}
};
class Cylinder:public Circle
{
public:
int height;
Cylinder() {
height = 0;
};
void set()
{
cout << "圆柱的高,输入height:";
cin >> height;
}
void display ()override
{
cout << "圆柱的高:" << height << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Point p;
p.set();
p.display();
Circle c;
c.set();
c.display();
Cylinder r;
r.set();
r.display();
return 0;
}
效果如下

题目三
先建立一个职工类Employee,包含数据成员name(职工姓名),ID(职工编号)。以它为基类,派生出经理类Manager和技术人员类Technician,在经理类中增加数据成员salary(代表经理的月工资),在技术人员类中增加数据成员wage(代表每小时的工资数)和hours(月工作时数)。在定义类时,所有类中必须包含有构造函数、析构函数、修改和获取所有数据成员的函数,以及纯虚函数计算职工的工资,输出职工的信息。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Employee
{
public:
string name;//职工姓名
int ID;//职工编号
virtual void Sum() const = 0; //纯虚函数
Employee(string s,int a)
{
name = s;
ID = a;
}
~Employee(){
cout << "Employee 析构" << endl;
}
void Change(string s, int x)
{
this->name = s;
this->ID = x;
}
void Set(string s,int x)
{
this->name = s;
this->ID = x;
}
};
class Manager:public Employee
{
public:
int salay;//经理的月工资
virtual void Sum() const {
cout << "经理的名字是:" << name << endl;
cout << "经理的ID是:" << ID << endl;
cout << "经理的工资是:" << salay << endl;
}
Manager(string s,int a ,int sa):Employee(s,a)
{
salay = sa;
}
~Manager(){
cout << "Manager 析构" << endl;
}
void Change(int a)
{
this->salay = a;
}
void Set(int a)
{
this->salay = a;
}
};
class Technician:public Employee
{
public:
int wage;//表示每小时的工资数
int hours;//月工作小时数
virtual void Sum() const {
cout << "技术工的名字是:" << name << endl;
cout << "技术工的ID是:" << ID << endl;
cout << "技术工的工资是:" << wage*hours*4 << endl;
}
Technician(string s,int a,int w,int h):Employee(s,a)
{
wage = w;
hours = h;
}
~Technician(){
cout << "Technician 析构" << endl;
}
void Change(int wage, int hours)
{
this->wage = wage;
this->hours = hours;
}
void Set(int wage,int hours)
{
this->wage = wage;
this->hours = hours;
}
};
int main()
{
Manager m("Jack", 001, 7000);
m.Set(1200);
m.Change(1000);
m.Sum();
Technician T("Tom", 002, 30, 178);
T.Set(40,180);
T.Change(50, 120);
T.Sum();
return 0;
}
实验效果

题目四
设计并实现一个日期类Date,要求:
(1)可以建立具有指定日期(年、月、日)的Date对象,默认日期是2012.1.1。
(2)可以从输出流输出一个格式为“年-月-日”的日期,其中年是四位数据,月、日可以是一位也可以是两位数据。
(3)可以动态地设置年、月、日。
(4)可以用运算符= =、!=、<和>对两个日期进行比较。
(5)可以用运算符++、–、+=、-=等完成天数的加减一天或若干天的操作
(6)Date类必须能够正确表达日期,不会出现类似于13月,32日一类的情况。Date类还必须处理闰年的问题,闰年包括:所有能被400整除的年份,以及能被4整除同时又不能被100整除的年份。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
int year;
int month;
int day;
Date() {
year = 2012;
month = 1;
day = 1;
};
Date(int x, int y, int z)
{
if (check(x, y, z))
{
this->year = x;
this->month = y;
this->day = z;
}
}
bool check(int y,int m,int d)
{
int num1[12] = { 31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
int num2[12] = { 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (m > 12 || m < 0)
{
//cout << "格式不正确" << endl;
return false;
}
else if (m >= 1 && m <= 12)//月份没问题
{
if (y % 400 == 0 || (y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0))//闰年
{
year = y;
month = m;
if (d <= num2[m - 1] && d >= 1)
{
day = d;
}
else {
//cout << "格式不正确" << endl;
return false;
}
}
else
{
year = y;
if (d <= num1[m - 1] && d >= 1)
{
day = d;
}
else
{
//cout << "格式错误" << endl;
return false;
}
}
}
}
void setdate(int a,int b,int c)
{
check(a, b, c);
}
void display()
{
cout << year <<"-"<< month <<"-" << day << endl;
}
bool operator == (Date& c2)
{
if (year == c2.year && month == c2.month && day == c2.day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
};
bool operator!=(Date& c2)
{
if (year == c2.year && month == c2.month && day == c2.day)
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
};
bool operator<(Date& c2)
{
check(c2.year, c2.month, c2.day);
if (year > c2.year)
{
return false;
}
else if(year < c2.year)
{
return true;
}
else if (year == c2.year){
if (month > c2.month){
return false;
}
else if (month < c2.month){
return true;
}
else if (month == c2.month){
if (day >= c2.day){
return false;
}
else if (day < c2.day){
return true;
}
}
}
};
bool operator >(Date& c2)
{
check(c2.year, c2.month, c2.day);
if (year < c2.year){
return false;
}
else if (year > c2.year){
return true;
}
else if (year == c2.year){
if (month < c2.month){
return false;
}
else if (month > c2.month){
return true;
}
else if (month == c2.month){
if (day <= c2.day){
return false;
}
else if (day > c2.day){
return true;
}
}
}
};
Date operator+=(int x)
{
Date d(year, month, day);
day = day + x;
int num1[12] = { 31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
int num2[12] = { 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0))
{
while (day > num2[month - 1])
{
day = day - num2[month - 1];
month++;
if (month > 12)
{
year++;
month = 1;
}
}
}
else
{
while (day > num1[month - 1])
{
day = day - num1[month - 1];
month++;
if (month > 12)
{
year++;
month = 1;
}
}
}
return d;
};
Date operator -=(int x){
Date d(year, month, day);
day = day - x;
int num1[12] = { 31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
int num2[12] = { 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)){
while (day <= 0){
month--;
if (month <= 0)
{
month = 12;
day = day + num2[month - 1];
year--;
}
else
{
day = day + num2[month - 1];
}
}
}
else
{
while (day <= 0)
{
month--;
if (month <= 0)
{
month = 12;
day = day + num1[month - 1];
year--;
}
else
{
day = day + num1[month - 1];
}
}
}
return d;
};
Date operator -- (){
Date d(year,month,day);
day = day - 1;
int num1[12] = { 31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
int num2[12] = { 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)){
while (day <= 0){
month--;
if (month <= 0)
{
month = 12;
day = day + num2[month-1];
year--;
}
else
{
day = day + num2[month - 1];
}
}
}
else
{
while(day <= 0)
{
month--;
if (month <= 0)
{
month = 12;
day = day + num1[month - 1];
year--;
}
else
{
day = day + num1[month - 1];
}
}
}
return d;
};
Date operator ++()
{
Date d(year,month,day);
day = day + 1;
int num1[12] = { 31,29,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
int num2[12] = { 31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (year % 400 == 0 || (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0))
{
while (day > num2[month - 1])
{
day = day - num2[month - 1];
month++;
if (month > 12)
{
year++;
month = 1;
}
}
}
else
{
while (day > num1[month - 1])
{
day = day - num1[month - 1];
month++;
if (month > 12)
{
year++;
month = 1;
}
}
}
return d;
};
};
int main()
{
Date d(2022, 11, 30);
d.display();
++d;
d.display();
--d;
d.display();
d += (14);
d.display();
d -= (20);
d.display();
Date d2(2011,12,13);
bool x = d > d2;
cout << x << endl;
bool y = d == d2;
cout << y << endl;
bool z = d != d2;
cout << z << endl;
bool m = d < d2;
cout << m << endl;
return 0;
}
实验效果

实验八
题目一
阅读下面的程序,写出程序运行的结果。
(一)
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
fstream out,in;
out.open("a.dat",ios::out);
out<<"on fact\n";
out<<"operating file \n";
out<<"is the same as inputing/outputing data on screen...\n";
out.close();
char buffer[80];
in.open("a.dat",ios::in);
while(!in.eof())
{
in.getline(buffer,80);
cout<<buffer<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
实验效果

(二)
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
class Worker{
private:
int number ,age;
char name[20];
double sal;
public:
Worker(){}
Worker(int num,char* Name,int Age, double Salary):number(num),age(Age),sal(Salary)
{strcpy(name,Name); }
void display() {cout<<number<<"\t"<<name<<"\t"<<age<<"\t"<<sal<<endl; }
};
int main(){
ofstream out("Worker.dat",ios::out|ios::binary);
Worker man[]={Worker(1,"张三",23,2320),Worker(2,"李四",32,2321),
Worker(3,"王五",34,2322),Worker(4,"刘六",27,2324),
Worker(5,"晓红",23,2325),Worker(6,"黄明",50,2326)};
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
out.write((char*)&man[i],sizeof(man[i]));
out.close();
Worker s1;
ifstream in("Employee.dat",ios::in|ios::binary);
in.seekg(2*(sizeof(s1)),ios::beg);
in.read((char*)&s1,sizeof(s1));
s1.display();
in.seekg(0,ios::beg);
in.read((char*)&s1,sizeof(s1));
s1.display();
in.close();
return 0;
}
有点问题
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
class Worker {
private:
int number, age;
//char name[20];
string name;
double sal;
public:
Worker() {}
Worker(int num, string Name, int Age, double Salary) :number(num), age(Age), sal(Salary)
{
name = Name;
//strcpy(name, Name);
}
void display() { cout << number << "\t" << name << "\t" << age << "\t" << sal << endl; }
};
int main() {
ofstream out("Worker.dat", ios::out | ios::binary);
Worker man[] = { Worker(1,"张三",23,2320),Worker(2,"李四",32,2321),
Worker(3,"王五",34,2322),Worker(4,"刘六",27,2324),
Worker(5,"晓红",23,2325),Worker(6,"黄明",50,2326) };
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
out.write((char*)&man[i], sizeof(man[i]));
out.close();
Worker s1;
ifstream in("Employee.dat", ios::in | ios::binary);
in.seekg(2 * (sizeof(s1)), ios::beg);
in.read((char*)&s1, sizeof(s1));
s1.display();
in.seekg(0, ios::beg);
in.read((char*)&s1, sizeof(s1));
s1.display();
in.close();
return 0;
}
实验效果

题目二
已知数据文件IN.DAT中存有20个整数,每个整数间用空格分隔。有一类Array的结构如下:
class Array{
int A[20];
public:
Array(){
for(int i=0;i<20;i++) A[i]=0;
}
int getNumberA(Array &a,int k){return a.A[k];}
void getdata();//读数据函数
void max_min(int &,int &);//排序函数
void putdata(int &,int &);//写结果数据函数
};
其中:
成员函数getdata()的功能为:从数据文件IN.DAT中把20个数据读出来存入数据成员A[]中。
成员函数max_min(int &,int &)的功能为:求数据成员A[]中20个整数的最大值和最小值。
成员函数putdata(int &,int &)的功能为:把求得的数据成员A[]中20个整数的最大值和最小值输出到数据文件OUT.DAT。
要求:在类外写出上述三个成员函数的实现代码,并在main函数中对该类进行测试。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
class Array {
int A[20];
int max, min;
public:
Array() {
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) A[i] = 0;
}
void setNumber()
{
int a[20];
ofstream outfile("IN.DAT",ios::out);//定义文件流对象,打开磁盘文件″f1.dat″
if (!outfile) //如果打开失败,outfile返回0值
{
cerr << "open error!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
cout << "enter 10 integer numbers :" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
outfile << a[i] << " ";
}
outfile.close();
}
int getNumberA(Array& a, int k) { return a.A[k]; }
void getdata(){
ifstream infile("IN.DAT", ios::in | ios::binary);
//定义输入文件流对象,以输入方式打开磁盘文件f1.dat
if (!infile){
cerr << "open error!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
infile >> A[i]; //从磁盘文件读入10个整数,顺序存放在a数组中
} //在显示器上顺序显示10个数
};//读数据函数
void max_min() {
min = A[0];
max = A[0];
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++){
if (min > A[i]){
min = A[i];
}
if (max < A[i]){
max = A[i];
}
}
cout << "最大值为:" << max << endl;
cout << "最小值为:" << min << endl;
};//排序函数
void putdata(){
int a[2];
ofstream outfile("OUT.DAT", ios::out);//定义文件流对象,打开磁盘文件″f1.dat″
if (!outfile) //如果打开失败,outfile返回0值
{
cerr << "open error!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
outfile << max << " ";
outfile << min << " ";
}
outfile.close();
};//写结果数据函数
};
int main()
{
Array a;
a.setNumber();
a.getdata();
a.max_min();
a.putdata();
return 0;
}
实验效果

题目三
3、假设有学生类Student,包括姓名、学校、专业、班级、电话号码、通信地址、邮政编码等数据成员。编程完成Student类的设计,从键盘输入10个同学的通信录信息,并将这10个同学的信息写入磁盘文件address.dat中。然后从address.dat文件中读取各同学信息并显示在屏幕上。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
string name;
string school;
string major;
int banji;
int number;
int dizhi;
int bianma;
void putdata()
{
ofstream outfile("address.dat", ios::out);//定义文件流对象,打开磁盘文件″f1.dat″
if (!outfile) //如果打开失败,outfile返回0值
{
cerr << "open error!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
cout << "输入姓名、学校、专业、班级、电话号码、通信地址、邮政编码" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
cout << "输入姓名:" ;
cin >> name;
outfile << name << " ";
cout << "输入学校名:" ;
cin >> school;
outfile << school << " ";
cout << "输入专业名:" ;
cin >> major;
outfile << major << " ";
cout << "输入班级名:" ;
cin >> banji;
outfile << banji << " ";
cout << "输入电话号码:" ;
cin >> number;
outfile << number << " ";
cout << "输入通信地址:" ;
cin >> dizhi;
outfile << dizhi << " ";
cout << "输入邮政编码:";
cin >> bianma;
outfile << bianma << " ";
}
outfile.close();
}
void getdata()
{
ifstream infile("address.dat", ios::in | ios::binary);
//定义输入文件流对象,以输入方式打开磁盘文件f1.dat
if (!infile) {
cerr << "open error!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
infile >> name;
cout << "姓名是:" <<name<< endl;
infile >> school;
cout << "学校是:" << school << endl;
infile >> major;
cout << "专业是:" << major << endl;
infile >> banji;
cout << "班级是:" << banji << endl;
infile >> number;
cout << "电话号码是:" << number << endl;
infile >> dizhi;
cout << "通信地址是:" << dizhi << endl;
infile >> bianma;
cout << "邮政编码是:" << bianma << endl;
}
}
};
int main()
{
Student s;
s.putdata();
s.getdata();
return 0;
}
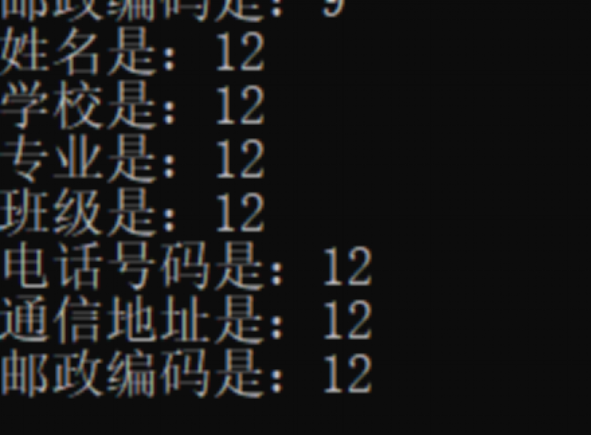
实验效果




![[附源码]计算机毕业设计ssm新能源电动汽车充电桩服务APP](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/90c5d8fcd0ec4ebfa2f979697cc2fafd.png)




![[附源码]计算机毕业设计现代诗歌交流平台Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c5a29dcc2d3c42659883d1690ac1d28f.png)