文章目录
- 环境准备
- 程序编写
环境准备
本机:MacBook Pro 系统:MacOS 13.4
-
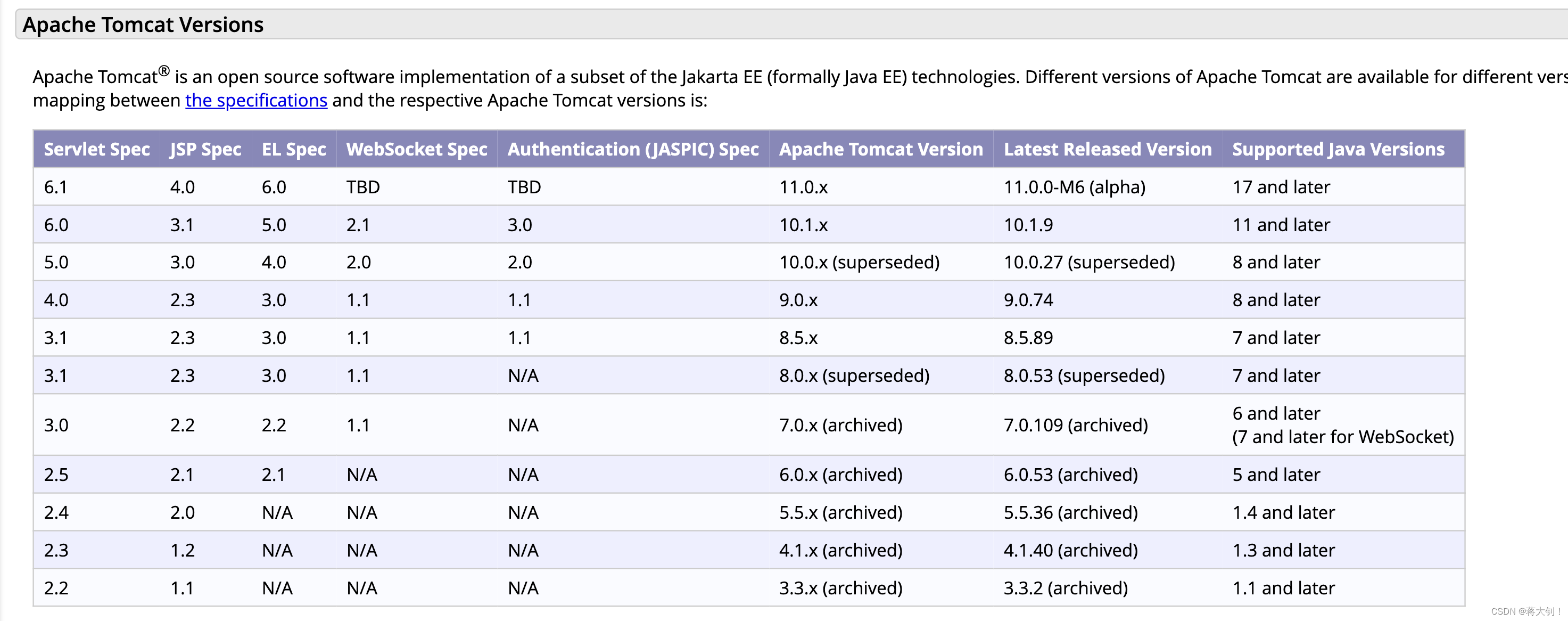
Tomcat 下载:Apache Tomcat® - Welcome!
这里我下载的是9.0.75版本
启动Tomcat容器碰到Bug:Tomcat started.但是就是没法访问到相关页面,同时jps也没有相关的进程,说明其实没启动起来。同时通过chown改变权限也没法解决问题。
Solution:
查看相关的版本对应记录,以及README的Release notes,发现apache-tomcat-10.1.9需要jdk11及以上,我本地是jdk8,重新下载tar.gz 9.0.75。
重新解压并且startup,可以访问http://localhost:8080了
-
记得需要配置本地的JAVA_HOME路径,我采用命令
vim ~/.bash_profileexport JAVA_HOME="/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk1.8.0_361.jdk/Contents/Home"
程序编写
- idea maven生成javaweb模版
-
pom中导入依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.jxz</groupId> <artifactId>MyJavaWeb</artifactId> <packaging>war</packaging> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>MyJavaWeb Maven Webapp</name> <url>http://maven.apache.org</url> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>servlet-api</artifactId> <version>2.5</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId> <version>2.3.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>3.8.1</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>MyJavaWeb</finalName> </build> </project> -
main目录下新建java包,并创建com/jxz/servlet目录,在其中放入最简单的HelloServlet,其继承自HttpServlet
package com.jxz.servlet; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; /** * @Author jiangxuzhao * @Description * @Date 2023/6/3 */ public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet { @Override protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { PrintWriter pw = resp.getWriter(); // 获取输出流 pw.print("hello jxz"); // 打印 } @Override protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { super.doGet(req, resp); } }其中的原理分析:
我们只实现了Get和Post方法,因为这是最普遍的两个Http请求投,我们也可以看到,其实doPost方法也只是复用了一下doGet方法,因为处理是一样的。那么为什么这样子就可以处理http请求了呢?HelloServlet -> public abstract class HttpServlet -> public abstract class GenericServlet -> implements Servlet
/** * Called by the servlet container to allow the servlet to respond to * a request. * * <p>This method is only called after the servlet's <code>init()</code> * method has completed successfully. * * <p> The status code of the response always should be set for a servlet * that throws or sends an error. * * * <p>Servlets typically run inside multithreaded servlet containers * that can handle multiple requests concurrently. Developers must * be aware to synchronize access to any shared resources such as files, * network connections, and as well as the servlet's class and instance * variables. * More information on multithreaded programming in Java is available in * <a href="http://java.sun.com/Series/Tutorial/java/threads/multithreaded.html"> * the Java tutorial on multi-threaded programming</a>. * * * @param req the <code>ServletRequest</code> object that contains * the client's request * * @param res the <code>ServletResponse</code> object that contains * the servlet's response * * @exception ServletException if an exception occurs that interferes * with the servlet's normal operation * * @exception IOException if an input or output exception occurs * */ public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException;从interface Servlet接口中的定义可以看出:service允许web容器处理请求request,而GenericServlet里面并没有对service()方法进行实现,HttpServlet对service()方法进行了重写,同时这里应用了模板模式,在service中定义了各种http请求方法头method的处理方式,在我们的子类HelloServlet中,让我们重写的doGet或者doPost等方法,子类被调用的时候也就是调用被重写的方法。
/** * * Receives standard HTTP requests from the public * <code>service</code> method and dispatches * them to the <code>do</code><i>XXX</i> methods defined in * this class. This method is an HTTP-specific version of the * {@link javax.servlet.Servlet#service} method. There's no * need to override this method. * * * * @param req the {@link HttpServletRequest} object that * contains the request the client made of * the servlet * * * @param resp the {@link HttpServletResponse} object that * contains the response the servlet returns * to the client * * * @exception IOException if an input or output error occurs * while the servlet is handling the * HTTP request * * @exception ServletException if the HTTP request * cannot be handled * * @see javax.servlet.Servlet#service * */ protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { String method = req.getMethod(); if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) { long lastModified = getLastModified(req); if (lastModified == -1) { // servlet doesn't support if-modified-since, no reason // to go through further expensive logic doGet(req, resp); } else { long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE); if (ifModifiedSince < (lastModified / 1000 * 1000)) { // If the servlet mod time is later, call doGet() // Round down to the nearest second for a proper compare // A ifModifiedSince of -1 will always be less maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); doGet(req, resp); } else { resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED); } } } else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) { long lastModified = getLastModified(req); maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); doHead(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) { doPost(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) { doPut(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) { doDelete(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) { doOptions(req,resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) { doTrace(req,resp); } else { // // Note that this means NO servlet supports whatever // method was requested, anywhere on this server. // String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented"); Object[] errArgs = new Object[1]; errArgs[0] = method; errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg); } } -
Web.xml中配置servlet,完成路径映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0" metadata-complete="true"> <!-- 注册servlet名字和类--> <servlet> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.jxz.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <!--配置Servlet的映射路径和对应的servlet名字--> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>hello</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/hellojxz</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app> -
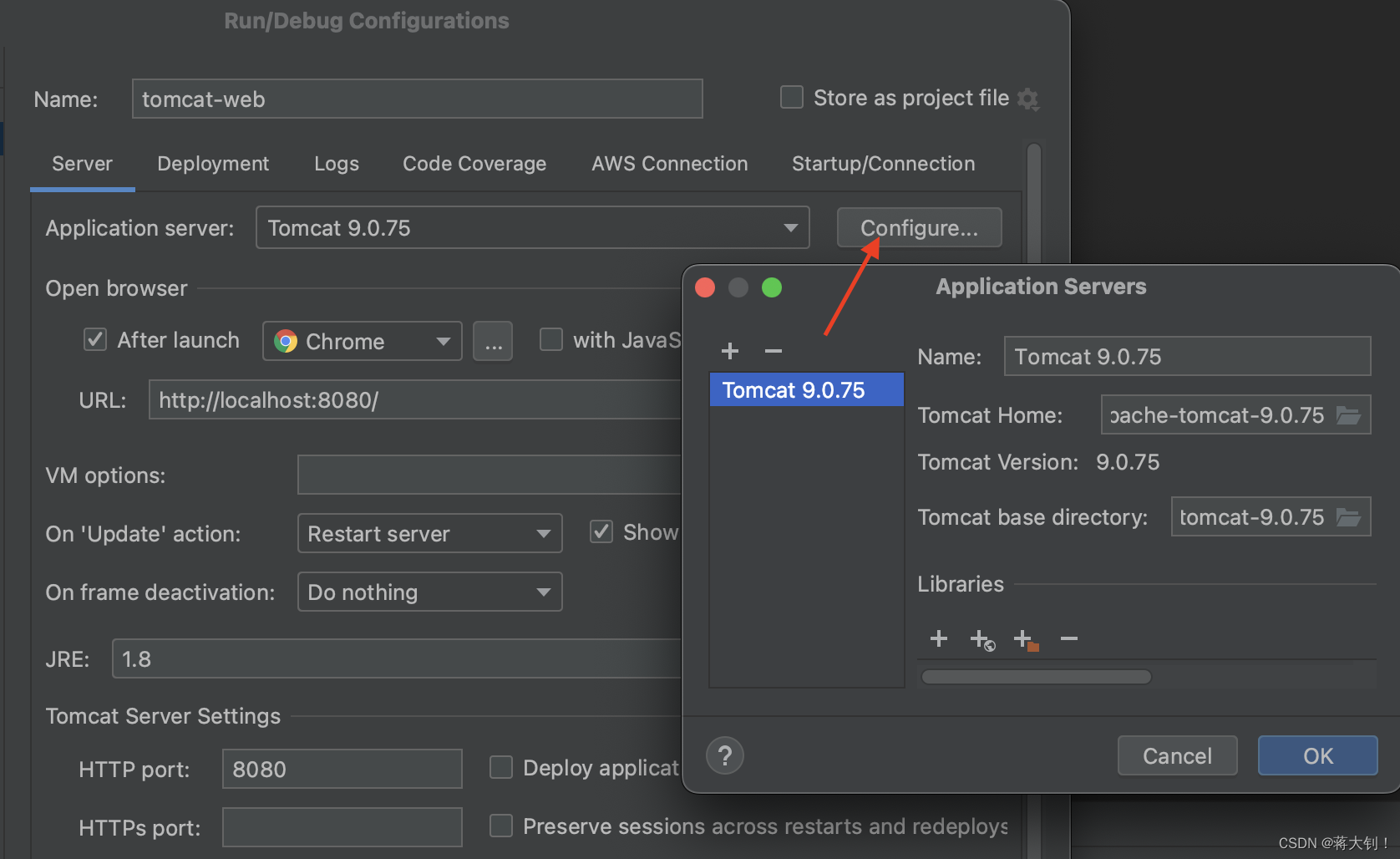
Run Configuration中配置web war包到tomcat服务器中
其中需要配置本地的web服务器:
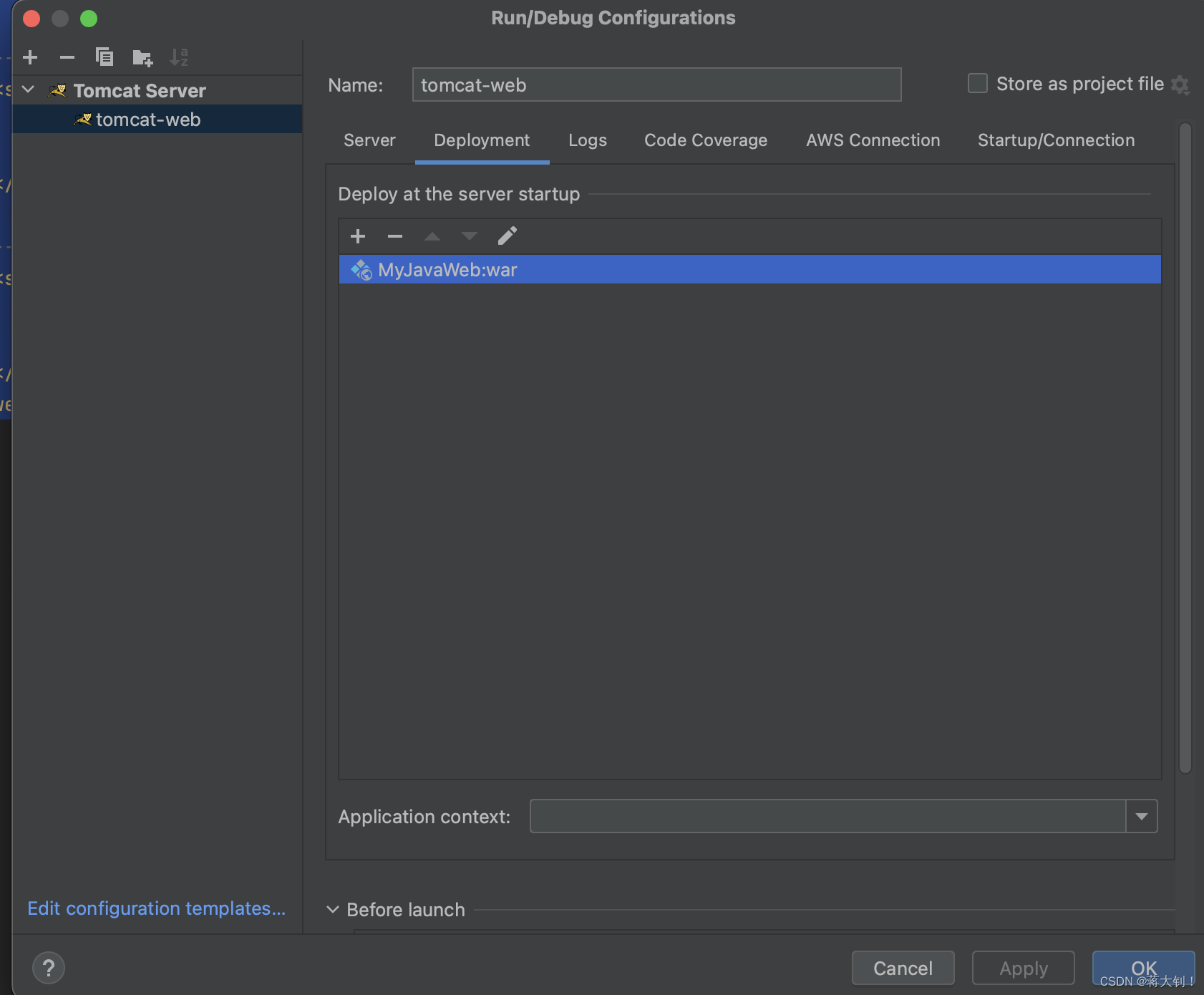
同时指定生成的Deployment war包
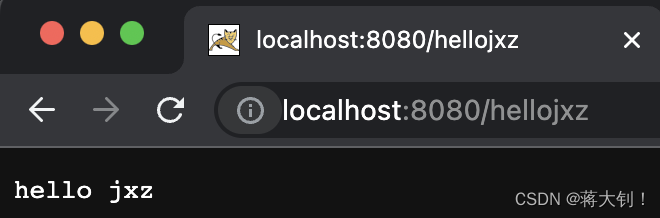
- 测试访问相关路径 http://localhost:8080/hellojxz
除此以外,一个servlet可以指定多个路径映射到相同的servlet,同时可以实现默认的请求路径映射,
<!-- 多个路径映射到相同的servlet-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hellojxz2</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- 默认的映射,直接访问localhost:8080映射到这里-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>