目录
- 1.使用示例
- 2.new ArrayList<>() 解析
- 2.1 空列表
- 2.2 默认大小的共享数组实例
- 2.3 构造方法
- 3.new ArrayList<>(initialCapacity) 解析
- 3.1 指定大小的共享数组实例
- 3.2 构造方法
- 4.add() 解析
- 4.1 容量大小
- 4.2 add() 解析
- 4.3 ensureCapacityInternal() 解析
- 1)默认初始容量
- 2)ensureCapacityInternal() 解析
- 3)ensureExplicitCapacity() 解析
- 3.1)结构修改次数
- 3.2)ensureExplicitCapacity() 解析
- 3.3)grow() 解析
- 3.3.1)最大容量大小
- 3.3.2)grow() 解析
- 3.3.3)hugeCapacity() 解析
- 5.get() 解析
- 5.1 rangeCheck() 解析
- 5.1.1 outOfBoundsMsg() 解析
- 5.2 elementData() 解析
- 6.remove() 解析
- 7.size() 解析
1.使用示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
System.out.println(list.get(0));
System.out.println(list.remove(1));
System.out.println(list.size());
}
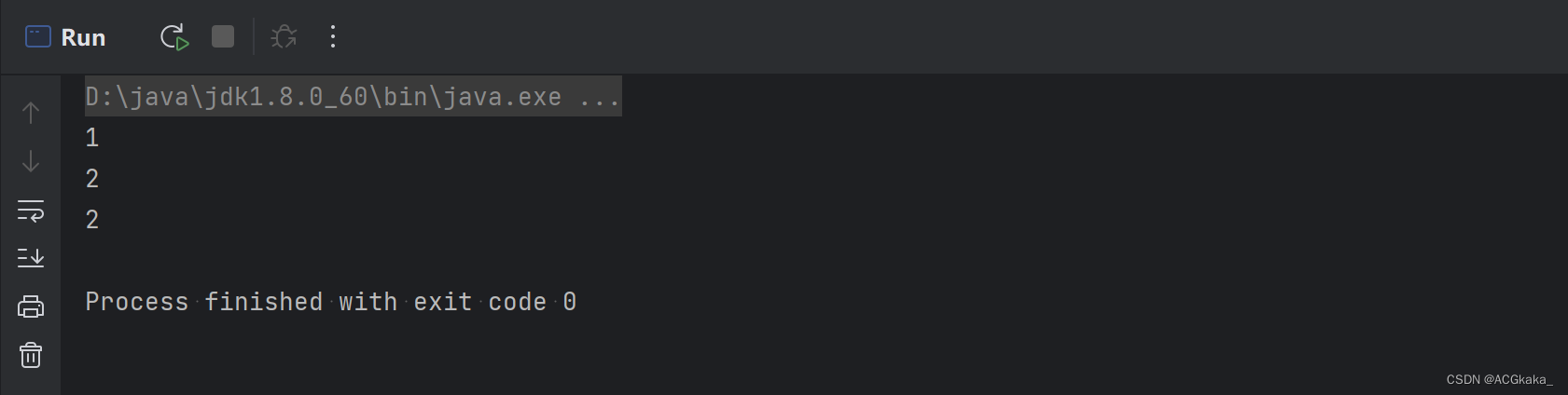
执行结果:
2.new ArrayList<>() 解析
2.1 空列表
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
* ---------------------------
* 存储ArrayList元素的数组缓冲区。ArrayList的容量就是这个数组缓冲区的长度。任何
* 带有elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA的空数组列表将在添加
* 第一个元素时扩展为DEFAULT_CAPACITY。
*/
// 非私有以简化嵌套类访问
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
2.2 默认大小的共享数组实例
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
* ---------------------------
* 用于默认大小的空实例的共享空数组实例。我们将其与EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA区分开来,以便
* 知道添加第一个元素时要膨胀多少。
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
2.3 构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
* ---------------------------
* 构造一个初始容量为10的空列表。
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
3.new ArrayList<>(initialCapacity) 解析
3.1 指定大小的共享数组实例
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
* ---------------------------
* 用于空实例的共享空数组实例。
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
3.2 构造方法
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity.
* ---------------------------
* 构造具有指定初始容量的空列表
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
* ---------------------------
* @param initialCapacity 列表的初始容量
* @throws IllegalArgumentException 如果指定的初始容量是负的
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
4.add() 解析
4.1 容量大小
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
* ---------------------------
* 数组列表的大小(包含的元素数量)。
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
4.2 add() 解析
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
* ---------------------------
* 将指定的元素追加到此列表的末尾。
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
* ---------------------------
* @param e 要添加到这个列表中的元素
* @return true (由Collection.add指定)
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
// 增加 modCount
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
4.3 ensureCapacityInternal() 解析
1)默认初始容量
/**
* Default initial capacity.
* ---------------------------
* 默认初始容量
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
2)ensureCapacityInternal() 解析
// 确保内部容量有效
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
// 判断 elementData 是否等于 默认大小的共享数组实例
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
// 默认最小容量为10,超过10则使用实际容量
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
// 确保最小容量可用
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
3)ensureExplicitCapacity() 解析
3.1)结构修改次数
/**
* The number of times this list has been <i>structurally modified</i>.
* Structural modifications are those that change the size of the
* list, or otherwise perturb it in such a fashion that iterations in
* progress may yield incorrect results.
* ---------------------------
* 这个列表在结构上被修改的次数。结构修改是指改变列表的大小,或者以某种方式扰乱
* 列表,从而使进行中的迭代可能产生不正确的结果。
*
* <p>This field is used by the iterator and list iterator implementation
* returned by the {@code iterator} and {@code listIterator} methods.
* If the value of this field changes unexpectedly, the iterator (or list
* iterator) will throw a {@code ConcurrentModificationException} in
* response to the {@code next}, {@code remove}, {@code previous},
* {@code set} or {@code add} operations. This provides
* <i>fail-fast</i> behavior, rather than non-deterministic behavior in
* the face of concurrent modification during iteration.
* ---------------------------
* 该字段由iterator和listtiterator方法返回的迭代器和列表迭代器实现使用。如果该
* 字段的值发生意外变化,迭代器(或列表迭代器)将抛出ConcurrentModificationException,
* 以响应next、remove、previous、set或add操作。这提供了快速故障行为,而不是在
* 迭代期间面对并发修改时的不确定性行为。
*
* <p><b>Use of this field by subclasses is optional.</b> If a subclass
* wishes to provide fail-fast iterators (and list iterators), then it
* merely has to increment this field in its {@code add(int, E)} and
* {@code remove(int)} methods (and any other methods that it overrides
* that result in structural modifications to the list). A single call to
* {@code add(int, E)} or {@code remove(int)} must add no more than
* one to this field, or the iterators (and list iterators) will throw
* bogus {@code ConcurrentModificationExceptions}. If an implementation
* does not wish to provide fail-fast iterators, this field may be
* ignored.
* ---------------------------
* 子类使用此字段是可选的。如果子类希望提供快速失败迭代器(和列表迭代器),那么它只
* 需要在其add(int, E)和remove(int)方法(以及它覆盖的导致列表结构修改的任何其他
* 方法)中增加该字段。单个调用add(int, E)或remove(int)必须向该字段添加不超过一
* 个,否则迭代器(和列表迭代器)将抛出虚假的concurrentmodificationexception。如
* 果实现不希望提供快速失败迭代器,则可以忽略此字段
*/
protected transient int modCount = 0;
3.2)ensureExplicitCapacity() 解析
// 确保容量明确
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 结构修改次数+1
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
// ---------------------------
// 考虑到溢出的代码
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
3.3)grow() 解析
3.3.1)最大容量大小
/**
* The maximum size of array to allocate.
* Some VMs reserve some header words in an array.
* Attempts to allocate larger arrays may result in
* OutOfMemoryError: Requested array size exceeds VM limit
* ---------------------------
* 要分配的数组的最大大小。有些虚拟机在数组中保留一些头字。尝试分配更大的数组可能会
* 导致OutOfMemoryError:请求的数组大小超过虚拟机限制(最大值为:2147483639)
*/
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
3.3.2)grow() 解析
/**
* Increases the capacity to ensure that it can hold at least the
* number of elements specified by the minimum capacity argument.
* ---------------------------
* 增加容量以确保它至少可以容纳最小容量参数指定的元素数量。
*
* @param minCapacity the desired minimum capacity
* ---------------------------
* @param minCapacity 所需的最小容量
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
// ---------------------------
// 考虑到溢出的代码
// 获取实际容量
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 新容量为实际容量的3/2
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
// 如果最小容量大于实际容量的3/2,则采用最小容量作为新容量,否则采用实际容量的3/2作为新容量
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
// 判断新容量是否超出最大容量大小
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
// 超出最大容量大小,则根据最小容量进行扩容
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
// ---------------------------
// 最小容量大小通常接近于实际大小,所以这是一种较优的方法。
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
3.3.3)hugeCapacity() 解析
// 根据最小容量进行扩容
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 最小容量小于0,则溢出
// Integer.MAX_VALUE + 1 = -2147483648
// (由于minCapacity=size+1,当minCapacity超过Integer.MAX_VALUE,就会变为负数,即溢出)
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
// 判断最小容量是否大于最大容量
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
// 大于则取int的最大值
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
// 小于则取最大容量
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
5.get() 解析
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
* ---------------------------
* 返回列表中指定位置的元素。
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* ---------------------------
* @param index 要返回的元素的索引
* @return 在此列表中指定位置的元素
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException 如果索引超出范围(index < 0 || index >= size())
*/
public E get(int index) {
// 检查范围
rangeCheck(index);
// 从数组中获取元素
return elementData(index);
}
5.1 rangeCheck() 解析
/**
* Checks if the given index is in range. If not, throws an appropriate
* runtime exception. This method does *not* check if the index is
* negative: It is always used immediately prior to an array access,
* which throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if index is negative.
* ---------------------------
* 检查给定的索引是否在范围内。如果不是,则抛出适当的运行时异常。该方法不检查索引
* 是否为负:它总是在数组访问之前立即使用,如果索引为负,则抛出
* ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException.
*/
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
5.1.1 outOfBoundsMsg() 解析
/**
* Constructs an IndexOutOfBoundsException detail message.
* Of the many possible refactorings of the error handling code,
* this "outlining" performs best with both server and client VMs.
* ---------------------------
* 构造 IndexOutOfBoundsException 详细信息。在许多可能的错误处理代码重构中,
* 这种“概述”在服务器和客户端vm中都表现最好。
*/
private String outOfBoundsMsg(int index) {
return "Index: "+index+", Size: "+size;
}
5.2 elementData() 解析
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E elementData(int index) {
// 根据索引,从数组中获取对象
return (E) elementData[index];
}
6.remove() 解析
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts any subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their
* indices).
* ---------------------------
* 移除此列表中指定位置的元素。将所有后续元素向左移动(从它们的索引中减去1)。
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element that was removed from the list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
* ---------------------------
* @param index 要删除元素的索引
* @return 从列表中删除的元素
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException 如果索引超出范围(index < 0 || index >= size())
*/
public E remove(int index) {
// 检查范围,参考 5.1
rangeCheck(index);
// 结构修改次数+1,参考 4.3 的 3.1)
modCount++;
// 从数组中获取元素,参考 5.2
E oldValue = elementData(index);
// 需要移动的元素数
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
// 将数组向前移动1位
// System.arraycopy(原数组, 原数组的起始位置, 目标数组, 目标数组的起始位置, 要copy的数组长度)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
// 清除数组末尾指向,方便GC进行垃圾回收
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
// 返回被删除的元素值
return oldValue;
}
7.size() 解析
/**
* Returns the number of elements in this list.
* ---------------------------
* 返回当前list中元素的个数。
*
* @return the number of elements in this list
* ---------------------------
* @return 当前list中元素的个数
*/
public int size() {
return size;
}
整理完毕,完结撒花~ 🌻