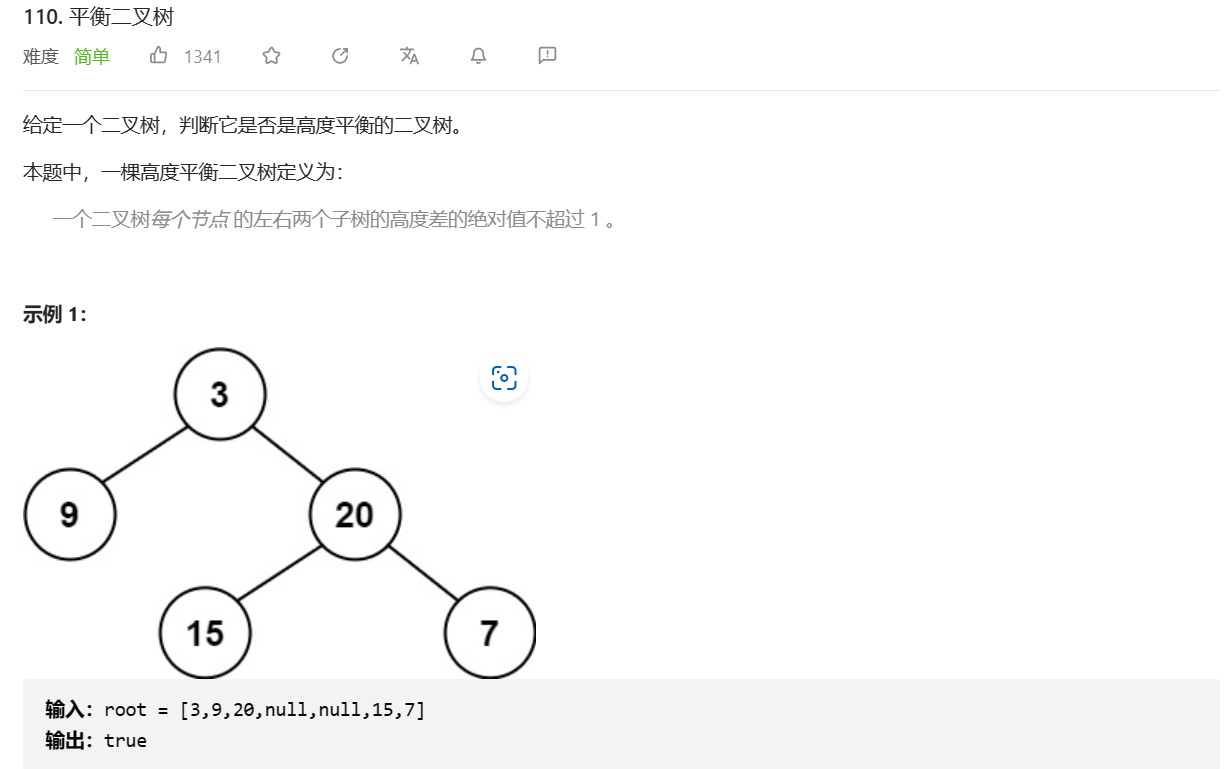
1. 递归法求解
递归三部曲:
- 确定递归函数的参数及其返回值
- 确定终止条件
- 确定单层递归逻辑
深度:从上往下
高度:从下往上
1.1 根据深度求解
- 构建求二叉树节点深度的函数(后序遍历)
- 递归求该树是否是平衡二叉树(前序遍历)
- 递归函数的参数只需要当前节点
TreeNode* cur,返回值为bool - 终止条件:当前节点为空,则直接返回
true - 单层递归逻辑:(1)判断当前节点(2)判断左子树(3)判断右子树
int lDepth = getDepth(root->left); int rDepth = getDepth(root->right); if(abs(lDepth - rDepth) > 1){ //判断中间节点是否满足条件 return false; } bool lflag = isBalanced(root->left); //判断左子树是否满足条件 bool rflag = isBalanced(root->right); //判断右子树是否满足条件 return lflag && rflag; - 递归函数的参数只需要当前节点
int getDepth(TreeNode* node){
if(node == NULL)
return 0;
return 1 + max(getDepth(node->left), getDepth(node->right));
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL)
return true;
int lDepth = getDepth(root->left);
int rDepth = getDepth(root->right);
if(abs(lDepth - rDepth) > 1){
return false;
}
return isBalanced(root->left) && isBalanced(root->right);
}
1.2 根据高度求解(后序遍历)
- 递归求高度
- 递归函数的参数只需要当前节点
TreeNode* node,返回值为以该节点为根节点树的高度
//-1表示已经不是平衡二叉树了,否则返回值为以该节点为根节点树的高度 int getHeight(TreeNode* node)- 终止条件:当前节点为空,直接返回0
- 单层递归逻辑
int lHeight = getHeight(node->left); //左 if(lHeight == -1) return -1; int rHeight = getHeight(node->right); //右 if(rHeight == -1) return -1; int result; if(abs(lHeight - rHeight) > 1) //中 result = -1; else result = 1 + max(lHeight, rHeight); //以当前节点为根节点的树的最大高度 return result; - 递归函数的参数只需要当前节点
// 返回以该节点为根节点的二叉树的高度,如果不是平衡二叉树了则返回-1
int getHeight(TreeNode* node) {
if (node == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = getHeight(node->left);
if (leftHeight == -1) return -1;
int rightHeight = getHeight(node->right);
if (rightHeight == -1) return -1;
return abs(leftHeight - rightHeight) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + max(leftHeight, rightHeight);
}
bool isBalanced(TreeNode* root) {
return getHeight(root) == -1 ? false : true;
}





![[图表]pyecharts模块-柱状图2](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c8b3348eeb34417cb2d867db12632e15.png#pic_center)
![【群智能算法改进】一种改进的算术优化算法 改进算术优化算法 改进AOA[1]【Matlab代码#37】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8e085f0699494594a1e2dad205f2b5a0.png#pic_center)


![[图表]pyecharts模块-反转柱状图](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4dbc4820d0ab49eca91130697d661f76.png#pic_center)