1、主要参考
(1)官网介绍
Colored point cloud registration — Open3D 0.16.0 documentation
2、原理和实现
2.1原理
本教程演示了使用几何形状和颜色进行配准的ICP变体。实现了[Park2017]算法。颜色信息锁定沿切平面的对齐。因此,该算法比以往的点云配准算法精度更高,鲁棒性更强,运行速度与ICP配准算法相当。本教程使用来自ICP的符号。
2.2 辅助显示工具类
为了演示彩色点云之间的对齐,draw_registration_result_original_color使用原始颜色呈现点云。
def draw_registration_result_original_color(source, target, transformation):
source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target],
zoom=0.5,
front=[-0.2458, -0.8088, 0.5342],
lookat=[1.7745, 2.2305, 0.9787],
up=[0.3109, -0.5878, -0.7468])2.3待测试的点云数据
下面的代码从两个文件读取一个源点云和一个目标点云。使用单位矩阵作为注册的初始化。
注意:np.identity(4),相当于没有选择平移变换
(1)测试代码
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
# import time
def draw_registration_result_original_color(source, target, transformation):
# source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
source_temp = deepcopy(source)
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target],
zoom=0.5,
front=[-0.2458, -0.8088, 0.5342],
lookat=[1.7745, 2.2305, 0.9787],
up=[0.3109, -0.5878, -0.7468])
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("1. Load two point clouds and show initial pose")
demo_colored_icp_pcds = o3d.data.DemoColoredICPPointClouds()
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_colored_icp_pcds.paths[0])
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_colored_icp_pcds.paths[1])
# draw initial alignment
current_transformation = np.identity(4)
draw_registration_result_original_color(source, target, current_transformation)(2)下载的文件

(3)显示的结果图

2.4 点对面ICP对齐测试(Point-to-plane ICP)
我们首先使用点到平面ICP作为基线方法(baseline approach)。下面的可视化显示了未对齐的绿色三角形纹理。这是因为几何约束不能防止两个平面滑动
(1)测试代码
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
# import time
def draw_registration_result_original_color(source, target, transformation):
# source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
source_temp = deepcopy(source)
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target],
zoom=0.5,
front=[-0.2458, -0.8088, 0.5342],
lookat=[1.7745, 2.2305, 0.9787],
up=[0.3109, -0.5878, -0.7468])
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("1. Load two point clouds and show initial pose")
demo_colored_icp_pcds = o3d.data.DemoColoredICPPointClouds()
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_colored_icp_pcds.paths[0])
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_colored_icp_pcds.paths[1])
# draw initial alignment
current_transformation = np.identity(4)
draw_registration_result_original_color(source, target, current_transformation)
# point to plane ICP
current_transformation = np.identity(4)
print("2. Point-to-plane ICP registration is applied on original point")
print(" clouds to refine the alignment. Distance threshold 0.02.")
result_icp = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp(
source, target, 0.02, current_transformation,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPlane())
print(result_icp)
draw_registration_result_original_color(source, target,
result_icp.transformation)(2)测试结果
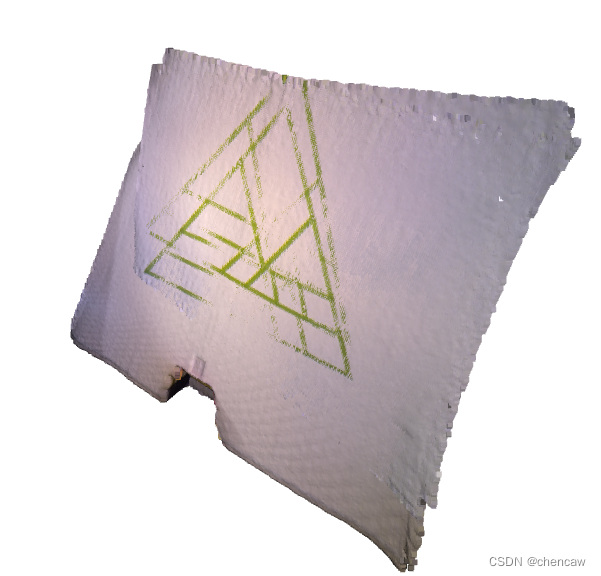
测试的参数如下:
clouds to refine the alignment. Distance threshold 0.02.
RegistrationResult with fitness=9.745825e-01, inlier_rmse=4.220433e-03, and correspondence_set size of 62729
Access transformation to get result.
3、彩色点云注册(Colored point cloud registration)
彩色点云配准的核心函数是registration_colored_icp。在[Park2017]之后,它运行了一个联合优化目标的ICP迭代(详见点到点ICP)。

其中T是要估计的变换矩阵。EC和EG分别是光度项和几何项。δ∈[0,1]是经经验确定的权重参数。几何术语EG与点对面ICP相同。

其中K为当前迭代中的对应集。Np是点p的法线。颜色项EC测量点q(记为C(q))的颜色与其在p的切平面上的投影颜色之间的差值。
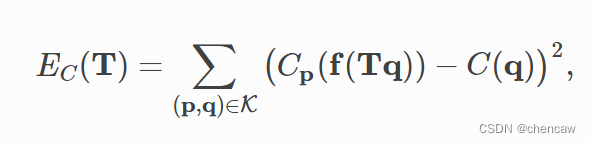
其中Cp(⋅)是一个预先计算的函数,连续定义在p的切平面上。函数(⋅)将一个3D点投影到切平面上。详情请参考[Park2017]。为了进一步提高效率,[Park2017]提出了一个多尺度注册方案。这已在以下脚本中实现。
3.1 彩色对齐的代码测试
PS:注意,逐步收敛!注意,体素逐渐变小!!!
(1)代码
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
from copy import deepcopy
# import time
def draw_registration_result_original_color(source, target, transformation):
# source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source)
source_temp = deepcopy(source)
source_temp.transform(transformation)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target],
zoom=0.5,
front=[-0.2458, -0.8088, 0.5342],
lookat=[1.7745, 2.2305, 0.9787],
up=[0.3109, -0.5878, -0.7468])
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("1. Load two point clouds and show initial pose")
demo_colored_icp_pcds = o3d.data.DemoColoredICPPointClouds()
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_colored_icp_pcds.paths[0])
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(demo_colored_icp_pcds.paths[1])
# draw initial alignment
current_transformation = np.identity(4)
draw_registration_result_original_color(source, target, current_transformation)
# point to plane ICP
current_transformation = np.identity(4)
print("2. Point-to-plane ICP registration is applied on original point")
print(" clouds to refine the alignment. Distance threshold 0.02.")
result_icp = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp(
source, target, 0.02, current_transformation,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPlane())
print(result_icp)
draw_registration_result_original_color(source, target,
result_icp.transformation)
# colored pointcloud registration
# This is implementation of following paper
# J. Park, Q.-Y. Zhou, V. Koltun,
# Colored Point Cloud Registration Revisited, ICCV 2017
voxel_radius = [0.04, 0.02, 0.01]
max_iter = [50, 30, 14]
current_transformation = np.identity(4)
print("3. Colored point cloud registration")
for scale in range(3):
iter = max_iter[scale]
radius = voxel_radius[scale]
print([iter, radius, scale])
print("3-1. Downsample with a voxel size %.2f" % radius)
source_down = source.voxel_down_sample(radius)
target_down = target.voxel_down_sample(radius)
print("3-2. Estimate normal.")
source_down.estimate_normals(
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius * 2, max_nn=30))
target_down.estimate_normals(
o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=radius * 2, max_nn=30))
print("3-3. Applying colored point cloud registration")
result_icp = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_colored_icp(
source_down, target_down, radius, current_transformation,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationForColoredICP(),
o3d.pipelines.registration.ICPConvergenceCriteria(relative_fitness=1e-6,
relative_rmse=1e-6,
max_iteration=iter))
current_transformation = result_icp.transformation
print(result_icp)
draw_registration_result_original_color(source, target,
result_icp.transformation)(2)显示的结果
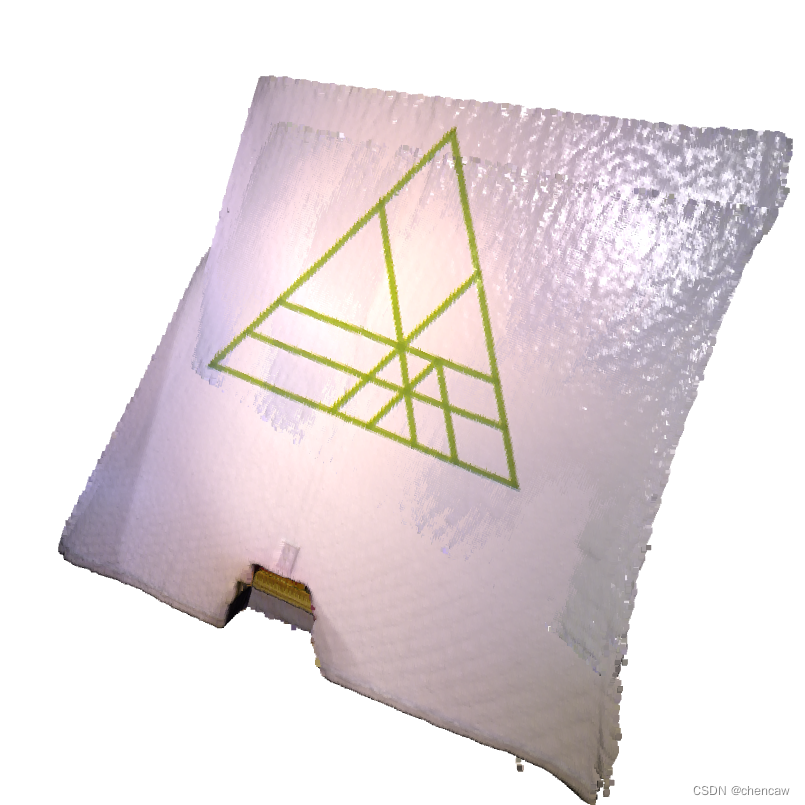
(3)测试的参数
 (4)说明
(4)说明
总的来说,使用voxel_down_sample创建了3层多分辨率点云。法线是用顶点法线估计来计算的。从粗到细,每个层都调用核心配准函数registration_colored_icp。lambda_geometric是registration_colored_icp的一个可选参数,它决定了λ eg +(1−λ)EC在总能量中的λ∈[0,1]。
输出是两个点云的紧密对齐。注意墙上的绿色三角形。





![[附源码]计算机毕业设计基于Springboot的中点游戏分享网站](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/98ff8829180a41329a838a8226c98889.png)