使用YOLOv8(You Only Look Once)和OpenCV实现车道线和车辆检测,目标是创建一个可以检测道路上的车道并识别车辆的系统,并估计它们与摄像头的距离。该项目结合了计算机视觉技术和深度学习物体检测。
1、系统主要功能
- 车道检测:使用边缘检测和霍夫线变换检测道路车道。
- 汽车检测:使用 YOLOv8 模型识别汽车并在汽车周围绘制边界框。
- 距离估计:使用边界框大小计算检测到的汽车与摄像头的距离。
2、环境要求
- OpenCV:用于图像处理和车道检测。
- Ultralytics YOLOv8:用于车辆检测。
- NumPy:用于数组操作。
pip install opencv-python-headless numpy ultralytics
opencv-python 和 opencv-python-headless 区别是 OpenCV 的 Python 包,主要区别在于是否包含 GUI 相关的功能。
opencv-python
- 包含 GUI 功能:支持窗口显示、鼠标事件等图形界面操作。
- 依赖:需要 GUI 库(如 GTK、Qt)支持。
- 适用场景:适用于需要显示图像或与用户交互的环境,如桌面应用。
opencv-python-headless
- 不包含 GUI 功能:去除了窗口显示和用户交互功能。
- 依赖:无需 GUI 库,适合无图形界面的环境。
- 适用场景:适用于服务器或无图形界面的环境,如远程服务器、Docker 容器。
选择建议
- 如果需要显示图像或与用户交互,选择
opencv-python。 - 如果仅需图像处理且无图形界面需求,选择
opencv-python-headless。
3、代码
import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
import time
from ultralytics import YOLO # YOLOv8 module
# Function to mask out the region of interest
def region_of_interest(img, vertices):
mask = np.zeros_like(img)
match_mask_color = 255
cv2.fillPoly(mask, vertices, match_mask_color)
masked_image = cv2.bitwise_and(img, mask)
return masked_image
# Function to draw the filled polygon between the lane lines
def draw_lane_lines(img, left_line, right_line, color=[0, 255, 0], thickness=10):
line_img = np.zeros_like(img)
poly_pts = np.array([[
(left_line[0], left_line[1]),
(left_line[2], left_line[3]),
(right_line[2], right_line[3]),
(right_line[0], right_line[1])
]], dtype=np.int32)
# Fill the polygon between the lines
cv2.fillPoly(line_img, poly_pts, color)
# Overlay the polygon onto the original image
img = cv2.addWeighted(img, 0.8, line_img, 0.5, 0.0)
return img
# The lane detection pipeline
def pipeline(image):
height = image.shape[0]
width = image.shape[1]
region_of_interest_vertices = [
(0, height),
(width / 2, height / 2),
(width, height),
]
# Convert to grayscale and apply Canny edge detection
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
cannyed_image = cv2.Canny(gray_image, 100, 200)
# Mask out the region of interest
cropped_image = region_of_interest(
cannyed_image,
np.array([region_of_interest_vertices], np.int32)
)
# Perform Hough Line Transformation to detect lines
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(
cropped_image,
rho=6,
theta=np.pi / 60,
threshold=160,
lines=np.array([]),
minLineLength=40,
maxLineGap=25
)
# Separating left and right lines based on slope
left_line_x = []
left_line_y = []
right_line_x = []
right_line_y = []
if lines is None:
return image
for line in lines:
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in line:
slope = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1) if (x2 - x1) != 0 else 0
if math.fabs(slope) < 0.5: # Ignore nearly horizontal lines
continue
if slope <= 0: # Left lane
left_line_x.extend([x1, x2])
left_line_y.extend([y1, y2])
else: # Right lane
right_line_x.extend([x1, x2])
right_line_y.extend([y1, y2])
# Fit a linear polynomial to the left and right lines
min_y = int(image.shape[0] * (3 / 5)) # Slightly below the middle of the image
max_y = image.shape[0] # Bottom of the image
if left_line_x and left_line_y:
poly_left = np.poly1d(np.polyfit(left_line_y, left_line_x, deg=1))
left_x_start = int(poly_left(max_y))
left_x_end = int(poly_left(min_y))
else:
left_x_start, left_x_end = 0, 0 # Defaults if no lines detected
if right_line_x and right_line_y:
poly_right = np.poly1d(np.polyfit(right_line_y, right_line_x, deg=1))
right_x_start = int(poly_right(max_y))
right_x_end = int(poly_right(min_y))
else:
right_x_start, right_x_end = 0, 0 # Defaults if no lines detected
# Create the filled polygon between the left and right lane lines
lane_image = draw_lane_lines(
image,
[left_x_start, max_y, left_x_end, min_y],
[right_x_start, max_y, right_x_end, min_y]
)
return lane_image
# Function to estimate distance based on bounding box size
def estimate_distance(bbox_width, bbox_height):
# For simplicity, assume the distance is inversely proportional to the box size
# This is a basic estimation, you may use camera calibration for more accuracy
focal_length = 1000 # Example focal length, modify based on camera setup
known_width = 2.0 # Approximate width of the car (in meters)
distance = (known_width * focal_length) / bbox_width # Basic distance estimation
return distance
# Main function to read and process video with YOLOv8
def process_video():
# Load the YOLOv8 model
model = YOLO('weights/yolov8n.pt')
# 或者加载官方模型
# model = YOLO("yolov8n.pt") # load an official model
# Open the video file
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('video/video.mp4')
# Check if video opened successfully
if not cap.isOpened():
print("Error: Unable to open video file.")
return
# Set the desired frame rate
target_fps = 30
frame_time = 1.0 / target_fps # Time per frame to maintain 30fps
# Resize to 720p (1280x720)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 1280)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 720)
# Loop through each frame
while cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
# Resize frame to 720p
resized_frame = cv2.resize(frame, (1280, 720))
# Run the lane detection pipeline
lane_frame = pipeline(resized_frame)
# Run YOLOv8 to detect cars in the current frame
results = model(resized_frame)
# Process the detections from YOLOv8
for result in results:
boxes = result.boxes
for box in boxes:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, box.xyxy[0]) # Bounding box coordinates
conf = box.conf[0] # Confidence score
cls = int(box.cls[0]) # Class ID
# Only draw bounding boxes for cars with confidence >= 0.5
if model.names[cls] == 'car' and conf >= 0.5:
label = f'{model.names[cls]} {conf:.2f}'
# Draw the bounding box
cv2.rectangle(lane_frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(lane_frame, label, (x1, y1 - 10),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 255), 2)
# Estimate the distance of the car
bbox_width = x2 - x1
bbox_height = y2 - y1
distance = estimate_distance(bbox_width, bbox_height)
# Display the estimated distance
distance_label = f'Distance: {distance:.2f}m'
cv2.putText(lane_frame, distance_label, (x1, y2 + 20),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255, 0, 0), 2)
# Display the resulting frame with both lane detection and car detection
cv2.imshow('Lane and Car Detection', lane_frame)
# Limit the frame rate to 30fps
time.sleep(frame_time)
# Break the loop when 'q' is pressed
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# Release video capture and close windows
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# Run the video processing function
process_video()
4、工作原理
4.1 车道线检测 Pipeline
车道线检测包括一下几个步骤:
Step 1: 屏蔽感兴趣区域(ROI)
只处理图像的下半部分(车道线通常是可见的)。
def region_of_interest(img, vertices):
mask = np.zeros_like(img)
match_mask_color = 255
cv2.fillPoly(mask, vertices, match_mask_color)
masked_image = cv2.bitwise_and(img, mask)
return masked_image
Step 2: 使用Canny进行边缘检测
将图像转换为灰度,并应用Canny边缘检测来突出显示边缘。
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
cannyed_image = cv2.Canny(gray_image, 100, 200)
Step 3: 霍夫线变换
霍夫线变换用于检测当前车道的线段。
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(
cropped_image,
rho=6,
theta=np.pi / 60,
threshold=160,
lines=np.array([]),
minLineLength=40,
maxLineGap=25
)
4.2 使用YOLOv8进行车辆检测
Step 1: 加载YOLOv8模型
我们使用预训练的YOLOv8模型来检测每一帧中的汽车(或者使用官方提供的模型)。
from ultralytics import YOLO
model = YOLO('weights/yolov8n.pt')
# model = YOLO('yolov8n.pt') #官方提供的模型
Step 2: 绘制边界框
对于每一辆检测到的汽车,绘制边界框,并显示类名(汽车)和置信度分数。
for box in boxes:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = map(int, box.xyxy[0])
conf = box.conf[0]
if model.names[cls] == 'car' and conf >= 0.5:
label = f'{model.names[cls]} {conf:.2f}'
cv2.rectangle(lane_frame, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(lane_frame, label, (x1, y1 - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 255, 255), 2)
Step 3:. 距离估计
根据边界框的大小估计到每辆检测到的汽车的距离。
def estimate_distance(bbox_width, bbox_height):
focal_length = 1000 # Example focal length
known_width = 2.0 # Approximate width of a car (in meters)
distance = (known_width * focal_length) / bbox_width
return distance
Step 4:. 视频处理 Pipeline
将车道检测、车辆检测和距离估计结合到一个实时视频处理pipeline中。
while cap.isOpened():
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
lane_frame = pipeline(resized_frame)
results = model(resized_frame)
for result in results:
# Draw bounding boxes and estimate distance
cv2.imshow('Lane and Car Detection', lane_frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
5、结果
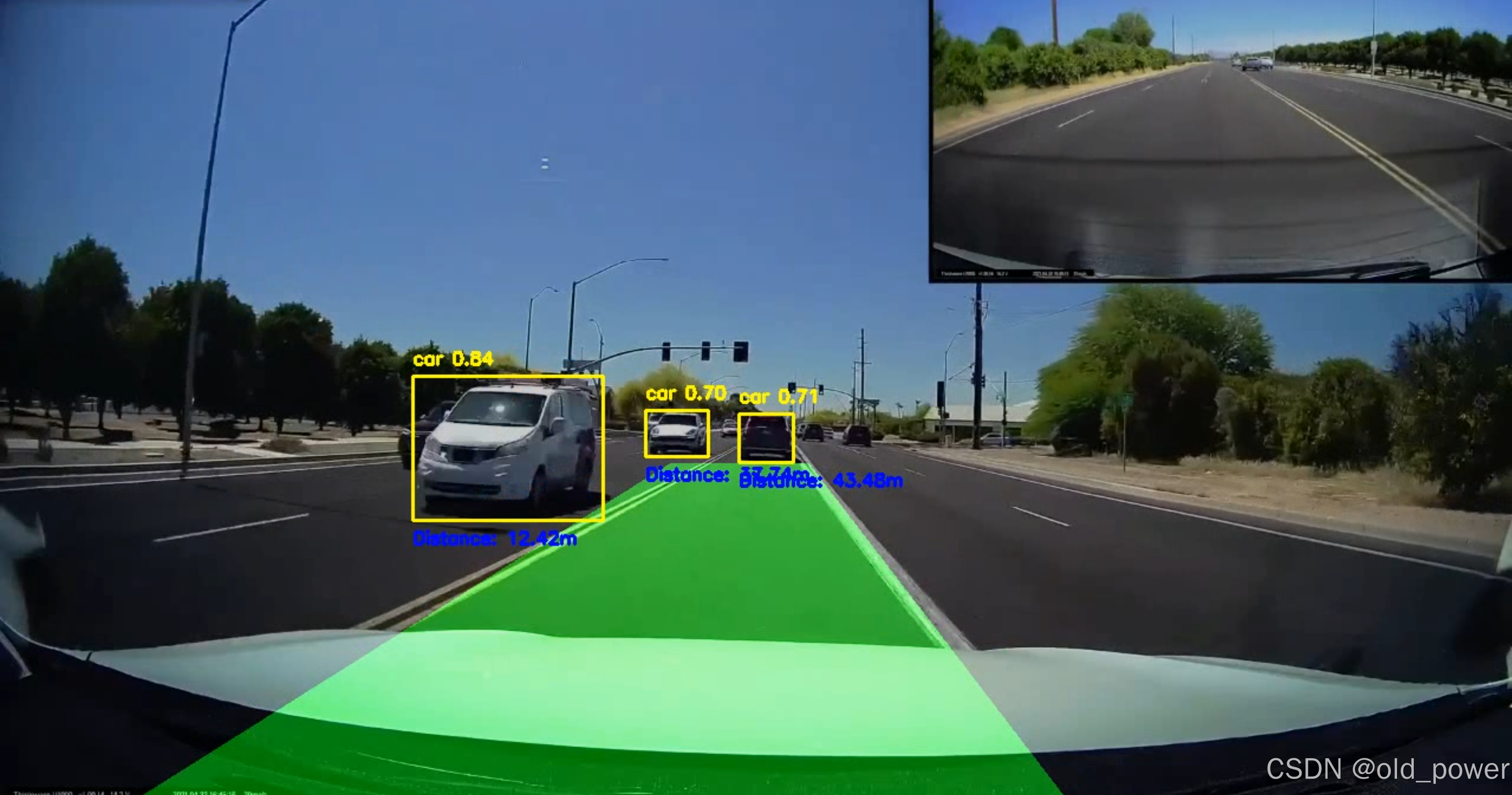
- 项目源码地址:
https://github.com/CityIsBetter/Lane_Detection