学完C语言之后,我就去阅读《C Primer Plus》这本经典的C语言书籍,对每一章的编程练习题都做了相关的解答,仅仅代表着我个人的解答思路,如有错误,请各位大佬帮忙点出!
有些题目函数定义在书本存在,这里就不提供需要的函数接口代码,测试截图也就不弄了。
1.修改程序清单17.2,让该程序既能正序也能逆序显示电影列表。一种 方法是修改链表的定义,可以双向遍历链表。另一种方法是用递归。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define TSIZE 45
struct film
{
char title[TSIZE];
int rating;
struct film* next;
};
void print_reverse_list(struct film* head)
{
if (head->next != NULL)
{
print_reverse_list(head->next);
}
printf("Movie: %s Rating: %d\n", head->title, head->rating);
}
char* s_gets(char* st, int n)
{
char* ret_val;
char* find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
{
*find = '\0';
}
else
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
}
return ret_val;
}
int main(void)
{
struct film* head = NULL;
struct film* prev, * current;
char input[TSIZE];
printf("Enter first movie title:\n");
while (s_gets(input, TSIZE) != NULL && input[0] != '\0')
{
current = (struct film*)malloc(sizeof(struct film));
if (head == NULL)
{
head = current;
}
else
{
prev->next = current;
}
current->next = NULL;
strcpy(current->title, input);
printf("Enter your rating <0-10>:\n");
scanf("%d", ¤t->rating);
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
printf("Enter next movie title (empty line to stop):\n");
prev = current;
}
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("No data entered. ");
}
else
{
printf("Here is the movie list:\n");
}
current = head;
while (current != NULL)
{
printf("Movie: %s Rating: %d\n",
current->title, current->rating);
current = current->next;
}
if (head != NULL)
{
printf("\nHere is the list in reverse order:\n");
print_reverse_list(head);
}
current = head;
while (current != NULL)
{
free(current);
current = current->next;
}
printf("Bye!\n");
return 0;
}
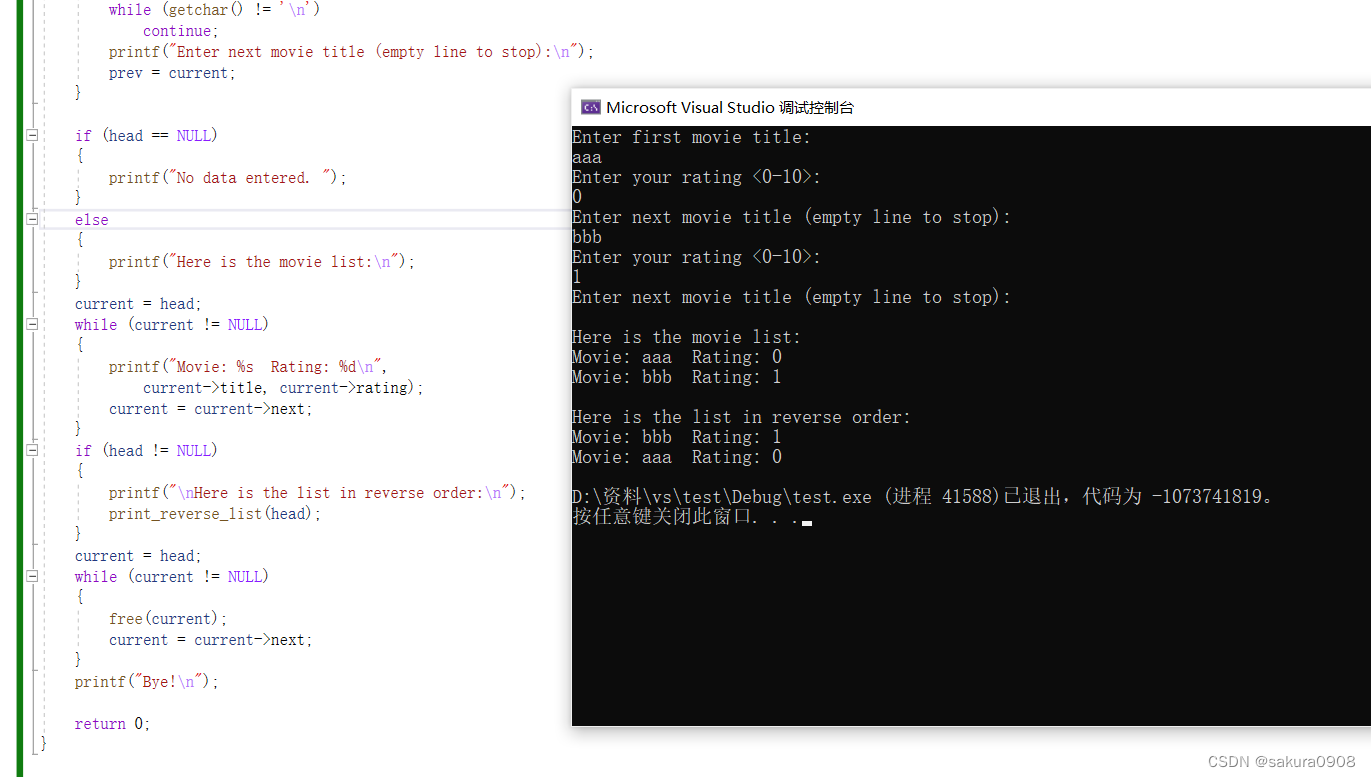
2.假设list.h(程序清单17.3)使用下面的list定义:
typedef struct list
{ Node * head; /* 指向list的开头 */
Node * end;/* 指向list的末尾 */ } List;
重写 list.c(程序清单 17.5)中的函数以适应新的定义,并通过 films.c(程序清单 17.4)测试最终的代码。
#ifndef LIST_H_
#define LIST_H_
#include <stdbool.h>
#define TSIZE 45
struct film
{
char title[TSIZE];
int rating;
};
typedef struct film Item;
typedef struct node
{
Item item;
struct node *next;
} Node;
typedef struct list
{
Node *head;
Node *end;
} List;
void InitializeList(List *plist);
bool ListIsEmpty(const List *plist);
bool ListIsFull(const List *plist);
unsigned int ListItemCount(const List *plist);
bool AddItem(Item item, List *plist);
void Traverse(const List *plist, void (*pfun)(Item item));
void EmptyTheList(List *plist);
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
static void CopyToNode(Item item, Node *pnode);
void InitializeList(List *plist)
{
(*plist).head = NULL;
(*plist).end = NULL;
return;
}
bool ListIsEmpty(const List *plist)
{
return NULL == (*plist).head;
}
bool ListIsFull(const List *plist)
{
Node *pt;
bool full;
pt = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (pt == NULL)
{
full = true;
}
else
{
full = false;
}
free(pt);
return full;
}
unsigned int ListItemCount(const List *plist)
{
unsigned int count = 0;
Node *pnode = (*plist).head; //使指针指向首结点;
while (pnode != NULL)
{
++count;
pnode = pnode->next;
}
return count;
}
bool AddItem(Item item, List *plist)
{
Node *pnew;
Node *scan = (*plist).head;
pnew = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (pnew == NULL)
{
return false;
}
CopyToNode(item, pnew);
pnew->next = NULL;
if (scan == NULL) //若是首结点则使头尾双指针同时指向此结点;
{
(*plist).head = pnew;
(*plist).end = pnew;
}
else
{
(*plist).end->next = pnew; //尾结点指针域指向新结点;
(*plist).end = pnew; //新结点成为尾结点;
}
return true;
}
void Traverse(const List *plist, void (*pfun)(Item item))
{
Node *pnode = (*plist).head;
while (pnode != NULL)
{
(*pfun)(pnode->item);
pnode = pnode->next;
}
return;
}
void EmptyTheList(List *plist)
{
Node *psave;
while ((*plist).head != NULL)
{
psave = (*plist).head->next;
free((*plist).head);
(*plist).head = psave;
}
return;
}
static void CopyToNode(Item item, Node *pnode)
{
pnode->item = item;
return;
}
3.假设list.h(程序清单17.3)使用下面的list定义:
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef struct list {
Item entries[MAXSIZE]; /* 内含项的数组 */
int items; /* list中的项数 */ } List;
重写 list.c(程序清单 17.5)中的函数以适应新的定义,并通过 films.c(程序清单 17.4)测试最终的代码。
#ifndef LIST_H_
#define LIST_H_
#include <stdbool.h>
#define TSIZE 45
struct film
{
char title[TSIZE];
int rating;
};
typedef struct film Item;
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef struct list
{
Item entries[MAXSIZE];
int items;
} List;
void InitializeList(List *plist);
bool ListIsEmpty(const List *plist);
bool ListIsFull(const List *plist);
unsigned int ListItemCount(const List *plist);
bool AddItem(Item item, List *plist);
void Traverse(const List *plist, void (*pfun)(Item item));
void EmptyTheList(List *plist);
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "list.h"
void InitializeList(List *plist)
{
plist->items = 0;
return;
}
bool ListIsEmpty(const List *plist)
{
return 0 == plist->items;
}
bool ListIsFull(const List *plist)
{
return MAXSIZE == plist->items;
}
unsigned int ListItemCount(const List *plist)
{
return plist->items;
}
bool AddItem(Item item, List *plist)
{
if (plist->items == MAXSIZE) //若项目数达到最大值则不可添加;
{
return false;
}
else //项目数未达到最大值则添加新项目到项目数组中并更新项的数量;
{
plist->entries[plist->items++] = item;
return true;
}
}
void Traverse(const List *plist, void (*pfun)(Item item))
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < plist->items; i++)
{
(*pfun)(plist->entries[i]); //使pun指向的函数作用于项目数组中的每一项;
}
return;
}
void EmptyTheList(List *plist)
{
plist->items = 0;
return;
}
4.重写mall.c(程序清单17.7),用两个队列模拟两个摊位。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "queue.h"
#define N 2
#define MIN_PER_HR 60.0
static struct
{
Queue line;
int hours, perhour, wait_time;
long cycle, cyclelimit, turnaways;
long customers, served, sum_line, line_wait;
double min_per_cust;
} malls[N]; //模拟2个摊位;
bool newcustomer(double x)
{
return rand() * x / RAND_MAX < 1 ? true : false;
}
Item customertime(long when)
{
Item cust;
cust.processtime = rand() % 3 + 1;
cust.arrive = when;
return cust;
}
int main(void)
{
int i;
Item temp;
srand((unsigned int)time(0));
puts("Case Study: Sigmund Lander's Advice Booth");
puts("Enter the number of simulation hours for the first mall:");
scanf("%d", &malls[0].hours);
malls[0].cyclelimit = MIN_PER_HR * malls[0].hours;
puts("Enter the number of simulation hours for the second mall:");
scanf("%d", &malls[1].hours);
malls[1].cyclelimit = MIN_PER_HR * malls[1].hours;
puts("Enter the average number of customers per hourfor the first mall:");
scanf("%d", &malls[0].perhour);
malls[0].min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR / malls[0].perhour;
puts("Enter the average number of customers per hourfor the second mall:");
scanf("%d", &malls[1].perhour);
malls[1].min_per_cust = MIN_PER_HR / malls[1].perhour;
for (i = 0; i < N; i++) //使用循环来控制2个摊位;
{
for (malls[i].cycle = 0; malls[i].cycle < malls[i].cyclelimit; malls[i].cycle++)
{
if (newcustomer(malls[i].min_per_cust))
{
if (QueueIsFull(&malls[i].line))
{
malls[i].turnaways++;
}
else
{
malls[i].customers++;
temp = customertime(malls[i].cycle);
EnQueue(temp, &malls[i].line);
}
}
if (malls[i].wait_time <= 0 && !QueueIsEmpty(&malls[i].line))
{
DeQueue(&temp, &malls[i].line);
malls[i].wait_time = temp.processtime;
malls[i].line_wait += malls[i].cycle - temp.arrive;
malls[i].served++;
}
if (malls[i].wait_time > 0)
{
malls[i].wait_time--;
}
malls[i].sum_line += QueueItemCount(&malls[i].line);
}
if (malls[i].customers > 0)
{
printf("\nHere are some messages for the %s mall:\n", 0 == i ? "first" : "second");
printf("customers accepted: %ld\n", malls[i].customers);
printf(" customers served: %ld\n", malls[i].served);
printf(" turnaways: %ld\n", malls[i].turnaways);
printf("average queue size: %.2f\n",
(double)malls[i].sum_line / malls[i].cyclelimit);
printf(" average wait time: %.2f minutes\n",
(double)malls[i].line_wait / malls[i].served);
}
else
{
printf("No customers for the %s mall!\n", 0 == i ? "first" : "second");
}
EmptyTheQueue(&malls[i].line);
}
puts("Bye!");
return 0;
}5.编写一个程序,提示用户输入一个字符串。然后该程序把该字符串的 字符逐个压入一个栈(参见复习题5),然后从栈中弹出这些字符,并显示 它们。结果显示为该字符串的逆序。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "stack.h"
#define SLEN 81
char* s_gets(char* st, int n)
{
char* find;
char* ret_val;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
{
*find = '\0';
}
else
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
}
return ret_val;
}
int main(void)
{
int i;
stack st;
item ch, temp[SLEN];
init(&st);
printf("Please enter a string (EOF to quit):\n");
while (s_gets(temp, SLEN) != NULL)
{
i = 0;
while (temp[i] != '\0')
{
push(&st, temp[i++]);
}
printf("Reversing order:\n");
while (!isempty(&st))
{
pop(&st, &ch); //顺序出栈即可得到原字符串的逆序;
putchar(ch);
}
puts("\nYou can enter a string again (EOF to quit):");
}
puts("Done.");
return 0;
}
#ifndef STACK_H_
#define STACK_H_
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAXSIZE 100
typedef char item; //栈的数据类型为item类型;
typedef struct
{
item data[MAXSIZE];
int top;
} stack;
void init(stack *st); //栈的初始化函数;
bool isempty(stack *st); //判断栈是否为空;
bool isfull(stack *st); //判断栈是否已满;
bool push(stack *st, item val); //令元素入栈;
bool pop(stack *st, item *val); //令元素出栈;
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#include "stack.h"
void init(stack *st)
{
st->top = 0;
return;
}
bool isempty(stack *st)
{
return 0 == st->top;
}
bool isfull(stack *st)
{
return MAXSIZE == st->top;
}
bool push(stack *st, item val)
{
if (isfull(st))
{
return false;
}
else
{
st->data[st->top++] = val;
return true;
}
}
bool pop(stack *st, item *val)
{
if (isempty(st))
{
return false;
}
else
{
*val = st->data[--st->top];
return true;
}
}
6.编写一个函数接受 3 个参数:一个数组名(内含已排序的整数)、该 数组的元素个数和待查找的整数。如果待查找的整数在数组中,那么该函数 返回 1;如果该数不在数组中,该函数则返回 0。用二分查找法实现。
#include <stdio.h>
#define SIZE 10
int binary_search(const int sorted[], int size, int val)
{
int mid;
int min = 0;
int max = size - 1;
int found = 0;
while (min < max)
{
mid = (min + max) / 2;
if (val < sorted[mid])
{
max = mid - 1;
}
else if (val > sorted[mid])
{
min = mid + 1;
}
else
{
found = 1;
break;
}
}
if (sorted[min] == val)
{
found = 1;
}
return found;
}
int main(void)
{
int num, found;
int nums[SIZE] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 };
printf("Please enter a number for searching (q to quit): ");
while (scanf("%d", &num) == 1)
{
found = binary_search(nums, SIZE, num);
if (1 == found)
{
printf("%d exists in the array.\n", num);
}
else
{
printf("%d doesn't exist in the array.\n", num);
}
printf("You can enter again (q to quit): ");
}
puts("Done.");
return 0;
}
7.编写一个程序,打开和读取一个文本文件,并统计文件中每个单词出 现的次数。用改进的二叉查找树储存单词及其出现的次数。程序在读入文件 后,会提供一个有3个选项的菜单。第1个选项是列出所有的单词和出现的次 数。第2个选项是让用户输入一个单词,程序报告该单词在文件中出现的次 数。第3个选项是退出。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "tree.h"
#define SLEN 81
char* s_gets(char* st, int n)
{
char* ret_val;
char* find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
{
*find = '\0';
}
else
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
}
return ret_val;
}
int menu(void)
{
int ch;
puts("==============================================");
puts(" Word counting program");
puts("Enter the letter corresponding to your choice:");
puts(" s) show word list f) find a word");
puts(" q) quit");
puts("==============================================");
printf("Please you choose: ");
while (ch = get_first(), NULL == strchr("sfq", ch))
{
printf("Please enter s, f or q: ");
}
return ch;
}
void showwords(const Tree* pt)
{
if (TreeIsEmpty(pt)) //使用二叉树存储的单词若为空则表示无单词;
{
puts("No words in this text.");
}
else
{
Traverse(pt, print_all_items);
}
return;
}
void findword(const Tree* pt)
{
char word[SLEN];
Item entry;
const Item* pi;
if (TreeIsEmpty(pt))
{
puts("No words in this text.");
return;
}
printf("Please enter a word: ");
scanf("%80s", word);
eatline();
strcpy(entry.wrd, word); //把word数组中的单词复制到二叉树的项目中;
pi = WhereInTree(&entry, pt); //寻找单词在二叉树中的位置;
if (NULL == pi)
{
printf("Word %s doesn't exist in this text.\n", word);
}
else
{
printf("Word %s appeared %d times in this text.\n", word, pi->count);
}
return;
}
void print_all_items(Item item)
{
printf("Word %s appeared %d times totally in this text.\n", item.wrd, item.count);
return;
}
int get_first(void)
{
int ch;
do
{
ch = tolower(getchar());
} while (isspace(ch));
eatline();
return ch;
}
void eatline(void)
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
return;
}
int main(void)
{
Tree wordcount;
FILE* fp;
char filename[SLEN];
char word[SLEN];
Item entry;
char choice;
printf("Please enter a filename: ");
s_gets(filename, SLEN);
if ((fp = fopen(filename, "r")) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can't open file %s\n", filename);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
InitializeTree(&wordcount); //初始化一个二叉树;
while (fscanf(fp, "%80s", word) == 1 && !TreeIsFull(&wordcount))
{
strcpy(entry.wrd, word);
AddItem(&entry, &wordcount);
}
while ((choice = menu()) != 'q')
{
switch (choice)
{
case 's':
{
showwords(&wordcount);
break;
}
case 'f':
{
findword(&wordcount);
break;
}
}
printf("\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n");
}
DeleteAll(&wordcount);
if (fclose(fp) != 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can't close file %s\n", filename);
}
puts("Done.");
return 0;
}
#ifndef _TREE_H_
#define _TREE_H_
#include <stdbool.h>
#define SLEN 81
typedef struct item
{
char wrd[SLEN];
int count;
} Item;
#define MAXITEMS 100
typedef struct node
{
Item item;
struct node *left;
struct node *right;
} Node;
typedef struct tree
{
Node *root;
int size;
} Tree;
void InitializeTree(Tree *ptree);
bool TreeIsEmpty(const Tree *ptree);
bool TreeIsFull(const Tree *ptree);
int TreeItemCount(const Tree *ptree);
bool AddItem(const Item *pi, Tree *ptree);
bool InTree(const Item *pi, const Tree *ptree);
bool DeleteItem(const Item *pi, Tree *ptree);
void Traverse(const Tree *ptree, void (*pfun)(Item item));
void DeleteAll(Tree *ptree);
const Item *WhereInTree(const Item *pi, const Tree *ptree);
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include "tree.h"
typedef struct pair
{
Node *parent;
Node *child;
} Pair;
static Node *MakeNode(const Item *pi);
static bool ToLeft(const Item *i1, const Item *i2);
static bool ToRight(const Item *i1, const Item *i2);
static void AddNode(Node *new_node, Node *root);
static void InOrder(const Node *root, void (*pfun)(Item item));
static Pair SeekItem(const Item *pi, const Tree *ptree);
static void DeleteNode(Node **ptr);
static void DeleteAllNodes(Node *ptr);
void InitializeTree(Tree *ptree)
{
ptree->root = NULL;
ptree->size = 0;
return;
}
bool TreeIsEmpty(const Tree *ptree)
{
return NULL == ptree->root;
}
bool TreeIsFull(const Tree *ptree)
{
return MAXITEMS == ptree->size;
}
int TreeItemCount(const Tree *ptree)
{
return ptree->size;
}
bool AddItem(const Item *pi, Tree *ptree)
{
Node *new_node;
Pair seek;
if (TreeIsFull(ptree))
{
fprintf(stderr, "No memory available!\n");
return false;
}
if ((seek = SeekItem(pi, ptree)).child != NULL)
{
seek.child->item.count++;
return true;
}
new_node = MakeNode(pi);
if (new_node == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ptree->size++;
if (ptree->root == NULL)
{
ptree->root = new_node;
}
else
{
AddNode(new_node, ptree->root);
}
return true;
}
bool InTree(const Item *pi, const Tree *ptree)
{
return (SeekItem(pi, ptree).child == NULL) ? false : true;
}
const Item *WhereInTree(const Item *pi, const Tree *ptree)
{
Node *pn;
pn = SeekItem(pi, ptree).child;
return NULL == pn ? NULL : &(pn->item);
}
bool DeleteItem(const Item *pi, Tree *ptree)
{
Pair look;
look = SeekItem(pi, ptree);
if (look.child == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if (look.child->item.count > 0)
{
look.child->item.count--;
}
else
{
if (look.parent == NULL)
{
DeleteNode(&ptree->root);
}
else if (look.parent->left == look.child)
{
DeleteNode(&look.parent->left);
}
else
{
DeleteNode(&look.parent->right);
}
ptree->size--;
}
return true;
}
void Traverse(const Tree *ptree, void (*pfun)(Item item))
{
if (ptree != NULL)
{
InOrder(ptree->root, pfun);
}
return;
}
void DeleteAll(Tree *ptree)
{
if (ptree != NULL)
{
DeleteAllNodes(ptree->root);
}
ptree->root = NULL;
ptree->size = 0;
return;
}
static void InOrder(const Node *root, void (*pfun)(Item item))
{
if (root != NULL)
{
InOrder(root->left, pfun);
(*pfun)(root->item);
InOrder(root->right, pfun);
}
return;
}
static void DeleteAllNodes(Node *root)
{
Node *pright;
if (root != NULL)
{
pright = root->right;
DeleteAllNodes(root->left);
free(root);
DeleteAllNodes(pright);
}
return;
}
static void AddNode(Node *new_node, Node *root)
{
if (ToLeft(&new_node->item, &root->item))
{
if (root->left == NULL)
{
root->left = new_node;
}
else
{
AddNode(new_node, root->left);
}
}
else if (ToRight(&new_node->item, &root->item))
{
if (root->right == NULL)
{
root->right = new_node;
}
else
{
AddNode(new_node, root->right);
}
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can't add repetitive item!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return;
}
static bool ToLeft(const Item *i1, const Item *i2)
{
return strcmp(i1->wrd, i2->wrd) < 0 ? true : false;
}
static bool ToRight(const Item *i1, const Item *i2)
{
return strcmp(i1->wrd, i2->wrd) > 0 ? true : false;
}
static Node *MakeNode(const Item *pi)
{
Node *new_node;
new_node = (Node *)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (new_node != NULL)
{
new_node->item = *pi;
new_node->item.count = 1;
new_node->left = NULL;
new_node->right = NULL;
}
return new_node;
}
static Pair SeekItem(const Item *pi, const Tree *ptree)
{
Pair look;
look.parent = NULL;
look.child = ptree->root;
if (look.child == NULL)
{
return look;
}
while (look.child != NULL)
{
if (ToLeft(pi, &(look.child->item)))
{
look.parent = look.child;
look.child = look.child->left;
}
else if (ToRight(pi, &(look.child->item)))
{
look.parent = look.child;
look.child = look.child->right;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return look;
}
static void DeleteNode(Node **ptr)
{
Node *temp;
if ((*ptr)->left == NULL)
{
temp = *ptr;
*ptr = (*ptr)->right;
free(temp);
}
else if ((*ptr)->right == NULL)
{
temp = *ptr;
*ptr = (*ptr)->left;
free(temp);
}
else
{
for (temp = (*ptr)->left; temp->right != NULL; temp = temp->right)
{
continue;
}
temp->right = (*ptr)->right;
temp = *ptr;
*ptr = (*ptr)->left;
free(temp);
}
return;
}
8.修改宠物俱乐部程序,把所有同名的宠物都储存在同一个节点中。当 用户选择查找宠物时,程序应询问用户该宠物的名字,然后列出该名字的所 有宠物(及其种类)。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "tree.h"
int menu(void)
{
int ch;
puts("Nerfville Pet Club Membership Program");
puts("Enter the letter corresponding to your choice:");
puts("a) add a pet l) show list of pets");
puts("n) number of pets f) find pets");
puts("d) delete a pet q) quit");
while ((ch = getchar()) != EOF)
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
ch = tolower(ch);
if (strchr("alrfndq", ch) == NULL)
{
puts("Please enter an a, l, f, n, d, or q:");
}
else
{
break;
}
}
if (ch == EOF)
{
ch = 'q';
}
return ch;
}
void addpet(Tree* pt)
{
Item temp;
if (TreeIsFull(pt))
{
puts("No room in the club!");
}
else
{
puts("Please enter name of pet:");
s_gets(temp.petname, SLEN);
my_malloc(&temp); //分配内存至项目中的指针域;
puts("Please enter pet kind:");
s_gets(temp.many_petkinds->petkind, SLEN);
uppercase(temp.petname);
uppercase(temp.many_petkinds->petkind);
AddItem(&temp, pt);
free(temp.many_petkinds);
}
return;
}
void showpets(const Tree* pt)
{
if (TreeIsEmpty(pt))
{
puts("No entries!");
}
else
{
Traverse(pt, printitem);
}
return;
}
void printitem(Item item)
{
if (1 == item.pets_count) //只有一个同名宠物的情况;
{
printf("Pet: %-19s Kind: %-19s\n", item.petname,
item.many_petkinds->petkind);
}
else //结点中包含有多个同名不同种宠物的情况;
{
print_all_pets(item);
}
return;
}
void findpet(const Tree* pt)
{
Item temp;
if (TreeIsEmpty(pt))
{
puts("No entries!");
return;
}
puts("Please enter name of pet you wish to find:");
s_gets(temp.petname, SLEN);
uppercase(temp.petname);
if (InTree(&temp, pt))
{
printf("All kinds of the %s pets:\n", temp.petname);
my_traverse(pt->root, print_same_pets, temp.petname);
//若是此宠物存在于俱乐部中则打印所有相同种类的宠物;
}
else
{
printf("%s is not a member.\n", temp.petname);
}
return;
}
void droppet(Tree* pt)
{
Item temp;
if (TreeIsEmpty(pt))
{
puts("No entries!");
return;
}
puts("Please enter name of pet you wish to delete:");
s_gets(temp.petname, SLEN);
my_malloc(&temp); //分配内存至项目中的指针域;
puts("Please enter pet kind:");
s_gets(temp.many_petkinds->petkind, SLEN);
uppercase(temp.petname);
uppercase(temp.many_petkinds->petkind);
printf("%s the %s ", temp.petname, temp.many_petkinds->petkind);
if (DeleteItem(&temp, pt))
{
printf("is dropped from the club.\n");
}
else
{
printf("is not a member.\n");
}
free(temp.many_petkinds);
return;
}
void uppercase(char* str)
{
while (*str)
{
*str = toupper(*str);
str++;
}
return;
}
char* s_gets(char* st, int n)
{
char* ret_val;
char* find;
ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
{
*find = '\0';
}
else
{
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
}
return ret_val;
}
void print_all_pets(Item item)
{
Kind* temp = item.many_petkinds;
while (temp != NULL)
{
printf("Pet: %-19s Kind: %-19s\n", item.petname,
temp->petkind);
temp = temp->next;
}
return;
}
void my_malloc(Item* item)
{
if ((item->many_petkinds = (Kind*)malloc(sizeof(Kind))) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return;
}
void print_same_pets(Item item, const char* str)
{
Kind* temp = item.many_petkinds;
while (temp != NULL)
{
if (0 == strcmp(item.petname, str)) //打印名字相同的不同种类的宠物;
{
printf("Pet: %-19s Kind: %-19s\n", item.petname,
temp->petkind);
}
temp = temp->next;
}
return;
}
void my_traverse(const Trnode* root, void (*pfun)(Item item, const char* temp), const char* str)
{
if (root != NULL)
{
my_traverse(root->left, pfun, str);
(*pfun)(root->item, str);
my_traverse(root->right, pfun, str);
}
return;
}
void pets_count(int* count, int* temp)
{
*count -= *temp;
*temp += *count;
return;
}
int main(void)
{
Tree pets;
int choice;
int count, temp;
count = temp = 0;
InitializeTree(&pets);
while ((choice = menu()) != 'q')
{
switch (choice)
{
case 'a':
{
addpet(&pets);
break;
}
case 'l':
{
showpets(&pets);
break;
}
case 'f':
{
findpet(&pets);
break;
}
case 'n':
{
count = TreeItemCount(&pets);
pets_count(&count, &temp);
printf("%d pets in club\n", count);
break;
}
case 'd':
{
droppet(&pets);
break;
}
default:
{
puts("Switching error");
}
}
}
DeleteAll(&pets);
puts("Bye.");
return 0;
}
#ifndef _TREE_H_
#define _TREE_H_
#include <stdbool.h>
#define SLEN 20
typedef struct kind
{
char petkind[SLEN];
struct kind *next;
} Kind;
//在二叉树接口中添加列表保存同名不同类的宠物;
typedef struct item
{
char petname[SLEN];
Kind *many_petkinds;
int pets_count;
} Item;
#define MAXITEMS 10
typedef struct trnode
{
Item item;
struct trnode *left;
struct trnode *right;
} Trnode;
typedef struct tree
{
Trnode *root;
int size;
} Tree;
void InitializeTree(Tree *ptree);
bool TreeIsEmpty(const Tree *ptree);
bool TreeIsFull(const Tree *ptree);
int TreeItemCount(const Tree *ptree);
bool AddItem(const Item *pi, Tree *ptree);
bool InTree(const Item *pi, const Tree *ptree);
bool DeleteItem(const Item *pi, Tree *ptree);
void Traverse(const Tree *ptree, void (*pfun)(Item item));
void DeleteAll(Tree *ptree);
#endif
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "tree.h"
typedef struct pair
{
Trnode *parent;
Trnode *child;
} Pair;
static Trnode *MakeNode(const Item *pi);
static bool ToLeft(const Item *i1, const Item *i2);
static bool ToRight(const Item *i1, const Item *i2);
static void AddNode(Trnode *new_node, Trnode *root);
static void InOrder(const Trnode *root, void (*pfun)(Item item));
static Pair SeekItem(const Item *pi, const Tree *ptree);
static void DeleteNode(Trnode **ptr);
static void DeleteAllNodes(Trnode *ptr);
static int all_pets_numbers(const Trnode *root);
void InitializeTree(Tree *ptree)
{
ptree->root = NULL;
ptree->size = 0;
return;
}
bool TreeIsEmpty(const Tree *ptree)
{
return NULL == ptree->root;
}
bool TreeIsFull(const Tree *ptree)
{
return MAXITEMS == ptree->size;
}
int TreeItemCount(const Tree *ptree)
{
return all_pets_numbers(ptree->root); //获取俱乐部中所有宠物的数量;
}
bool AddItem(const Item *pi, Tree *ptree)
{
Trnode *find;
Trnode *new_node;
if (TreeIsFull(ptree))
{
fprintf(stderr, "Tree is full\n");
return false;
}
if ((find = SeekItem(pi, ptree).child) != NULL)
{
Kind *temp;
Kind *node;
for (temp = find->item.many_petkinds; temp != NULL; temp = temp->next)
{
if (strcmp(pi->many_petkinds->petkind, temp->petkind) == 0)
{
break;
}
}
if (temp != NULL) //若temp为NULL则说明用户输入的宠物名字和种类与俱乐部中宠物相重复,故无法添加;
{
fprintf(stderr, "Can't add duplicate item!\n");
return false;
}
else
{
if ((node = (Kind *)malloc(sizeof(Kind))) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed!\n");
return false;
}
else
{
strcpy(node->petkind, pi->many_petkinds->petkind);
node->next = NULL;
for (temp = find->item.many_petkinds; temp->next != NULL; temp = temp->next)
{
continue;
}
temp->next = node;
find->item.pets_count++;
return true;
}
}
}
new_node = MakeNode(pi);
if (new_node == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Couldn't create node.\n");
return false;
}
ptree->size++;
if (ptree->root == NULL)
{
ptree->root = new_node;
}
else
{
AddNode(new_node, ptree->root);
}
return true;
}
bool InTree(const Item *pi, const Tree *ptree)
{
return (SeekItem(pi, ptree).child == NULL) ? false : true;
}
bool DeleteItem(const Item *pi, Tree *ptree)
{
Pair look;
look = SeekItem(pi, ptree);
if (look.child == NULL)
{
return false;
}
if (look.child->item.pets_count != 1) //结点中有多个同名不同类的宠物;
{
//↓使用链表顺序遍历找到符合用户输入的宠物;
Kind *prior;
Kind *current;
for (prior = current = look.child->item.many_petkinds; current != NULL; current = current->next)
{
if (strcmp(current->petkind, pi->many_petkinds->petkind) == 0)
{
break;
}
prior = current;
}
if (current != NULL) //找到用户输入种类的宠物;
{
prior->next = current->next;
free(current);
look.child->item.pets_count--;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
else
{
//↓若用户输入的宠物只有一种且俱乐部中存在此种宠物则删除整个结点;
if (0 == strcmp(look.child->item.many_petkinds->petkind, pi->many_petkinds->petkind))
{
if (look.parent == NULL)
{
DeleteNode(&ptree->root);
}
else if (look.parent->left == look.child)
{
DeleteNode(&look.parent->left);
}
else
{
DeleteNode(&look.parent->right);
}
ptree->size--;
return true;
}
else //若用户输入的宠物种类不存在则返回false;
{
return false;
}
}
}
void Traverse(const Tree *ptree, void (*pfun)(Item item))
{
if (ptree != NULL)
{
InOrder(ptree->root, pfun);
}
return;
}
void DeleteAll(Tree *ptree)
{
if (ptree != NULL)
{
DeleteAllNodes(ptree->root);
}
ptree->root = NULL;
ptree->size = 0;
return;
}
static void InOrder(const Trnode *root, void (*pfun)(Item item))
{
if (root != NULL)
{
InOrder(root->left, pfun);
(*pfun)(root->item);
InOrder(root->right, pfun);
}
return;
}
static void DeleteAllNodes(Trnode *root)
{
Trnode *pright;
if (root != NULL)
{
pright = root->right;
DeleteAllNodes(root->left);
Kind *temp;
while (root->item.many_petkinds != NULL)
{
temp = root->item.many_petkinds->next;
free(root->item.many_petkinds);
root->item.many_petkinds = temp;
}
free(root);
DeleteAllNodes(pright);
}
return;
}
static void AddNode(Trnode *new_node, Trnode *root)
{
if (ToLeft(&new_node->item, &root->item))
{
if (root->left == NULL)
{
root->left = new_node;
}
else
{
AddNode(new_node, root->left);
}
}
else if (ToRight(&new_node->item, &root->item))
{
if (root->right == NULL)
{
root->right = new_node;
}
else
{
AddNode(new_node, root->right);
}
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "location error in AddNode()\n");
exit(1);
}
return;
}
static bool ToLeft(const Item *i1, const Item *i2)
{
return strcmp(i1->petname, i2->petname) < 0 ? true : false;
}
static bool ToRight(const Item *i1, const Item *i2)
{
return strcmp(i1->petname, i2->petname) > 0 ? true : false;
}
static Trnode *MakeNode(const Item *pi)
{
Kind *temp;
Trnode *new_node;
if ((new_node = (Trnode *)malloc(sizeof(Trnode))) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if ((temp = (Kind *)malloc(sizeof(Kind))) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed!\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
strcpy(new_node->item.petname, pi->petname);
strcpy(temp->petkind, pi->many_petkinds->petkind);
temp->next = NULL;
new_node->item.many_petkinds = temp;
new_node->item.pets_count = 1;
new_node->left = NULL;
new_node->right = NULL;
return new_node;
}
static Pair SeekItem(const Item *pi, const Tree *ptree)
{
Pair look;
look.parent = NULL;
look.child = ptree->root;
if (look.child == NULL)
{
return look;
}
while (look.child != NULL)
{
if (ToLeft(pi, &(look.child->item)))
{
look.parent = look.child;
look.child = look.child->left;
}
else if (ToRight(pi, &(look.child->item)))
{
look.parent = look.child;
look.child = look.child->right;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return look;
}
static void DeleteNode(Trnode **ptr)
{
Kind *tp;
Trnode *temp;
if ((*ptr)->left == NULL)
{
temp = *ptr;
*ptr = (*ptr)->right;
}
else if ((*ptr)->right == NULL)
{
temp = *ptr;
*ptr = (*ptr)->left;
}
else
{
for (temp = (*ptr)->left; temp->right != NULL; temp = temp->right)
{
continue;
}
temp->right = (*ptr)->right;
temp = *ptr;
*ptr = (*ptr)->left;
}
while (temp->item.many_petkinds != NULL)
{
tp = temp->item.many_petkinds->next;
free(temp->item.many_petkinds);
temp->item.many_petkinds = tp;
}
free(temp);
return;
}
static int all_pets_numbers(const Trnode *root)
{
static int count = 0;
if (root != NULL)
{
all_pets_numbers(root->left);
count += root->item.pets_count; //使用递归累加所有结点中的同名不同类的宠物数量;
all_pets_numbers(root->right);
}
return count;
}