目录
基本概述
ServerSocketChannel
打开 ServerSocketChannel
关闭 ServerSocketChannel
监听新的连接
阻塞模式
非阻塞模式
SocketChannel
SocketChannel 介绍
SocketChannel 特征
创建 SocketChannel
连接校验
读写模式
读写
DatagramChannel
打开 DatagramChannel
接收数据
发送数据
连接
DatagramChannel 示例
基本概述
(1)SocketChannel 就是 NIO 对于非阻塞 socket 操作的支持的组件,其在 socket 上 封装了一层,主要是支持了非阻塞的读写。同时改进了传统的单向流 API,,Channel同时支持读写。
(2)socket 通道类主要分为 DatagramChannel、SocketChannel 和 ServerSocketChannel,它们在被实例化时都会创建一个对等 socket 对象。要把一个 socket 通道置于非阻塞模式,我们要依靠所有 socket 通道类的公有超级类: SelectableChannel。就绪选择(readiness selection)是一种可以用来查询通道的 机制,该查询可以判断通道是否准备好执行一个目标操作,如读或写。非阻塞 I/O 和 可选择性是紧密相连的,那也正是管理阻塞模式的 API 代码要在 SelectableChannel 超级类中定义的原因。
(3)设置或重新设置一个通道的阻塞模式是很简单的,只要调用 configureBlocking( )方法即可,传递参数值为 true 则设为阻塞模式,参数值为 false 值设为非阻塞模式。可以通过调用 isBlocking( )方法来判断某个 socket 通道当前处于 哪种模式。
AbstractSelectableChannel.java 中实现的 configureBlocking()方法如下:

ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel 是一个基于通道的 socket 监听器。它同我们所熟悉的java.net.ServerSocket 执行相同的任务,不过它增加了通道语义,因此能够在非阻塞 模式下运行。
由于 ServerSocketChannel 没有 bind()方法,因此有必要取出对等的 socket 并使用 它来绑定到一个端口以开始监听连接。我们也是使用对等 ServerSocket 的 API 来根 据需要设置其他的 socket 选项。
同 java.net.ServerSocket 一样,ServerSocketChannel 也有 accept( )方法。 ServerSocketChannel 的 accept()方法会返回 SocketChannel 类型对象, SocketChannel 可以在非阻塞模式下运行。
以下代码演示了如何使用一个非阻塞的 accept( )方法:
public class FileChannelAccept {
public static final String GREETING = "Hello java nio.\r\n";
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception {
int port = 1234; // default
if (argv.length > 0) {
port = Integer.parseInt(argv[0]);
}
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(GREETING.getBytes());
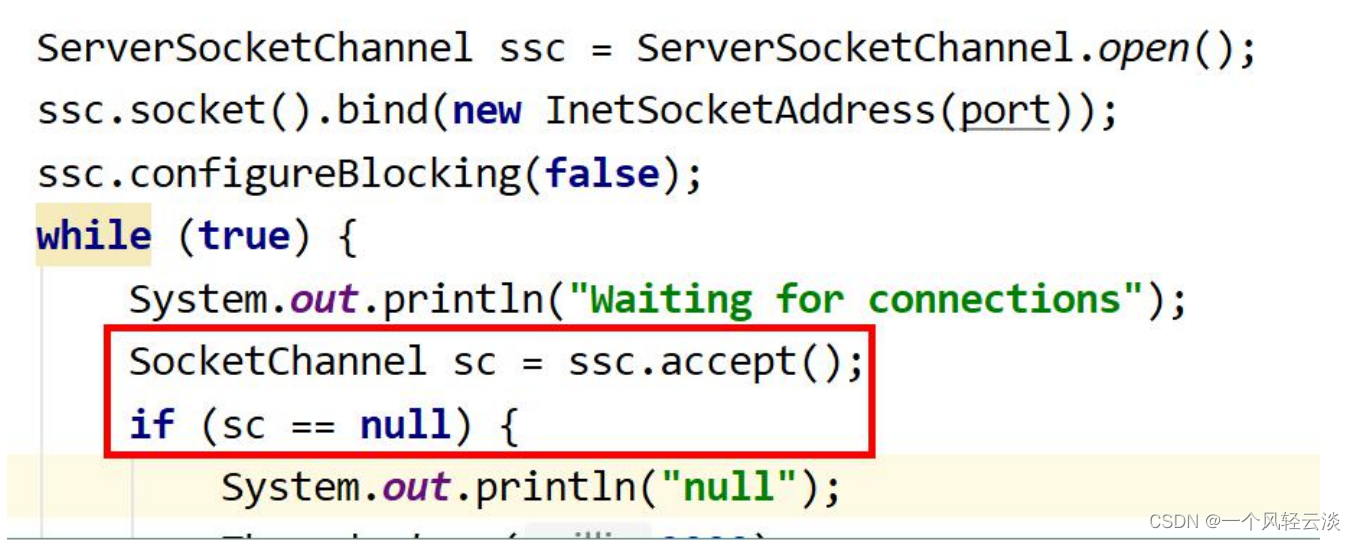
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port));
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
while (true) {
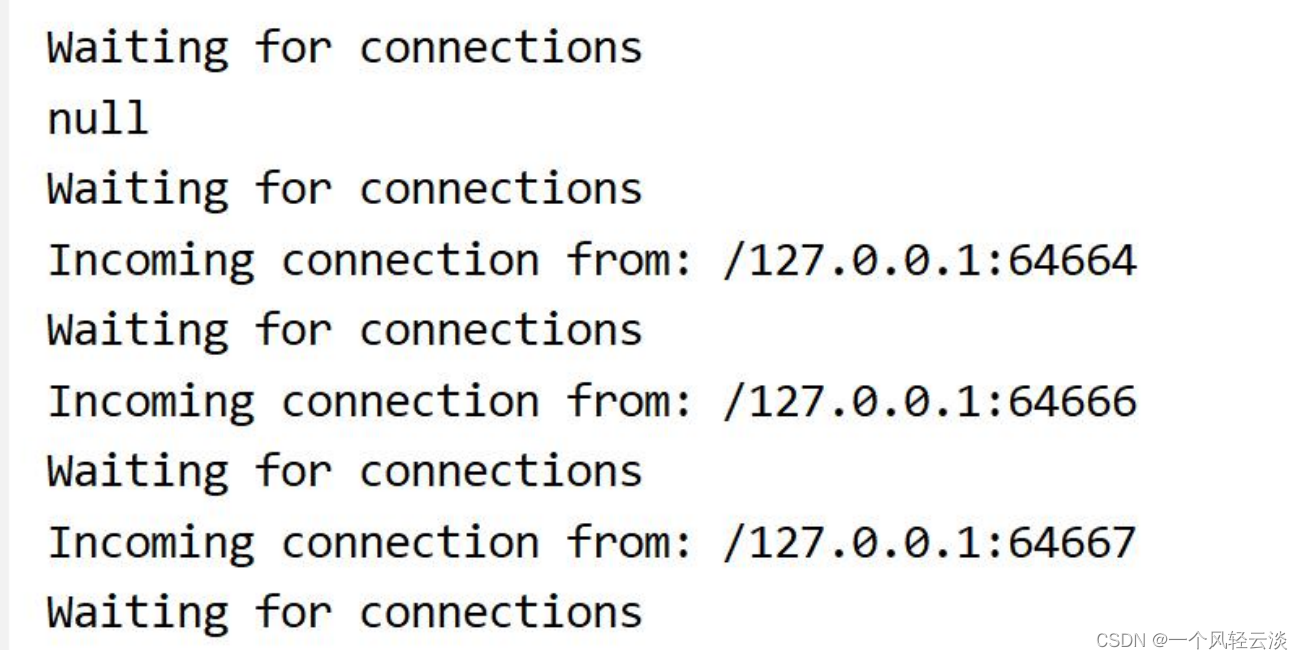
System.out.println("Waiting for connections");
SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();
if (sc == null) {
System.out.println("null");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} else {
System.out.println("Incoming connection from: " +
sc.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress());
buffer.rewind();
sc.write(buffer);
sc.close();
}
}
}
} 
打开 ServerSocketChannel
通过调用 ServerSocketChannel.open() 方法来打开 ServerSocketChannel.
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
关闭 ServerSocketChannel
通过调用 ServerSocketChannel.close() 方法来关闭 ServerSocketChannel.
serverSocketChannel.close();
监听新的连接
通过 ServerSocketChannel.accept() 方法监听新进的连接。当 accept()方法返回时候,它返回一个包含新进来的连接的 SocketChannel。因此, accept()方法会一直阻塞 到有新连接到达。
通常不会仅仅只监听一个连接,在 while 循环中调用 accept()方法. 如下面的例子:

阻塞模式
会在 SocketChannel sc = ssc.accept();这里阻塞住进程。
非阻塞模式
ServerSocketChannel 可以设置成非阻塞模式。在非阻塞模式下,accept() 方法会立 刻返回,如果还没有新进来的连接,返回的将是 null。 因此,需要检查返回的 SocketChannel 是否是 null.如:
SocketChannel
SocketChannel 介绍
Java NIO 中的 SocketChannel 是一个连接到 TCP 网络套接字的通道。
A selectable channel for stream-oriented connecting sockets.
以上是 Java docs 中对于 SocketChannel 的描述:SocketChannel 是一种面向流连接 sockets 套接字的可选择通道。从这里可以看出:
SocketChannel 是用来连接 Socket 套接字
SocketChannel 主要用途用来处理网络 I/O 的通道
SocketChannel 是基于 TCP 连接传输
SocketChannel 实现了可选择通道,可以被多路复用的
SocketChannel 特征
- 对于已经存在的 socket 不能创建 SocketChannel
- SocketChannel 中提供的 open 接口创建的 Channel 并没有进行网络级联,需要使 用 connect 接口连接到指定地址
- 未进行连接的 SocketChannle 执行 I/O 操作时,会抛出NotYetConnectedException
- SocketChannel 支持两种 I/O 模式:阻塞式和非阻塞式
- SocketChannel 支持异步关闭。如果 SocketChannel 在一个线程上 read 阻塞,另 一个线程对该 SocketChannel 调用 shutdownInput,则读阻塞的线程将返回-1 表示没有 读取任何数据;如果 SocketChannel 在一个线程上 write 阻塞,另一个线程对该 SocketChannel 调用 shutdownWrite,则写阻塞的线程将抛出AsynchronousCloseException
- SocketChannel 支持设定参数
- SO_SNDBUF 套接字发送缓冲区大小
- SO_RCVBUF 套接字接收缓冲区大小
- SO_KEEPALIVE 保活连接
- O_REUSEADDR 复用地址
- SO_LINGER 有数据传输时延缓关闭 Channel (只有在非阻塞模式下有用)
- TCP_NODELAY 禁用 Nagle 算法
创建 SocketChannel
方式一:
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new
InetSocketAddress("www.baidu.com", 80));方式二:
SocketChannel socketChanne2 = SocketChannel.open();
socketChanne2.connect(new InetSocketAddress("www.baidu.com", 80));直接使用有参 open api 或者使用无参 open api,但是在无参 open 只是创建了一个SocketChannel 对象,并没有进行实质的 tcp 连接。
连接校验
socketChannel.isOpen(); // 测试 SocketChannel 是否为 open 状态
socketChannel.isConnected(); //测试 SocketChannel 是否已经被连接
socketChannel.isConnectionPending(); //测试 SocketChannel 是否正在进行连接
socketChannel.finishConnect(); //校验正在进行套接字连接的 SocketChannel是否已经完成连接读写模式
前面提到 SocketChannel 支持阻塞和非阻塞两种模式:
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);通过以上方法设置 SocketChannel 的读写模式。false 表示非阻塞,true 表示阻塞。
读写
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(
new InetSocketAddress("www.baidu.com", 80));
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("read over");以上为阻塞式读,当执行到 read 出,线程将阻塞,控制台将无法打印 read over
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(
new InetSocketAddress("www.baidu.com", 80));
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(16);
socketChannel.read(byteBuffer);
socketChannel.close();
System.out.println("read over");以上为非阻塞读,控制台将打印 read over 读写都是面向缓冲区,这个读写方式与前文中的FileChannel 相同。
DatagramChannel
正如 SocketChannel 对应 Socket,ServerSocketChannel 对应 ServerSocket,每 一个 DatagramChannel 对象也有一个关联的 DatagramSocket 对象。正如 SocketChannel 模拟连接导向的流协议(如 TCP/IP),DatagramChannel 则模拟包 导向的无连接协议(如 UDP/IP)。DatagramChannel 是无连接的,每个数据报 (datagram)都是一个自包含的实体,拥有它自己的目的地址及不依赖其他数据报的 数据负载。与面向流的的 socket 不同,DatagramChannel 可以发送单独的数据报给 不同的目的地址。同样,DatagramChannel 对象也可以接收来自任意地址的数据包。 每个到达的数据报都含有关于它来自何处的信息(源地址)
打开 DatagramChannel
DatagramChannel server = DatagramChannel.open();
server.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(10086));此例子是打开 10086 端口接收 UDP 数据包
接收数据
通过 receive()接收 UDP 包
ByteBuffer receiveBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
receiveBuffer.clear();
SocketAddress receiveAddr = server.receive(receiveBuffer);SocketAddress 可以获得发包的 ip、端口等信息,用 toString 查看,格式如下 /127.0.0.1:57126
发送数据
通过 send()发送 UDP 包
DatagramChannel server = DatagramChannel.open();
ByteBuffer sendBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("client send".getBytes());
server.send(sendBuffer, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10086));连接
UDP 不存在真正意义上的连接,这里的连接是向特定服务地址用 read 和 write 接收发送数据包。
client.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",10086));
int readSize= client.read(sendBuffer);
server.write(sendBuffer);read()和 write()只有在 connect()后才能使用,不然会抛 NotYetConnectedException 异常。用 read()接收时,如果没有接收到包,会抛 PortUnreachableException 异常。
DatagramChannel 示例
客户端发送,服务端接收的例子
/**
* 发包的 datagram
*
* @throws IOException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Test
public void sendDatagram() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
DatagramChannel sendChannel= DatagramChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress sendAddress= new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",
9999);
while (true) {
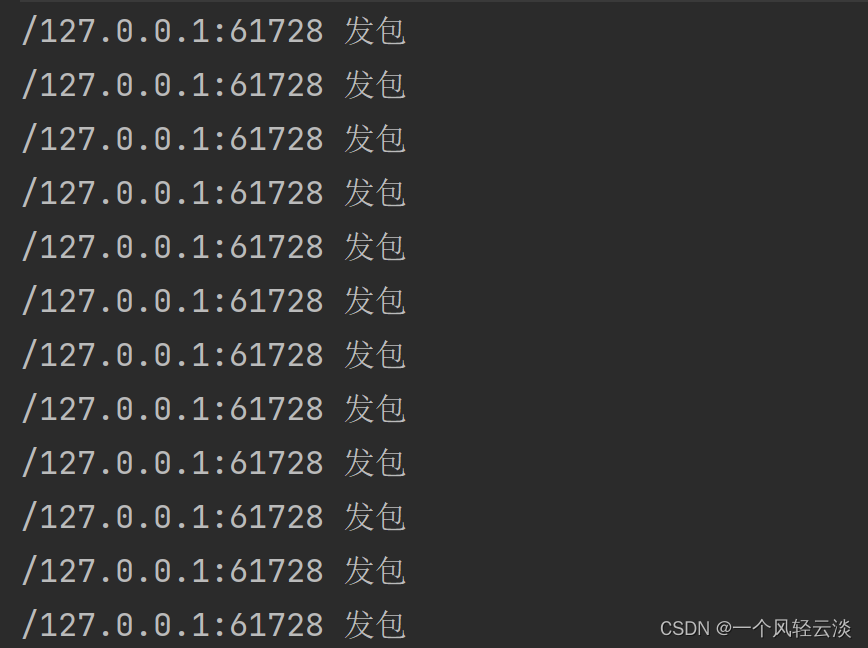
sendChannel.send(ByteBuffer.wrap("发包".getBytes("UTF-8")), sendAddress);
System.out.println("发包端发包");
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
}
/**
* 收包端
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void receive() throws IOException {
DatagramChannel receiveChannel= DatagramChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress receiveAddress= new InetSocketAddress(9999);
receiveChannel.bind(receiveAddress);
ByteBuffer receiveBuffer= ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while (true) {
receiveBuffer.clear();
SocketAddress sendAddress= receiveChannel.receive(receiveBuffer);
receiveBuffer.flip();
System.out.print(sendAddress.toString() + " ");
System.out.println(Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(receiveBuffer));
}
} 
/**
* 只接收和发送 9999 的数据包
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void testConect1() throws IOException {
DatagramChannel connChannel = DatagramChannel.open();
connChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9998));
connChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9999));
connChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap("发包".getBytes("UTF-8")));
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while (true) {
try {
readBuffer.clear();
connChannel.read(readBuffer);
readBuffer.flip();
System.out.println(Charset.forName("UTF-8").decode(readBuffer));
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}