目录
46. 全排列 Permutations 🌟🌟
47. 全排列 II Permutations II 🌟🌟
48. 旋转图像 Rotate Image 🌟🌟
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏 🌟
Golang每日一练 专栏
Python每日一练 专栏
C/C++每日一练 专栏
Java每日一练 专栏
46. 全排列 Permutations
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1] 输出:[[0,1],[1,0]]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1] 输出:[[1]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 6-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有整数 互不相同
代码: 回溯法
fn permute(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut res: Vec<Vec<i32>> = Vec::new();
if nums.len() == 0 {
return res;
}
let mut used: Vec<bool> = vec![false; nums.len()];
fn backtrack(path: &mut Vec<i32>, res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, nums: &Vec<i32>, used: &mut Vec<bool>) {
if path.len() == nums.len() {
let tmp = path.clone();
res.push(tmp);
return;
}
for i in 0..nums.len() {
if !used[i] {
used[i] = true;
path.push(nums[i]);
backtrack(path, res, nums, used);
path.pop();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
backtrack(&mut Vec::new(), &mut res, &nums, &mut used);
return res;
}
fn main() {
println!("{:?}", permute(vec![1, 2, 3]));
println!("{:?}", permute(vec![0, 1]));
println!("{:?}", permute(vec![1]));
}输出:
[[1, 2, 3], [1, 3, 2], [2, 1, 3], [2, 3, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 2, 1]]
[[0, 1], [1, 0]]
[[1]]
代码2: 字典序法
fn permute(nums: &mut [i32]) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut res = vec![];
if nums.len() == 1 {
res.push(nums.to_vec());
return res;
}
nums.sort();
loop {
let tmp = nums.to_vec();
res.push(tmp);
let (mut i, mut j) = (nums.len() - 2, nums.len() - 1);
while i > 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1] {
i -= 1;
}
if i == 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1] {
break;
}
while nums[j] <= nums[i] {
j -= 1;
}
nums.swap(i, j);
nums[i + 1..].reverse();
}
res
}
fn main() {
let mut nums = [1, 2, 3];
println!("{:?}", permute(&mut nums));
let mut nums = [0, 1];
println!("{:?}", permute(&mut nums));
let mut nums = [1];
println!("{:?}", permute(&mut nums));
}
代码3: DFS
fn permute(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
fn dfs(nums: &Vec<i32>, index: usize, p: &mut Vec<i32>, res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, used: &mut Vec<bool>) {
if index == nums.len() {
let temp = p.clone();
res.push(temp);
return;
}
for i in 0..nums.len() {
if !used[i] {
used[i] = true;
p.push(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, index + 1, p, res, used);
p.pop();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
if nums.len() == 0 {
return vec![];
}
let mut used: Vec<bool> = vec![false; nums.len()];
let mut p: Vec<i32> = vec![];
let mut res: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![];
dfs(&nums, 0, &mut p, &mut res, &mut used);
return res;
}
fn main() {
println!("{:?}", permute(vec![1, 2, 3]));
println!("{:?}", permute(vec![0, 1]));
println!("{:?}", permute(vec![1]));
}47. 全排列 II Permutations II
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列 nums ,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,2] 输出: [[1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 8-10 <= nums[i] <= 10
代码1: 回溯法
fn permute_unique(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
fn backtrack(path: &mut Vec<i32>, res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, nums: &Vec<i32>, used: &mut Vec<bool>) {
if path.len() == nums.len() {
let tmp = path.clone();
res.push(tmp);
return;
}
for i in 0..nums.len() {
if used[i] || (i > 0 && !used[i - 1] && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
path.push(nums[i]);
backtrack(path, res, nums, used);
path.pop();
used[i] = false;
}
}
let mut nums_copy = nums.clone();
nums_copy.sort();
let mut used: Vec<bool> = vec![false; nums.len()];
let mut path: Vec<i32> = vec![];
let mut res: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![];
backtrack(&mut path, &mut res, &nums_copy, &mut used);
return res;
}
fn main() {
println!("{:?}", permute_unique(vec![1, 1, 2]));
println!("{:?}", permute_unique(vec![1, 2, 3]));
}输出:
[[1, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [2, 1, 1]]
[[1, 2, 3], [1, 3, 2], [2, 1, 3], [2, 3, 1], [3, 1, 2], [3, 2, 1]]
代码2: 字典序法
fn permute_unique(nums: &mut [i32]) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut res = vec![];
if nums.is_empty() {
return res;
}
nums.sort();
let len = nums.len();
let (mut i, mut j) = (len - 2, len - 1);
loop {
let tmp = nums.to_vec();
res.push(tmp);
while i > 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1] {
i -= 1;
}
if i == 0 && nums[i] >= nums[i + 1] {
break;
}
while j > 0 && nums[j] <= nums[i] {
j -= 1;
}
if nums[j] == nums[i] && j > i + 1 {
continue;
}
nums.swap(i, j);
nums[i + 1..].reverse();
if i == 0 && j == 1 {
break;
}
i = len - 2;
j = len - 1;
}
res
}
fn main() {
let mut nums = [1, 1, 2];
println!("{:?}", permute_unique(&mut nums));
let mut nums = [1, 2, 3];
println!("{:?}", permute_unique(&mut nums));
}
代码3: DFS
fn permute_unique(nums: &mut [i32]) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut res = vec![];
if nums.is_empty() {
return res;
}
let mut used = vec![false; nums.len()];
let mut p = vec![];
nums.sort();
dfs(nums, 0, &mut p, &mut res, &mut used);
res
}
fn dfs(nums: &[i32], index: usize, p: &mut Vec<i32>, res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, used: &mut [bool]) {
if index == nums.len() {
res.push(p.clone());
return;
}
for i in 0..nums.len() {
if !used[i] {
if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1] {
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
p.push(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, index + 1, p, res, used);
p.pop();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
fn main() {
let mut nums = [1, 1, 2];
println!("{:?}", permute_unique(&mut nums));
let mut nums = [1, 2, 3];
println!("{:?}", permute_unique(&mut nums));
}
fn permute_unique(nums: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
fn dfs(nums: &[i32], index: usize, p: &mut Vec<i32>, res: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>, used: &mut [bool]) {
if index == nums.len() {
res.push(p.clone());
return;
}
for i in 0..nums.len() {
if !used[i] {
if i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1] {
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
p.push(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, index + 1, p, res, used);
p.pop();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
if nums.is_empty() {
return vec![];
}
let mut nums_copy = nums.clone();
nums_copy.sort();
let mut res: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![];
let mut used = vec![false; nums.len()];
dfs(&nums_copy, 0, &mut vec![], &mut res, &mut used);
res
}
fn main() {
println!("{:?}", permute_unique(vec![1, 1, 2]));
println!("{:?}", permute_unique(vec![1, 2, 3]));
}48. 旋转图像 Rotate Image
给定一个 n × n 的二维矩阵 matrix 表示一个图像。请你将图像顺时针旋转 90 度。
你必须在
原地 旋转图像,这意味着你需要直接修改输入的二维矩阵。请不要 使用另一个矩阵来旋转图像。
示例 1:
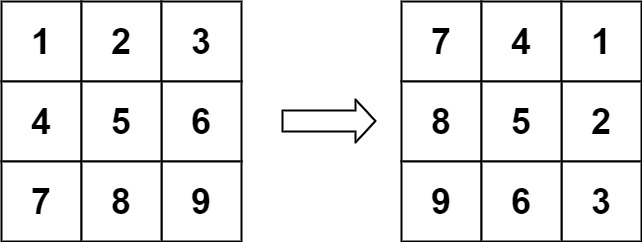
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 输出:[[7,4,1],[8,5,2],[9,6,3]]
示例 2:
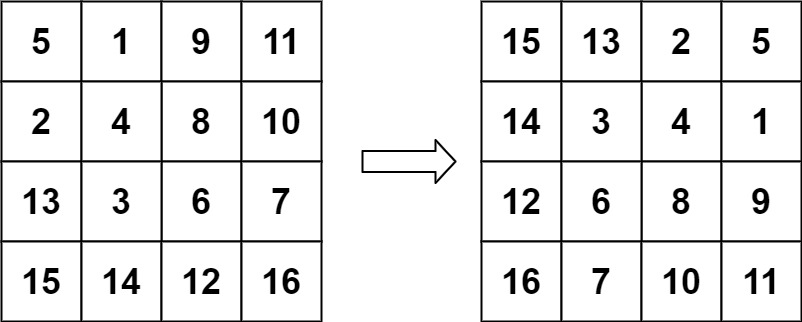
输入:matrix = [[5,1,9,11],[2,4,8,10],[13,3,6,7],[15,14,12,16]] 输出:[[15,13,2,5],[14,3,4,1],[12,6,8,9],[16,7,10,11]]
提示:
n == matrix.length == matrix[i].length1 <= n <= 20-1000 <= matrix[i][j] <= 1000
代码1: 转置加翻转
先转置矩阵,然后翻转每一行即可得到顺时针旋转 90 度后的矩阵。
fn rotate(matrix: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) {
let n = matrix.len();
// 转置矩阵
for i in 0..n {
for j in i..n {
let temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i] = temp;
}
}
// 翻转每一行
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..n / 2 {
let temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i][n - j - 1];
matrix[i][n - j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
fn main() {
let mut matrix = vec![vec![1, 2, 3], vec![4, 5, 6], vec![7, 8, 9]];
rotate(&mut matrix);
println!("{:?}", matrix);
let mut matrix = vec![vec![5, 1, 9, 11], vec![2, 4, 8, 10], vec![13, 3, 6, 7], vec![15, 14, 12, 16]];
rotate(&mut matrix);
println!("{:?}", matrix);
}
输出:
[[7, 4, 1], [8, 5, 2], [9, 6, 3]]
[[15, 13, 2, 5], [14, 3, 4, 1], [12, 6, 8, 9], [16, 7, 10, 11]]
代码2: 分块翻转
将矩阵分成四个部分,并将每个部分按顺时针旋转 90 度。
fn rotate(matrix: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) {
let n = matrix.len();
// 转置矩阵
for i in 0..n {
for j in i..n {
let temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i] = temp;
}
}
// 翻转每一行
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..n / 2 {
let temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i][n - j - 1];
matrix[i][n - j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
fn main() {
let mut matrix = vec![vec![1, 2, 3], vec![4, 5, 6], vec![7, 8, 9]];
rotate(&mut matrix);
println!("{:?}", matrix);
let mut matrix = vec![vec![5, 1, 9, 11], vec![2, 4, 8, 10], vec![13, 3, 6, 7], vec![15, 14, 12, 16]];
rotate(&mut matrix);
println!("{:?}", matrix);
}
代码3: 对角线变换+水平翻转
将矩阵分成四个部分,并将每个部分按顺时针旋转 90 度。
fn rotate(matrix: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) {
let row = matrix.len();
if row <= 0 {
return;
}
let column = matrix[0].len();
// 对角线变换
for i in 0..row {
for j in i + 1..column {
let temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i] = temp;
}
}
// 竖直轴对称翻转
let half_column = column / 2;
for i in 0..row {
for j in 0..half_column {
let temp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[i][column - j - 1];
matrix[i][column - j - 1] = temp;
}
}
}
fn main() {
let mut matrix = vec![vec![1, 2, 3], vec![4, 5, 6], vec![7, 8, 9]];
rotate(&mut matrix);
println!("{:?}", matrix);
let mut matrix = vec![vec![5, 1, 9, 11], vec![2, 4, 8, 10], vec![13, 3, 6, 7], vec![15, 14, 12, 16]];
rotate(&mut matrix);
println!("{:?}", matrix);
}
翻转+旋转原理C代码
/*
* clockwise rotate 顺时针旋转
* first reverse up to down, then swap the symmetry
* 1 2 3 7 8 9 7 4 1
* 4 5 6 => 4 5 6 => 8 5 2
* 7 8 9 1 2 3 9 6 3
*/
void rotate(vector<vector<int> > &matrix) {
reverse(matrix.begin(), matrix.end());
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < matrix[i].size(); ++j)
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);
}
}
/*
* anticlockwise rotate 逆时针旋转
* first reverse left to right, then swap the symmetry
* 1 2 3 3 2 1 3 6 9
* 4 5 6 => 6 5 4 => 2 5 8
* 7 8 9 9 8 7 1 4 7
*/
void anti_rotate(vector<vector<int> > &matrix) {
for (auto vi : matrix) reverse(vi.begin(), vi.end());
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < matrix[i].size(); ++j)
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);
}
}
🌟 每日一练刷题专栏 🌟
✨ 持续,努力奋斗做强刷题搬运工!
👍 点赞,你的认可是我坚持的动力!
🌟 收藏,你的青睐是我努力的方向!
✎ 评论,你的意见是我进步的财富!
☸ 主页:https://hannyang.blog.csdn.net/
|
| Rust每日一练 专栏(2023.5.16~)更新中... |
|
| Golang每日一练 专栏(2023.3.11~)更新中... |
|
| Python每日一练 专栏(2023.2.18~2023.5.18)暂停更 |
|
| C/C++每日一练 专栏(2023.2.18~2023.5.18)暂停更 |
|
| Java每日一练 专栏(2023.3.11~2023.5.18)暂停更 |