一、获取bean的三种方式:
1.根据bean的id获取:
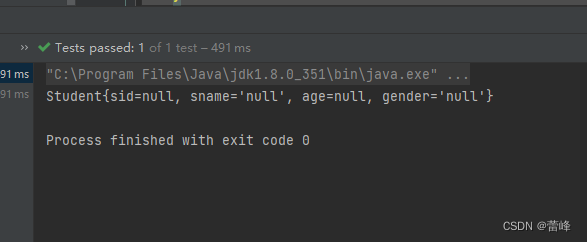
Student studentOne = (Student) ioc.getBean("studentOne");2.获取bean所需要的类型的class对象:
Student student = ioc.getBean(Student.class);我们运行之后如下所示:
如果我们在bean里面添加如下代码:
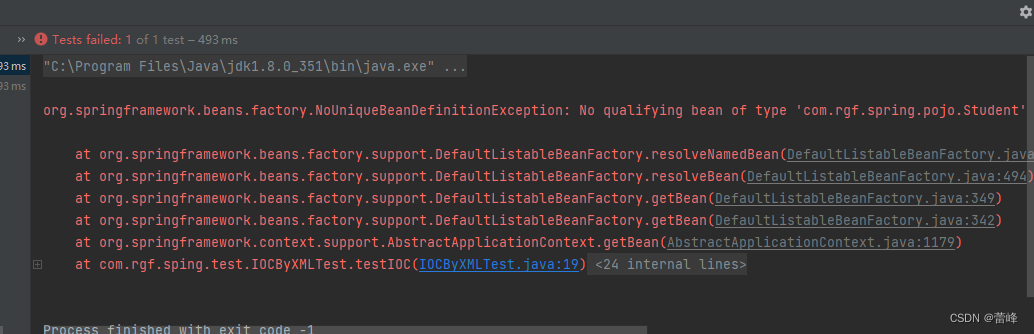
<bean id="studentOne" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"></bean> <bean id="studentTwo" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"></bean>我们发现运行之后,如下所示:
面对这种情况,我们要确保只有一个,即为单例的。
设置单例还是多例:
根据类型获取bean时,要求IOC容器中有且只有一个类型匹配的bean
若没有任何一个类型匹配的bean,此时抛出异常:NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
若有多个类型匹配的bean,此时抛出异常:NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException
3.根据bean的id和类型获取:
获取bean,获取bean所需要的类型和id
Student student = ioc.getBean("studentOne", Student.class);注意:当根据类型获取Bean时,要求ioc容器中指定类型的bean有且只能有一个
扩展:如果组件类(交给IOC管理的类)实现了接口,根据接口类型可以获取bean:
我们创建接口Person:
package com.rgf.spring.pojo; public interface Person { }之后我们让该类Student继承该接口:
package com.rgf.spring.pojo; public class Student implements Person{ private Integer sid; private String sname; private Integer age; private String gender; public Student() { } public Student(Integer sid, String sname, Integer age, String gender) { this.sid = sid; this.sname = sname; this.age = age; this.gender = gender; } public Integer getSid() { return sid; } public void setSid(Integer sid) { this.sid = sid; } public String getSname() { return sname; } public void setSname(String sname) { this.sname = sname; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public String getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "sid=" + sid + ", sname='" + sname + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", gender='" + gender + '\'' + '}'; } }之后我们进入测试类如下所示:
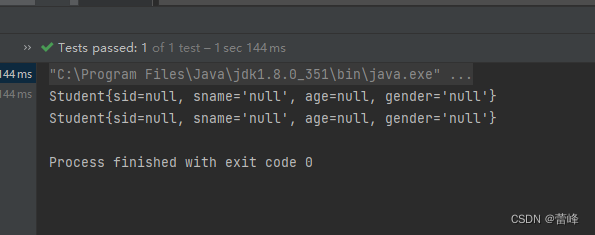
package com.rgf.sping.test; import com.rgf.spring.pojo.Person; import com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class IOCByXMLTest { /** * 获取bean的三种方式: * 1.根据bean的id获取 * 2.根据bean的类型获取 * 注意:根据类型获取bean时,要求ioc容器中有且只有一个类型匹配的bean。 * 若没有任何一个类型匹配的bean,此时抛出异常:NoSuchBeanDefinitionException * 若有多个类型类型匹配的bean,此时抛出异常:BeanDefinitionParsingException * 3.根据bean的id和类型获取 * 结论: * 根据类型来获取Bean时,在满足bean唯一性的前提下,其实只是看:|对象 instanceof 指定的类型|的返回的结果, * 只要返回的是true,就可以认定为和类型匹配,能够获取到。 * 即通过bean的类型,bean所继承的类的类型,bean所实现的接口的类型都可以获取bean */ @Test public void testIOC(){ //获取IOC容器 ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml"); //获取bean,获取bean所需要的类型和id // Student student = ioc.getBean("studentOne", Student.class); //System.out.println(student); //我们当前通过Student类型获取了bean之后,把咱们所获取的对象通过向上转型赋值给了他的接口对象 Person student = ioc.getBean(Student.class); System.out.println(student); Person person = ioc.getBean(Person.class); System.out.println(person); } }我们运行之后如下所示:
我们可以通过接口类型来获取bean,但是前提是bean是唯一的。
如果一个接口有多个实现类,这些实现类都配置了bean,根据接口类是不可以获取bean的,因为bean是不唯一的呢
根据类型来获取Bean时,在满足bean唯一性的前提下,其实只是看:对象 instanceof 指定的类型 的返回的结果,只要返回的是true,就可以认定为和类型匹配,能够获取到。
二、依赖注入
1.依赖注入之setter注入:
IOC资源注入的一个具体实现为依赖注入:
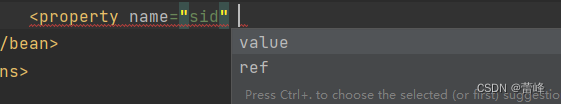
ref为引用,value为赋一个普通的值。
我们在IOC文件里面写入如下所示:
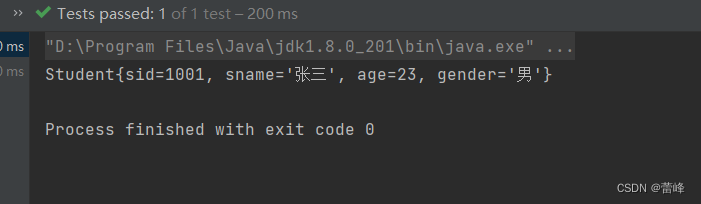
<bean id="studentTwo" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <property name="sid" value="1001"></property> <property name="sname" value="张三"></property> <property name="age" value="23"></property> <property name="gender" value="男"></property> </bean>property:通过成员变量的set方法进行赋值
name:设置需要赋值的属性名(和set方法有关)
value:设置为属性所赋的值
我们的测试类如下所示:
@Test public void TestDI(){ //获取IOC容器 ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml"); Student student = ioc.getBean("studentTwo", Student.class); System.out.println(student); }运行之后如下所示:
2.依赖注入之构造器注入(有参构造)
我们在student里面的有参构造如下所示:
public Student(Integer sid, String sname, Integer age, String gender) { this.sid = sid; this.sname = sname; this.age = age; this.gender = gender; }我们进行设置构造器注入:
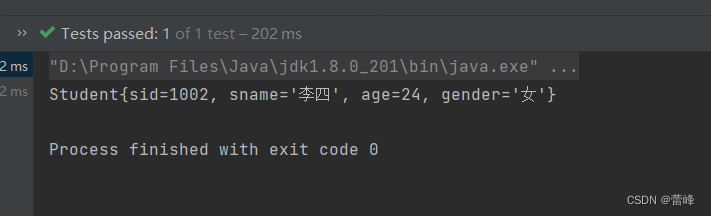
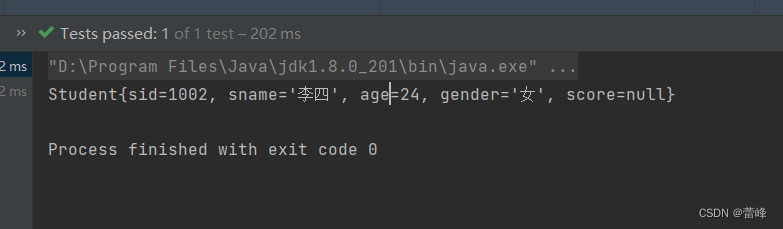
<bean id="studentThree" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <!--如果只有一个有参构造,则可以直接来为我们按照参数顺序进行赋值--> <!--利用有参构造对依赖进行注入所用标签为:constructor-arg--> <constructor-arg value="1002"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="李四"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="24"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="女"></constructor-arg> </bean>我们的测试类如下所示:
@Test public void TestDI(){ //获取IOC容器 ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml"); Student student = ioc.getBean("studentThree", Student.class); System.out.println(student); }我们运行之后如下所示:
当我们创建多个构造器如下所示:
public Student(Integer sid, String sname, String gender,Integer age) { this.sid = sid; this.sname = sname; this.gender = gender; this.age = age; } public Student(Integer sid, String sname, String gender,Double score) { this.sid = sid; this.sname = sname; this.gender = gender; this.score=score; }我们的bean如下所示:
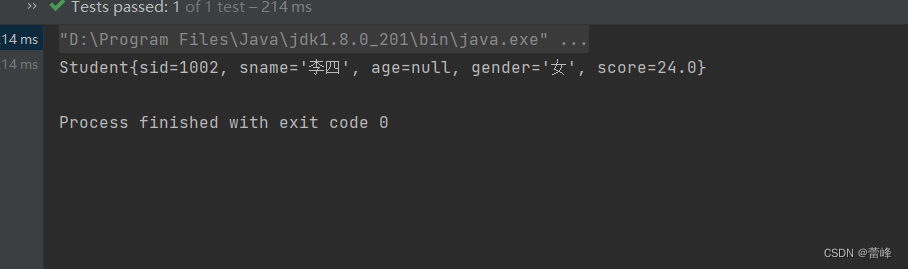
<bean id="studentThree" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <!--如果只有一个有参构造,则可以直接来为我们按照参数顺序进行赋值--> <!--利用有参构造对依赖进行注入所用标签为:constructor-arg--> <constructor-arg value="1002"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="李四"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="女"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="24" ></constructor-arg> </bean>我们运行之后如下所示:
此时我们发现age为null,当有多个构造器的时候,我们进行如下所示:
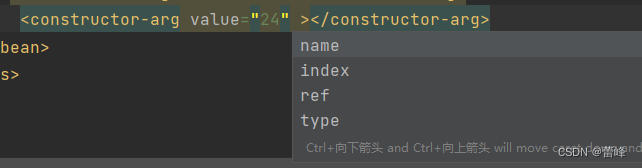
type:设置当前参数的类型
ref:引用
name:参数名
index:索引
我们修改如下所示:
<bean id="studentThree" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <!--如果只有一个有参构造,则可以直接来为我们按照参数顺序进行赋值--> <!--利用有参构造对依赖进行注入所用标签为:constructor-arg--> <constructor-arg value="1002"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="李四"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="女"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="24" name="age"></constructor-arg> </bean>测试之后如下所示:
3.依赖注入之特殊值处理
(1)字面量赋值
赋值空对象,利用如下所示:利用<null/>标签,赋值空对象
<bean id="studentFour" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <property name="sid" value="1002"></property> <property name="sname" value="王五"></property> <property name="gender" > <null/> </property> </bean>我们要在赋值里面采用特殊字符:
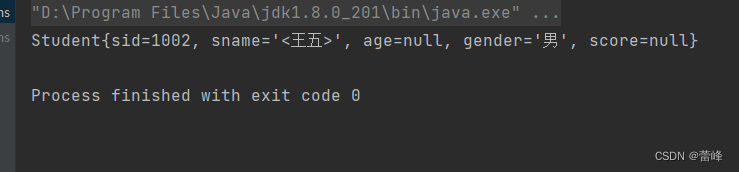
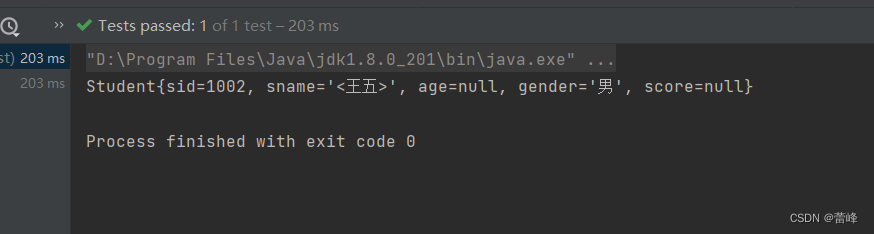
小于号在XML文档中用来定义标签的开始,不能随便使用(<:< >:>)
<property name="sname" value="<王五>"></property>则会报错,我们应该如下所示进行利用:
<property name="sname" value="<王五>"></property>我们运行之后如下所示:
<:< >:%gt;
CDATA中的C代表Character,是文本、字符的含义,CDATA就表示纯文本数据
XML解析器看到CDATA节就知道这里是纯文本,就不会当作XML标签或属性来解析
<property name="sname"><value><![CDATA[<王五>]]></value></property> <!--快捷键为CD-->我们运行之后如下所示:
CDATA节其中的内容会原样解析<![CDATA[...]]>
CDATA节是xml中一个特殊的标签,因此不能写在一个属性中
4. 依赖注入之为类类型的属性赋值
4.1引用外部的bean
我们进行创建Clazz类:
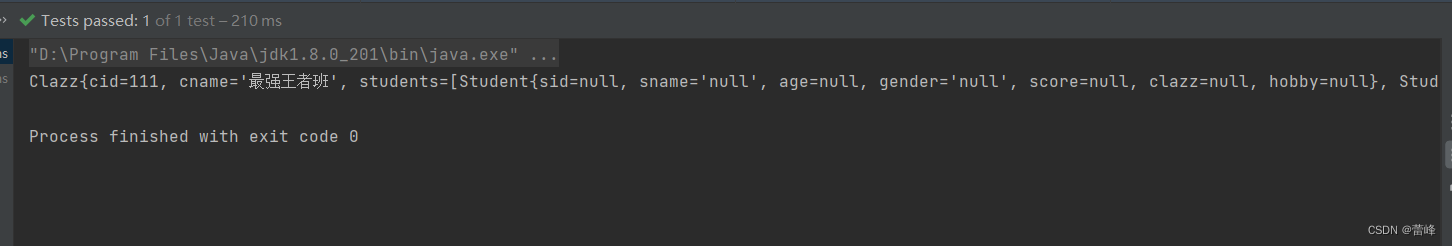
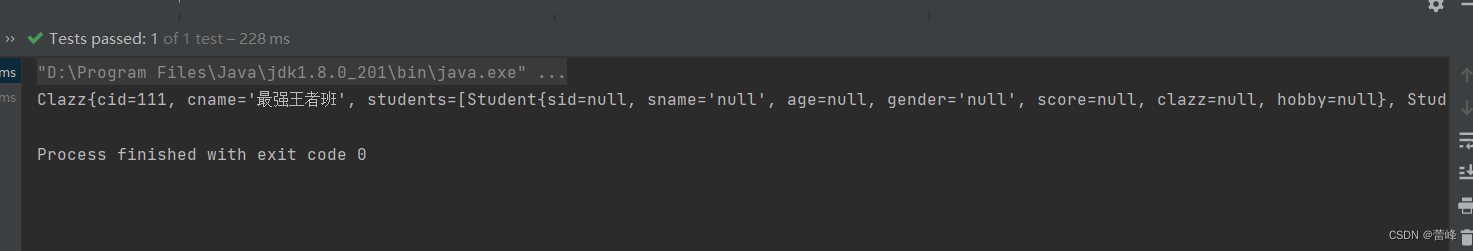
package com.rgf.spring.pojo; public class Clazz { private Integer cid; private String cname; public Clazz() { } public Clazz(Integer cid, String cname) { this.cid = cid; this.cname = cname; } public Integer getCid() { return cid; } public void setCid(Integer cid) { this.cid = cid; } public String getCname() { return cname; } public void setCname(String cname) { this.cname = cname; } @Override public String toString() { return "Clazz{" + "cid=" + cid + ", cname='" + cname + '\'' + '}'; } }我们在配置文件里面加载如下bean:
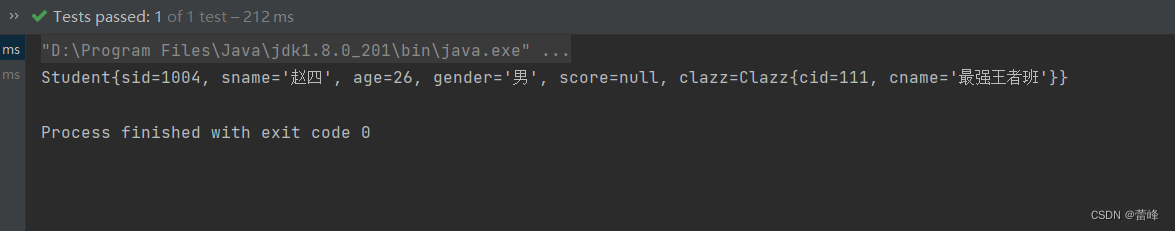
<bean id="studentFive" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <property name="sid" value="1004"></property> <property name="sname" value="赵四"></property> <property name="age" value="26"></property> <property name="gender" value="男"></property> <property name="clazz" ref="classOne"></property> </bean> <bean id="classOne" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Clazz"> <property name="cid" value="111"></property> <property name="cname" value="最强王者班"></property> </bean>ref:引用IOC容器中的某个bean的id,然后把我们当前的这个bean所对应的对象来为当前的属性进行赋值。
我们进行测试如下:
@Test public void TestDI(){ //获取IOC容器 ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml"); Student student = ioc.getBean("studentFive", Student.class); System.out.println(student); }运行之后如下所示:
4.2级联方式
通过我们当前对象.属性来进行赋值,
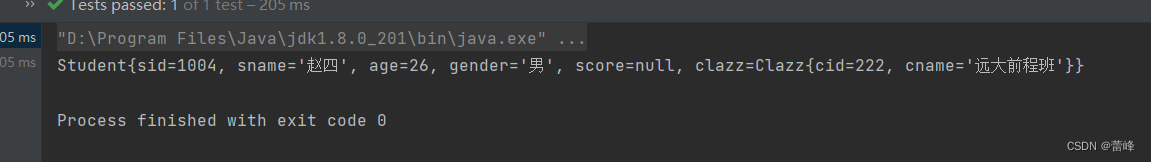
<bean id="studentFive" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <property name="sid" value="1004"></property> <property name="sname" value="赵四"></property> <property name="age" value="26"></property> <property name="gender" value="男"></property> <property name="clazz.cid" value="222"></property> <property name="clazz.cname" value="远大前程班"></property> </bean>我们进行测试之后发现进行了报错。
我们发现先将此进行赋值之后,不再报错:
<bean id="clazzOne" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Clazz"> <property name="cid" value="111"></property> <property name="cname" value="最强王者班"></property> </bean> <bean id="studentSix" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <property name="sid" value="1004"></property> <property name="sname" value="赵四"></property> <property name="age" value="26"></property> <property name="gender" value="男"></property> <property name="clazz" ref="clazzOne"></property> <property name="clazz.cid" value="222"></property> <property name="clazz.cname" value="远大前程班"></property> </bean>
相当于对此进行修改,
级联的方式,要保证提前为clazz属性赋值或者实例化
4.3内部bean
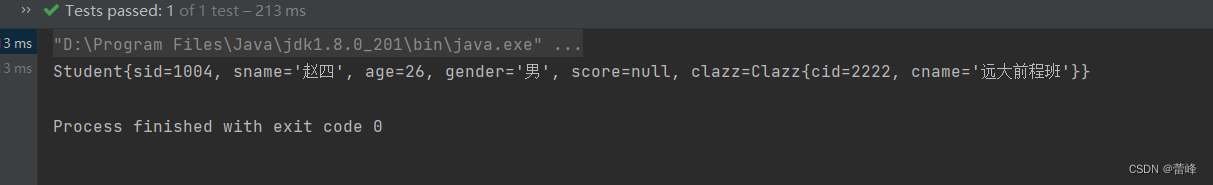
<bean id="studentSix" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <property name="sid" value="1004"></property> <property name="sname" value="赵四"></property> <property name="age" value="26"></property> <property name="gender" value="男"></property> <property name="clazz"> <bean id="clazzInner" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Clazz"> <property name="cid" value="2222"></property> <property name="cname" value="远大前程班"></property> </bean> </property>我们测试如下:
@Test public void TestDI(){ //获取IOC容器 ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml"); Student student = ioc.getBean("studentSix", Student.class); System.out.println(student); }我们运行之后如下所示:
内部bean是否能在bean的内部来使用:
我们进行测试如下所示:
@Test public void TestDI(){ //获取IOC容器 ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml"); Clazz clazz = ioc.getBean("clazzInner", Clazz.class); System.out.println(clazz); }运行之后我们发现出现了报错:NoSuchBeanDefinitionException
所以内部bean只能在当前bean的内部使用,不能直接通过IOC容器来获取的。
5.依赖注入之为数组类型的属性赋值
package com.rgf.spring.pojo; import java.util.Arrays; public class Student implements Person { private Integer sid; private String sname; private Integer age; private String gender; private Double score; private Clazz clazz; private String[] hobby; public String[] getHobby() { return hobby; } public void setHobby(String[] hobby) { this.hobby = hobby; } public Student() { } public Clazz getClazz() { return clazz; } public void setClazz(Clazz clazz) { this.clazz = clazz; } public Double getScore() { return score; } @Override public String toString() { return "Student{" + "sid=" + sid + ", sname='" + sname + '\'' + ", age=" + age + ", gender='" + gender + '\'' + ", score=" + score + ", clazz=" + clazz + ", hobby=" + Arrays.toString(hobby) + '}'; } public void setScore(Double score) { this.score = score; } public Student(Integer sid, String sname, String gender,Integer age) { this.sid = sid; this.sname = sname; this.gender = gender; this.age = age; } public Student(Integer sid, String sname, String gender,Double score) { this.sid = sid; this.sname = sname; this.gender = gender; this.score=score; } public Integer getSid() { return sid; } public void setSid(Integer sid) { this.sid = sid; } public String getSname() { return sname; } public void setSname(String sname) { this.sname = sname; } public Integer getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(Integer age) { this.age = age; } public String getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(String gender) { this.gender = gender; } }我们载入如下bean:
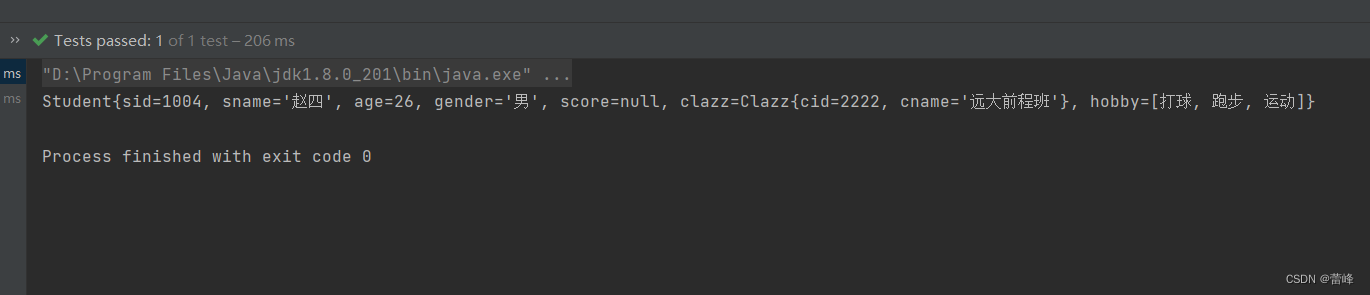
<bean id="studentSix" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <property name="sid" value="1004"></property> <property name="sname" value="赵四"></property> <property name="age" value="26"></property> <property name="gender" value="男"></property> <property name="clazz"> <bean id="clazzInner" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Clazz"> <property name="cid" value="2222"></property> <property name="cname" value="远大前程班"></property> </bean> </property> <!--字面量数值--> <property name="hobby"> <array> <value>打球</value> <value>跑步</value> <value>运动</value> </array> </property>我们测试之后如下所示:
如果是类类型的数组,我们将如下所示:
<property name="hobby"> <array> <ref bean="" </array> </property> <!--类类型的数组id放入即可-->
6.依赖注入之为list集合类型的属性赋值
我们进行创建如下类:
package com.rgf.spring.pojo; import java.util.List; public class Clazz { private Integer cid; private String cname; private List<Student> students; public List<Student> getStudents() { return students; } public void setStudents(List<Student> students) { this.students = students; } public Clazz() { } public Clazz(Integer cid, String cname) { this.cid = cid; this.cname = cname; } public Integer getCid() { return cid; } public void setCid(Integer cid) { this.cid = cid; } public String getCname() { return cname; } public void setCname(String cname) { this.cname = cname; } @Override public String toString() { return "Clazz{" + "cid=" + cid + ", cname='" + cname + '\'' + ", students=" + students + '}'; } }我们为集合载入bean:
<bean id="clazzOne" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Clazz"> <property name="cid" value="111"></property> <property name="cname" value="最强王者班"></property> <property name="students"> <list> <ref bean="studentOne"></ref> <ref bean="studentTwo"></ref> <ref bean="studentThree"></ref> </list> </property> </bean>我们所调用的bean内容如下:
<bean id="studentOne" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"></bean> <bean id="studentTwo" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <property name="sid" value="1001"></property> <property name="sname" value="张三"></property> <property name="age" value="23"></property> <property name="gender" value="男"></property> </bean> <bean id="studentThree" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <!--如果只有一个有参构造,则可以直接来为我们按照参数顺序进行赋值--> <!--利用有参构造对依赖进行注入所用标签为:constructor-arg--> <constructor-arg value="1002"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="李四"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="女"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg value="24" name="age"></constructor-arg> </bean>我们测试类如下所示:
@Test public void TestDI(){ //获取IOC容器 ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml"); Clazz clazz = ioc.getBean("clazzOne", Clazz.class); System.out.println(clazz); }我们进行运行之后如下所示:
我们里面的集合类型的bean,如下所示:
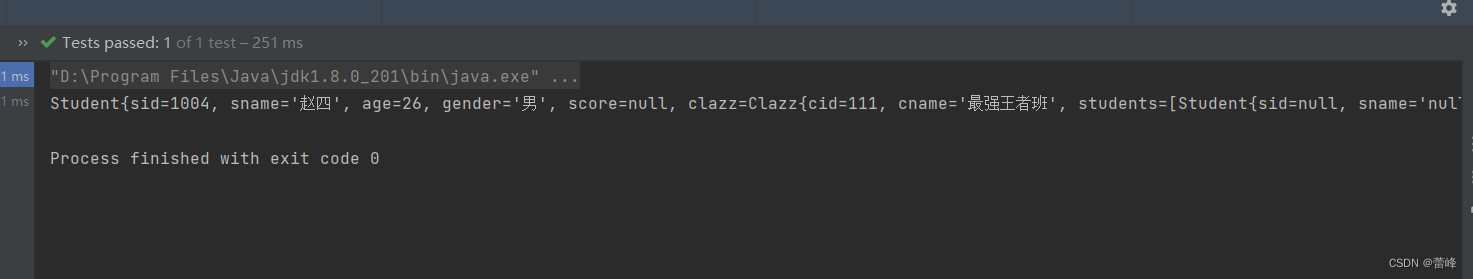
<bean id="clazzOne" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Clazz"> <property name="cid" value="111"></property> <property name="cname" value="最强王者班"></property> <property name="students" ref="studentList"></property> </bean> <!--配置一个集合类型的bean,需要使用util的约束--> <util:list id="studentList"> <ref bean="studentOne"></ref> <ref bean="studentTwo"></ref> <ref bean="studentThree"></ref> </util:list>我们继续进行测试,发现与我们所看到的一致:
7.依赖注入之为map集合类型的属性赋值
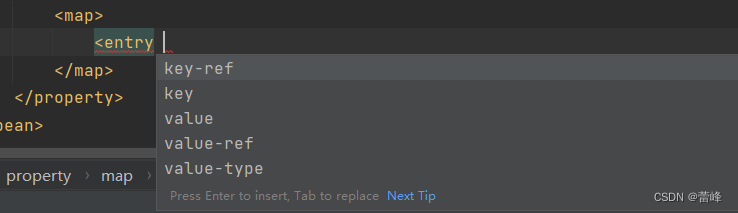
entry:在java中,表示的是一个类型,表示的是map集合里面的键和值。表示一个键值对。
key-ref:引用某一个bean作为键的值(键为类类型)
value:直接为value赋值(值为字面量)
(value-ref:引用某一个bean,来作为value值。(值为类类型)
key:键为字面量类型
我们所载入的bean如下所示:
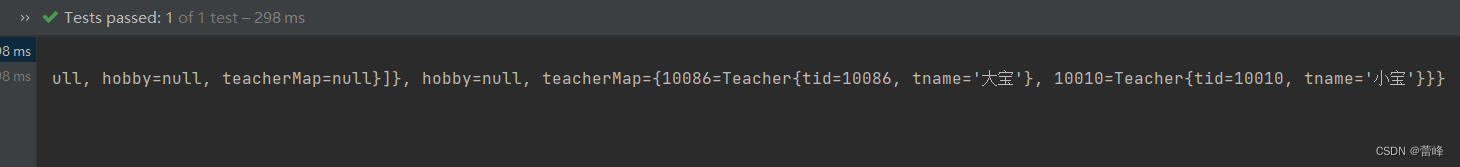
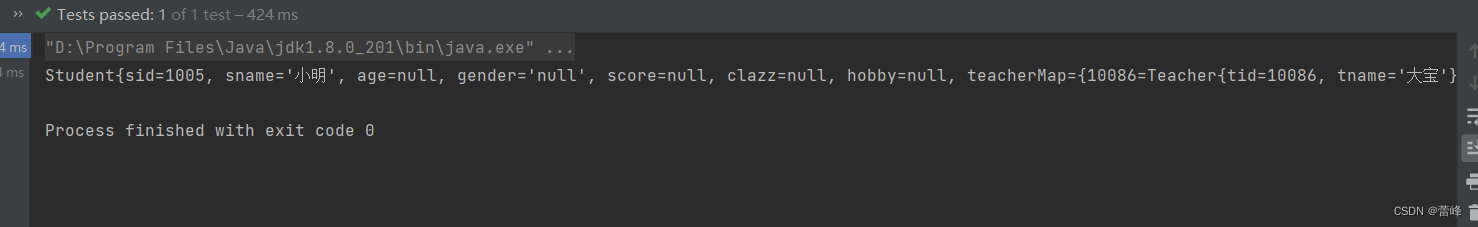
<bean id="studentFive" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <property name="sid" value="1004"></property> <property name="sname" value="赵四"></property> <property name="age" value="26"></property> <property name="gender" value="男"></property> <property name="clazz" ref="clazzOne"></property> <property name="teacherMap"> <map> <entry key="10086" value-ref="teacherOne"></entry> <entry key="10010" value-ref="teacherTwo"></entry> </map> </property> </bean> <bean id="teacherOne" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Teacher"> <property name="tid" value="10086"></property> <property name="tname" value="大宝"></property> </bean> <bean id="teacherTwo" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Teacher"> <property name="tid" value="10010"></property> <property name="tname" value="小宝"></property> </bean>我们进行测试:
@Test public void TestDI(){ //获取IOC容器 ApplicationContext ioc=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml"); Student clazz = ioc.getBean("studentFive", Student.class); System.out.println(clazz); }
我们利用另一种方法如下所示:
<bean id="studentFive" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student"> <property name="sid" value="1004"></property> <property name="sname" value="赵四"></property> <property name="age" value="26"></property> <property name="gender" value="男"></property> <property name="clazz" ref="clazzOne"></property> <property name="teacherMap" ref="teacherMap"></property> </bean> <util:map id="teacherMap" > <entry key="10086" value-ref="teacherOne"></entry> <entry key="10010" value-ref="teacherTwo"></entry> </util:map> <bean id="teacherOne" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Teacher"> <property name="tid" value="10086"></property> <property name="tname" value="大宝"></property> </bean> <bean id="teacherTwo" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Teacher"> <property name="tid" value="10010"></property> <property name="tname" value="小宝"></property> </bean>我们进行测试之后输出如下所示:
8.依赖注入之p命名空间
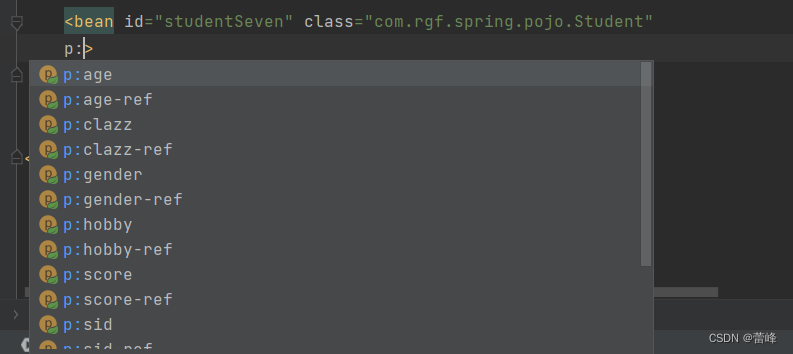
p标签命名的时候需要如下约束:
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"我们发现每个p都有两个值:
字面量使用p:不带ref进行赋值,p:带ref为赋值的是类类型的。
我们所进行设计的代码如下所示:
<bean id="studentSeven" class="com.rgf.spring.pojo.Student" p:sid="1005" p:sname="小明" p:teacherMap-ref="teacherMap"> </bean>我们运行之后如下所示: