一 前言
ES 全称 Elasticsearch 是一款分布式的全文搜索引擎,在互联网公司中,这款搜索引擎一直被程序员们所推崇。常见的使用场景如ELK日志分析,电商APP的商品推荐,社交APP的同城用户推荐等等。今天结合自己平时的一些学习对它与SpringBoot的基础集成以及一些实际项目中的使用做点小总结。
二 ElasticSearch详细介绍
ElasticSearch是一款非常强大的、基于Lucene的开源搜索及分析引擎;它是一个实时的分布式搜索分析引擎,它能让你以前所未有的速度和规模,去探索你的数据。
在当前软件行业中,搜索是一个软件系统或平台的基本功能, 学习ElasticSearch就可以为相应的软件打造出良好的搜索体验。其次,ElasticSearch具备非常强的大数据分析能力。虽然Hadoop也可以做大数据分析,但是有时候分析数据可能出现等待时间很长的情况。而ElasticSearch的分析能力更为突出,具备Hadoop不具备的能力。在当今大数据时代,掌握近实时的搜索和分析能力,才能掌握核心竞争力,洞见未来。
ElasticSearch的主要功能及应用场景

-
主要功能:
1)海量数据的分布式存储以及集群管理,达到了服务与数据的高可用以及水平扩展;
2)近实时搜索,性能卓越。对结构化、全文、地理位置等类型数据的处理;
3)海量数据的近实时分析(聚合功能)
-
应用场景:
1)网站搜索、垂直搜索、代码搜索;
2)日志管理与分析、安全指标监控、应用性能监控、Web抓取舆情分析;
ElasticSearch基础概念
-
Near Realtime(NRT) 近实时。数据提交索引后,立马就可以搜索到。
-
Cluster 集群,一个集群由一个唯一的名字标识,默认为“elasticsearch”。集群名称非常重要,具有相同集群名的节点才会组成一个集群。集群名称可以在配置文件中指定。
-
Node 节点:存储集群的数据,参与集群的索引和搜索功能。像集群有名字,节点也有自己的名称,默认在启动时会以一个随机的UUID的前七个字符作为节点的名字,你可以为其指定任意的名字。通过集群名在网络中发现同伴组成集群。一个节点也可是集群。
-
Index 索引: 一个索引是一个文档的集合(等同于solr中的集合)。每个索引有唯一的名字,通过这个名字来操作它。一个集群中可以有任意多个索引。
-
Type 类型:指在一个索引中,可以索引不同类型的文档,如用户数据、博客数据。从6.0.0 版本起已废弃,一个索引中只存放一类数据。
-
Document 文档:被索引的一条数据,索引的基本信息单元,以JSON格式来表示。
-
Shard 分片:当索引上的数据量太大的时候,我们通常会将一个索引上的数据进行水平拆分,拆分出来的每个数据库叫作一个分片。在一个多分片的索引中写入数据时,通过路由来确定具体写入那一个分片中,所以在创建索引时需要指定分片的数量,并且分片的数量一旦确定就不能更改。分片后的索引带来了规模上(数据水平切分)和性能上(并行执行)的提升。每个分片都是Luence中的一个索引文件,每个分片必须有一个主分片和零到多个副本分片。
-
Replication 备份:是指对主分片的备份, 一个分片可以有多个备份(副本)。主分片和备份分片都可以对外提供查询服务,写操作时先在主分片上完成,然后分发到备份上。当主分片不可用时,会在备份的分片中选举出一个作为主分片,所以备份不仅可以提升系统的高可用性能,还可以提升搜索时的并发性能。但是若副本太多的话,在写操作时会增加数据同步的负担。
-
Settings:对集群中索引的定义,比如一个索引默认的分片数、副本数等信息。
-
Mapping:类似于关系型数据库中的表结构信息,用于定义索引中字段(Field)的存储类型、分词方式、是否存储等信息。Elasticsearch中的mapping是可以动态识别的。如果没有特殊需求,则不需要手动创建mapping,因为Elasticsearch会自动根据数据格式识别它的类型,但是当需要对某些字段添加特殊属性(比如:定义使用其他分词器、是否分词、是否存储等)时,就需要手动设置mapping了。一个索引的mapping一旦创建,若已经存储了数据,就不可修改了。
-
Analyzer:字段的分词方式的定义。一个analyzer通常由一个tokenizer、零到多个filter组成。比如默认的标准Analyzer包含一个标准的tokenizer和三个filter:Standard Token Filter、Lower Case Token Filter、Stop Token Filter。
Elasticsearch的节点的分类
-
主节点(Master Node):也叫作主节点,主节点负责创建索引、删除索引、分配分片、追踪集群中的节点状态等工作。Elasticsearch中的主节点的工作量相对较轻。用户的请求可以发往任何一个节点,并由该节点负责分发请求、收集结果等操作,而并不需要经过主节点转发。通过在配置文件中设置node.master=true来设置该节点成为候选主节点(但该节点不一定是主节点,主节点是集群在候选节点中选举出来的),在Elasticsearch集群中只有候选节点才有选举权和被选举权。其他节点是不参与选举工作的。
-
数据节点(Data Node):数据节点,负责数据的存储和相关具体操作,比如索引数据的创建、修改、删除、搜索、聚合。所以,数据节点对机器配置要求比较高,首先需要有足够的磁盘空间来存储数据,其次数据操作对系统CPU、Memory和I/O的性能消耗都很大。通常随着集群的扩大,需要增加更多的数据节点来提高可用性。通过在配置文件中设置node.data=true来设置该节点成为数据节点。
-
客户端节点(Client Node):就是既不做候选主节点也不做数据节点的节点,只负责请求的分发、汇总等,也就是下面要说到的协调节点的角色。其实任何一个节点都可以完成这样的工作,单独增加这样的节点更多地是为了提高并发性。可在配置文件中设置该节点成为数据节点:
node.master=false
node.data=false-
部落节点(Tribe Node):部落节点可以跨越多个集群,它可以接收每个集群的状态,然后合并成一个全局集群的状态,它可以读写所有集群节点上的数据,在配置文件中通过如下设置使节点成为部落节点:
tribe:
one:
cluster.name: cluster_one
two:
cluster.name: cluster_two因为Tribe Node要在Elasticsearch 7.0以后移除,所以不建议使用。
-
协调节点(Coordinating Node):协调节点,是一种角色,而不是真实的Elasticsearch的节点,我们没有办法通过配置项来配置哪个节点为协调节点。集群中的任何节点都可以充当协调节点的角色。当一个节点A收到用户的查询请求后,会把查询语句分发到其他的节点,然后合并各个节点返回的查询结果,最好返回一个完整的数据集给用户。在这个过程中,节点A扮演的就是协调节点的角色。由此可见,协调节点会对CPU、Memory和I/O要求比较高。 集群的状态有Green、Yellow和Red三种,如下所述:
-
Green:绿色,健康。所有的主分片和副本分片都可正常工作,集群100%健康。
-
Yellow:黄色,预警。所有的主分片都可以正常工作,但至少有一个副本分片是不能正常工作的。此时集群可以正常工作,但是集群的高可用性在某种程度上被弱化。
-
Red:红色,集群不可正常使用。集群中至少有一个分片的主分片及它的全部副本分片都不可正常工作。这时虽然集群的查询操作还可以进行,但是也只能返回部分数据(其他正常分片的数据可以返回),而分配到这个分片上的写入请求将会报错,最终会导致数据的丢失。
ES和数据库的对比
| EDBMS | ElasticSearch |
|---|---|
| 数据库(database) | 索引(index) |
| 表(table) | 类型(type)(6.0.0废弃) |
| 行(row) | 文档(document) |
| 列(column) | 字段(field) |
| 表结构(schema) | 映射(mapping) |
| 索引 | 倒排索引 |
| SQL | 查询DSL |
| 查询 | GET ... |
| 更新 | PUT ... |
| 删除 | DELETE ... |
三 基础实践
因为ES将数据以json格式存储在索引库中,为了方便,实践阶段就不专门建立数据库了,数据直接用ES进行存储(实际不适合数据存储)。基本流程如下:
Step1:导入ES依赖
这里尽量指定ES以来的版本于自己ES服务一致,有时候版本不一致会报错。笔者这里的数据直接从京东爬取了,因此导入了jsoup依赖,做数据爬取。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.yy</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-demo08-elasticsearch</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-demo08-elasticsearch</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<!-- 自定义es版本依赖,保证和本地版本一致-->
<elasticsearch.version>7.6.1</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.jsoup/jsoup 用于爬取数据-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jsoup</groupId>
<artifactId>jsoup</artifactId>
<version>1.14.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.78</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Step2:配置ES客户端连接
笔者这里ES在本地,并且没有设置集群,因此只需要设置基本的客户端连接就行了,没有太多花里胡哨的东西。
package com.yy.config;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class ElasticSearchClientConfig {
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient() {
return new RestHighLevelClient(
RestClient.builder(
new HttpHost("127.0.0.1", 9200, "http")));
}
}Step3:利用jsoup编写数据爬取类
在这之前还需要定义一个实体类,封装爬取数据。
package com.yy.config.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Content {
private String id;
private String img;
private String price;
private String title;
}利用jsoup解析京东购物页面的URL,爬取部分数据作为实践数据。
package com.yy.util;
import com.yy.config.pojo.Content;
import org.jsoup.Jsoup;
import org.jsoup.nodes.Document;
import org.jsoup.nodes.Element;
import org.jsoup.select.Elements;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class HtmlParseUtil {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new HtmlParseUtil().parseJD("java").forEach(System.out::println);
}
public List<Content> parseJD(String keywords) throws IOException {
String url = "https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=" + keywords;
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new URL(url), 30000);
Element element = document.getElementById("J_goodsList");
Elements li = element.getElementsByTag("li");
ArrayList<Content> goodslist = new ArrayList<>();
for (Element el : li) {
String img = el.getElementsByTag("img").eq(0).attr("data-lazy-img");
String price = el.getElementsByClass("p-price").eq(0).text();
String title = el.getElementsByClass("p-name").eq(0).text();
System.out.println("=====================");
System.out.println(img);
System.out.println(price);
System.out.println(title);
Content content = new Content();
content.setImg(img);
content.setPrice(price);
content.setTitle(title);
goodslist.add(content);
}
return goodslist;
}
}Step4:实现基础业务功能
在业务层中实现基础增删改查操作,并将爬取数据放入ES索引中。
package com.yy.config.Service;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.yy.config.pojo.Content;
import com.yy.util.HtmlParseUtil;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.text.Text;
import org.elasticsearch.common.unit.TimeValue;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.TermQueryBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHit;
import org.elasticsearch.search.builder.SearchSourceBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.fetch.subphase.highlight.HighlightBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.search.fetch.subphase.highlight.HighlightField;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ContentService {
@Autowired
private RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
//解析数据放入es的索引中
public Boolean parseContent(String keywords) throws IOException {
List<Content> contents = new HtmlParseUtil().parseJD(keywords);
//把查询的数据放入es中
BulkRequest bulkRequest = new BulkRequest();
bulkRequest.timeout("2m");
for (int i = 0; i < contents.size(); i++) {
bulkRequest.add(
new IndexRequest("my_goods")
.source(JSON.toJSONString(contents.get(i)), XContentType.JSON));
}
BulkResponse bulk = restHighLevelClient.bulk(bulkRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
return !bulk.hasFailures();
}
/**
* 分页查询ES索引库中的信息
* @param keyword 搜索关键词
* @param pageNo 第几页
* @param pageSize size
* @return 数据集合
* @throws IOException
*/
public List<Map<String, Object>> searchPage(String keyword, int pageNo, int pageSize) throws IOException {
if (pageNo <= 1) {
pageNo = 1;
}
//条件搜索
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest("my_goods");
SearchSourceBuilder builder = new SearchSourceBuilder();
//分页
builder.from(pageNo-1);
builder.size(pageSize);
//精准匹配
TermQueryBuilder titles = QueryBuilders.termQuery("title", keyword);
builder.query(titles);
builder.timeout(new TimeValue(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
//高亮设置
HighlightBuilder highlightBuilder = new HighlightBuilder();
highlightBuilder.field("title");
highlightBuilder.preTags("<span style='color:red'>");
highlightBuilder.postTags("</span>");
builder.highlighter(highlightBuilder);
//执行搜索
searchRequest.source(builder);
SearchResponse search = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//解析结果
ArrayList<Map<String, Object>> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (SearchHit hit : search.getHits().getHits()) {
Map<String, HighlightField> highlightFields = hit.getHighlightFields();
HighlightField title = highlightFields.get("title");
Map<String, Object> sourceAsMap = hit.getSourceAsMap();//原来的的结果
//解析高亮字段
if (title != null) {
Text[] fragments = title.fragments();
StringBuilder nText = new StringBuilder();
for (Text text : fragments) {
nText.append(text);
}
sourceAsMap.put("title", nText.toString());
}
list.add(sourceAsMap);
}
return list;
}
/**
* 手动增加一条信息
* @param content 新增对象
* @throws IOException
*/
public String addContent(Content content) throws IOException {
//创建请求
IndexRequest goods = new IndexRequest("my_goods");
//规则 put/my_goods/_doc/id
goods.id(content.getId());
goods.timeout(TimeValue.timeValueSeconds(1));
//将我们的数据放入请求 json
goods.source(JSON.toJSONString(content), XContentType.JSON);
//客户端发送请求
IndexResponse ir = restHighLevelClient.index(goods, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("打印响应状态信息---》{}",ir.status() );
return ir.status().getStatus()==200?"插入数据成功!":"插入数据失败~";
}
/**
* 删除一条信息
* @param id 对应id
* @throws IOException
*/
public String deleteOne(String id) throws IOException {
DeleteRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteRequest("my_goods", id);
deleteRequest.timeout("1s");
DeleteResponse response = restHighLevelClient.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("打印响应结果状态信息---》{}", response.status());
return response.status().getStatus()==200?"删除成功!":"删除失败~";
}
/**
* 修改某数据
* @param content 更新数据
* @throws IOException
*/
public String updateOne(Content content) throws IOException {
UpdateRequest updateRequest = new UpdateRequest("my_goods", content.getId());
updateRequest.timeout("1s");
updateRequest.doc(JSON.toJSONString(content),XContentType.JSON);
UpdateResponse response = restHighLevelClient.update(updateRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
log.info("打印响应结果状态信息---》{}", response.status());
return response.status().getStatus()==200?"更新成功!":"更新失败~";
}
}实现数据解析业务后,后续通过接口即可爬取对应的信息到ES索引库中了。
Step5:构建Cotroller接口
package com.yy.config.controller;
import com.yy.config.Service.ContentService;
import com.yy.config.pojo.Content;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
public class ContentController {
@Autowired
private ContentService contentService;
@GetMapping("/parse/{keyword}")
public Boolean parse(@PathVariable("keyword") String keyword) throws IOException {
return contentService.parseContent(keyword);
}
@GetMapping("/search/{keyword}/{pageNo}/{pageSize}")
public List<Map<String, Object>> search(
@PathVariable("keyword") String keyword,
@PathVariable("pageNo") int pageNo,
@PathVariable("pageSize") int pageSize) throws IOException {
return contentService.searchPage(keyword, pageNo, pageSize);
}
@PostMapping("/update")
public String update(@RequestBody Content content) throws IOException {
return contentService.updateOne(content);
}
@PostMapping("/add")
public String add(@RequestBody Content content) throws IOException {
return contentService.addContent(content);
}
@DeleteMapping("/delete/{id}")
public String delete(@PathVariable String id) throws IOException {
return contentService.deleteOne(id);
}
}基础操作接口实现成功后,再启动项目之前,还需要启动本地的ES服务,有准备的可以同时开启ES-head-master和kibana等可视化平台,方便查看功能实现结果。
Step6:接口测试
首先测试parse/{keyword}接口,解析爬取的数据并将其放入ES索引库,这样ES就有数据信息了。笔者这里依此存放了Java、Vue、Linux、Go的信息数据。
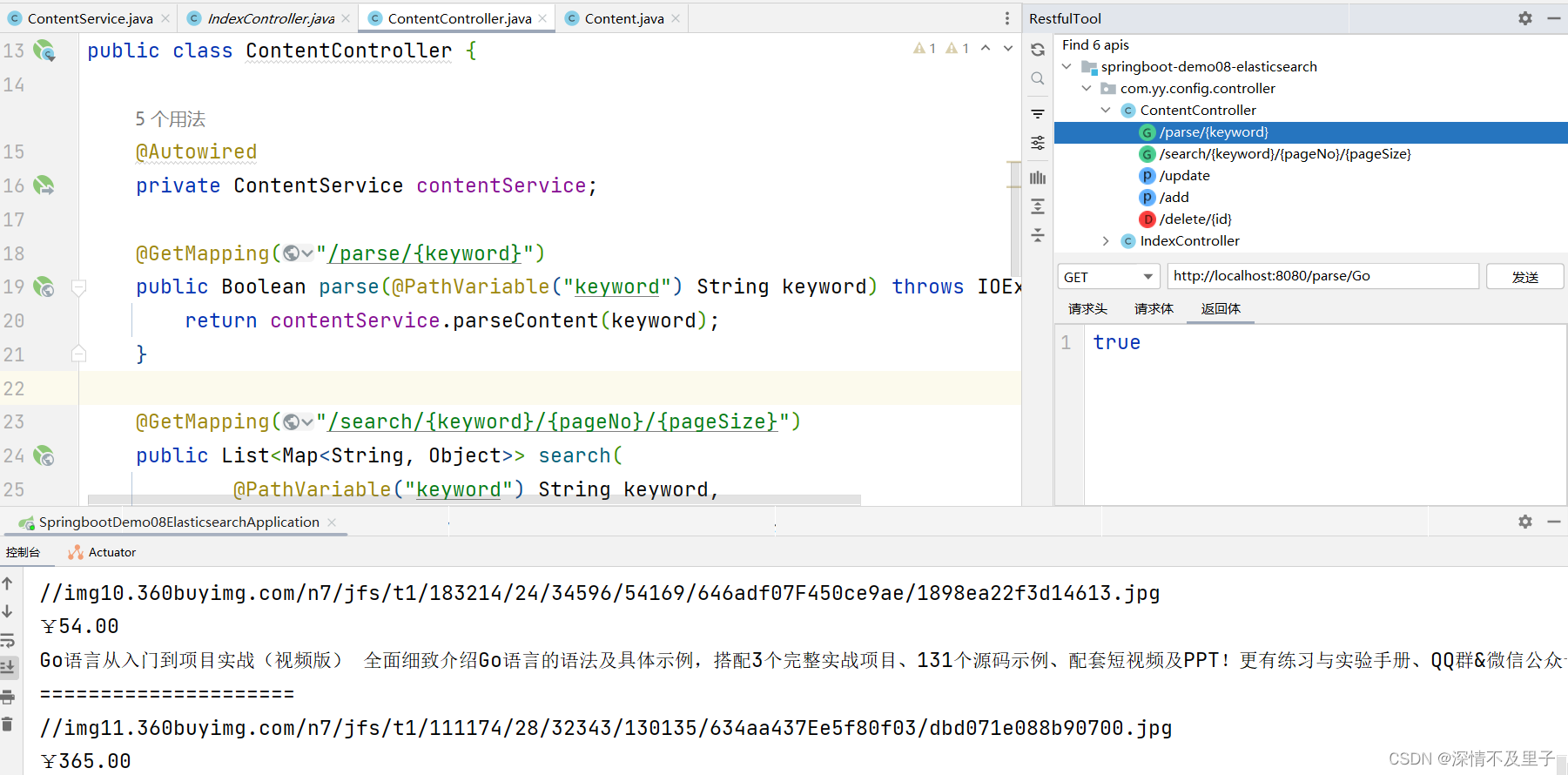
接口测试成功后通过es-head-master查看数据是否已存入ES。
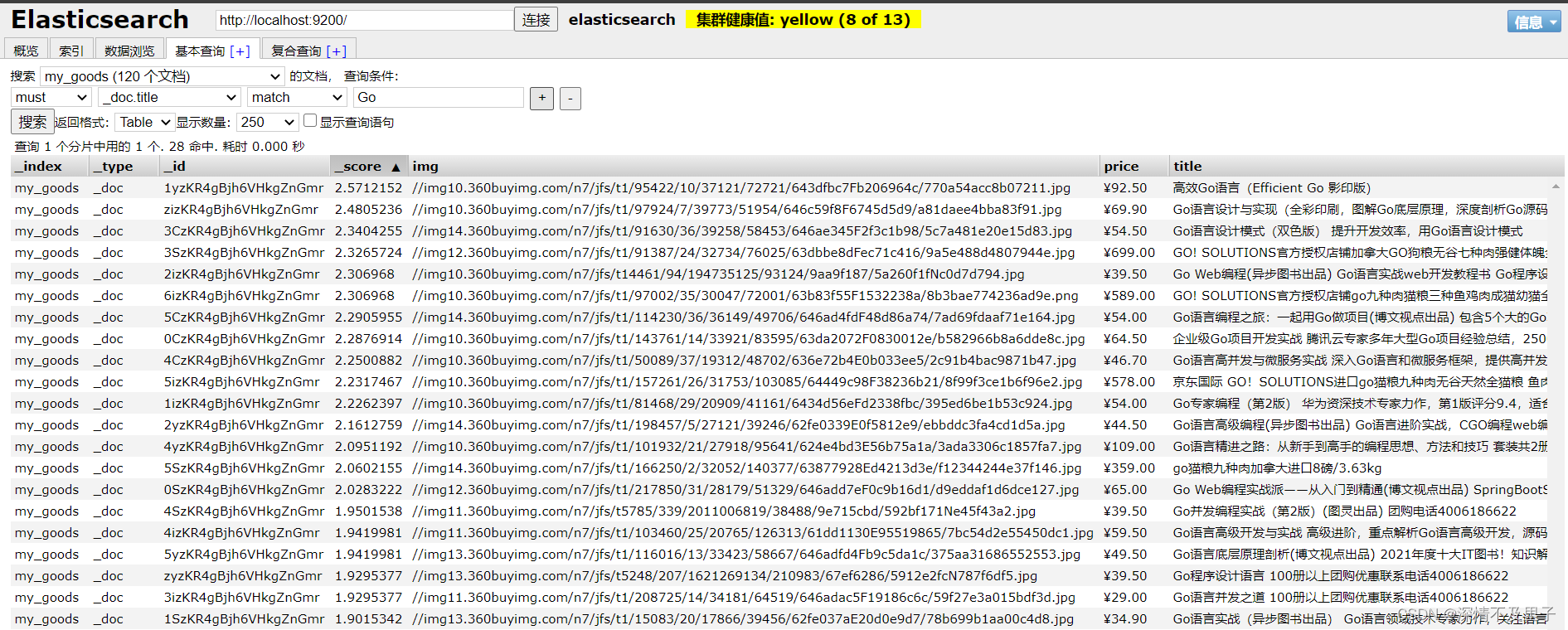
数据导入基本完成。
测试分页查询,查询前3条带有Vue的数据:

数据已查询到,并且对应关键字已经用高亮显示,由于测试原因,这里并不能直接观察高亮结果,但是如果前端解析就可见了。
测试新增一条数据结果:
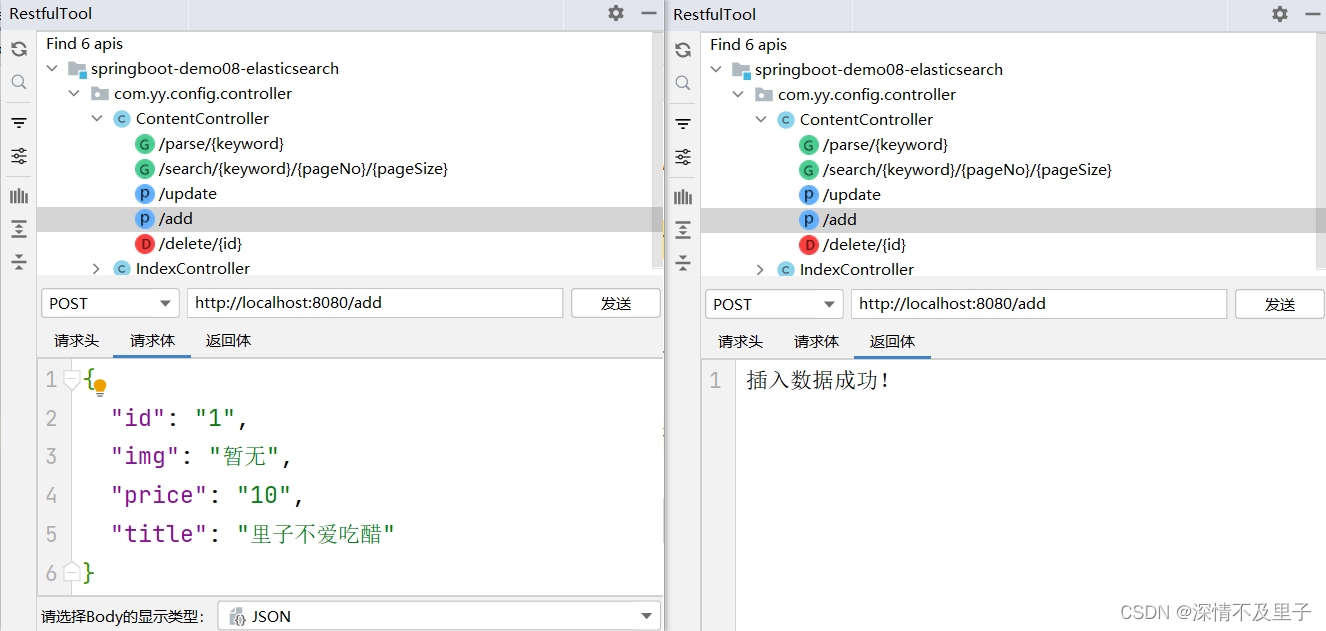
并且在可视化查询中也插入成功:

相应的更新、删除也能实现预期结果,这里就不重复展示接口测试结果了。这里要注意的是,笔者在代码层面使用的是termQuery精确查找,因此只会返会有的结果,如果match匹配的话可能会出现很多带有查询字段的结果。
四 实际使用中的ES数据同步
以上只是学习过程中的ES集成SpringBoot的基础操作使用。在日常项目使用中一般不会用它做数据存储,作为一个优秀的数据搜索和分析引擎,一般在日志收集和数据搜索上被广泛应用。这里只分享一个作为数据搜索时的中间件的简单使用方式。
这里以一个商城微服务项目为例,因为在商城系统中搜索服务肯定占主流的,用户根据商品关键字检索商品信息。如果只用数据库必然会承受大量访问压力。此时ES作为商品信息检索中间件使用的重要性就体现出来了。当前台界面加载的时候数据库执行一次查询操作并将查询的商品数据同步到ES索引库中,当用户搜索商品时,直接从ES库查询数据,避免用户频繁的直接对数据库查询操作。并且ES提供的高亮也能让查询信息更加清晰。
基本流程图如下:
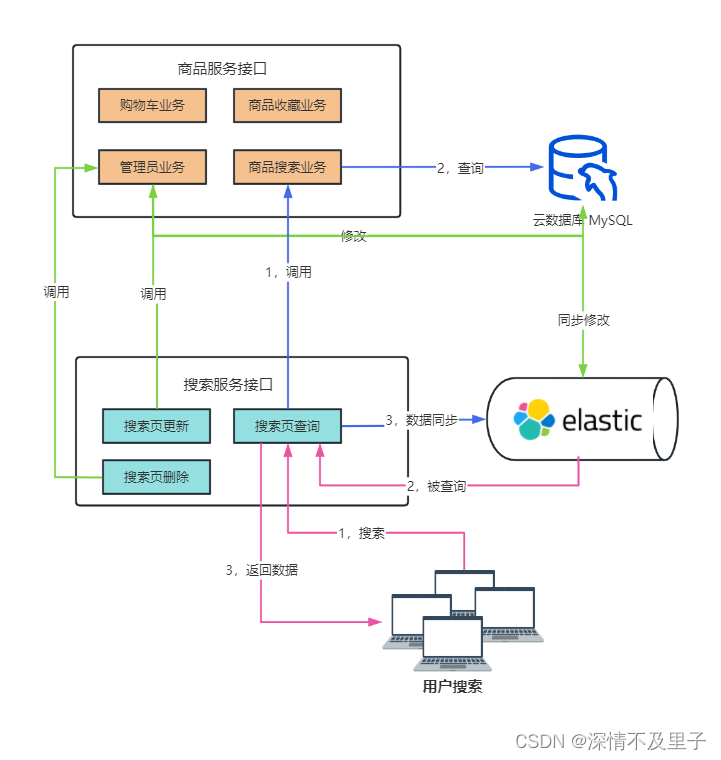
当两个服务都启动时,搜索服务在运行时首先检查ES服务中是否存在商品信息索引并建立新的索引表。然后调用商品服务接口中的商品搜索业务,向数据库查询所有商品数据,并将查询到的数据转换为JSON同步插入到ES中。此时当用户调用商品搜索时直接从ES库返回商品数据信息,而不是从数据库查询。当管理员对数据库执行相应地增删操作时,也会在业务逻辑中同时添加对ES的同步修改(也是容易出现数据一致性的环节)。步骤如下:
Step1:ES客户端访问配置
这里导入依赖就省略不再重复赘述了,依赖于ES服务尽量一致就行。
package com.yy.Config;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.Jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author young
* Date 2023/2/12 16:46
* Description: es搜索引擎客户端配置
*/
@Configuration
public class ElasticSearchConfiguration {
/**
* 配置es客户端
* @return RestHighLevelClient客户端访问配置
*/
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient(){
return new RestHighLevelClient(
RestClient.builder(HttpHost.create("http://localhost:9200")));
}
}Step2:配置监听器实现数据同步
这里配置一个监听器继承ApplicationRunner接口即可,并实现接口里面的run(ApplicationArguments args)方法,这个接口可以让项目在启动时候初始化一些信息,也就是在初始化时,将建立的索引及查询的商品信息同步到ES库中。
package com.yy.listener;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.yy.client.ProductClient;
import com.yy.constants.SearchIndex;
import com.yy.doc.ProductDoc;
import com.yy.pojo.Product;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.index.reindex.DeleteByQueryRequest;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.index.GeoIndexDefinition;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.test.context.TestPropertySource;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author young
* Date 2023/2/12 16:46
* Description: 数据同步
*/
@Component
@Slf4j
public class SpringBootListener implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
private ProductClient productClient;
@Resource
private RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
/**
* 需要在此方法,完成es数据的同步!
* 1.判断下es中product索引是否存在
* 2.不存在,java代码创建一个
* 3.存在删除原来的数据
* 4.查询商品全部数据
* 5.进行es库的更新工作[插入]
* @param args
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
//判断es中是否存在product的索引
GetIndexRequest indexDefinition = new GetIndexRequest(SearchIndex.PRODUCT);
boolean exists = restHighLevelClient.indices().exists(indexDefinition, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
//判断处理
if (exists){
//存在 删除所有数据
DeleteByQueryRequest queryRequest = new DeleteByQueryRequest(SearchIndex.PRODUCT);
//全部删除
queryRequest.setQuery(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
restHighLevelClient.deleteByQuery(queryRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}else{
//不存在的话创建product新的索引表
CreateIndexRequest createIndexRequest = new CreateIndexRequest(SearchIndex.PRODUCT);
String indexStr = "{\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"productId\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\",\n" +
" \"index\":true\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"productName\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_smart\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"categoryId\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"productTitle\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_smart\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"productIntro\":{\n" +
" \"type\":\"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_smart\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"productPicture\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"productPrice\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"double\",\n" +
" \"index\": true\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"productSellingPrice\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"double\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"productNum\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"productSales\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"all\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}\n";
createIndexRequest.source(indexStr, XContentType.JSON);
restHighLevelClient.indices().create(createIndexRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
//执行查询数据操作
List<Product> productList = productClient.listProduct();
//批量数据插入操作
BulkRequest bulkRequest = new BulkRequest();
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
for (Product product : productList) {
ProductDoc productDoc = new ProductDoc(product);
//用于插入数据的作用
IndexRequest indexRequest = new IndexRequest(SearchIndex.PRODUCT);
//将productDoc转换成JSON格式并插入es中
String s = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(productDoc);
indexRequest.source(s,XContentType.JSON);
bulkRequest.add(indexRequest);
}
restHighLevelClient.bulk(bulkRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
}Step3:搜索业务实现
主要是对关键字的分页查询,以及商品信息同步的插入、更新及删除操作,当管理员修改商品信息时调用该业务实现的接口同步修改ES。
package com.yy.service.impl;
import cn.hutool.core.text.CharSequenceUtil;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.yy.Result;
import com.yy.constants.ResultEnum;
import com.yy.constants.SearchIndex;
import com.yy.doc.ProductDoc;
import com.yy.exception.MyException;
import com.yy.param.ProductSearchParam;
import com.yy.pojo.Product;
import com.yy.service.SearchService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.search.SearchResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHit;
import org.elasticsearch.search.SearchHits;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author young
* Date 2023/2/12 17:12
* Description: store-cloud
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class SearchServiceImpl implements SearchService {
@Resource
private RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient;
/**
* 根据关键字和分页进行数据库数据查询
* 1. 判断关键字是否为null null查询全部 不为null all 字段查询
* 2. 添加分页属性
* 3. es查询
* 4. 结果处理
* @param productSearchParam
* @return
*/
@Override
public Result search(ProductSearchParam productSearchParam) {
SearchRequest searchRequest = new SearchRequest(SearchIndex.PRODUCT);
String search = productSearchParam.getSearch();
if (CharSequenceUtil.isEmpty(search)){
//null 不添加all关键字,查询全部即可
//查询全部
searchRequest.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
}else {
//不为null则添加all匹配
searchRequest.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all",search));
}
//进行分页数据添加
//偏移量 (当前页数-1)*页容量
searchRequest.source().from((productSearchParam.getCurrentPage()-1)*productSearchParam.getPageSize());
searchRequest.source().size(productSearchParam.getPageSize());
SearchResponse searchResponse = null;
try {
searchResponse = restHighLevelClient.search(searchRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new MyException(ResultEnum.ERROR.getCode(),e.getMessage());
}
SearchHits hits = searchResponse.getHits();
//查询符合的数据
long total = hits.getTotalHits().value;
//获得数据集合
SearchHit[] hitsList = hits.getHits();
List<Product> products = new ArrayList<>();
//json处理器处理数据格式转换
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
for (SearchHit documentFields : hitsList) {
//查询的内容数据! productDoc模型对应的json数据
String source = documentFields.getSourceAsString();
Product product = null;
try {
//productDoc all - product 如果没有all的属性,会报错! jackson提供忽略没有属性的注解
//TODO: 修改product的实体类,添加忽略没有属性的注解!
product=objectMapper.readValue(source,Product.class);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
products.add(product);
}
Result result = Result.ok(products,total);
log.info("es的搜索业务执行完毕,结果数据为:{}",result);
return result;
}
/**
* 商品同步 : 插入和更新
*
* @param product
* @return
*/
@Override
public Result save(Product product) throws IOException {
IndexRequest indexRequest
= new IndexRequest(SearchIndex.PRODUCT).id(product.getProductId().toString());
ProductDoc productDoc = new ProductDoc(product);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
String json = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(productDoc);
indexRequest.source(json, XContentType.JSON);
restHighLevelClient.index(indexRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
return Result.ok().message("数据同步成功!");
}
/**
* 进行es库的商品删除
*
* @param productId
* @return
*/
@Override
public Result remove(Integer productId) throws IOException {
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest(SearchIndex.PRODUCT).id(productId.toString());
restHighLevelClient.delete(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
return Result.ok().message("es库的数据删除成功!");
}
}Step4:实现搜索服务接口
构建Controller层,保证接口可用性。
package com.yy.controller;
import com.yy.Result;
import com.yy.param.ProductSearchParam;
import com.yy.pojo.Product;
import com.yy.service.impl.SearchServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* @author young
* Date 2023/2/12 17:12
* Description: 搜索服务接口
*/
@RequestMapping("/search")
@RestController
public class ElasticSearchController {
@Resource
private SearchServiceImpl searchService;
@PostMapping("product")
public Result searchProduct(@RequestBody ProductSearchParam productSearchParam){
return searchService.search(productSearchParam);
}
/**
* 同步調用,進行商品插入!覆蓋更新的!
* @param product
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("save")
public Result saveProduct(@RequestBody Product product) throws IOException {
return searchService.save(product);
}
@DeleteMapping("remove")
public Result removeProduct(@RequestParam Integer productId) throws IOException {
return searchService.remove(productId);
}
}Step5:商品服务业务远程调用搜索接口
这里为了方便只展示部分有关业务实现过程...
@Service
@Slf4j
public class ProductServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ProductMapper, Product> implements ProductService {
//引入客户端
@Autowired
private SearchClient searchClient;
……
/**
* 商品保存业务
* 1. 商品数据保存
* 2. 商品的图片详情切割和保存
* 3. 搜索数据库的数据添加
* 4. 清空商品相关的缓存数据
* @param productSaveParam
* @return
*/
@CacheEvict(value = "list.product",allEntries = true)
@Override
@CostTime
public Result adminSave(ProductSaveParam productSaveParam) {
Product product = new Product();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(productSaveParam,product);
int rows = productMapper.insert(product); //商品数据插入
log.info("ProductServiceImpl.adminSave业务结束,结果:{}",rows);
//商品图片获取 +
String pictures = productSaveParam.getPictures();
if (!CharSequenceUtil.isEmpty(pictures)){
//截取特殊字符串的时候 \\ [] 包含 $ + * | ?
String[] urls = pictures.split("\\+");
for (String url : urls) {
Picture picture = new Picture();
picture.setProductId(product.getProductId());
picture.setProductPicture(url);
pictureMapper.insert(picture); //插入商品的图片
}
}
//同步搜索服务的数据
searchClient.saveOrUpdate(product);
return Result.ok().message("商品数据添加成功!");
}
/**
* 商品数据更新
* 1.更新商品数据
* 2.同步搜索服务数据即可
* @param product
* @return
*/
@Override
public Result adminUpdate(Product product) {
productMapper.updateById(product);
//同步搜索服务的数据
searchClient.saveOrUpdate(product);
return Result.ok().message("商品数据更新成功!");
}
……
}后续关于商品服务的接口就不一一陈列了,直接运行服务测试即可。
Step6:数据同步测试
启动两个服务后在ElasticSearch-head-mater中就可以看到数据基本已经全部同步到ES中了。
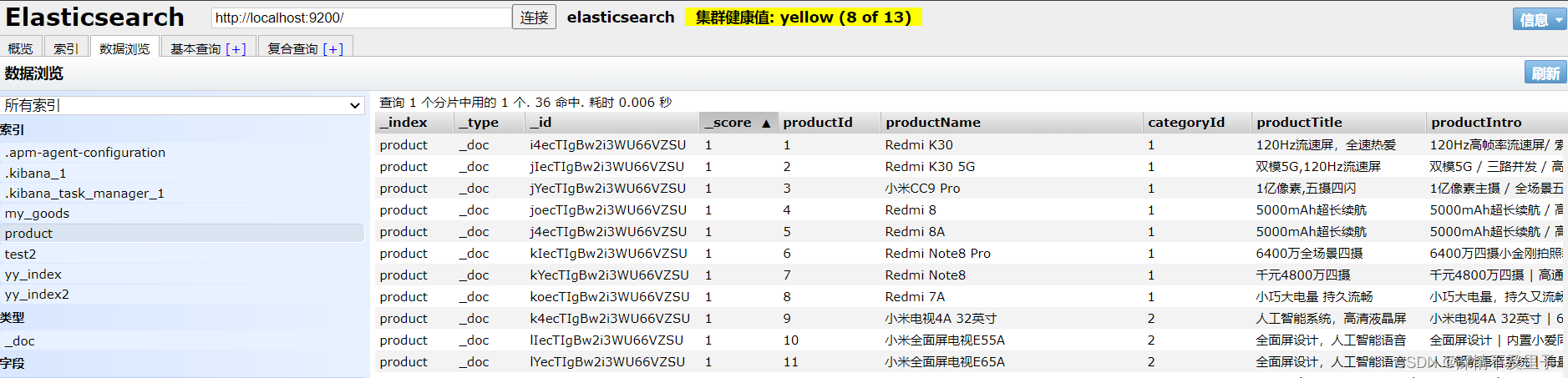
测试分页查询商品结果:
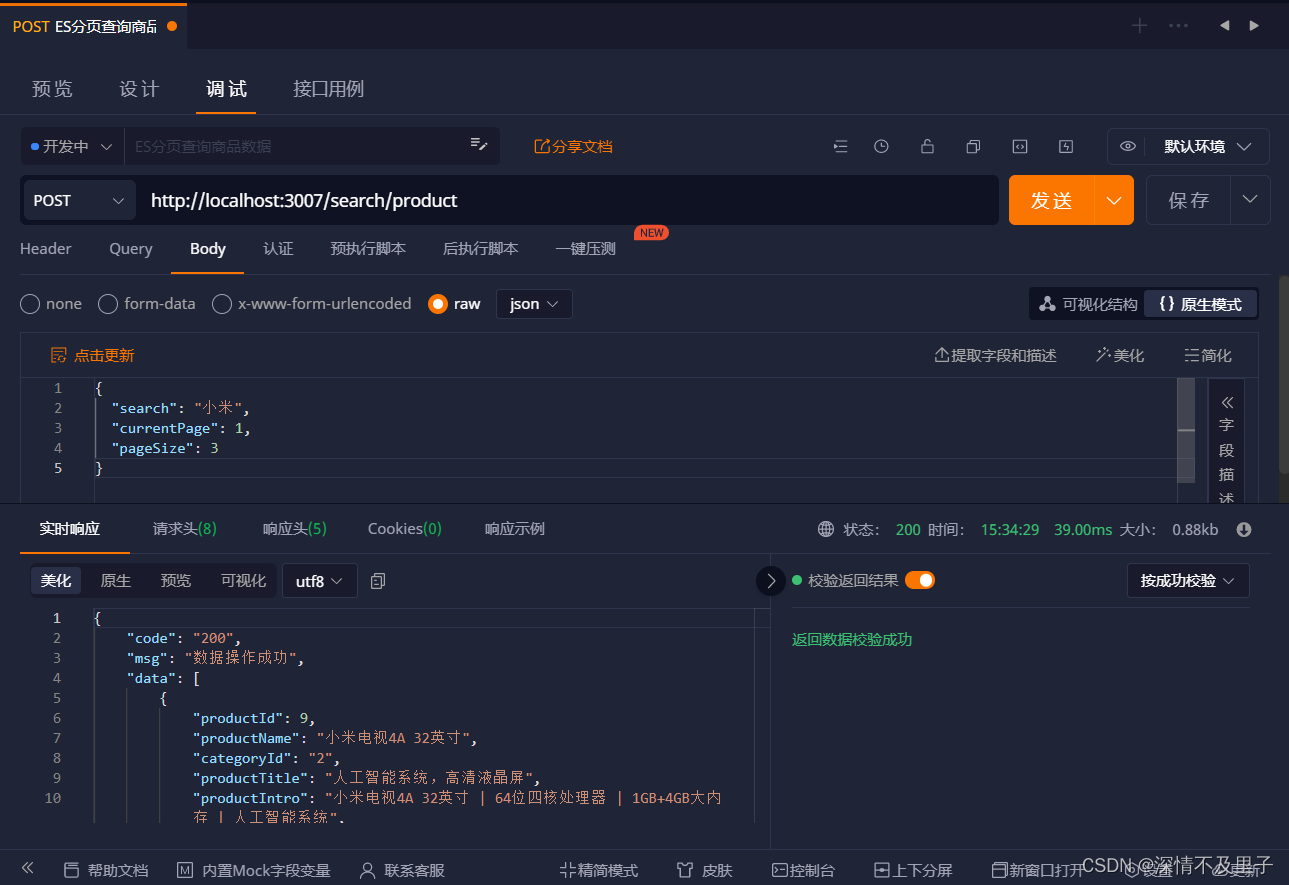
测试添加商品结果:
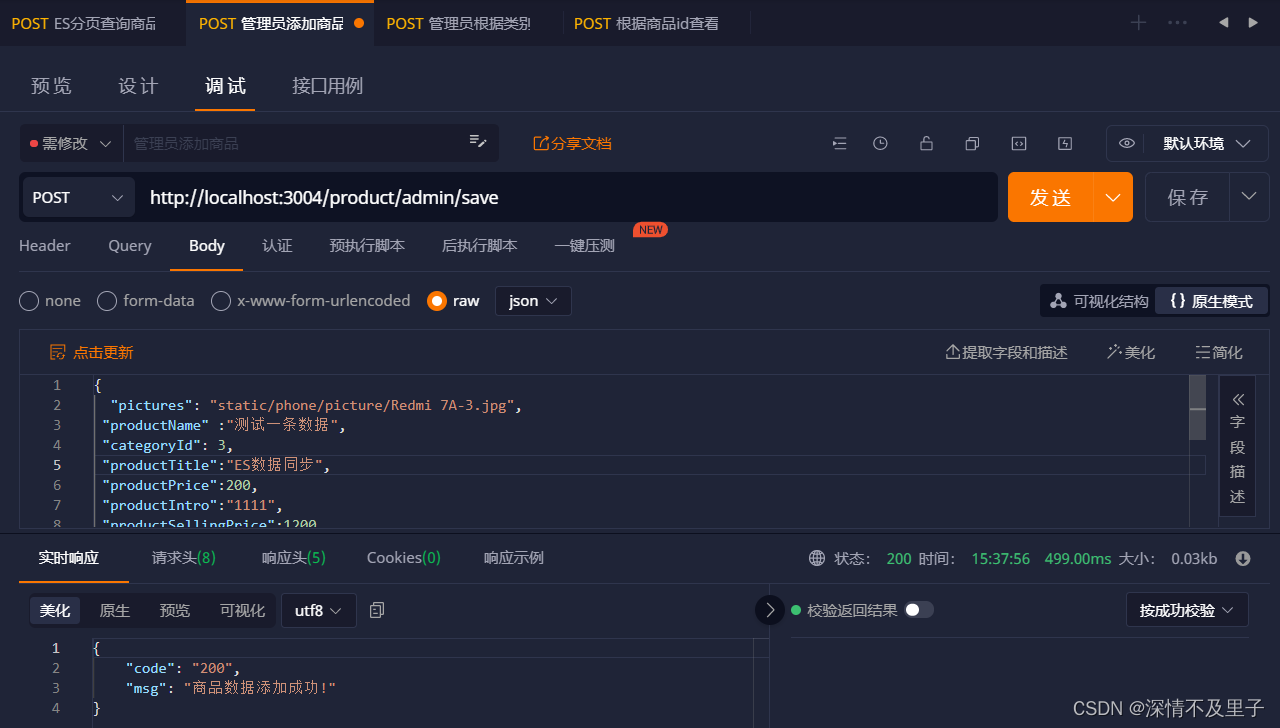
此时插入的一条新数据就成功了,查看ES库和数据库是否同时插入数据:
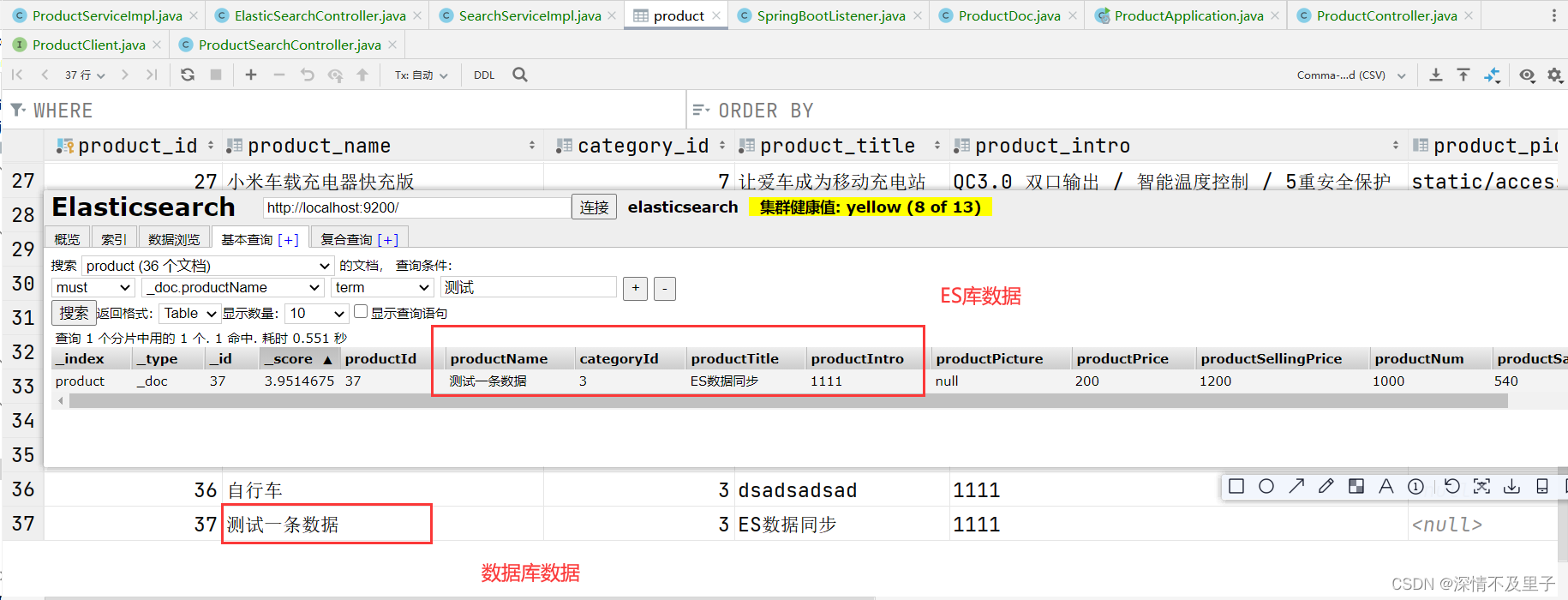
测试结果符合预期。相应的删除操作也是能同时删除数据库数据与ES库中的商品信息。
五 小总结
Elasticsearch作为一个开源搜索引擎,它在内部使用Luence做索引与搜索,通过对Lucene的封装,提供了一套简单一致的RESTful API。
Elasticsearch也是一种分布式的搜索引擎架构,可以很简单地扩展到上百个服务节点,并支持PB级别的数据查询,使系统具备高可用和高并发性。
因此它在分布式环境下作为搜索中间件的使用上确实有不错表现。从架构层面来讲,流传的一句话是:没有什么是加一层不能解决的。在搜索领域加一层ES作为中间件确实能减少数据层检索访问压力,并且极大提高大数据下的数据搜索效率。但是多一层中间件也就意味着系统复杂程度更高一层,带来的系统风险(比如数据一致性问题)也是相对的。因此学习之余,合理应用各类技术,如何趋利避害也是一个学习者应该好好考虑的~
部分基础概念参考ElasticSearch详解
更多关于ElasticSearch的学习可自行参考ElasticSearch官网
学习资料源码后续根据需求会放在Gitee或者Gitub中,ES服务安装包(含ES-7.6.1版本、ElasticSearch-head-master、kibana-7.6.1、ik分词器压缩包)基本已配置完毕的压缩包可在资源获取或者直接找笔者拿。


![CodeForces.1786A2.发牌.[中等][flg标识][数学规律][双色牌]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8137059c129646c0887c16f8199edc50.png)