目录
一、裁剪和标签的设置
二、模型的预测输出的边界框回归
一、裁剪和标签的设置

1、添加偏移量,得到偏移后的边界框
jittered_anno = [self._get_jittered_box(a, s) for a in data[s + '_anno']]2、以偏移后的边界框为中心,进行裁剪
首先以偏移边界框面积的倍裁剪搜索区域,
crop_sz = torch.ceil(torch.sqrt(w * h) * self.search_area_factor[s])然后进行裁剪填充
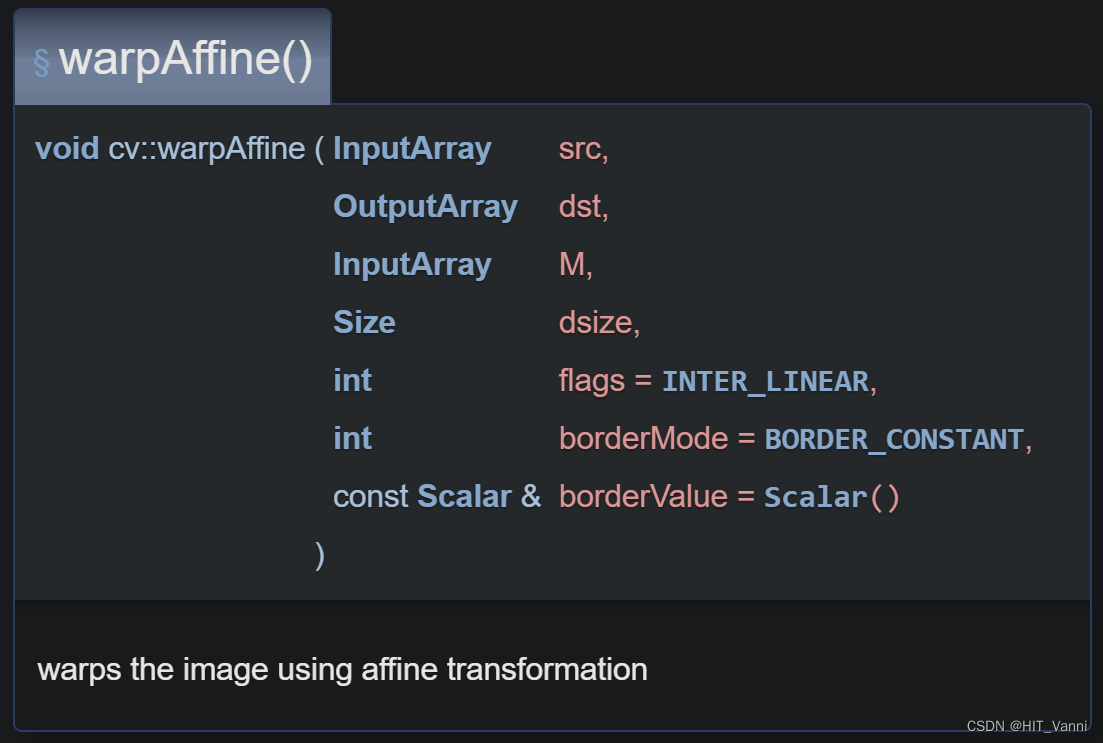
def sample_target(im, target_bb, search_area_factor, output_sz=None, mask=None):
""" Extracts a square crop centered at target_bb box, of area search_area_factor^2 times target_bb area
args:
im - cv image
target_bb - target box [x, y, w, h]
search_area_factor - Ratio of crop size to target size
output_sz - (float) Size to which the extracted crop is resized (always square). If None, no resizing is done.
returns:
cv image - extracted crop
float - the factor by which the crop has been resized to make the crop size equal output_size
"""
if not isinstance(target_bb, list):
x, y, w, h = target_bb.tolist()
else:
x, y, w, h = target_bb
# Crop image
crop_sz = math.ceil(math.sqrt(w * h) * search_area_factor) # 466
if crop_sz < 1:
raise Exception('Too small bounding box.')
x1 = round(x + 0.5 * w - crop_sz * 0.5)
x2 = x1 + crop_sz
y1 = round(y + 0.5 * h - crop_sz * 0.5)
y2 = y1 + crop_sz
x1_pad = max(0, -x1)
x2_pad = max(x2 - im.shape[1] + 1, 0)
y1_pad = max(0, -y1)
y2_pad = max(y2 - im.shape[0] + 1, 0)
# Crop target
im_crop = im[y1 + y1_pad:y2 - y2_pad, x1 + x1_pad:x2 - x2_pad, :] # ndarray:(466,466,3)
if mask is not None:
mask_crop = mask[y1 + y1_pad:y2 - y2_pad, x1 + x1_pad:x2 - x2_pad] # Tensor:(466,466)
# Pad
im_crop_padded = cv.copyMakeBorder(im_crop, y1_pad, y2_pad, x1_pad, x2_pad, cv.BORDER_CONSTANT) # ndarray:(466,466,3) 如果裁剪区域超出边界则填充
# deal with attention mask
H, W, _ = im_crop_padded.shape # 446, 446, 3
att_mask = np.ones((H,W)) # ndarray:(466,466)
end_x, end_y = -x2_pad, -y2_pad # 0, 0
if y2_pad == 0:
end_y = None
if x2_pad == 0:
end_x = None
att_mask[y1_pad:end_y, x1_pad:end_x] = 0
if mask is not None: # True
mask_crop_padded = F.pad(mask_crop, pad=(x1_pad, x2_pad, y1_pad, y2_pad), mode='constant', value=0)3、进行resize
if output_sz is not None: # True
resize_factor = output_sz / crop_sz
im_crop_padded = cv.resize(im_crop_padded, (output_sz, output_sz)) # ndarray:(128,128,3)
att_mask = cv.resize(att_mask, (output_sz, output_sz)).astype(np.bool_) # ndarray:(128,128,3) bool型
if mask is None:
return im_crop_padded, resize_factor, att_mask
mask_crop_padded = \
F.interpolate(mask_crop_padded[None, None], (output_sz, output_sz), mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)[0, 0] # Tensor:(128,128)
return im_crop_padded, resize_factor, att_mask, mask_crop_paddedresize成输入大小,这里记录了 output_sz/crop_sz的大小,后面要用。这一步已经确定了裁剪的输入图像,但是标签还没对齐。
4、对齐标签
def transform_image_to_crop(box_in: torch.Tensor, box_extract: torch.Tensor, resize_factor: float,
crop_sz: torch.Tensor, normalize=False) -> torch.Tensor:
""" Transform the box co-ordinates from the original image co-ordinates to the co-ordinates of the cropped image
args:
box_in - the box for which the co-ordinates are to be transformed
box_extract - the box about which the image crop has been extracted.
resize_factor - the ratio between the original image scale and the scale of the image crop
crop_sz - size of the cropped image
returns:
torch.Tensor - transformed co-ordinates of box_in
"""
box_extract_center = box_extract[0:2] + 0.5 * box_extract[2:4]
box_in_center = box_in[0:2] + 0.5 * box_in[2:4]
box_out_center = (crop_sz - 1) / 2 + (box_in_center - box_extract_center) * resize_factor
box_out_wh = box_in[2:4] * resize_factor
box_out = torch.cat((box_out_center - 0.5 * box_out_wh, box_out_wh))
if normalize:
return box_out / crop_sz[0]
else:
return box_out首先计算偏移边界框的中心坐标和ground truth 边界框的中心坐标
其中x和y为边界框的左上角顶点坐标。
接下来对齐标签
outputsz为需要输入的大小,
之后将中心坐标形式转成了左顶点坐标的形式 (x,y,w,h),然后进行了归一化
return box_out / crop_sz[0]都除以了 输入的尺寸,比如384,256
5、生成head需要预测的标签
经过上述操作还没完,只是对齐了gt bbox 和裁剪输入,还需要生成模型预测的标签。
1)分类标签,
由 gt bbox的中心坐标生成高斯图
def generate_heatmap(bboxes, patch_size=320, stride=16): # Tensor:(1,4,4), 256, 16
"""
Generate ground truth heatmap same as CenterNet
Args:
bboxes (torch.Tensor): shape of [num_search, bs, 4]
Returns:
gaussian_maps: list of generated heatmap
"""
gaussian_maps = []
heatmap_size = patch_size // stride # 16
for single_patch_bboxes in bboxes: # Tensor:(4,4)
bs = single_patch_bboxes.shape[0] # 4
gt_scoremap = torch.zeros(bs, heatmap_size, heatmap_size) # Tensor:(4,16,16)
classes = torch.arange(bs).to(torch.long) # tensor:([0,1,2,3])
bbox = single_patch_bboxes * heatmap_size # Tensor:(4,4)
wh = bbox[:, 2:] # Tensor:(4,2)
centers_int = (bbox[:, :2] + wh / 2).round() # Tensor:(4,2) 中心点
CenterNetHeatMap.generate_score_map(gt_scoremap, classes, wh, centers_int, 0.7)
gaussian_maps.append(gt_scoremap.to(bbox.device))
return gaussian_maps2) 回归标签
就是 gt bbox本身,但是,需要注意的是,这里的gt bbox已经归一化。
而且网络的输出是 得分图,size 和 offset,所以回归标签不是直接的,而是间接的。
二、模型的预测输出的边界框回归
经过输出头的输出包含三个
score_map_ctr, size_map, offset_map = self.get_score_map(x) # Tensor:(4,1,16,16) , Tensor:(4,2,16,16), Tensor:(4,2,16,16)回归边界框
def cal_bbox(self, score_map_ctr, size_map, offset_map, return_score=False):
max_score, idx = torch.max(score_map_ctr.flatten(1), dim=1, keepdim=True) # shape都是 Tensor:(4,1) 按 batch 拿出最大的得分和所对应的索引
idx_y = idx // self.feat_sz # Tensor:(4,1)
idx_x = idx % self.feat_sz # Tensor:(4,1)
idx = idx.unsqueeze(1).expand(idx.shape[0], 2, 1) # Tensor:(4,2,1)
size = size_map.flatten(2).gather(dim=2, index=idx) # Tensor:(4,2,1)
offset = offset_map.flatten(2).gather(dim=2, index=idx).squeeze(-1) # Tensor:(4,2)
# bbox = torch.cat([idx_x - size[:, 0] / 2, idx_y - size[:, 1] / 2,
# idx_x + size[:, 0] / 2, idx_y + size[:, 1] / 2], dim=1) / self.feat_sz
# cx, cy, w, h
bbox = torch.cat([(idx_x.to(torch.float) + offset[:, :1]) / self.feat_sz,
(idx_y.to(torch.float) + offset[:, 1:]) / self.feat_sz,
size.squeeze(-1)], dim=1) # Tensor:(4,4)
if return_score:
return bbox, max_score
return bbox这里的是中心坐标的形式。训练阶段直接用他们呢计算损失函数。
推理阶段,
pred_box = (pred_boxes.mean(
dim=0) * self.params.search_size / resize_factor).tolist() # (cx, cy, w, h) [0,1] 乘上search size去规一化去规一化,将预测的bbox 转换成 裁剪图片的尺度,并且注意这里实现的是将裁剪图片的尺度与原图片保持在同一尺度上。
def map_box_back(self, pred_box: list, resize_factor: float):
cx_prev, cy_prev = self.state[0] + 0.5 * self.state[2], self.state[1] + 0.5 * self.state[3]
cx, cy, w, h = pred_box
half_side = 0.5 * self.params.search_size / resize_factor
cx_real = cx + (cx_prev - half_side)
cy_real = cy + (cy_prev - half_side)
return [cx_real - 0.5 * w, cy_real - 0.5 * h, w, h]这里的self.state为前一帧的预测 bbox。此时,预测的bbox为在裁剪图片中的坐标,所以想要将他返回原img上的坐标需要 计算裁剪图片的坐标系与原img的坐标系的相对坐标变换,因此,用前一阵预测的bbox的中心坐标减去裁剪图片的中心坐标就得到了相对坐标变换,直接加上相对坐标即可得到预测的原img的坐标。