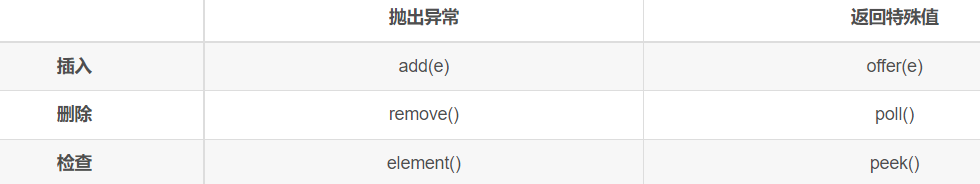
1、Queue队列
先进先出
2、双端队列 --- Deque
Deque的实现类是LinkedList,ArrayDeque,LinkedBlockingDeque。
ArrayDeque底层实现是数组,LinkedList底层实现是链表。

双端队列可以作为普通队列使用,也可以作为栈使用。Java官方推荐使用Deque替代Stack使用
103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
给你二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 锯齿形层序遍历 。(即先从左往右,再从右往左进行下一层遍历,以此类推,层与层之间交替进行)。
解题思路:
这个题是一个变形的二叉树层序遍历,可以用BFS求解,值得注意的是,每隔一层,输出的值顺序是相反的。
- 本来想的是利用双端队列直接排列节点的顺序,奇数层和偶数层的时候,分别从头插入和从尾插入,但是调试了几次用例没通过,元素的添加和取出比较绕
- 其实完全可以按照正常的BFS模板去写,奇数层和偶数层的时候,利用一个双端队列作为一个中转,分别从头插入和从尾插入当前节点,然后在转为list链表。
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return res;
}
ArrayDeque<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offerFirst(root);
int level = 1;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// 这里定义一个双端队列
ArrayDeque<Integer> list = new ArrayDeque<>();
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode treeNode = queue.poll();
// 这里把当前值存入双端队列,根据层数不同,选择插入尾部或者头部
if (level % 2 != 0) {
list.offerLast(treeNode.val);
} else {
list.offerFirst(treeNode.val);
}
if (treeNode.left != null) {
queue.offerLast(treeNode.left);
}
if (treeNode.right != null) {
queue.offerLast(treeNode.right);
}
}
// 这个把临时创建的双端队列存入结果数据中
res.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
level++;
}
return res;
}
}3、优先级队列 -- PriorityQueue
队列是先进先出,优先级队列就是在队列的基础上,增加了一个优先级的概念。
1.使用无序数组实现
offer:直接插入在数组最后面
poll:定义一个max指针,先指向最后面,然后不断往前遍历,如果前面的优先级大,那么就更新max的值,找到最大的max,删除该位置元素,然后后面数组向前移动
peek:先找到max指针,然后返回该位置的值
2、使用有序数组实现
offer:把数据插入到数组最后面,与前一个进行比较,如果比他小,则交换位置
poll : 移除最后一个元素
peek: 返回最后一个元素
3、使用堆实现
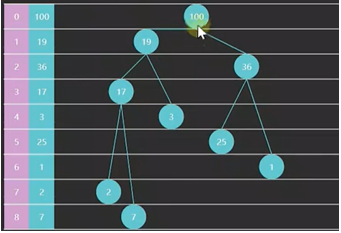
堆:是一种基于树的数据结构,通常用完全二叉树实现,有如下特性:
- 大顶堆:任一节点与C与他的父节点P,有P.value ≥ C.value
- 小顶堆:任一节点与C与他的父节点P,有P.value ≤ C.value
如图就是一个大顶堆,粉色为索引,蓝色为优先级数据。
从索引0开始存储节点数据有如下规律:
- 节点i的父节点索引为 floor((i-1)/2) ,i>0
- 节点i的左子节点为 2i+1,右子节点为 2i+2,当然索引都要小于堆容量size
// 插入元素:
// 1、假设插入到最后的位置,
// 2、把要插入的元素优先级和父节点比较,如果比他大,交换位置,一直保持大顶堆
// 3、直到要插入的元素比父节点小了,或者是根节点了,就把当前元素插到这个位置。
public boolean offer(Priority offered) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
int child = size;
size++;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0 && offered.priority > array[parent].priority) {
array[child] = array[parent];
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
array[child] = offered;
return true;
}
// 移除元素
// 1、其实移除的就是根节点元素,但是要保持大顶堆,就需要进行额外操作
// 2、把最后一个元素替换到根节点的位置,然后和左右子节点比较,把大的节点提上来
// 3、不选循环提节点的操作,直到节点的位置比子节点都大
public Priority poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
swap(0, size - 1);
size--;
Priority removed = array[size];
down(0);// 根节点下沉
return removed;
}
// 将元素下沉,构建大顶堆
private void down(int parent) {
int left = 2 * parent + 1;
int right = left + 1;
int max = parent;
if (left < size && array[left].priority > array[max].priority) {
max = left;
}
if (right < size && array[right].priority > array[max].priority) {
max = right;
}
if (max != parent) {
swap(parent, max);
down(max);
}
}
// 交换节点位置
private void swap(int x, int y) {
Priority temp = array[x];
array[x] = temp;
array[y] = temp;
} // 堆顶元素
public Priority peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
return array[0];
}23、合并 K 个升序链表
解题:
之前学习链表的时候,我们知道了怎么合并两个有序链表,那么合并多个有序链表,就循环遍历,两两合并就可以了。
现在,学习了优先级链表,也可以用该数据结构进行解题。
采用小顶堆,Java代码中可以直接使用 PriorityQueue,将给出的多个链表中的头节点放到优先级队列中,然后取出最小的一个节点 (如果这个节点在原来链表中有next节点,那么就把next节点在加入优先级队列中。不断循环,就可以得到排序的链表。)
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode newList = new ListNode();
ListNode head = newList;
PriorityQueue<ListNode> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<ListNode>() {
@Override
public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2) {
return o1.val - o2.val;
}
});
for (ListNode l : lists) {
if (l != null) {
priorityQueue.add(l);
}
}
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
ListNode curr = priorityQueue.poll();
head.next = curr;
head = head.next;
if (curr.next != null) {
priorityQueue.add(curr.next);
}
}
return newList.next;
}
}
也可以吧所有的节点都加入到优先级链表中,然后在一个个取出来,但是会占用很大的堆空间。4、阻塞队列
适用于生产者消费者模式,消费的时候,要保证已经有东西生产出来了,生产的时候,要保证队列没有满。
阻塞队列,单锁实现。
public class MyBlockingQueue {
private final int[] array;
private int head;
private int tail;
private int size;
// 可重入锁
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition headWaits = lock.newCondition();
private Condition tailWaits = lock.newCondition();
public MyBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
this.array = new int[capacity];
}
public void offer(int value) throws InterruptedException {
// 加锁
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (isFull()) { //while循环,防止虚假唤醒
// 满了就等待
tailWaits.await();
}
// 添加元素
array[tail] = value;
if (++tail == array.length) {
tail = 0;
}
size++;
// 唤醒poll方法
headWaits.signal();
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 添加一个等待时间
public boolean offer(int value, Long timeout) throws InterruptedException {
// 加锁
lock.lockInterruptibly();
long nanos = TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS.toNanos(timeout);
try {
while (isFull()) { //while循环,防止虚假唤醒
// 满了就等待
if (nanos > 0) {
// 假设要求等待5s,返回值就是等待后还剩余的时间。
// 假设等待了1s后,被唤醒,但是又被其他线程抢了锁,这里就要重新等待,但是不能等待5s,而是4s
nanos = tailWaits.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return false;
}
// 添加元素
array[tail] = value;
if (++tail == array.length) {
tail = 0;
}
size++;
// 唤醒poll方法
headWaits.signal();
return true;
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
}
public int poll() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (isEmpty()) { //while循环,防止虚假唤醒
// 满了就等待
headWaits.await();
}
int res = array[head];
array[head] = 0;
if (++head == array.length) {
head = 0;
}
size--;
// 唤醒offer方法
tailWaits.signal();
return res;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public int peek() {
return array[head];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return size == array.length;
}
}上述代码,offer和poll操作用的是同一把锁,因此这两个操作是相互干扰的,即一个执行的时候,另外一个会阻塞,这样是不合理的。
因此,可以使用两把锁,分别控制offer和poll操作,但是这个会引入一个问题,就是size++/size-- 的问题。因为++/--操作不是原子性的,那么,在多线程的情况下就是不安全的(为什么一把锁的时候是线程安全呢?因为一把锁的时候,offer拿锁,poll会阻塞,因此在size++的过程中,就不可能出现size++的操作,故是线程安全的,而两把锁的时候,offer和poll互不影响,因此就可能在size++的时候出现size-- 导致线程不安全。)
两把锁代码如下,每个锁控制着自己对应的Condition,因此唤醒操作只能在锁存在的时候才可以唤醒。为了避免死锁,需要保证一把锁解开后,才可以去给另一把锁上锁。
private ReentrantLock tailLock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition tailWaits = tailLock.newCondition();
private ReentrantLock headLock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition headWaits = headLock.newCondition();
private AtomicInteger size; // 原子性
public void offer(int value) throws InterruptedException {
// 加锁
tailLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (isFull()) { //while循环,防止虚假唤醒
// 满了就等待
tailWaits.await();
}
// 添加元素
array[tail] = value;
if (++tail == array.length) {
tail = 0;
}
size.getAndIncrement();
} finally {
// 解锁
tailLock.unlock();
}
headLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 唤醒poll方法,只能在tailLock锁解锁之后唤醒,避免死锁
headWaits.signal();
} finally {
headLock.unlock();
}
}
public int poll() throws InterruptedException {
headLock.lockInterruptibly();
int res;
try {
while (isEmpty()) { //while循环,防止虚假唤醒
// 满了就等待
headWaits.await();
}
res = array[head];
array[head] = 0;
if (++head == array.length) {
head = 0;
}
size.getAndDecrement();
} finally {
headLock.unlock();
}
tailLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 唤醒offer方法,只能在headLock锁解锁之后唤醒,避免死锁
tailWaits.signal();
} finally {
tailLock.unlock();
}
return res;
}上述代码实现了两把锁分别控制offer和poll,但是还存在一个问题,就是每次offer的时候,为了唤醒poll,还是给headlock加了锁;每次poll的时候为了唤醒offer,还是给taillock加了锁,为了提升效率,可以做如下优化:
思想:级联思想
- offer的时候:只有队列中元素从0到1,才触发唤醒poll操作,其余的poll线程唤醒交给poll方法自身
- poll的时候:只有队列中元素从满到不满才触发唤醒offer操作,如遇offer线程唤醒交给offer自身。
优化代码如下:
public void offer(int value) throws InterruptedException { // 加锁 tailLock.lockInterruptibly(); int c; // 记录队列增加前的元素个数 try { while (isFull()) { //while循环,防止虚假唤醒 // 满了就等待 tailWaits.await(); } // 添加元素 array[tail] = value; if (++tail == array.length) { tail = 0; } c = size.getAndIncrement(); // 队列中元素不满,唤醒其他offer线程 if (c < array.length - 1) { tailWaits.signal(); } } finally { // 解锁 tailLock.unlock(); } // 队列中元素从0到1,才触发唤醒poll操作 if (c == 0) { headLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { // 唤醒poll方法,只能在tailLock锁解锁之后唤醒,避免死锁 headWaits.signal(); } finally { headLock.unlock(); } } } public int poll() throws InterruptedException { headLock.lockInterruptibly(); int res; int c; // 记录队列减少前的元素个数 try { while (isEmpty()) { //while循环,防止虚假唤醒 // 满了就等待 headWaits.await(); } res = array[head]; array[head] = 0; if (++head == array.length) { head = 0; } c = size.getAndDecrement(); // 队列中有元素,唤醒其他poll线程 if (c > 1) { headWaits.signal(); } } finally { headLock.unlock(); } // 队列从满到不满的时候,加锁唤醒offer线程 if (c == array.length) { tailLock.lockInterruptibly(); try { // 唤醒offer方法,只能在headLock锁解锁之后唤醒,避免死锁 tailWaits.signal(); } finally { tailLock.unlock(); } } return res; }