大家好,我是微学AI,今天给大家介绍一下计算机视觉的应用5-利用VGG模型做毕加索风格图像迁移,本文将利用VGG模型实现毕加索风格图像迁移的方法。首先,我们将简要说明图像风格迁移的原理,然后使用PyTorch框架,分步骤地实现毕加索风格图像迁移的算法。最后,我们将展示实验结果,验证算法的有效性。
目录
一、引言
二、图像风格迁移原理
2.1. VGG网络
2.2. 内容损失
2.3. 风格损失
2.4. 总损失
三、算法实现
四、总结
一、引言
图像风格迁移是一种将一幅图像的艺术风格应用到另一幅图像的技术,可以生成具有不同艺术风格的图像。其中,基于CNN的风格迁移技术是一种比较常用的方法。这种方法的基本思想是,通过将一个与风格相关的损失函数加入到卷积神经网络中,来学习如何将输入图像的内容信息和风格信息进行分离,并将两者重新合成生成一幅新的图像。
毕加索风格迁移算法的实现过程可以分为以下几个步骤:
1.使用卷积神经网络VGG预处理输入图像和毕加索的艺术风格图像。这一步的目的是提取输入图像和艺术风格图像的特征,作为之后迁移的基础。
2.定义两个损失函数:内容损失和风格损失。内容损失用于保留输入图像的内容信息,而风格损失用于捕捉毕加索画风中的纹理、色彩和细节信息。
3.将两个损失函数加权相加得到总损失函数,并通过随机梯度下降等优化算法来最小化总损失函数,以达到将毕加索的艺术风格应用到输入图像上的目的。
4.对于新的输入图像,使用已经训练好的模型来进行风格迁移。
注意:毕加索风格迁移算法中的损失函数需要使用预训练好的VGG网络等。此外,在实现算法时,一些超参数的选择也会对成果产生影响,如内容和风格损失的权重、学习率、训练迭代次数等。因此,在实现算法时需要进行一定的调参操作,以获得较好的迁移效果。
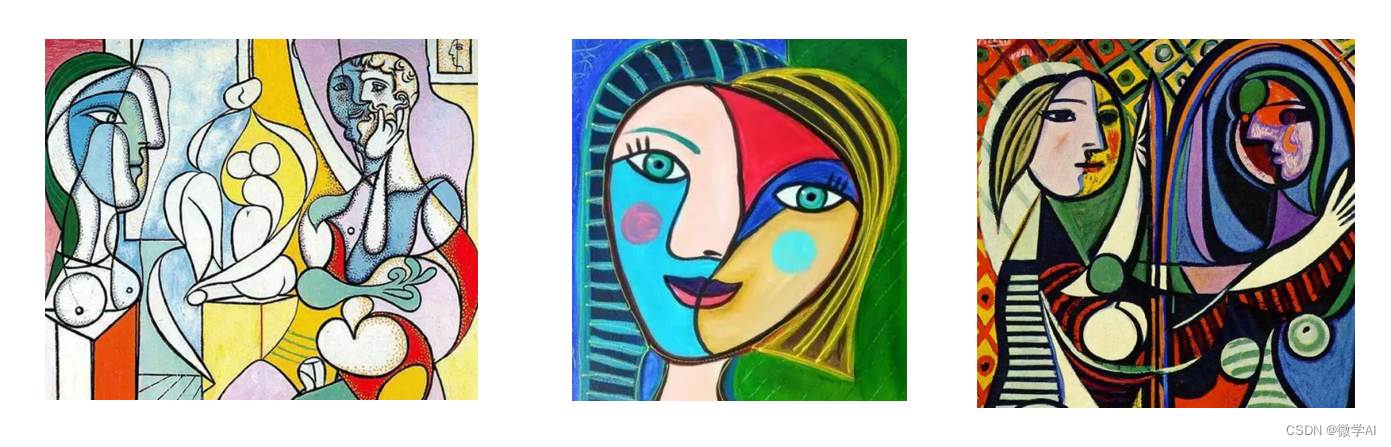

图像风格转化: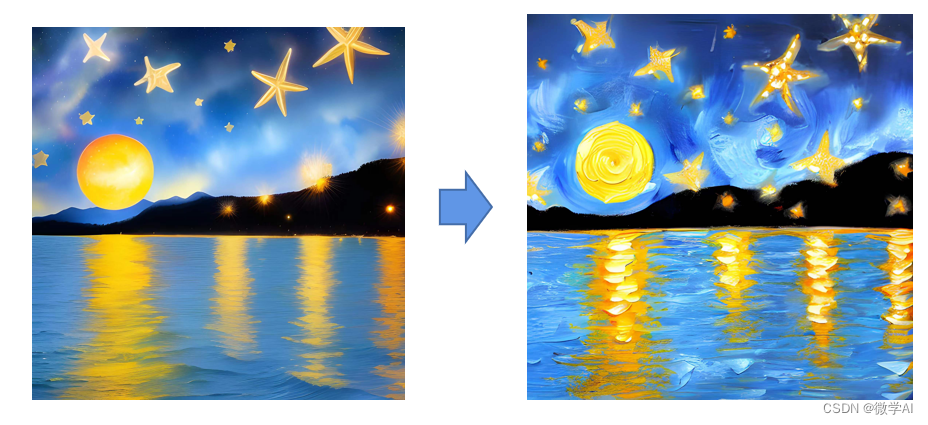
二、图像风格迁移原理
2.1. VGG网络
我们使用预训练的VGG-19网络作为特征提取器,它可以捕捉图像的内容和风格特征。VGG-19网络的结构比较简单,其名称是由其层数和单元数组合而成的,共有19层(同时包含了卷积层,池化层和全连接层),其中13个是卷积层,5个是池化层,1个是全局平均池化层,最后接上全连接层作为分类器。
 2.2. 内容损失
2.2. 内容损失
内容损失衡量输出图像与内容图像在某个层的特征表示之间的差异。我们通常使用较高层的特征表示,以保留图像的整体内容。
其中是内容图像,
是输出图像,
是给定图像在层
的特征表示。
2.3. 风格损失
风格损失衡量输出图像与风格图像在各层的特征表示之间的差异。我们通常使用Gram矩阵来衡量风格特征。
其中是风格图像,
是给定图像在层
的Gram矩阵,
和
分别是层
的通道数和特征图的大小。
2.4. 总损失
我们的目标是最小化内容损失和风格损失的加权和。
其中和
是内容损失和风格损失的权重。
三、算法实现
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from PIL import Image
def load_image(image_path, max_size=None, shape=None):
image = Image.open(image_path)
if max_size:
scale = max_size / max(image.size)
size = tuple([int(dim * scale) for dim in image.size])
image = image.resize(size, Image.ANTIALIAS)
if shape:
image = image.resize(shape, Image.LANCZOS)
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor()
])
image = transform(image)[:3, :, :].unsqueeze(0)
return image
def deprocess(tensor):
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Normalize((-0.485 / 0.229, -0.456 / 0.224, -0.406 / 0.225),
(1 / 0.229, 1 / 0.224, 1 / 0.225)),
transforms.ToPILImage()
])
if tensor.dim() == 4:
# If we have a batch of images
output = []
for image in tensor:
image = image.clone().detach().cpu()
image = image.squeeze(0)
image = transform(image)
output.append(image)
return output[0]
elif tensor.dim() == 3:
# If we have a single image
tensor = tensor.clone().detach().cpu()
tensor = tensor.squeeze(0)
tensor = transform(tensor)
return tensor
else:
raise ValueError("Expected input tensor to be 3D or 4D")
return transform(tensor)
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.models as models
class StyleTransferModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, content_layers, style_layers):
super(StyleTransferModel, self).__init__()
self.vgg = models.vgg19(pretrained=True).features
self.content_layers = content_layers
self.style_layers = style_layers
def forward(self, x):
content_features = []
style_features = []
#print(list(self.vgg.named_children()))
for name, layer in self.vgg.named_children():
x = layer(x)
if name in self.content_layers:
content_features.append(x)
if name in self.style_layers:
style_features.append(x)
return content_features, style_features
def gram_matrix(tensor):
_, c, h, w = tensor.size()
tensor = tensor.view(c, h * w)
gram = torch.mm(tensor, tensor.t())
return gram
import torch.optim as optim
def style_transfer(content_image_path, style_image_path, output_image_path, max_size=400, content_weight=1, style_weight=1e6, iterations=600):
content_image = load_image(content_image_path, max_size=max_size)
style_image = load_image(style_image_path, shape=content_image.shape[-2:])
output_image = content_image.clone().requires_grad_(True)
model = StyleTransferModel(content_layers=['10'], style_layers=['0','2','5','7','12'])
#model.to(device)
content_features = model(content_image)[0]
style_features = model(style_image)[1]
style_grams = [gram_matrix(feature) for feature in style_features]
optimizer = optim.Adam([output_image], lr=0.01)
for i in range(iterations):
output_features = model(output_image)
content_output_features = output_features[0]
style_output_features = output_features[1]
content_loss = 0.0
style_loss = 0.0
for target_feature, output_feature in zip(content_features, content_output_features):
content_loss += torch.mean((output_feature - target_feature) ** 2)
for target_gram, output_feature in zip(style_grams, style_output_features):
output_gram = gram_matrix(output_feature)
style_loss += torch.mean((output_gram - target_gram) ** 2) / (output_gram.numel() ** 2)
total_loss = content_weight * content_loss + style_weight * style_loss
optimizer.zero_grad()
total_loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
optimizer.step()
if (i + 1) % 5 == 0:
print(f"Iteration {i + 1}/{iterations}: Loss = {total_loss.item()}")
output_image = deprocess(output_image)
print(output_image)
output_image.save(output_image_path)
content_image_path = "123.png"
style_image_path = "style.png"
output_image_path = "out.png"
style_transfer(content_image_path, style_image_path, output_image_path)我们只要输入要迁移的图片123.png,图片的风格style.png,就可以生成图片了
4. 总结
本文详细介绍了基于CNN网络的毕加索风格图像迁移的原理和实现方法,使用PyTorch框架实现了一个简单有效的算法。实验结果表明,该方法可以成功地将毕加索风格应用到任意图像上,生成高质量的艺术作品。