IMU 积分进行航迹推算
Reference https://github.com/gaoxiang12/slam_in_autonomous_driving
1.0 递推方程推导
\quad
连续时间内的 IMU 运动学方程:
R
˙
=
R
ω
∧
q
=
1
2
q
ω
˙
p
˙
=
v
v
˙
=
a
\dot{\mathbf{R}}=\mathbf{R}\omega ^{\wedge} \\ \dot{\mathbf{q}=\frac{1}{2}\mathbf{q}\omega}\\ \dot{\mathbf{p}}=v \\ \dot{\mathbf{v}}=a
R˙=Rω∧q=21qω˙p˙=vv˙=a
\quad
这些物理量带上角标之后应该写作
R
w
b
,
p
w
b
\mathbf{R_{wb},p_{wb}}
Rwb,pwb,对应世界坐标系,它在求导之后就是车辆在世界坐标系下的速度与加速度
v
w
,
a
w
\mathbf{v_w}, \mathbf{a_w}
vw,aw 。在不考虑地球自传的时候,也可以简单的将 车辆行驶的打的视为固定的世界坐标系,这时 IMU 的测量值
ω
~
,
a
~
\widetilde{\omega } ,\widetilde{a}
ω
,a
就是车辆本身的角速度,以及车体系下的加速度:
a
~
=
R
⊤
a
,
ω
~
=
ω
.
\begin{aligned} \tilde{\boldsymbol{a}} & =\boldsymbol{R}^{\top} \boldsymbol{a}, \\ \tilde{\boldsymbol{\omega}} & =\boldsymbol{\omega} . \end{aligned}
a~ω~=R⊤a,=ω.
\quad
注意
R
⊤
\mathbf{R}^{\top}
R⊤ 带下标之后就是
R
b
w
\mathbf{R_{bw}}
Rbw。它将世界系下的物理量转换到车体系。然而,实际的车辆、机器人都在地球表面运行。这些系统受到重力的影响,所以我们应该把重 力写在系统方程中。在绝大多数 IMU 系统中,我们可以忽略地球自转的干扰,从而把 IMU 测量 值写为:
a
~
=
R
⊤
(
a
−
g
)
,
ω
~
=
ω
.
\begin{aligned} \tilde{\boldsymbol{a}} & =\boldsymbol{R}^{\top} \boldsymbol{(a-g)}, \\ \tilde{\boldsymbol{\omega}} & =\boldsymbol{\omega} . \end{aligned}
a~ω~=R⊤(a−g),=ω.
\quad
g
\mathbf{g}
g 为地球的重力。当然,如果在无重力环境下测量物体加速度,就不会出现重力项。注意这里
g
\mathbf{g}
g的符号和坐标系定义相关。我们的车体系和世界系都是
Z
Z
Z 轴向上,于是
g
\mathbf{g}
g 通常取 值
(
0
,
0
,
−
9.8
)
⊤
(0, 0, −9.8)^⊤
(0,0,−9.8)⊤。假设有一个水平放置的IMU,其读数此时应当为
(
0
,
0
,
9.8
)
⊤
(0, 0, 9.8)^⊤
(0,0,9.8)⊤,为什么呢?因为此时真正的加速度应该为
(
0
,
0
,
0
)
⊤
(0, 0, 0)^⊤
(0,0,0)⊤,但是由于地球重力的影响,其输出结果会减去
g
\mathbf{g}
g ,所以输出结果就是
(
0
,
0
,
9.8
)
⊤
(0, 0, 9.8)^⊤
(0,0,9.8)⊤。
\quad
在大多数系统中,我们认为 IMU 的噪声由两部分组成:测量噪声(measurement noise)与零偏(bias)。记陀螺仪和加速度计的测量噪声分别为
η
g
η_g
ηg,
η
a
η_a
ηa,同时记零偏为
b
g
b_g
bg,
b
a
b_a
ba,下标
g
g
g 表示陀螺仪,
a
a
a 表示加速度计。那么这几个参数在测量方程中体现为:
a
~
=
R
⊤
(
a
−
g
)
+
b
a
+
η
a
ω
~
=
ω
+
b
g
+
η
g
.
\begin{aligned} \tilde{\boldsymbol{a}} & =\boldsymbol{R}^{\top}(\boldsymbol{a}-\boldsymbol{g})+\boldsymbol{b}_{a}+\boldsymbol{\eta}_{a} \\ \tilde{\boldsymbol{\omega}} & =\boldsymbol{\omega}+\boldsymbol{b}_{g}+\boldsymbol{\eta}_{g} . \end{aligned}
a~ω~=R⊤(a−g)+ba+ηa=ω+bg+ηg.
\quad
于是,我们直接把测量模型代入运动学方程,忽略测量噪声影响,即可得到连续时间下的积分 模型:
R
˙
=
R
(
ω
~
−
b
g
)
∧
,
或
q
˙
=
q
[
0
,
1
2
(
ω
~
−
b
g
)
]
,
p
˙
=
v
,
v
˙
=
R
(
a
~
−
b
a
)
+
g
.
\begin{aligned} \dot{\boldsymbol{R}} & =\boldsymbol{R}\left(\tilde{\boldsymbol{\omega}}-\boldsymbol{b}_{g}\right)^{\wedge}, \quad \text { 或 } \dot{\boldsymbol{q}}=\boldsymbol{q}\left[0, \frac{1}{2}\left(\tilde{\boldsymbol{\omega}}-\boldsymbol{b}_{g}\right)\right], \\ \dot{\boldsymbol{p}} & =\boldsymbol{v}, \\ \dot{\boldsymbol{v}} & =\boldsymbol{R}\left(\tilde{\boldsymbol{a}}-\boldsymbol{b}_{a}\right)+\boldsymbol{g} . \end{aligned}
R˙p˙v˙=R(ω~−bg)∧, 或 q˙=q[0,21(ω~−bg)],=v,=R(a~−ba)+g.
\quad
有时候我们也把
p
,
v
,
q
p, v, q
p,v,q 称为
P
V
Q
PVQ
PVQ 状态。该方程可以从时间
t
t
t积分至
t
+
∆
t
t + ∆t
t+∆t,推出下一个时刻的状态情况:
R
(
t
+
Δ
t
)
=
R
(
t
)
Exp
(
(
ω
~
−
b
g
)
Δ
t
)
,
或
q
(
t
+
Δ
t
)
=
q
(
t
)
[
1
,
1
2
(
ω
~
−
b
g
)
Δ
t
]
,
\begin{aligned} \boldsymbol{R}(t+\Delta t) & =\boldsymbol{R}(t) \operatorname{Exp}\left(\left(\tilde{\boldsymbol{\omega}}-\boldsymbol{b}_{g}\right) \Delta t\right), \quad \text { 或 } \boldsymbol{q}(t+\Delta t)=\boldsymbol{q}(t)\left[1, \frac{1}{2}\left(\tilde{\boldsymbol{\omega}}-\boldsymbol{b}_{g}\right) \Delta t\right], \\ \end{aligned}
R(t+Δt)=R(t)Exp((ω~−bg)Δt), 或 q(t+Δt)=q(t)[1,21(ω~−bg)Δt],
\quad
这里我们先不考虑白噪声
η
a
\boldsymbol{\eta}_{a}
ηa,则IMU的测量方程有:
a
~
=
R
⊤
(
a
−
g
)
+
b
a
+
η
a
a
~
−
b
a
=
R
⊤
(
a
−
g
)
R
(
a
~
−
b
a
)
=
a
−
g
a
=
R
(
a
~
−
b
a
)
+
g
\begin{aligned} \tilde{\boldsymbol{a}} &=\boldsymbol{R}^{\top}(\boldsymbol{a}-\boldsymbol{g})+\boldsymbol{b}_{a}+\boldsymbol{\eta}_{a}\\ \tilde{\boldsymbol{a}} -\boldsymbol{b}_{a}&=\boldsymbol{R}^{\top}(\boldsymbol{a}-\boldsymbol{g}) \\ \boldsymbol{R}(\tilde{\boldsymbol{a}} -\boldsymbol{b}_{a})&=\boldsymbol{a}-\boldsymbol{g}\\ \boldsymbol{a}&=\boldsymbol{R}(\tilde{\boldsymbol{a}} -\boldsymbol{b}_{a}) + \boldsymbol{g} \end{aligned}
a~a~−baR(a~−ba)a=R⊤(a−g)+ba+ηa=R⊤(a−g)=a−g=R(a~−ba)+g
\quad
速度的递推,我们知道
v
(
t
+
Δ
t
)
=
v
(
t
)
+
a
t
\boldsymbol{v}(t+\Delta t) = \boldsymbol{v}(t) + \mathbf{a}t
v(t+Δt)=v(t)+at。
v
(
t
+
Δ
t
)
=
v
(
t
)
+
a
Δ
t
=
v
(
t
)
+
(
R
(
t
)
(
a
~
−
b
a
)
+
g
)
Δ
t
=
v
(
t
)
+
R
(
t
)
(
a
~
−
b
a
)
Δ
t
+
g
Δ
t
.
\begin{aligned} \boldsymbol{v}(t+\Delta t) & =\boldsymbol{v}(t)+ \mathbf{a}\Delta t \\ & =\boldsymbol{v}(t)+ \left( \boldsymbol{R}(t)\left(\tilde{\boldsymbol{a}}-\boldsymbol{b}_{a}\right) +\boldsymbol{g} \right)\Delta t \\ &=\boldsymbol{v}(t)+\boldsymbol{R}(t)\left(\tilde{\boldsymbol{a}}-\boldsymbol{b}_{a}\right) \Delta t+\boldsymbol{g} \Delta t . \end{aligned}
v(t+Δt)=v(t)+aΔt=v(t)+(R(t)(a~−ba)+g)Δt=v(t)+R(t)(a~−ba)Δt+gΔt.
\quad
位置的递推,我们知道
p
(
t
+
Δ
t
)
=
p
(
t
)
+
v
Δ
t
+
1
2
a
t
2
\boldsymbol{p}(t+\Delta t) =\boldsymbol{p}(t)+\mathbf{v}\Delta t + \frac{1}{2}\mathbf{at^2}
p(t+Δt)=p(t)+vΔt+21at2,则有:
p
(
t
+
Δ
t
)
=
p
(
t
)
+
v
Δ
t
+
1
2
a
t
2
=
p
(
t
)
+
v
Δ
t
+
1
2
(
R
(
t
)
(
a
~
−
b
a
)
+
g
)
t
2
=
p
(
t
)
+
v
Δ
t
+
1
2
(
R
(
t
)
(
a
~
−
b
a
)
)
Δ
t
2
+
1
2
g
Δ
t
2
\begin{aligned} \boldsymbol{p}(t+\Delta t) & =\boldsymbol{p}(t)+\boldsymbol{v} \Delta t+\frac{1}{2} \mathbf{a}t^2\\ & =\boldsymbol{p}(t)+\boldsymbol{v} \Delta t+\frac{1}{2} \left(\boldsymbol{R(t)}(\tilde{\boldsymbol{a}} -\boldsymbol{b}_{a}) + \boldsymbol{g} \right)t^2\\ & =\boldsymbol{p}(t)+\boldsymbol{v} \Delta t+\frac{1}{2}\left(\boldsymbol{R}(t)\left(\tilde{\boldsymbol{a}}-\boldsymbol{b}_{a}\right)\right) \Delta t^{2}+\frac{1}{2} \boldsymbol{g} \Delta t^{2}\\ \end{aligned}
p(t+Δt)=p(t)+vΔt+21at2=p(t)+vΔt+21(R(t)(a~−ba)+g)t2=p(t)+vΔt+21(R(t)(a~−ba))Δt2+21gΔt2
2.0 代码实现
2.1 数据集介绍
这里使用的高博书中带的数据集,数据集的格式为:
# timestamp gx gy gz ax ay az
2.2 具体代码实现
代码实现主要有三个文件
common.hpp主要用户存放 IMU 数据结构体和读取和保存数据。imu_integration.hpp主要存放 IMU数据的处理和航迹推算实现类。run_imu_integration.cpp程序入口函数。
如下命令运行
./run_imu_integration --txt_file_path="../slam_in_auto_driving/chapter3/dataset/10.txt" --output_inter_trajectory_path="./output_trajectory.txt"
common.hpp
#ifndef COMMON_HPP
#define COMMON_HPP
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Core>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Dense>
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
struct IMUMsg
{
IMUMsg() = default;
IMUMsg(double timestamp, Eigen::Vector3d gyro, Eigen::Vector3d acc)
: timestamp_(timestamp), acc_(acc), gyro_(gyro){};
double timestamp_{0.0};
Eigen::Vector3d acc_;
Eigen::Vector3d gyro_;
};
struct IMUIntegrationResult
{
IMUIntegrationResult() = default;
IMUIntegrationResult(const double ×tamp, const Eigen::Vector3d &P,
const Eigen::Quaterniond &Q, const Eigen::Vector3d &V)
: timestamp_(timestamp), P_(P), V_(V), Q_(Q){};
double timestamp_{0.0};
Eigen::Vector3d P_;
Eigen::Vector3d V_;
Eigen::Quaterniond Q_;
};
inline void ReadImuMsg(std::ifstream &fin, std::vector<IMUMsg> &imu_msg)
{
if (!fin)
{
std::cerr << "Coule not find file\n";
return;
}
while (!fin.eof())
{
std::string line;
std::getline(fin, line);
if (line.empty())
{
continue;
}
if (line[0] == '#')
{
continue;
}
std::stringstream ss;
ss << line;
std::string data_type;
ss >> data_type;
if (data_type == "IMU")
{
double time, gx, gy, gz, ax, ay, az;
ss >> time >> gx >> gy >> gz >> ax >> ay >> az;
imu_msg.push_back(IMUMsg(time, Eigen::Vector3d(gx, gy, gz),
Eigen::Vector3d(ax, ay, az)));
}
}
std::cout << "Read IMU msgs success\n";
}
inline void SaveImuIntegrationResult(
const std::string &file_path,
const std::vector<IMUIntegrationResult> &imu_inte_result)
{
std::ofstream fout(file_path);
for (const auto &imu_traj : imu_inte_result)
{
fout << std::setprecision(18) << imu_traj.timestamp_ << " " << std::setprecision(9);
fout << imu_traj.P_(0) << " " << imu_traj.P_(1) << " " << imu_traj.P_(2) << " ";
fout << imu_traj.Q_.w() << " " << imu_traj.Q_.x() << " " << imu_traj.Q_.y() << " " << imu_traj.Q_.z() << " ";
fout << imu_traj.V_(0) << " " << imu_traj.V_(1) << " " << imu_traj.V_(2) << " ";
fout << std::endl;
}
}
#endif // COMMON_HPP
imu_integration.hpp
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Core>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Dense>
#include <sophus/so3.hpp>
#include "common.hpp"
class ImuIntegration
{
public:
ImuIntegration() = default;
~ImuIntegration() = default;
ImuIntegration(const Eigen::Vector3d &gravity, const Eigen::Vector3d &init_bg,
const Eigen::Vector3d &init_ba)
: gravity_(gravity), init_ba_(init_ba), init_bg_(init_bg)
{
}
void AddNewImgMessage(const IMUMsg &imu_msg)
{
// Final P: -3.38794e+06 5.73752e+06 -512933
// 其实第一帧 IMU 数据也可以不判断,因为后面有 dt<0.1 的判断
if (first_imu_)
{
first_imu_ = false;
timestamp_ = imu_msg.timestamp_;
}
double dt = imu_msg.timestamp_ - timestamp_;
if (dt > 0 && dt < 0.1)
{
P_ = P_ + V_ * dt + 0.5 * (R_ * (imu_msg.acc_ - init_ba_)) * dt * dt +
0.5 * gravity_ * dt * dt;
V_ = V_ + R_ * (imu_msg.acc_ - init_ba_) * dt + gravity_ * dt;
R_ = R_ * Sophus::SO3d::exp((imu_msg.gyro_ - init_bg_) * dt);
}
timestamp_ = imu_msg.timestamp_;
}
Eigen::Vector3d GetPosition() const { return P_; }
Eigen::Vector3d GetVelocity() const { return V_; }
Eigen::Quaterniond GetRotation() const { return R_.unit_quaternion(); }
private:
Sophus::SO3d R_;
Eigen::Quaterniond R_quaternion_ = Eigen::Quaterniond::UnitRandom();
Eigen::Vector3d P_ = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero();
Eigen::Vector3d V_ = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero();
Eigen::Vector3d gravity_ = Eigen::Vector3d(0, 0, -9.81);
Eigen::Vector3d init_ba_ = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero();
Eigen::Vector3d init_bg_ = Eigen::Vector3d::Zero();
double timestamp_{0.0};
bool first_imu_{true};
};
run_imu_integration.cpp
#include <gflags/gflags.h>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Core>
#include <eigen3/Eigen/Dense>
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
#include "common.hpp"
#include "imu_integration.hpp"
DEFINE_string(txt_file_path, "../slam_in_auto_driving/chapter3/dataset/10.txt",
"Imu integration file");
DEFINE_string(output_inter_trajectory_path, "./output_trajectory.txt",
"output trajectory file");
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
google::ParseCommandLineFlags(&argc, &argv, true);
std::ifstream fin(FLAGS_txt_file_path);
std::vector<IMUMsg> imu_msgs;
std::vector<IMUIntegrationResult> imu_inter_result;
ReadImuMsg(fin, imu_msgs);
// 该实验中,我们假设零偏已知
Eigen::Vector3d gravity(0, 0, -9.8); // 重力方向
Eigen::Vector3d init_bg(00.000224886, -7.61038e-05, -0.000742259);
Eigen::Vector3d init_ba(-0.165205, 0.0926887, 0.0058049);
ImuIntegration imu_integration(gravity, init_bg, init_ba);
for (auto &imu_msg : imu_msgs)
{
imu_integration.AddNewImgMessage(imu_msg);
imu_inter_result.push_back(IMUIntegrationResult(
imu_msg.timestamp_, imu_integration.GetPosition(),
imu_integration.GetRotation(), imu_integration.GetVelocity()));
}
SaveImuIntegrationResult(FLAGS_output_inter_trajectory_path,
imu_inter_result);
// 高博书中程序输出的结果
// T: 1624429630.2702086
// P : -3387943.36 5737523.81 -512933.307
// Q : 0.982857044 -0.132676506 0.0940114453 0.0868954789
// V : -572.166705 4626.10758 -496.605214
std::cout << "Final P: " << imu_integration.GetPosition().transpose()
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Final V: " << imu_integration.GetVelocity().transpose()
<< std::endl;
std::cout << "Final Q: " << imu_integration.GetRotation().coeffs().transpose()
<< std::endl;
return 0;
}
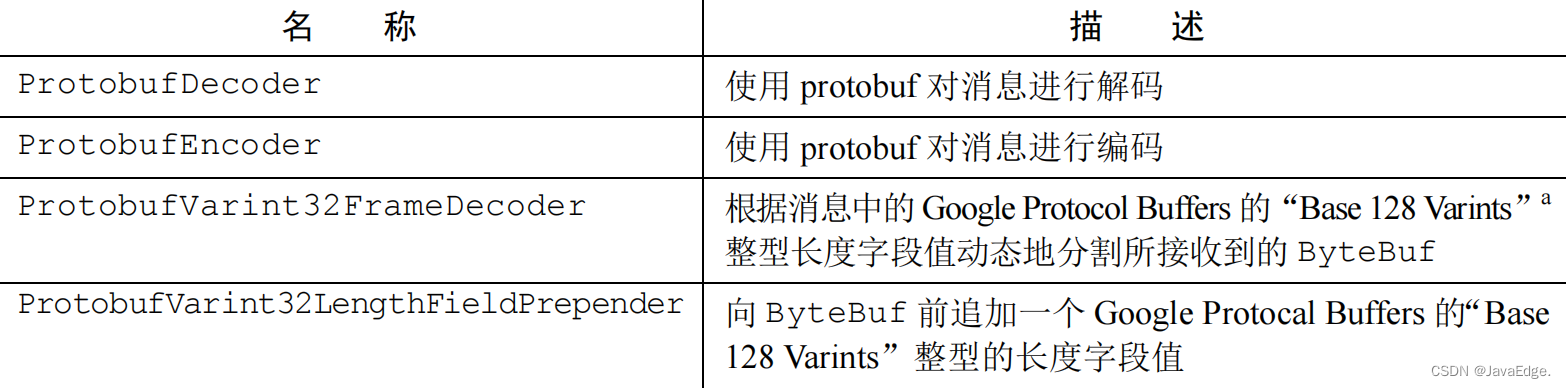
输出结果可视化:
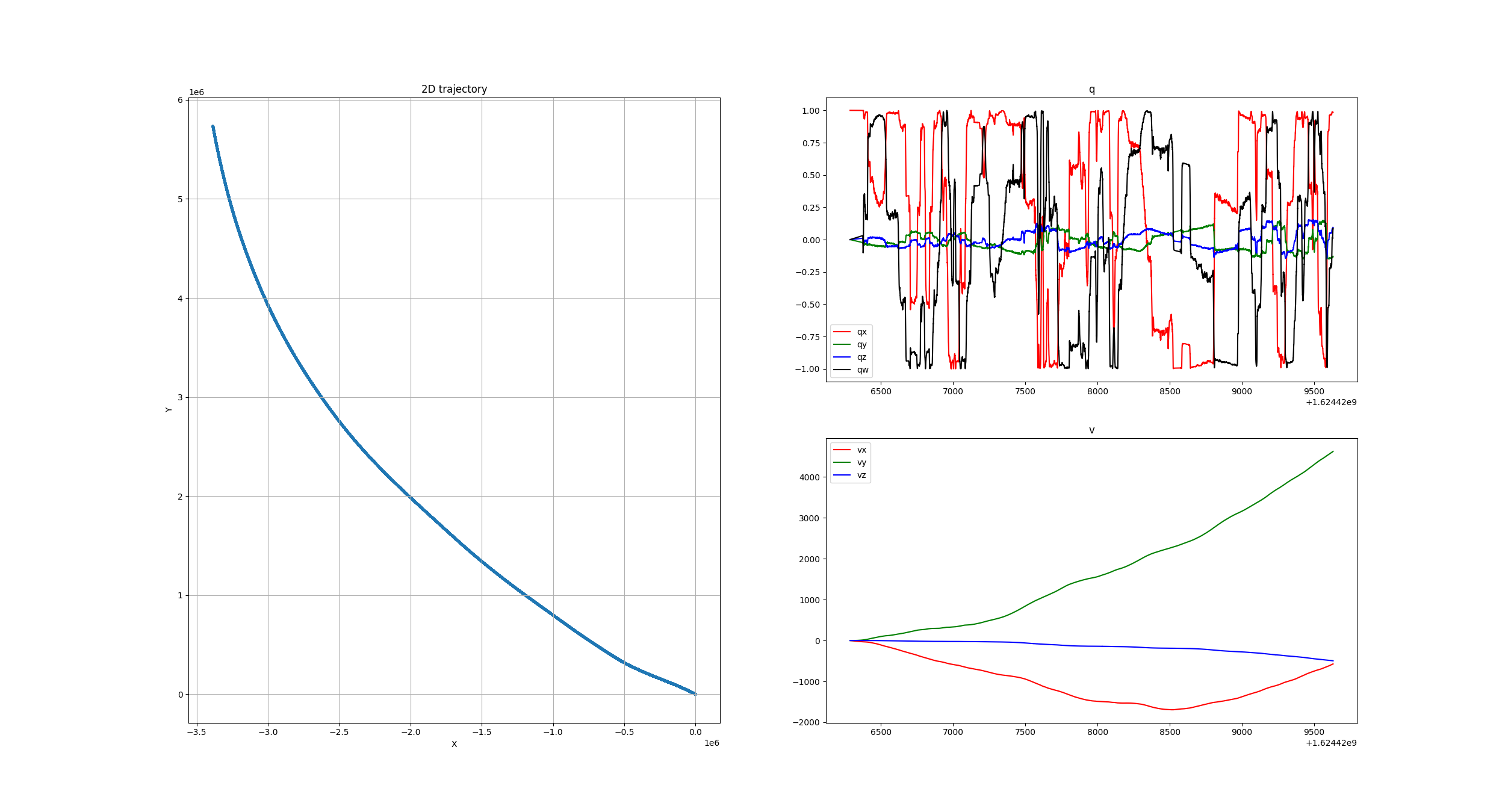
可视化程序,运行:
python3 draw_imu_integration.py ./output_trajectory.txt
# coding=UTF-8
import sys
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print('Please input valid file')
exit(1)
else:
path = sys.argv[1]
path_data = np.loadtxt(path)
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (16.0, 12.0)
# 轨迹
plt.subplot(121)
plt.scatter(path_data[:, 1], path_data[:, 2], s=2)
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('Y')
plt.grid()
plt.title('2D trajectory')
# 姿态
plt.subplot(222)
plt.plot(path_data[:, 0], path_data[:, 4], 'r')
plt.plot(path_data[:, 0], path_data[:, 5], 'g')
plt.plot(path_data[:, 0], path_data[:, 6], 'b')
plt.plot(path_data[:, 0], path_data[:, 7], 'k')
plt.title('q')
plt.legend(['qx', 'qy', 'qz', 'qw'])
# 速度
plt.subplot(224)
plt.plot(path_data[:, 0], path_data[:, 8], 'r')
plt.plot(path_data[:, 0], path_data[:, 9], 'g')
plt.plot(path_data[:, 0], path_data[:, 10], 'b')
plt.title('v')
plt.legend(['vx', 'vy', 'vz'])
plt.show()
exit(1)
![[CTF/网络安全] 攻防世界 weak_auth 解题详析](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/746b839a42ac476fb440ba06e661e720.png#pic_center)