题目详情:06-图1 列出连通集
给定一个有N个顶点和E条边的无向图,请用DFS和BFS分别列出其所有的连通集。假设顶点从0到N−1编号。进行搜索时,假设我们总是从编号最小的顶点出发,按编号递增的顺序访问邻接点。
输入格式:
输入第1行给出2个整数N(0<N≤10)和E,分别是图的顶点数和边数。随后E行,每行给出一条边的两个端点。每行中的数字之间用1空格分隔。
输出格式:
按照"{ v1 v2 ... vk }"的格式,每行输出一个连通集。先输出DFS的结果,再输出BFS的结果。
输入样例:
8 6
0 7
0 1
2 0
4 1
2 4
3 5
输出样例:
{ 0 1 4 2 7 }
{ 3 5 }
{ 6 }
{ 0 1 2 7 4 }
{ 3 5 }
{ 6 }
代码长度限制
16 KB
时间限制
400 ms
内存限制
64 MB
主要思路:
三个重要模块:
(一)图的存储
这次尝试的是用二维邻接矩阵,以后有机会尝试一位邻接矩阵和邻接表
二维邻接矩阵关键四步:
(1)定义图的数据结构,分为图节点与边节点两部分
/*图节点*/
typedef struct GraphNode* PToGraphNode;
struct GraphNode {
int VertexNums;
int EdgeNums;
int WeightBetweenTwoEdge[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
};
typedef PToGraphNode MatrixGraph;
/*边界点*/
typedef struct EdgeNode* PToEdgeNode;
struct EdgeNode {
int Start, End;
int Weight;
};
typedef PToEdgeNode Edge;
(2)创建一个没有边的图
MatrixGraph CreateGraph() {
int vertixNums;
scanf("%d", &vertixNums);
MatrixGraph Graph = (MatrixGraph)malloc(sizeof(struct GraphNode));
Graph -> VertexNums = vertixNums;
Graph -> EdgeNums = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < (Graph -> VertexNums); i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < (Graph -> VertexNums); j++) {
Graph -> WeightBetweenTwoEdge[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return Graph;
}
(3)插入边
void InsertEdge(MatrixGraph graph, Edge edge) {
graph -> WeightBetweenTwoEdge[edge -> Start][edge -> End] = edge -> Weight;
graph -> WeightBetweenTwoEdge[edge -> End][edge -> Start] = edge -> Weight;
}
(4)创建图
MatrixGraph BuildGraph() {
MatrixGraph graph = CreateGraph();
scanf("%d", &(graph -> EdgeNums));
if((graph -> EdgeNums) != 0) {
for(int i = 0; i < (graph -> EdgeNums); i++) {
Edge edge = (Edge)malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeNode));
scanf("%d %d", &(edge -> Start), &(edge -> End));
edge -> Weight = WEIGHT;
InsertEdge(graph, edge);
}
}
return graph;
}
(二)DFS的实现
关于图的DFS 有常规思路如下:
void DFS(u) {
vis[u] = true; // 设置为已访问
Visit[u] //访问节点
for(从u出发能达到的所有顶点v) // 枚举从u出发可以到达的所有顶点
if vis[v] == false // 没有被访问
DFS(v) // 递归访问
}
void DFSTravel(G) {
for(G所有顶点u)
if vis[u] == false
DFS(u)
}
(三)BFS的实现
BFS常规思路
void BFS(int u) {
queue q;
q.push(u);
inq[u] = true; // 设置 u 已经入队
while(!q.empty()) {
Visit[q.front()] //取出队首元素进行访问
for(从u出发可到达所有顶点v)
if(inq[v] == false)
将 v 入队
inq[v] = true
}
}
void BFSTravel() {
for(G所有顶点u) {
if(inq[u] == false)
BFS(u)
}
}
代码实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 11
#define WEIGHT 1
/*用邻接矩阵定义图的数据结构*/
/*图节点*/
typedef struct GraphNode* PToGraphNode;
struct GraphNode {
int VertexNums;
int EdgeNums;
int WeightBetweenTwoEdge[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
};
typedef PToGraphNode MatrixGraph;
/*边界点*/
typedef struct EdgeNode* PToEdgeNode;
struct EdgeNode {
int Start, End;
int Weight;
};
typedef PToEdgeNode Edge;
/*---------------------------*/
/*初始化一个无边的图*/
MatrixGraph CreateGraph() {
int vertixNums;
scanf("%d", &vertixNums);
MatrixGraph Graph = (MatrixGraph)malloc(sizeof(struct GraphNode));
Graph -> VertexNums = vertixNums;
Graph -> EdgeNums = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < (Graph -> VertexNums); i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < (Graph -> VertexNums); j++) {
Graph -> WeightBetweenTwoEdge[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return Graph;
}
/*边的插入*/
void InsertEdge(MatrixGraph graph, Edge edge) {
graph -> WeightBetweenTwoEdge[edge -> Start][edge -> End] = edge -> Weight;
graph -> WeightBetweenTwoEdge[edge -> End][edge -> Start] = edge -> Weight;
}
/*创建图*/
MatrixGraph BuildGraph() {
MatrixGraph graph = CreateGraph();
scanf("%d", &(graph -> EdgeNums));
if((graph -> EdgeNums) != 0) {
for(int i = 0; i < (graph -> EdgeNums); i++) {
Edge edge = (Edge)malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeNode));
scanf("%d %d", &(edge -> Start), &(edge -> End));
edge -> Weight = WEIGHT;
InsertEdge(graph, edge);
}
}
return graph;
}
int Visited[MAX_SIZE];
void DFS(MatrixGraph graph, int index) {
Visited[index] = 1;
printf("%d ", index);
/*遍历当下节点(下标为index)所有相邻节点*/
for(int i = 0; i < (graph -> VertexNums); i++) {
/*判断当下节点的相邻节点,两个节点间连通且相邻的节点没有访问过*/
if(graph -> WeightBetweenTwoEdge[index][i] == WEIGHT && Visited[i] == 0) {
Visited[i] = 1;
DFS(graph, i);
}
}
return;
}
void Erase(int* array, int num) {
for(int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
array[i] = 0;
}
return;
}
/*先实现循环队列*/
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 10
typedef struct {
int data[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
int count;
} CircularQueue;
void initialize_queue(CircularQueue* queue) {
queue->front = 0;
queue->rear = -1;
queue->count = 0;
}
int is_full(CircularQueue* queue) {
return (queue->count == MAX_QUEUE_SIZE);
}
int is_empty(CircularQueue* queue) {
return (queue->count == 0);
}
int enqueue(CircularQueue* queue, int data) {
if(is_full(queue)) {
return 0;
}
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE; //因为是循环,所以不是简单加1,还要取余
queue->data[queue->rear] = data;
(queue->count)++;
return 1;
}
int dequeue(CircularQueue* queue) {
if(is_empty(queue)) {
return -1;
}
int data = queue->data[queue->front];
queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
queue->count--;
return data;
}
void BFS(MatrixGraph graph, int index) {
CircularQueue queue;
initialize_queue(&queue);
Visited[index] = 1;
enqueue(&queue, index);
while(!is_empty(&queue)) {
index = dequeue(&queue);
printf("%d ", index);
for(int i = 0; i < (graph -> VertexNums); i++) {
if(Visited[i] == 0 && graph -> WeightBetweenTwoEdge[index][i] == WEIGHT) {
Visited[i] = 1;
enqueue(&queue, i);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
MatrixGraph graph = BuildGraph();
for(int i = 0; i < (graph -> VertexNums); i++) {
if(Visited[i] == 0) { //表示一个连通集的开始
printf("{ ");
DFS(graph, i);
printf("}\n");
}
}
Erase(Visited, MAX_SIZE);
for(int i = 0; i < (graph -> VertexNums); i++) {
if(Visited[i] == 0) {
printf("{ ");
BFS(graph, i);
printf("}\n");
}
}
return 0;
}题目详情:06-图2 Saving James Bond - Easy Version
This time let us consider the situation in the movie "Live and Let Die" in which James Bond, the world's most famous spy, was captured by a group of drug dealers. He was sent to a small piece of land at the center of a lake filled with crocodiles. There he performed the most daring action to escape -- he jumped onto the head of the nearest crocodile! Before the animal realized what was happening, James jumped again onto the next big head... Finally he reached the bank before the last crocodile could bite him (actually the stunt man was caught by the big mouth and barely escaped with his extra thick boot).
Assume that the lake is a 100 by 100 square one. Assume that the center of the lake is at (0,0) and the northeast corner at (50,50). The central island is a disk centered at (0,0) with the diameter of 15. A number of crocodiles are in the lake at various positions. Given the coordinates of each crocodile and the distance that James could jump, you must tell him whether or not he can escape.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts with a line containing two positive integers N (≤100), the number of crocodiles, and D, the maximum distance that James could jump. Then N lines follow, each containing the (x,y) location of a crocodile. Note that no two crocodiles are staying at the same position.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line "Yes" if James can escape, or "No" if not.
Sample Input 1:
14 20
25 -15
-25 28
8 49
29 15
-35 -2
5 28
27 -29
-8 -28
-20 -35
-25 -20
-13 29
-30 15
-35 40
12 12
Sample Output 1:
Yes
Sample Input 2:
4 13
-12 12
12 12
-12 -12
12 -12
Sample Output 2:
No
代码长度限制
16 KB
时间限制
400 ms
内存限制
64 MB
简单翻译:
就是在以所给的最远跳跃距离为半径这个限制,看能不能找到一条从湖心到湖岸的路径
主要思路:
(一)利用图,将人,鳄鱼和岸都视为节点,分为第一跳,中间跳与最后跳上岸三种情况,如果满足,只要满足限制条件就在两个节点之间插入边,然后利用DFS遍历图看有无路径即可
虽然但是,还是有一个测试点过不了……先贴在这边,看看以后能不能看出问题
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 101
#define WEIGHT 1
#define ISLANDRADIUS 7.5
#define BOUND 50
typedef struct GraphNode* PToGraphNode;
struct GraphNode {
int VertexNums;
int EdgeNums;
int WeightBetweenTwoNodes[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
};
typedef PToGraphNode MatrixGraph;
typedef struct EdgeNode* PToEdgeNode;
struct EdgeNode {
int Start, End;
int Weight;
};
typedef PToEdgeNode Edge;
MatrixGraph CreateEmptyGraph(int vertexNums) {
MatrixGraph graph = (MatrixGraph)malloc(sizeof(struct GraphNode));
graph -> VertexNums = vertexNums;
graph -> EdgeNums = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < (graph -> VertexNums); i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < (graph -> VertexNums); j++) {
graph -> WeightBetweenTwoNodes[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return graph;
}
Edge InitalEdge(int start, int end, int weight) {
Edge edge = (Edge)malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeNode));
edge -> Start = start;
edge -> End = end;
edge -> Weight = weight;
return edge;
}
void InsertEdge(MatrixGraph graph, Edge edge) {
int start = edge -> Start;
int end = edge -> End;
graph -> WeightBetweenTwoNodes[start][end] = edge -> Weight;
graph -> WeightBetweenTwoNodes[end][start] = edge -> Weight;
return;
}
typedef struct VertexNode* PToVettex;
struct VertexNode {
int XLabel, Ylabel;
};
typedef PToVettex Vertex;
int Max(int a, int b) {
return a > b ? a : b;
}
MatrixGraph BuildGraph() {
int crocodileNums, maxDistance;
scanf("%d %d", &crocodileNums, &maxDistance);
MatrixGraph graph = CreateEmptyGraph(crocodileNums + 2);
Vertex vertex = (Vertex)malloc(sizeof(struct VertexNode) * (crocodileNums + 1));
//0号节点代表湖心岛,1~vertixNums节点代表鳄鱼
for(int i = 1; i <= crocodileNums; i++) {
scanf("%d %d", &(vertex[i].XLabel), &(vertex[i].Ylabel));
}
//判断从小岛可以跳到几只鳄鱼背上,如果可以,就在岛代表的节点与鳄鱼代表的节点之间插入一条边
for(int i = 1; i <= crocodileNums; i++) {
int distanceSquare = pow(vertex[i].XLabel, 2) + pow(vertex[i].Ylabel, 2);
if(pow((ISLANDRADIUS + maxDistance), 2) >= distanceSquare) {
Edge edge = InitalEdge(0, i, WEIGHT);
InsertEdge(graph, edge);
free(edge);
}
}
//判断是否可以在两条鳄鱼间跳跃
for(int i = 1; i <= crocodileNums; i++) {
int plotStartX = vertex[i].XLabel;
int plotStartY = vertex[i].Ylabel;
for(int j = i + 1; j <= crocodileNums; j++) {
int plotEndX = vertex[j].XLabel;
int plotEndY = vertex[j].Ylabel;
int distanceSquare = pow((plotEndX - plotStartX), 2) + pow((plotEndY - plotStartY), 2);
if(distanceSquare <= pow(maxDistance, 2)) {
Edge edge = InitalEdge(i, j, WEIGHT);
InsertEdge(graph, edge);
free(edge);
}
}
}
//判断是否可以从鳄鱼跳到岸上
for(int i = 1; i <= crocodileNums; i++) {
int absPlotXLabel = abs(vertex[i].XLabel);
int absPlotYLabel = abs(vertex[i].Ylabel);
if(absPlotXLabel + maxDistance >= 50 || absPlotYLabel + maxDistance >= 50) {
Edge edge = InitalEdge(i, crocodileNums + 1, WEIGHT);
InsertEdge(graph, edge);
free(edge);
}
}
return graph;
}
int Visited[MAX_SIZE];
int flag = 0;
void DFS(MatrixGraph graph, int index) {
Visited[index] = 1;
if(index == (graph -> VertexNums) - 1) { //表示岸边的节点的下标是总结点数-1
flag = 1;
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i < (graph -> VertexNums); i++) {
if(graph -> WeightBetweenTwoNodes[index][i] == WEIGHT && Visited[i] == 0) {
DFS(graph, i);
}
}
}
int main() {
MatrixGraph graph = BuildGraph();
DFS(graph, 0);
if(flag == 1) printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
system("pause");
return 0;
}贴一下别人正确的代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<math.h>
#define MaxVertexNum 100
#define Diameter 15
typedef int Crocodile;
typedef struct LocOfCro{
int x;
int y;
}Location;
int Nc, distance;
bool visited[MaxVertexNum] = { false };
Location crocodiles[MaxVertexNum];
void AddCrocodile();
void Save007(Location Crocodile[]);
int DFS(Crocodile V);
bool IsSafe(Crocodile V);
bool FirstJump(V);
bool Jump(V, W);
int main() {
AddCrocodile();
Save007(crocodiles);
return 0;
}
void AddCrocodile() {
int v1, v2;
scanf("%d", &Nc);
/* CreateLocation */
for (int i = 0; i < Nc; i++) {
crocodiles[i].x = crocodiles[i].y = -1;
}
scanf("%d", &distance);
for (int i = 0; i < Nc; i++) {
scanf("%d %d", &v1, &v2);
/* AddCrocodile */
crocodiles[i].x = v1;
crocodiles[i].y = v2;
}
}
int DFS(Crocodile i) {
int answer = 0;
visited[i] = true;
if (IsSafe(i))
answer = 1;
else {
for (int j = 0; j < Nc; j++)
if (!visited[j] && Jump(i,j)) {
answer = DFS(j);
if (answer == 1)
break;
}
}
return answer;
}
void Save007(Location crocodiles[]) {
int answer = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Nc; i++) {
if (!visited[i] && FirstJump(i)) {
answer = DFS(i);
if (answer == 1) break;
}
}
if (answer == 1) printf("Yes");
else printf("No");
}
bool IsSafe(Crocodile i) {
return (abs(crocodiles[i].x) + distance >= 50) || (abs(crocodiles[i].y) + distance >= 50);
}
bool FirstJump(Crocodile i) {
return sqrt(pow(crocodiles[i].x + 0.0, 2) + pow(crocodiles[i].y + 0.0, 2)) <= (Diameter / 2 + distance);
}
bool Jump(int V, int W) {
return sqrt((crocodiles[V].x - crocodiles[W].x) * (crocodiles[V].x - crocodiles[W].x)
+ (crocodiles[V].y - crocodiles[W].y) * (crocodiles[V].y - crocodiles[W].y)) <= distance;
}(二)不用图(有空再想想吧)
题目详情:06-图3 六度空间
“六度空间”理论又称作“六度分隔(Six Degrees of Separation)”理论。这个理论可以通俗地阐述为:“你和任何一个陌生人之间所间隔的人不会超过六个,也就是说,最多通过五个人你就能够认识任何一个陌生人。”如图1所示。
“六度空间”理论又称作“六度分隔(Six Degrees of Separation)”理论。这个理论可以通俗地阐述为:“你和任何一个陌生人之间所间隔的人不会超过六个,也就是说,最多通过五个人你就能够认识任何一个陌生人。”如图1所示。
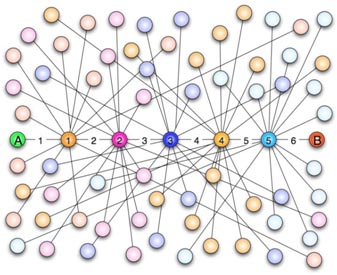
图1 六度空间示意图
“六度空间”理论虽然得到广泛的认同,并且正在得到越来越多的应用。但是数十年来,试图验证这个理论始终是许多社会学家努力追求的目标。然而由于历史的原因,这样的研究具有太大的局限性和困难。随着当代人的联络主要依赖于电话、短信、微信以及因特网上即时通信等工具,能够体现社交网络关系的一手数据已经逐渐使得“六度空间”理论的验证成为可能。
假如给你一个社交网络图,请你对每个节点计算符合“六度空间”理论的结点占结点总数的百分比。
输入格式:
输入第1行给出两个正整数,分别表示社交网络图的结点数N(1<N≤103,表示人数)、边数M(≤33×N,表示社交关系数)。随后的M行对应M条边,每行给出一对正整数,分别是该条边直接连通的两个结点的编号(节点从1到N编号)。
输出格式:
对每个结点输出与该结点距离不超过6的结点数占结点总数的百分比,精确到小数点后2位。每个结节点输出一行,格式为“结点编号:(空格)百分比%”。
输入样例:
10 9
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 9
9 10
输出样例:
1: 70.00%
2: 80.00%
3: 90.00%
4: 100.00%
5: 100.00%
6: 100.00%
7: 100.00%
8: 90.00%
9: 80.00%
10: 70.00%
代码长度限制
16 KB
时间限制
2500 ms
内存限制
64 MB
主要思路:
利用BFS搜索,难点在于如何判断最后一个节点从而积累层数,解决方法是要先深刻理解BFS就是拓展层序遍历,弹出的是中心节点,加入的是围绕其的节点,所以分别记录当前层最后一个节点与上一层最后一个节点,当现在的中心节点等于上一层的最后一个节点就说明有一层遍历完了
第一次写错误:
(1)忽视了节点是从1开始编号的
(2)人计数时从1开始,因为当前节点也在内
(3)一开始用DFS,但有问题,具体原因可以参见这篇文章
代码实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 1005
#define WEIGHT 1
typedef struct GraphNode* PToGraphNode;
struct GraphNode {
int VertexNums;
int EdgeNums;
int WeightBetweenTwoNodes[MAX_SIZE][MAX_SIZE];
};
typedef PToGraphNode MatrixGraph;
typedef struct EdgeNode* PToEdgeNode;
struct EdgeNode {
int Start, End;
int Weight;
};
typedef PToEdgeNode Edge;
MatrixGraph CreateEmptyGraph(int vertexNums) {
MatrixGraph graph = (MatrixGraph)malloc(sizeof(struct GraphNode));
graph -> VertexNums = vertexNums;
graph -> EdgeNums = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= vertexNums; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= vertexNums; j++) {
graph -> WeightBetweenTwoNodes[i][j] = 0;
}
}
return graph;
}
void InsertEdge(MatrixGraph graph, Edge edge) {
int start = edge -> Start;
int end = edge -> End;
graph -> WeightBetweenTwoNodes[start][end] = edge -> Weight;
graph -> WeightBetweenTwoNodes[end][start] = edge -> Weight;
return;
}
MatrixGraph BuildGraph() {
int vertexNums;
scanf("%d", &vertexNums);
MatrixGraph graph = CreateEmptyGraph(vertexNums);
scanf("%d", &(graph -> EdgeNums));
for(int i = 1; i <= (graph -> EdgeNums); i++) {
int start, end;
scanf("%d %d", &start, &end);
Edge edge = (Edge)malloc(sizeof(struct EdgeNode));
edge -> Start = start;
edge -> End = end;
edge -> Weight = WEIGHT;
InsertEdge(graph, edge);
free(edge);
}
return graph;
}
/*先实现循环队列*/
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 1005
typedef struct {
int data[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
int front;
int rear;
int count;
} CircularQueue;
void initialize_queue(CircularQueue* queue) {
queue->front = 0;
queue->rear = -1;
queue->count = 0;
}
int is_full(CircularQueue* queue) {
return (queue->count == MAX_QUEUE_SIZE);
}
int is_empty(CircularQueue* queue) {
return (queue->count == 0);
}
int enqueue(CircularQueue* queue, int data) {
if(is_full(queue)) {
return 0;
}
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE; //因为是循环,所以不是简单加1,还要取余
queue->data[queue->rear] = data;
(queue->count)++;
return 1;
}
int dequeue(CircularQueue* queue) {
if(is_empty(queue)) {
return -1;
}
int data = queue->data[queue->front];
queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
queue->count--;
return data;
}
int Visited[MAX_SIZE];
int PeopleInside = 1;
void Clear(int* array, int size) {
for(int i = 1; i <= size; i++) array[i] = 0;
return;
}
int peopleInside = 1;
void BFS(MatrixGraph graph, int center) { //用center命名更符合BFS搜索本质,一个节点为中心将其临近节点全部压入
CircularQueue myQueue;
initialize_queue(&myQueue);
Visited[center] = 1;
enqueue(&myQueue, center);
int thisLevelTail = -1;
int level = 0;
int lastTail = center;
while(!is_empty(&myQueue)) {
center = dequeue(&myQueue);
for(int i = 1; i <= (graph -> VertexNums); i++) {
if(Visited[i] == 0 && graph -> WeightBetweenTwoNodes[center][i] == WEIGHT) {
enqueue(&myQueue, i);
thisLevelTail = i; //thisleveltail记录的是这一层的最后一个
Visited[i] = 1;
peopleInside++;
}
}
if(center == lastTail) { //如果这一层中心点到了上一层末尾,说明队列里之后存放就是下一层节点了
level++;
lastTail = thisLevelTail;
}
if(level == 6) break;
}
}
int main() {
MatrixGraph graph = BuildGraph();
int totalPeople = graph -> VertexNums;
for(int i = 1; i <= totalPeople; i++) {
Clear(Visited, totalPeople);
BFS(graph, i);
printf("%d: %.2f\%\n", i, 1.0 * peopleInside / (totalPeople) * 100);
peopleInside = 1;
}
return 0;
}
![[算法] ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的优缺点比较及使用场景](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ca65ad5cc13e426980d309780a554c60.gif)