一.简介
Spring Security 是 Spring 家族中的一个安全管理框架。
一般来说,常见的安全管理技术栈的组合是这样的:
- SSM + Shiro
- Spring Boot/Spring Cloud + Spring Security
对于一个权限管理框架而言,无论是 Shiro 还是 Spring Security,最核心的功能,无非就是两方面:
- 认证
- 授权
认证就是我们常说的登录,授权就是权限鉴别,看看请求是否具备相应的权限。
虽然就是一个简简单单的登录,可是也能玩出很多花样来。
Spring Security 支持多种不同的认证方式,这些认证方式有的是 Spring Security 自己提供的认证功能,有的是第三方标准组织制订的,主要有如下一些:
一些比较常见的认证方式:
- HTTP BASIC authentication headers:基于IETF RFC 标准。
- HTTP Digest authentication headers:基于IETF RFC 标准。
- HTTP X.509 client certificate exchange:基于IETF RFC 标准。
- LDAP:跨平台身份验证。
- Form-based authentication:基于表单的身份验证。
- Run-as authentication:用户用户临时以某一个身份登录。
- OpenID authentication:去中心化认证。
除了这些常见的认证方式之外,一些比较冷门的认证方式,Spring Security 也提供了支持,比如:
- Jasig Central Authentication Service:单点登录。
- Automatic “remember-me” authentication:记住我登录(允许一些非敏感操作)。
- Anonymous authentication:匿名登录。
作为一个开放的平台,Spring Security 提供的认证机制不仅仅是上面这些。如果上面这些认证机制依然无法满足你的需求,我们也可以自己定制认证逻辑。当我们需要和一些“老破旧”的系统进行集成时,自定义认证逻辑就显得非常重要了。
除了认证,剩下的就是授权了。
Spring Security 支持基于 URL 的请求授权(例如微人事)、支持方法访问授权以及对象访问授权。
这批文章,学习使用springboot框架集成spring security,实现一个简单的demo例子。
二.项目创建
使用idea创建springboot项目,这个自行百度怎么用idea创建springboot项目。
在 Spring Boot 中使用 Spring Security 非常容易,引入依赖即可,截图如下:
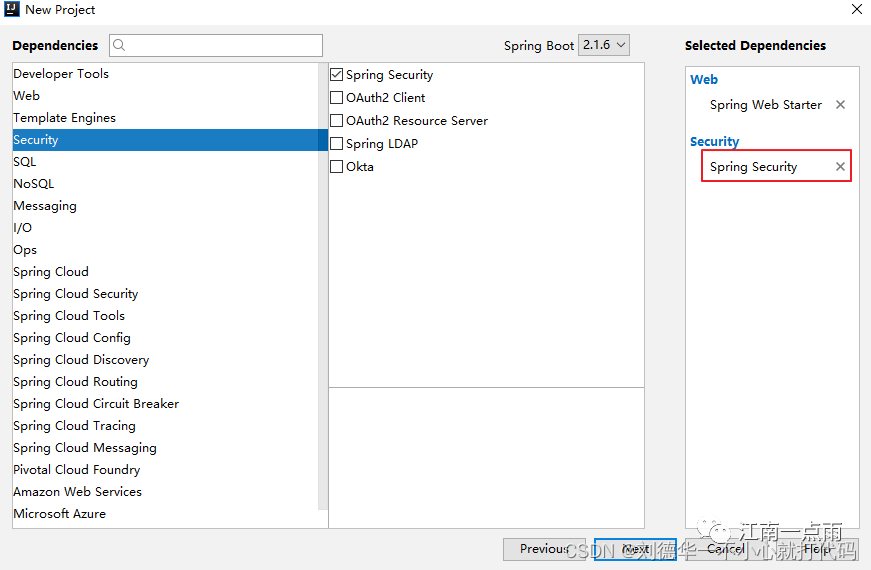
pom.xml 中的 Spring Security 依赖,代码如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
只要加入依赖,项目的所有接口都会被自动保护起来。
三.初次体验
创建一个 HelloController类,代码如下:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
}
访问 /hello ,需要登录之后才能访问,截图如下:
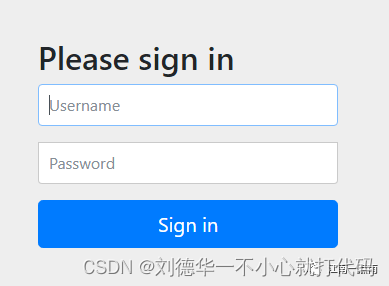
当用户从浏览器发送请求访问 /hello 接口时,服务端会返回 302 响应码,让客户端重定向到 /login 页面,用户在 /login 页面登录,登陆成功之后,就会自动跳转到 /hello 接口。
另外,也可以使用 POSTMAN 来发送请求,使用 POSTMAN 发送请求时,可以将用户信息放在请求头中(这样可以避免重定向到登录页面),截图如下:
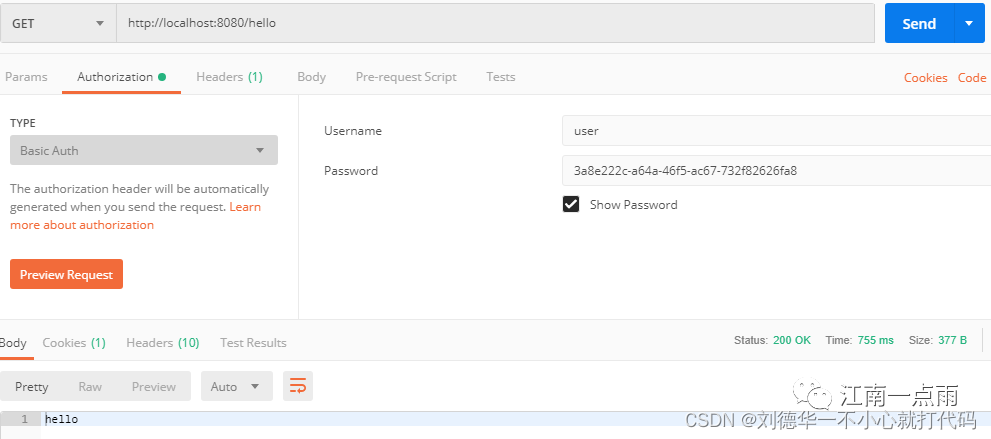
通过以上两种不同的登录方式,可以看出,Spring Security 支持两种不同的认证方式:
- 通过 form 表单来认证
- 通过 HttpBasic 来认证
三.用户名配置
默认情况下,登录的用户名是 user ,密码则是项目启动时随机生成的字符串,可以从启动的控制台日志中看到默认密码,截图如下:
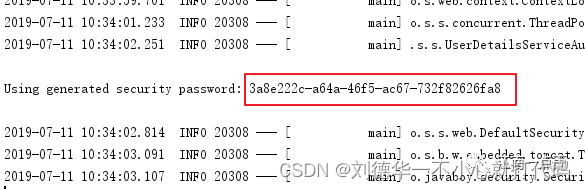
这个随机生成的密码,每次启动时都会变。对登录的用户名/密码进行配置,有三种不同的方式:
- 在 application.properties 中进行配置
- 通过 Java 代码配置在内存中
- 通过 Java 从数据库中加载
前两种比较简单,第三种代码量略大,本文就先来看看前两种,第三种后面再单独写文章介绍
3.1配置文件配置用户名/密码
可以直接在 application.properties 文件中配置用户的基本信息,代码如下:
spring.security.user.name=javaboy
spring.security.user.password=123
配置完成后,重启项目,就可以使用这里配置的用户名/密码登录了。
3.2Java 配置用户名/密码
也可以在 Java 代码中配置用户名密码,首先需要创建一个 Spring Security 的配置类,集成自 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 类,代码如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
//下面这两行配置表示在内存中配置了两个用户
auth.inMemoryAuthentication()
.withUser("javaboy").roles("admin").password("$2a$10$OR3VSksVAmCzc.7WeaRPR.t0wyCsIj24k0Bne8iKWV1o.V9wsP8Xe")
.and()
.withUser("lisi").roles("user").password("$2a$10$p1H8iWa8I4.CA.7Z8bwLjes91ZpY.rYREGHQEInNtAp4NzL6PLKxi");
}
@Bean
PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
这里我们在 configure 方法中配置了两个用户,用户的密码都是加密之后的字符串(明文是 123),从 Spring5 开始,强制要求密码要加密,如果非不想加密,可以使用一个过期的 PasswordEncoder 的实例 NoOpPasswordEncoder,但是不建议这么做,毕竟不安全。
Spring Security 中提供了 BCryptPasswordEncoder 密码编码工具,可以非常方便的实现密码的加密加盐,相同明文加密出来的结果总是不同,这样就不需要用户去额外保存 盐的字段了,这一点比 Shiro 要方便很多。
四.用户名配置
对于登录接口,登录成功后的响应,登录失败后的响应,我们都可以在 WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter 的实现类中进行配置。代码如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
VerifyCodeFilter verifyCodeFilter;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.addFilterBefore(verifyCodeFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class);
http
.authorizeRequests()//开启登录配置
.antMatchers("/hello").hasRole("admin")//表示访问 /hello 这个接口,需要具备 admin 这个角色
.anyRequest().authenticated()//表示剩余的其他接口,登录之后就能访问
.and()
.formLogin()
//定义登录页面,未登录时,访问一个需要登录之后才能访问的接口,会自动跳转到该页面
.loginPage("/login_p")
//登录处理接口
.loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin")
//定义登录时,用户名的 key,默认为 username
.usernameParameter("uname")
//定义登录时,用户密码的 key,默认为 password
.passwordParameter("passwd")
//登录成功的处理器
.successHandler(new AuthenticationSuccessHandler() {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationSuccess(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.write("success");
out.flush();
}
})
.failureHandler(new AuthenticationFailureHandler() {
@Override
public void onAuthenticationFailure(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, AuthenticationException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.write("fail");
out.flush();
}
})
.permitAll()//和表单登录相关的接口统统都直接通过
.and()
.logout()
.logoutUrl("/logout")
.logoutSuccessHandler(new LogoutSuccessHandler() {
@Override
public void onLogoutSuccess(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException {
resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8");
PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter();
out.write("logout success");
out.flush();
}
})
.permitAll()
.and()
.httpBasic()
.and()
.csrf().disable();
}
}
我们可以在 successHandler 方法中,配置登录成功的回调,如果是前后端分离开发的话,登录成功后返回 JSON 即可,同理,failureHandler 方法中配置登录失败的回调,logoutSuccessHandler 中则配置注销成功的回调。
五.忽略拦截
如果某一个请求地址不需要拦截的话,有两种方式实现:
- 设置该地址匿名访问
- 直接过滤掉该地址,即该地址不走 Spring Security 过滤器链
推荐使用第二种方案,代码如下:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void configure(WebSecurity web) throws Exception {
web.ignoring().antMatchers("/vercode");
}
}
Spring Security 另外一个强大之处就是它可以结合 OAuth2