概述
TreeSet ,基于 TreeSet 的 Set 实现类。在业务中,如果我们有排重+ 排序的需求,一般会考虑使用 TreeSet
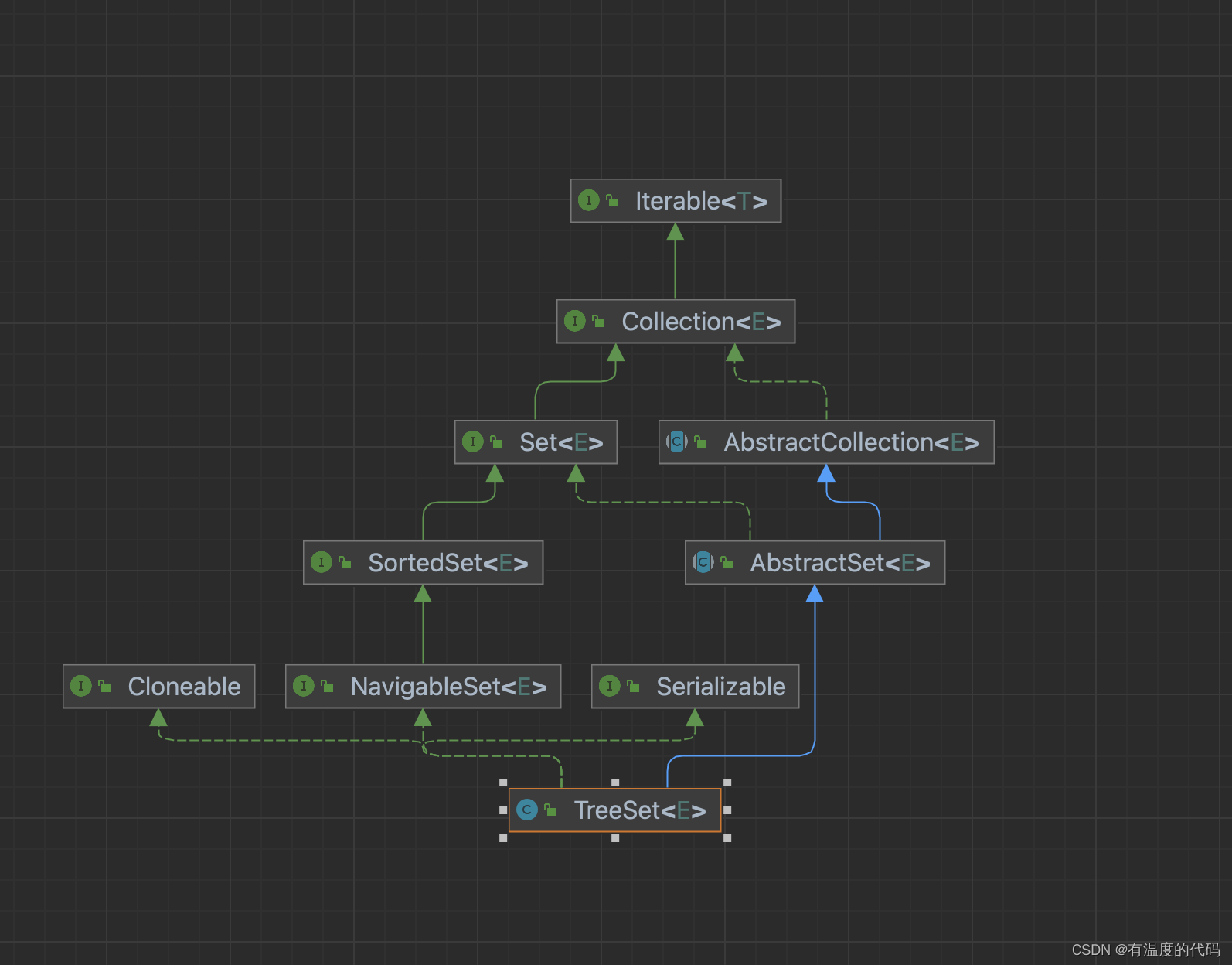
#TreeSet的继承关系
TreeSet的内部属性

m 的 key ,存储 HashSet 的每个 key 。
map 的 value ,因为 TreeSet 没有 value 的需要,所以使用一个统一的 PRESENT
构造方法
// TreeSet.java
TreeSet(NavigableMap<E,Object> m) {
this.m = m;
}
public TreeSet() {
this(new TreeMap<>());
}
public TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
this(new TreeMap<>(comparator));
}
public TreeSet(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
// 批量添加
addAll(c);
}
public TreeSet(SortedSet<E> s) {
this(s.comparator());
// 批量添加
addAll(s);
}
添加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
m 的value值就是。private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
是一个final类型的value,所有的key的value都是一样的
移除元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return m.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
查找单个元素
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return m.containsKey(o);
}
查找接近的元素
在 NavigableSet 中,定义了四个查找接近的元素:
#lower(E e) 方法,小于 e 的 key
#floor(E e) 方法,小于等于 e 的 key
#higher(E e) 方法,大于 e 的 key
#ceiling(E e) 方法,大于等于 e 的 key
// TreeSet.java
public E lower(E e) {
return m.lowerKey(e);
}
public E floor(E e) {
return m.floorKey(e);
}
public E ceiling(E e) {
return m.ceilingKey(e);
}
public E higher(E e) {
return m.higherKey(e);
}
SortedMap中提供了获取首尾元素的功能
first() 方法,获得首个 key
public E first() {
return m.firstKey();
}
pollFirst() 方法,获得并移除首个 key
public E pollFirst() {
Map.Entry<E,?> e = m.pollFirstEntry();
return (e == null) ? null : e.getKey();
}
last() 方法,获得尾部 key
public E last() {
return m.lastKey();
}
pollLast() 方法,获得并移除尾部 key
public E pollLast() {
Map.Entry<E,?> e = m.pollLastEntry();
return (e == null) ? null : e.getKey();
}
总结
》TreeSet 是基于 TreeMap 的 Set 实现类