springboot配置多个数据源【详解】
- 前言,什么是数据源与数据库连接池
- 一、配置文件进行配置:
- 1.导入依赖:
- 二、编写配置类:
- 1.用来指定包扫描、指定sqlSessionTemplateRef
- 2,用来指定mapper.xml的路径
- 3.Mybatis主数据源ds1配置:
- 4.Mybatis第二个ds2数据源配置:
- 5.Mybatis第三个数据源配置(另一种配置方法):
- 6.代码解释:
- 7.注意事项:
- 三、测试与使用:
- Service层:
- Controller层:
- 五、拓展(整合druid)
- 连接池:
前言,什么是数据源与数据库连接池
说SpringBoot的多数据源配置之前,我们先了解下DataSource。
在java中,操作数据库有很多方式,在众多方式中除了JDBC外还有DataSource对象。
DataSource可以看作数据源:
它封装了数据库参数,连接数据库,程序中操作DataSource对象即可对数据库进行增删改查操作。
不同方式中使用的DataSource对象不同。列举如下:
dbcp框架中的DataSource类是:org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource
c3p0框架的DataSource类是:com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource
MyBatis框架的DataSource类是:org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource
Druid框架的DataSource类是:com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
对于DataSource的一些实现,经常被叫做数据库连接池,
比如Druid官方文档中说“Druid是Java语言中最好的数据库连接池“,本质核心就是DataSource的一个实现类,作为中间层使用,并且基本上都提供了附带的其他的服务,也就是说不仅仅实现了核心建筑,也基于核心之上构建了很多的外围建设。
数据源和数据库连接池的关系:
- 数据源建立多个数据库连接,这些数据库连接会保存在数据库连接池中,
- 当需要访问数据库时,只需要从数据库连接池中获取空闲的数据库连接,
- 当程序访问数据库结束时,数据库连接会放回数据库连接池中。
在最开始学习JDBC的时候,我们自己获取一个数据连接的操作是这样的:
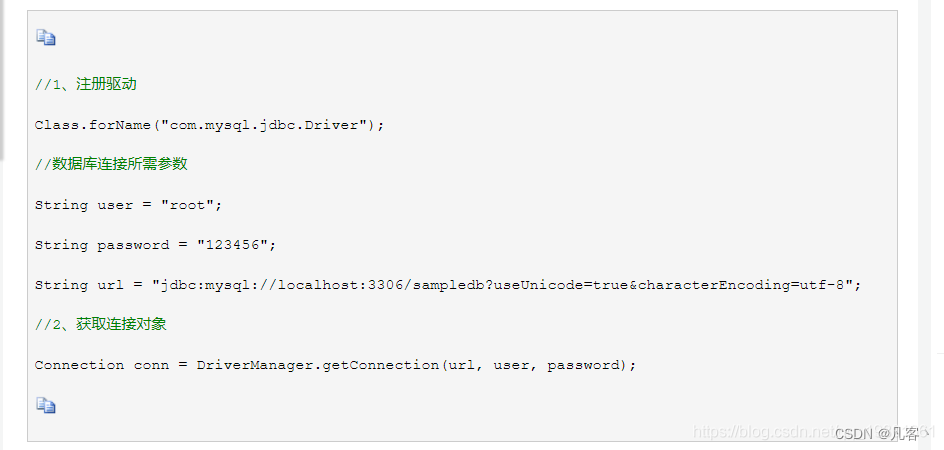
学习JDBC的时候,直接使用DriverManager的这种形式,通常需要将驱动程序硬编码到项目中(JDBC4.0后可以自动注册驱动程序)。
而且最重要的是通过DriverManager的getConnection方法获取的连接,是建立与数据库的连接。
但是建立与数据库的连接是一项较耗资源的工作,频繁的进行数据库连接建立操作会产生较大的系统开销。
DataSource中获取的连接来自于连接池中,虽然池中的连接从根本上来说其实也还是从DriverManager获取而来。
DataSource就是DriverManager的一种替代角色,拥有对外提供连接的能力。
接下来看SpringBoot如何整合多数据源。
一、配置文件进行配置:
1.导入依赖:
如果你新增的数据库数据源和目前的数据库不同,记得引入新数据库的驱动依赖,比如 MySQL 和 PGSQL。
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<version>42.2.7</version>
</dependency>
首先,需要在配置文件中配置多数据源的连接信息;
这里采用yml配置文件,其他类型配置文件同理
我配置了两个数据源,一个名字叫ds1数据源,一个名字叫ds2数据源,如果你想配置更多的数据源,继续加就行了
spring:
# 数据源配置
datasource:
ds1: #数据源1
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # mysql的驱动你可以配置别的关系型数据库
url: jdbc:mysql://ip:3306/db1 #数据源地址
username: root # 用户名
password: root # 密码
ds2: # 数据源2
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver # mysql的驱动你可以配置别的关系型数据库
url: jdbc:mysql://ip:3307/db2#数据源地址
username: root # 用户名
password: root # 密码
二、编写配置类:
编写Springboot的配置类:
mybatis多数据源切换的原理是根据不同包,调用不同的数据源,
你只需要把你的mapper.java和mapper.xml 写在某个package中,springboot自动帮你实现数据源切换。
核心代码就这两句:
1.用来指定包扫描、指定sqlSessionTemplateRef
@MapperScan(basePackages ="com.web.ds2.**.dao",
sqlSessionTemplateRef = "ds2SqlSessionTemplate")
2,用来指定mapper.xml的路径
sqlSessionFactory.
setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().
getResources("classpath*:com/web/ds2/**/*.xml"));
详细代码如下:
3.Mybatis主数据源ds1配置:
/**
* Mybatis主数据源ds1配置
* 多数据源配置依赖数据源配置
* @see DataSourceConfig
*/
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages ="com.web.ds1.**.dao", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "ds1SqlSessionTemplate")
public class MybatisPlusConfig4ds1 {
@Bean(name = "dataSource1")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.ds1")
@Primary
public DataSource dataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
//主数据源 ds1数据源
@Primary
@Bean("ds1SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory ds1SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("ds1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource);
sqlSessionFactory.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().
getResources("classpath*:com/web/ds1/**/*.xml"));
return sqlSessionFactory.getObject();
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "ds1TransactionManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager ds1TransactionManager(@Qualifier("ds1DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Primary
@Bean(name = "ds1SqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate ds1SqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("ds1SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
4.Mybatis第二个ds2数据源配置:
/**
* Mybatis 第二个ds2数据源配置
* 多数据源配置依赖数据源配置
* @see DataSourceConfig
*/
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages ="com.web.ds2.**.dao", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "ds2SqlSessionTemplate")
public class MybatisPlusConfig4ds2 {
@Bean(name = "dataSource2")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.ds2")
public DataSource dataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
//ds2数据源
@Bean("ds2SqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactory ds2SqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("ds2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource);
sqlSessionFactory.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().
getResources("classpath*:com/web/ds2/**/*.xml"));
return sqlSessionFactory.getObject();
}
//事务支持
@Bean(name = "ds2TransactionManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager ds2TransactionManager(@Qualifier("ds2DataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "ds2SqlSessionTemplate")
public SqlSessionTemplate ds2SqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("ds2SqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
5.Mybatis第三个数据源配置(另一种配置方法):
有DataSourceTransactionManager 事务管理
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.MybatisConfiguration;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.spring.MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
@Configuration
@EnableJpaRepositories({"xxx.xxx.xx.xx.xx"})
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"xx.xx.xx.xx.xx.xx"}, sqlSessionFactoryRef = "sqlSessionFactory")
public class PrimaryDataSourceConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mybatis-plus.configuration")
public MybatisConfiguration globalConfiguration() {
return new MybatisConfiguration();
}
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.primary")
@Primary
public DataSource dataSource() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionFactory")
@Primary
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("dataSource") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new MybatisSqlSessionFactoryBean();
bean.setDataSource(dataSource);
//这里将下划线映射为驼峰的配置引入
bean.setConfiguration(globalConfiguration());
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mappers/*.xml"));
return bean.getObject();
}
@Bean(name = "transactionManager")
@Primary
public DataSourceTransactionManager transactionManager(@Qualifier("dataSource") DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "sqlSessionTemplate")
@Primary
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(@Qualifier("sqlSessionFactory") SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
6.代码解释:
- @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “spring.datasource.ds1”):使用spring.datasource.ds1开头的配置。
- @Qualifier:指定数据源名称,与Bean中的name属性原理相同,主要是为了确保注入成功;
- @Primary:声明这是一个主数据源(默认数据源),多数据源配置时必不可少。
- @Qualifier:显式选择传入的 Bean。
7.注意事项:
因为已经在两个数据源中分别配置了扫描的 Mapper 路径,如果你之前在 SpringBoot 启动类中也使用了 Mapper 扫描注解,需要删掉。
三、测试与使用:
Service层:
@Service
public class TestService {
@Resource
private ClusterMapper clusterMapper;
@Resource
private MasterMapper masterMapper;
public List<HashMap<String, Object>> queryBooks() {
return masterMapper.queryBooks(); //指定的配置类扫描的是一个包
}
public List<HashMap<String, Object>> queryOrders() {
return clusterMapper.queryOrders(); //指定的配置类扫描的是另一个包
}
}
Controller层:
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/test", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public class TestController {
@Resource
private TestService testService;
@RequestMapping("/books")
public List<HashMap<String, Object>> queryBooks() {
return testService.queryBooks();
}
@RequestMapping("/orders")
public List<HashMap<String, Object>> queryOrders() {
return testService.queryOrders();
}
}
五、拓展(整合druid)
连接池:
其实在多数据源改造中,我们一般情况下都不会使用默认的 JDBC 连接方式,往往都需要引入连接池进行连接优化,不然你可能会经常遇到数据源连接被断开等报错日志。
其实数据源切换连接池数据源也是十分简单的,直接引入连接池依赖,然后把创建 dataSource 的部分换成连接池数据源创建即可。
下面以阿里的 Druid 为例,先引入连接池数据源依赖。
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置文件中,添加 Druid 的一些配置。
spring.datasource.datasource2.initialSize=3 # 根据自己情况设置
spring.datasource.datasource2.minIdle=3
spring.datasource.datasource2.maxActive=20
改写 dataSource 这个Bean 的创建代码部分:
/**
* Mybatis 第二个ds2数据源配置
* 多数据源配置依赖数据源配置
* @see DataSourceConfig
*/
@Configuration
@MapperScan(basePackages ="com.web.ds2.**.dao", sqlSessionTemplateRef = "ds2SqlSessionTemplate")
public class MybatisPlusConfig4ds2 {
@Value("${spring.datasource.datasource2.jdbc-url}")
private String url;
@Value("${spring.datasource.datasource2.driver-class-name}")
private String driverClassName;
@Value("${spring.datasource.datasource2.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${spring.datasource.datasource2.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${spring.datasource.datasource2.initialSize}")
private int initialSize;
@Value("${spring.datasource.datasource2.minIdle}")
private int minIdle;
@Value("${spring.datasource.datasource2.maxActive}")
private int maxActive;
@Bean(name = "dataSource2")
public DataSource dataSource() {
//用druid要 new DruidDataSource() 实现类,Spring Boot 默认是不注入druid这些属性值的,需要自己绑定
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setInitialSize(initialSize);
dataSource.setMinIdle(minIdle);
dataSource.setMaxActive(maxActive);
return dataSource;
}
//...
}
设置数据源连接属性参考,在上述改写dataSource 配置类代码中注意路径结构按需配置
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=utf8&useUnicode=true&useSSL=false
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
# 连接池类型:使用druid
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定
#druid 数据源专有配置
initialSize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入
#如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority
#则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j
filters: stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
导入依赖
<!-- 使用Druid产生的日志功能log4j -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
编写DruidConfig类,使用其监控功能
package com.rui.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.WebStatFilter;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource druidDataSource(){
return new DruidDataSource();
}
//后台监控功能 :web.xml ServletRegistrationBean
//因为SpringBoot 内置了servlet容器,所以没有web.xml, 替代方法ServletRegistrationBean
//Druid 数据源具有监控的功能,并提供了一个 web 界面方便用户查看,类似安装 路由器 时,人家也提供了一个默认的 web 页面。
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean<StatViewServlet> bean = new ServletRegistrationBean<>(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
HashMap<String, String> initParameter = new HashMap<>();
//增加配置
initParameter.put("loginUsername","admin");
initParameter.put("loginPassword","123456");
//允许谁可以访问
initParameter.put("allow","");
//deny:Druid 后台拒绝谁访问
//initParams.put("rui", "192.168.1.20");表示禁止此ip访问
//设置初始化参数
bean.setInitParameters(initParameter);
return bean;
}
//配置 Druid 监控 之 web 监控的 filter//WebStatFilter:用于配置Web和Druid数据源之间的管理关联监控统计
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
HashMap<String, String> initParameter = new HashMap<>();
//这些东西不进行统计
initParameter.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*");
//设置初始化参数
bean.setInitParameters(initParameter);
return bean;
}
}
我们可以选择访问 :http://localhost:8080/druid/login.html,就可以看到它强大的监控功能了。
建议:
建议去使用mybatis-plus 集成 多数据源。
更多配置介绍请看 --> springboot整合druid多数据源配置