1123 Is It a Complete AVL Tree
分数 30
全屏浏览题目
作者 CHEN, Yue
单位 浙江大学
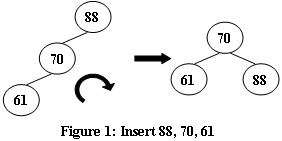
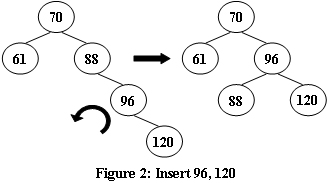
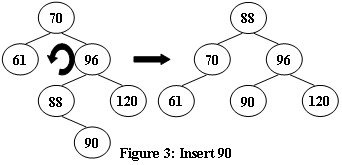
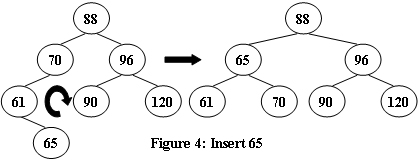
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
|
|
|
|---|---|
|
|
|
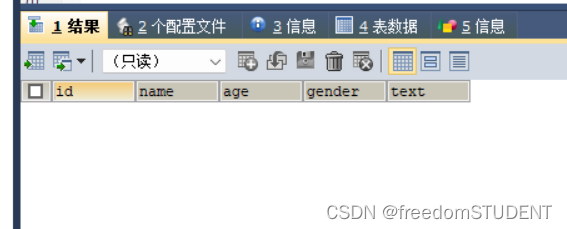
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to output the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree, and to tell if it is a complete binary tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤ 20). Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, insert the keys one by one into an initially empty AVL tree. Then first print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the resulting AVL tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by a space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line. Then in the next line, print YES if the tree is complete, or NO if not.
Sample Input 1:
5
88 70 61 63 65
Sample Output 1:
70 63 88 61 65
YES
Sample Input 2:
8
88 70 61 96 120 90 65 68
Sample Output 2:
88 65 96 61 70 90 120 68
NO
代码长度限制
16 KB
时间限制
400 ms
内存限制
64 MB
中间没注释的代码是二叉平衡树的基本操作见
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_66329385/article/details/130672224
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=30;
int n;
int l[N],r[N],h[N],v[N],idx;//分别为左子树,右子树,高度,结点权值,当前节点
int q[N],pos[N];//前者保存层序遍历的结点顺序,后者记录在堆中各结点的下标(用于判断是否为完全二叉树)
void updata(int u){
h[u]=max(h[l[u]],h[r[u]])+1;
}
void R(int &u){
int t=l[u];
l[u]=r[t],r[t]=u;
updata(u),updata(t);
u=t;
}
void L(int &u){
int t=r[u];
r[u]=l[t],l[t]=u;
updata(u),updata(t);
u=t;
}
int Balpha(int u){
return h[l[u]]-h[r[u]];
}
void insert(int &u,int x){
if(!u){
u=++idx,v[u]=x;
}
else if(x<v[u]){
insert(l[u],x);
if(Balpha(u)==2){
if(Balpha(l[u])==1)R(u);
else L(l[u]),R(u);
}
}
else{
insert(r[u],x);
if(Balpha(u)==-2){
if(Balpha(r[u])==-1)L(u);
else R(r[u]),L(u);
}
}
updata(u);
}
bool bfs(int root){//模拟队列的层序遍历+判断是否为完全二叉树
int hh=0,tt=0;
q[0]=root;//保存根结点
pos[q[0]]=1;//记录根结点在堆中的下标这里以1为例(0也可)
while(hh<=tt){
int t=q[hh++];//获取当前队头元素
if(pos[t]>n)return false;//若在堆中的位置大于n则不是完全二叉树
if(l[t])q[++tt]=l[t],pos[l[t]]=pos[t]*2;//若队头元素有左子树则入队并记录当前元素在堆中的位置
if(r[t])q[++tt]=r[t],pos[r[t]]=pos[t]*2+1;//若队头元素有右子树则入队并记录当前元素在堆中的位置
}
return true;//若堆位置从1到n都有元素,则是完全二叉树
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
int root=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int x;
cin>>x;
insert(root,x);//插入结点
}
bool res=bfs(root);//res作为是否为完全二叉树的标记
cout<<v[q[0]];//输出
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)cout<<' '<< v[q[i]];//输出
cout<<endl;
if(res)cout<<"YES"<<endl;
else cout<<"NO"<<endl;
return 0;
}
![Prompt工程师指南[从基础到进阶篇]:用于开发和优化提示,以有效地使用语言模型(LMs)进行各种应用和研究主题](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/ed258197ba9c79ff2534a8eff66e28da.png)



![[GXYCTF2019]BabyUpload1](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/53399c8c116f415182edad129448e1e7.png)