C++官网参考链接:https://cplusplus.com/reference/list/list/list/
公有成员函数
<list>
std::list::list
C++98
默认构造函数 (1)
explicit list (const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
填充构造函数 (2)
explicit list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type(), const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
范围构造函数 (3)
template <class InputIterator> list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
复制构造函数 (4)
list (const list& x);
C++11
默认构造函数 (1)
explicit list (const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
填充构造函数 (2)
explicit list (size_type n);
list (size_type n, const value_type& val, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
范围构造函数 (3)
template <class InputIterator> list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
复制构造函数 (4)
list (const list& x);
list (const list& x, const allocator_type& alloc);
移动构造函数 (5)
list (list&& x);
list (list&& x, const allocator_type& alloc);
initializer list (6)
list (initializer_list<value_type> il, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
C++14
默认构造函数 (1)
list();
explicit list (const allocator_type& alloc);
填充构造函数 (2)
explicit list (size_type n, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
list (size_type n, const value_type& val, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
范围构造函数 (3)
template <class InputIterator> list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
复制构造函数 (4)
list (const list& x);
list (const list& x, const allocator_type& alloc);
移动构造函数 (5)
list (list&& x);
list (list&& x, const allocator_type& alloc);
初始化列表构造函数 (6)
list (initializer_list<value_type> il, const allocator_type& alloc = allocator_type());
构造列表
构造一个list容器对象,根据使用的构造函数版本初始化它的内容:
C++98
(1)空容器构造函数(默认构造函数)
构造一个空容器,不包含任何元素。
(2)构造函数
构造一个包含n个元素的容器。每个元素都是val的副本。
(3)构造函数
构造一个包含与范围[first,last)相同数量元素的容器,每个元素以相同的顺序从该范围中相应的元素构造。
(4)拷贝构造函数
以相同的顺序,用x中每个元素的副本构造一个容器。
容器保持alloc的内部副本,该副本用于在其生命周期内分配存储空间。
复制构造函数(4)创建一个容器,该容器保存并使用x的分配器的副本。
使用这个内部分配器(internal allocator)来分配元素的存储空间。
C++11
(1)空容器构造函数(默认构造函数)
构造一个空(empty)容器,不包含任何元素。
(2)填充构造函数
构造一个包含n个元素的容器。每个元素都是val(如果提供)的副本。
(3)构造函数
构造一个包含与范围[first,last)相同数量元素的容器,每个元素的位置都是从该范围中相应的元素以相同的顺序构造的。
(4)复制构造函数(和使用分配器复制)
以相同的顺序,用x中每个元素的副本构造一个容器。
(5)移动构造函数(和使用分配器移动)
构造一个获取x元素的容器。
如果指定了alloc且与x的分配器不同,则移动元素。否则,不构造任何元素(它们的所有权直接转移)。
x处于未指定但有效的状态。
(6)初始化列表构造函数
用il中每个元素的副本以相同的顺序构造一个容器。
容器保留了一个alloc的内部副本,该副本用于为其元素分配和释放存储空间,以及构造和销毁它们(由其allocator_traits指定)。
如果没有alloc实参传递给构造函数,则使用默认构造的分配器,以下情况除外:
-复制构造函数(4,第一个签名)创建一个容器,该容器保存并使用通过在x的分配器上调用适当的selected_on_container_copy_construction特性返回的分配器的副本。
-移动构造函数(5,第一个签名)获取x的分配器。
通过使用适当的实参调用allocator_traits::construct来复制、移动或以其他方式构造所有元素。
形参
alloc
分配器对象。
容器保留并使用这个分配器的内部副本。
成员类型allocator_type是容器使用的内部分配器类型,在list中定义为它的第二个模板形参(Alloc)的别名。
如果allocator_type是默认分配器(allocator)的实例化(它没有状态),这是不相关的。
n
初始容器大小(即,在构造时容器中元素的数量)。
成员类型size_type是无符号整型。
val
值来填充容器。容器中的n个元素都初始化为该值的一个副本。
成员类型value_type是容器中元素的类型,在list中定义为其第一个模板形参(T)的别名。
first,last
输入迭代器(Input iterators)到范围内的初始和最终位置。使用的范围是[first,last),它包括first和last之间的所有元素,包括由first指向的元素,但不包括由last指向的元素。
函数模板实参InputIterator应该是一个输入迭代器(input iterator)类型,它指向可以构造value_type对象的类型元素。
x
相同类型的另一个list对象(具有相同的类模板实参),其内容被复制或获取。
il
一个initializer_list对象。
这些对象是由初始化器列表声明器自动构造的。
成员类型value_type是容器中元素的类型,在list中定义为其第一个模板形参(T)的别名。
用例
// constructing lists
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
int main ()
{
// constructors used in the same order as described above:
std::list<int> first; // empty list of ints
std::list<int> second (4,100); // four ints with value 100
std::list<int> third (second.begin(),second.end()); // iterating through second
std::list<int> fourth (third); // a copy of third
// the iterator constructor can also be used to construct from arrays:
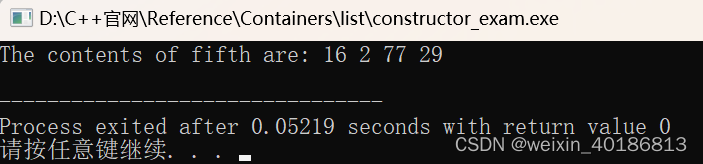
int myints[] = {16,2,77,29};
std::list<int> fifth (myints, myints + sizeof(myints) / sizeof(int) );
std::cout << "The contents of fifth are: ";
for (std::list<int>::iterator it = fifth.begin(); it != fifth.end(); it++)
std::cout << *it << ' ';
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
输出:
复杂性
对于默认构造函数(1)和移动构造函数(5),都是常量(除非alloc不同于x的分配器)。
对于所有其他情况,结果容器中的元素数量中是线性的。
迭代器的有效性
如果元素被移动的话,移动构造函数(5)会使指向x元素的迭代器、指针和引用失效。
数据竞争
所有复制的元素都被访问。
移动构造函数(5)修改x。
异常安全
强保证:在抛出异常的情况下没有影响。
如果元素结构的适当实参不支持allocator_traits::construct,或者由[first,last)指定的范围无效,则会导致未定义的行为。





![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot人事管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20cef50c26be4e88b673a9b9602ac316.png)