前言:大家好,这里是YY;此篇博客主要是操作符重载的应用;包含【流插入,流提取】【>,<,>=,<=,】【+,-,+=,-=】【前置++,后置++,前置--,后置--】
PS:最后的模块有完整代码演示;如果对你有帮助,希望能够关注,赞,收藏,谢谢!
目录
一.流插入,流提取
1.为什么流插入<<不能写成成员函数
2.流插入写在类外访问类内成员的方法——友元
3.代码展示:
二.基本运算符重载【>,>=,<,<=等】
1.代码展示:
三.基本运算符重载【+,+=,-,-=】(日期与天数的运算)
1.代码展示:
四.基本运算符重载【前置++,后置++等】
1.机制说明:
1.如何设置返回类型?
2.如何在定义与声明中区分前后置?
2.代码展示:
五. 减法的重载(日期-日期)
六.完整代码实现
一.流插入,流提取
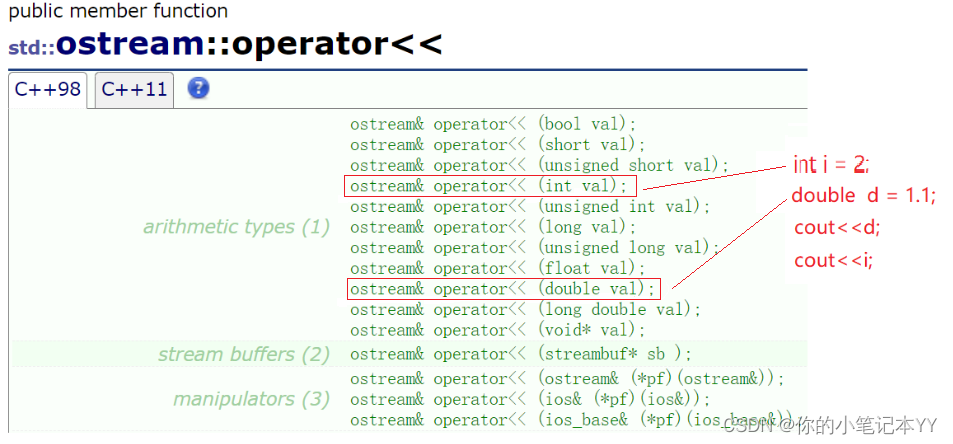
【流插入的库是在iostream里,流提取的库是在ostream里】
- 可以支持内置类型是因为在库里面实现了
- 可以支持自定义类型,是因为人为进行了函数重载
图示:
此时:cout<<d相当于count.operator(d)
1.为什么流插入<<不能写成成员函数
// 流插入不能写成成员函数? //因为Date对象默认占用第一个参数,就是做了左操作数 如果按照正常使用场景实现出来: count<<d1; 如果写在成员函数里会表现出 count.operator<<(d) 访问不了成员 只有写成 d1 << cout; 才会在成员函数里表现出 d1.operator<<(count) 才能进行传参,访问成员
因此为了使用操作合乎习惯,又要让流插入能够访问成员,只能将流插入重载写在类外(虽然流提取不会出现这种情况,为了统一,一并写在类外)
2.流插入写在类外访问类内成员的方法——友元
但是类内的成员是private(私有的),我们可以通过友元(声明操作符重载函数能进入类内访问的权限)
3.代码展示:
头文件部分:
#pragma once #include<iostream> #include<assert.h> using namespace std; class Date { // 友元函数声明 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d); friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d); public: Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1); void Print() const { cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl; } Date(const Date& d) // 错误写法:(不加引用)编译报错,会引发无穷递归 { // 拷贝构造 _year = d._year; _month = d._month; _day = d._day; } int GetMonthDay(int year, int month); private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; //虽然友元已经声明,但那与函数声明不同,仅是表示权限 //这里还是要再次进行函数声明 ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d); istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
.c文件部分:
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d) { out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl; return out; } istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d) { int year, month, day; in >> year >> month >> day; if (month > 0 && month < 13 && day > 0 && day <= d.GetMonthDay(year, month)) { d._year = year; d._month = month; d._day = day; } else { cout << "非法日期" << endl; assert(false); } return in; }
二.基本运算符重载【>,>=,<,<=等】
1.代码展示:
类内声明:
PS:加const,可以让普通变量和const变量都能调用该函数(具体知识点可见YY的C++知识合集博客,关于const的解读)
bool operator<(const Date& x) const; //相当于bool operator<(const Date* const this,const Date& x);,下列声明同理 bool operator==(const Date& x) const; bool operator<=(const Date& x) const; bool operator>(const Date& x) const; bool operator>=(const Date& x) const; bool operator!=(const Date& x) const;
.c文件实现:
PS:在函数实现过程中可以使用技巧"复用"
(多个函数只需要复用一个定义即可,具体代码)
bool Date::operator==(const Date& x) const { return _year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day == x._day; } bool Date::operator<(const Date& x) const { if (_year < x._year) { return true; } else if (_year == x._year && _month < x._month) { return true; } else if (_year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day < x._day) { return true; } return false; } //直接利用一个<的复用完成其他定义 bool Date::operator<=(const Date& x) const { return *this < x || *this == x; } bool Date::operator>(const Date& x) const { return !(*this <= x); } bool Date::operator>=(const Date & x) const { return !(*this < x); } bool Date::operator!=(const Date& x) const { return !(*this == x); }
三.基本运算符重载【+,+=,-,-=】(日期与天数的运算)
1.代码展示:
类内声明:
PS:加const,可以让普通变量和const变量都能调用该函数(具体知识点可见YY的C++知识合集博客,关于const的解读)
PS:const加在后面表示const Date* this ;表明在该成员函数中不能对类的任何成员进行修改,而+=,-=是要实现对类内成员的改变,因此不能加;
Date& operator+=(int day); Date operator+(int day) const; Date& operator-=(int day); Date operator-(int day) const;
.c文件实现:
Date& Date::operator+=(int day) { if (day < 0) { return *this -= -day; } _day += day; while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) { _day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month); ++_month; if (_month == 13) { ++_year; _month = 1; } } return *this; } // d1 + 100 Date Date::operator+(int day) const { //复用+= Date tmp(*this); tmp += day; return tmp; /*tmp._day += day; while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month)) { tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month); ++tmp._month; if (tmp._month == 13) { ++tmp._year; tmp._month = 1; } } return tmp; */ } Date& Date::operator-=(int day) { if (day < 0) { return *this += -day; } _day -= day; while (_day <= 0) { --_month; if (_month == 0) { _month = 12; --_year; } _day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month); } return *this; } Date Date::operator-(int day) const { Date tmp = *this; tmp -= day; return tmp; }
四.基本运算符重载【前置++,后置++等】
1.机制说明:
1.如何设置返回类型?
- 前置的是【先赋值后使用】:返回的是本身(Date&接收)(引用提高效率)
- 后置的是【先使用后赋值】:返回的是临时变量(Date接收)(不用引用,因为临时变量出作用域即销毁,引用会变成野引用)
2.如何在定义与声明中区分前后置?
- 增加参数int,构成函数重载
2.代码展示:
类内声明:
//增加这个int参数不是为了接收具体的值,仅仅是占位,跟前置++构成重载 Date& operator++(); Date operator++(int); Date& operator--(); Date operator--(int);
.c内实现:
// 前置++ Date& Date::operator++() { *this += 1; return *this; } // 后置++ // 增加这个int参数不是为了接收具体的值,仅仅是占位,跟前置++构成重载 Date Date::operator++(int) { Date tmp = *this; *this += 1; return tmp; } Date& Date::operator--() { *this -= 1; return *this; } Date Date::operator--(int) { Date tmp = *this; *this -= 1; return tmp; }
五. 减法的重载(日期-日期)
技巧:
- 预设大小:得以计算绝对值
- 预设flag:得以实现最终结果
.c文件实现:
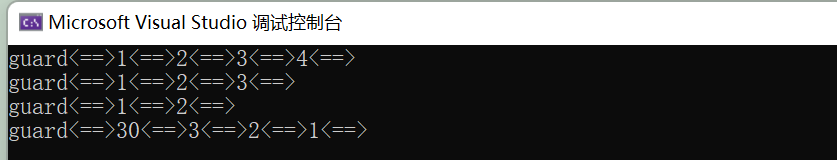
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const { Date max = *this; Date min = d; int flag = 1; if (*this < d) { max = d; min = *this; flag = -1; } int n = 0; while (min != max) { ++min; ++n; } return n * flag; }
六.完整代码实现
头文件:
#pragma once #include<iostream> #include<assert.h> using namespace std; class Date { // 友元函数声明 friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d); friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d); public: Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1); void Print() const { cout << _year << "-" << _month << "-" << _day << endl; } Date(const Date& d) // 错误写法:编译报错,会引发无穷递归 { _year = d._year; _month = d._month; _day = d._day; } bool operator<(const Date& x) const; bool operator==(const Date& x) const; bool operator<=(const Date& x) const; bool operator>(const Date& x) const; bool operator>=(const Date& x) const; bool operator!=(const Date& x) const; int GetMonthDay(int year, int month); // d1 + 100 Date& operator+=(int day); Date operator+(int day) const; Date& operator-=(int day); Date operator-(int day) const; Date& operator++(); Date operator++(int); Date& operator--(); Date operator--(int); int operator-(const Date& d) const; // 流插入不能写成成员函数? // 因为Date对象默认占用第一个参数,就是做了左操作数 // 写出来就一定是下面这样子,不符合使用习惯 //d1 << cout; // d1.operator<<(cout); //void operator<<(ostream& out); /*int GetYear() { return _year; }*/ private: int _year; int _month; int _day; }; ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d); istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
.c文件:
#include "Date.h" Date::Date(int year, int month, int day) { if (month > 0 && month < 13 && day > 0 && day <= GetMonthDay(year, month)) { _year = year; _month = month; _day = day; } else { cout << "非法日期" << endl; assert(false); } } bool Date::operator<(const Date& x) const { if (_year < x._year) { return true; } else if (_year == x._year && _month < x._month) { return true; } else if (_year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day < x._day) { return true; } return false; } bool Date::operator==(const Date& x) const { return _year == x._year && _month == x._month && _day == x._day; } // 复用 // d1 <= d2 bool Date::operator<=(const Date& x) const { return *this < x || *this == x; } bool Date::operator>(const Date& x) const { return !(*this <= x); } bool Date::operator>=(const Date & x) const { return !(*this < x); } bool Date::operator!=(const Date& x) const { return !(*this == x); } int Date::GetMonthDay(int year, int month) { static int daysArr[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 }; //if (((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)) && month == 2) if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0))) { return 29; } else { return daysArr[month]; } } Date& Date::operator+=(int day) { if (day < 0) { return *this -= -day; } _day += day; while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month)) { _day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month); ++_month; if (_month == 13) { ++_year; _month = 1; } } return *this; } // d1 + 100 Date Date::operator+(int day) const { Date tmp(*this); tmp += day; return tmp; /*tmp._day += day; while (tmp._day > GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month)) { tmp._day -= GetMonthDay(tmp._year, tmp._month); ++tmp._month; if (tmp._month == 13) { ++tmp._year; tmp._month = 1; } } return tmp; */ } Date& Date::operator-=(int day) { if (day < 0) { return *this += -day; } _day -= day; while (_day <= 0) { --_month; if (_month == 0) { _month = 12; --_year; } _day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month); } return *this; } Date Date::operator-(int day) const { Date tmp = *this; tmp -= day; return tmp; } // 前置++ Date& Date::operator++() { *this += 1; return *this; } // 后置++ // 增加这个int参数不是为了接收具体的值,仅仅是占位,跟前置++构成重载 Date Date::operator++(int) { Date tmp = *this; *this += 1; return tmp; } Date& Date::operator--() { *this -= 1; return *this; } Date Date::operator--(int) { Date tmp = *this; *this -= 1; return tmp; } // d1 - d2; int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const { Date max = *this; Date min = d; int flag = 1; if (*this < d) { max = d; min = *this; flag = -1; } int n = 0; while (min != max) { ++min; ++n; } return n * flag; } //void Date::operator<<(ostream& out) //{ // out << _year << "年" << _month << "月" << _day << "日" << endl; //} // 21:20继续 ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d) { out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日" << endl; return out; } istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d) { int year, month, day; in >> year >> month >> day; if (month > 0 && month < 13 && day > 0 && day <= d.GetMonthDay(year, month)) { d._year = year; d._month = month; d._day = day; } else { cout << "非法日期" << endl; assert(false); } return in; }