一、电路连接
主控芯片选型为:STM32F407ZGT6,SPI FLASH选型为:W25Q256JV。
采用了两片32MB的片外SPI FLASH,电路如图所示。
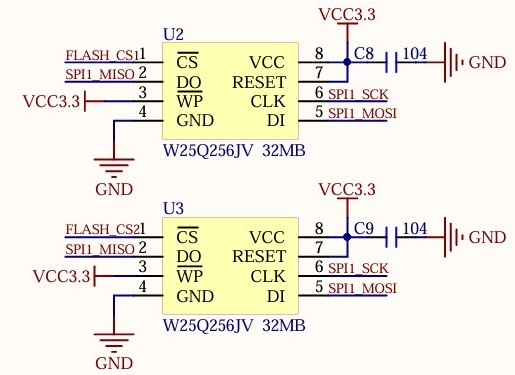
SPI FLASH与主控芯片的连接方式如表所示。
| STM32F407GT6 | W25Q256JV |
|---|---|
| PB3 | SPI1_SCK |
| PB4 | SPI1_MISO |
| PB5 | SPI1_MOSI |
| PB7 | FLASH_CS1 |
| PB8 | FLASH_CS2 |
二、SPI FLASH直接读写
本文采用硬件SPI通信,分为四个文件,分别为:spi.c、spi.h、flash.c、flash.h。
2.1 spi.c源文件
spi.c源文件如下,主要进行spi硬件初始化和收发函数定义。
#include "spi.h"
SPI_HandleTypeDef hspi1;
static u8 pRx = 0;
void SPI_Init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_SPI1_CLK_ENABLE();
GPIO_InitStructure.Pin = SPI1_CLK | SPI1_MISO | SPI1_MOSI;
GPIO_InitStructure.Mode = GPIO_MODE_AF_PP;
GPIO_InitStructure.Pull = GPIO_PULLUP;
GPIO_InitStructure.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_VERY_HIGH;
GPIO_InitStructure.Alternate = GPIO_AF5_SPI1;
HAL_GPIO_Init(SPI1_PORT, &GPIO_InitStructure);
hspi1.Instance = SPI1;
hspi1.Init.Mode = SPI_MODE_MASTER;
hspi1.Init.Direction = SPI_DIRECTION_2LINES;
hspi1.Init.DataSize = SPI_DATASIZE_8BIT;
hspi1.Init.CLKPolarity = SPI_POLARITY_HIGH;
hspi1.Init.CLKPhase = SPI_PHASE_2EDGE;
hspi1.Init.NSS = SPI_NSS_SOFT;
hspi1.Init.BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BAUDRATEPRESCALER_2;
hspi1.Init.FirstBit = SPI_FIRSTBIT_MSB;
hspi1.Init.TIMode = SPI_TIMODE_DISABLE;
hspi1.Init.CRCCalculation = SPI_CRCCALCULATION_ENABLE;
hspi1.Init.CRCPolynomial = 7;
HAL_SPI_Init(&hspi1);
}
u8 SPI1_ReadWriteByte(u8 data)
{
HAL_SPI_TransmitReceive(&hspi1, &data, &pRx, 1, 10);
return pRx;
}
2.2 spi.h头文件
spi.h头文件如下,主要定义了接口
#ifndef _SPI_H_
#define _SPI_H_
#include "system.h"
#include "delay.h"
#define SPI1_CLK GPIO_PIN_3
#define SPI1_MISO GPIO_PIN_4
#define SPI1_MOSI GPIO_PIN_5
#define SPI1_PORT GPIOB
extern SPI_HandleTypeDef hspi1;
extern void SPI_Init(void);
extern u8 SPI1_ReadWriteByte(u8 data);
#endif2.3 flash.c源文件
flash.c源文件如下,主要进行W25Q256JV的硬件初始化和一些设置函数。
#include "flash.h"
void W25Q256_Init(uint16_t selectChip)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
__HAL_RCC_GPIOB_CLK_ENABLE();
GPIO_InitStructure.Pin = selectChip;
GPIO_InitStructure.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStructure.Pull = GPIO_PULLUP;
GPIO_InitStructure.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_HIGH;
HAL_GPIO_Init(FLASH_PORT, &GPIO_InitStructure);
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
SPI_Init();
delay_ms(1);
W25Q256_4BDSet(selectChip);
}
void W25Q256_4BDSet(uint16_t selectChip)
{
u8 Reg3;
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
Reg3 = SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_ReadStatusReg3);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_WriteEnable);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_WriteStatusReg3);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(Reg3 | (1<<2));
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
delay_us(3);
}
u8 W25Q256_Read_SR(uint16_t selectChip, u8 Reg)
{
u8 byte = 0;
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(Reg);
byte = SPI1_ReadWriteByte(0xff);
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
return byte;
}
void W25Q256_Write_SR(uint16_t selectChip, u8 Reg, u8 sr)
{
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(Reg);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(sr);
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
}
void W25Q256_Write_Enable(uint16_t selectChip)
{
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_WriteEnable);
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
}
void W25Q256_Write_Disable(uint16_t selectChip)
{
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_WriteDisable);
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
}
u16 W25Q256_ReadID(uint16_t selectChip)
{
u16 Temp = 0;
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_ManufactDeviceID);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(0x00);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(0x00);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(0x00);
Temp |= SPI1_ReadWriteByte(0x00)<<8;
Temp |= SPI1_ReadWriteByte(0x00);
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
return Temp;
}
void W25Q256_Read(uint16_t selectChip, u8* pBuffer,u32 ReadAddr,u16 NumByteToRead)
{
u16 i;
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_ReadData4BA);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)((ReadAddr)>>24));
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)((ReadAddr)>>16));
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)((ReadAddr)>>8));
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)ReadAddr);
for (i = 0; i < NumByteToRead; i++)
{
pBuffer[i] = SPI1_ReadWriteByte(0XFF); //循环读数
}
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
}
static void W25Q256_Write_Page(uint16_t selectChip, u8* pBuffer, u32 WriteAddr, u16 NumByteToWrite)
{
u16 i;
W25Q256_Write_Enable(selectChip);
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_PageProgram4BA);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)((WriteAddr)>>24));
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)((WriteAddr)>>16));
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)((WriteAddr)>>8));
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)WriteAddr);
for(i = 0;i < NumByteToWrite; i++)
{
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(pBuffer[i]);
}
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
W25Q256_Wait_Busy(selectChip);
}
static void W25Q256_Write_NoCheck(uint16_t selectChip, u8* pBuffer, u32 WriteAddr, u16 NumByteToWrite)
{
u16 pageremain;
pageremain = 256 - WriteAddr % 256; // 单页剩余的字节数
if(NumByteToWrite <= pageremain)
{
pageremain = NumByteToWrite; // 不大于256个字节
}
while(1)
{
W25Q256_Write_Page(selectChip, pBuffer, WriteAddr, pageremain);
if(NumByteToWrite == pageremain)
{
break;
}
else
{
pBuffer += pageremain;
WriteAddr += pageremain;
NumByteToWrite -= pageremain;
if(NumByteToWrite > 256)
{
pageremain = 256;
}
else
{
pageremain = NumByteToWrite;
}
}
}
}
u8 W25Q256_BUFFER[4096];
void W25Q256_Write(uint16_t selectChip, u8* pBuffer, u32 WriteAddr, u16 NumByteToWrite)
{
u32 secpos;
u16 secoff;
u16 secremain;
u16 i;
u8 *W25Q256_BUF;
W25Q256_BUF = W25Q256_BUFFER;
secpos = WriteAddr/4096;//扇区地址
secoff = WriteAddr%4096;//在扇区内的偏移
secremain = 4096-secoff;//扇区剩余空间大小
if(NumByteToWrite <= secremain)
{
secremain = NumByteToWrite;//不大于4096个字节
}
while(1)
{
W25Q256_Read(selectChip, W25Q256_BUF, secpos*4096, 4096);//读出整个扇区的内容
for(i = 0; i < secremain; i++)//校验数据
{
if(W25Q256_BUF[secoff+i] != 0XFF)
{
break;
}
}
if(i < secremain) //需要擦除
{
W25Q256_Erase_Sector(selectChip, secpos); //擦除这个扇区
for(i = 0; i < secremain; i++) //复制
{
W25Q256_BUF[i+secoff] = pBuffer[i];
}
W25Q256_Write_NoCheck(selectChip, W25Q256_BUF, secpos*4096, 4096);//写入整个扇区
}
else
{
W25Q256_Write_NoCheck(selectChip, pBuffer, WriteAddr, secremain);//写已经擦除了的,直接写入扇区剩余区间.
}
if(NumByteToWrite == secremain)
{
break;//写入结束了
}
else//写入未结束
{
secpos++;//扇区地址增1
secoff = 0;//偏移位置为0
pBuffer += secremain; //指针偏移
WriteAddr += secremain;//写地址偏移
NumByteToWrite -= secremain; //字节数递减
if(NumByteToWrite > 4096)
{
secremain=4096; //下一个扇区还是写不完
}
else
{
secremain = NumByteToWrite; //下一个扇区可以写完了
}
}
}
}
void W25Q256_Erase_Chip(uint16_t selectChip)
{
W25Q256_Write_Enable(selectChip);
W25Q256_Wait_Busy(selectChip);
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_ChipErase);
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
W25Q256_Wait_Busy(selectChip);
}
void W25Q256_Erase_Sector(uint16_t selectChip, u32 Dst_Addr)
{
Dst_Addr *= 4096;
W25Q256_Write_Enable(selectChip);
W25Q256_Wait_Busy(selectChip);
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_SectorErase4BA);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)((Dst_Addr)>>24));
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)((Dst_Addr)>>16));
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)((Dst_Addr)>>8));
SPI1_ReadWriteByte((u8)Dst_Addr);
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
W25Q256_Wait_Busy(selectChip);
}
void W25Q256_Wait_Busy(uint16_t selectChip)
{
while((W25Q256_Read_SR(selectChip, W25Q256_ReadStatusReg1) & 0x01) == 0x01);
}
void W25Q256_Power_Down(uint16_t selectChip)
{
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_PowerDown);
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
delay_us(3);
}
void W25Q256_WAKEUP(uint16_t selectChip)
{
FLAS_CS_ENABLE(selectChip);
SPI1_ReadWriteByte(W25Q256_ReleasePowerDown);
FLAS_CS_DISABLE(selectChip);
delay_us(3);
}
2.4 flash.h头文件
flash.h头文件如下:
#ifndef _FLASH_H_
#define _FLASH_H_
#include "system.h"
#include "spi.h"
#define FLASH1 GPIO_PIN_7
#define FLASH2 GPIO_PIN_8
#define FLASH_PORT GPIOB
#define FLAS_CS_ENABLE(x) HAL_GPIO_WritePin(FLASH_PORT, x, GPIO_PIN_RESET)
#define FLAS_CS_DISABLE(x) HAL_GPIO_WritePin(FLASH_PORT, x, GPIO_PIN_SET)
// W25Q256指令集 4字节地址
#define W25Q256_WriteEnable 0x06
#define W25Q256_SRWriteEnable 0x50
#define W25Q256_WriteDisable 0x04
#define W25Q256_ReleasePowerDown 0xAB
#define W25Q256_ManufactDeviceID 0x90
#define W25Q256_JedecDeviceID 0x9F
#define W25Q256_ReadUniqueID 0x4B
#define W25Q256_ReadData 0x03
#define W25Q256_ReadData4BA 0x13
#define W25Q256_FastReadData 0x0B
#define W25Q256_FastReadData4BA 0x0C
#define W25Q256_PageProgram 0x02
#define W25Q256_PageProgram4BA 0x12
#define W25Q256_SectorErase 0x20
#define W25Q256_SectorErase4BA 0x21
#define W25Q256_BlockErase32 0x52
#define W25Q256_BlockErase64 0xD8
#define W25Q256_BlockErase644BA 0xDC
#define W25Q256_ChipErase 0xC7
#define W25Q256_ReadStatusReg1 0x05
#define W25Q256_WriteStatusReg1 0x01
#define W25Q256_ReadStatusReg2 0x35
#define W25Q256_WriteStatusReg2 0x31
#define W25Q256_ReadStatusReg3 0x15
#define W25Q256_WriteStatusReg3 0x11
#define W25Q256_ReadExtAddrReg 0xC8
#define W25Q256_WriteExtAddrReg 0xC5
#define W25Q256_ReadSfdpReg 0x5A
#define W25Q256_EraseSecReg 0x44
#define W25Q256_ProgramSecReg 0x42
#define W25Q256_ReadSecReg 0x48
#define W25Q256_GlobalBlockLock 0x7E
#define W25Q256_GlobalBlockUlock 0x98
#define W25Q256_ReadBlockLock 0x3D
#define W25Q256_IndivBlockLock 0x36
#define W25Q256_IndivBlockUlock 0x39
#define W25Q256_EraProSuspend 0x75
#define W25Q256_RraProResume 0x7A
#define W25Q256_PowerDown 0xB9
#define W25Q256_Enter4BAMode 0xB7
#define W25Q256_Exit4BAMode 0xE9
#define W25Q256_EnableReset 0x66
#define W25Q256_ResetDev 0x99
extern void W25Q256_Init(uint16_t selectChip);
extern void W25Q256_4BDSet(uint16_t selectChip);
extern u8 W25Q256_Read_SR(uint16_t selectChip, u8 Reg);
extern void W25Q256_Write_SR(uint16_t selectChip, u8 Reg, u8 sr);
extern void W25Q256_Write_Enable(uint16_t selectChip);
extern void W25Q256_Write_Disable(uint16_t selectChip);
extern u16 W25Q256_ReadID(uint16_t selectChip);
extern void W25Q256_Read(uint16_t selectChip, u8* pBuffer,u32 ReadAddr,u16 NumByteToRead);
extern void W25Q256_Write(uint16_t selectChip, u8* pBuffer, u32 WriteAddr, u16 NumByteToWrite);
extern void W25Q256_Erase_Chip(uint16_t selectChip);
extern void W25Q256_Erase_Sector(uint16_t selectChip, u32 Dst_Addr);
extern void W25Q256_Wait_Busy(uint16_t selectChip);
extern void W25Q256_Power_Down(uint16_t selectChip);
extern void W25Q256_WAKEUP(uint16_t selectChip);
#endif
通过这四个文件可以实现对两片flash的读写操作。
三、FATFS文件系统移植
3.1 源码下载
源码下载地址:http://elm-chan.org/fsw/ff/00index_e.html
下载的版本是:R0.15a

3.2 源码目录
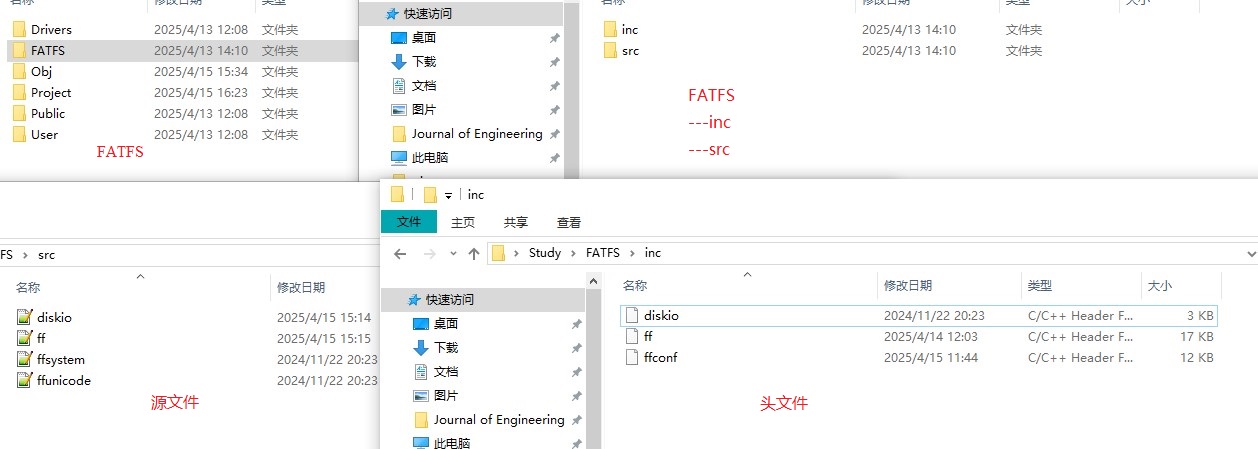
FATFS下载解压缩后,如图:

documents文件夹下存放一些帮助文档之类的,可以不用考虑,用到的时候再去百度。
source文件夹下存放FATFS文件系统源码,包括diskio.c、diskio.h、ff.c、ff.h、ffconf.h、ffsystem.c、ffunicode.c,共四个源码和三个头文件。后续需配置只需要修改diskio.c和ffconf.h两个文件即可。

3.3 源码复制到自己的工程
① 将FATFS源码中的七个文件复制到自己的工程文件夹中:
② 将源文件添加至keil工程

③ 添加头文件路径

此时点击编译会报错和警告,需要对源文件的信息进行配置。
3.4 修改diskio.c
3.4.1 添加头文件
spi.h和flash.h为第二章中的两个头文件,定义了与硬件直接交互的代码。delay.h为延时头文件。

3.4.2 定义设备驱动号
将原来代码中的0、1、2三个硬件驱动号删掉定义自己的设备。我有两块SPI FLASH,所以定义了两个设备驱动号。


3.4.3 修改disk_status函数
这个函数是查询设备状态的函数,我们使用flash.c中定义的W25Q256_ReadID函数读W25Q256的设备ID号,如果能正确读取,则系统状态正常。
原来的代码是:

修改后的代码是:

3.4.4 修改disk_initialize函数
这个函数是对设备进行初始化的函数,在代码中调用flash.c中定义的W25Q256_Init函数对设备进行初始化。
原来的代码是:

修改后的代码是:

3.4.5 修改disk_read函数
这个函数是对文件进行读的操作,直接调用flash.c中的W25Q256_Read函数即可。
原来的代码是:

修改后的代码是:(sector和count左移12位的原因分别:LBA_t定义的sector是扇区的逻辑地址,即0,1,2...,通过左移12位(乘4096)获得扇区的物理地址;count是读取多少个字节的内容)

3.4.6 修改disk_write函数
这个函数是对文件进行写操作的函数,直接调用flash.c中的W25Q256_Write函数即可,在flash.c中每次写都会先擦除在写入,所以此处不需要再进行扇区擦除,如果W25Q256_Write函数中未进行擦除操作,则在此处还需进行擦除在写入,否则会写入出错。
原来的代码是:

修改后的代码是:

3.4.7 修改disk_ioctl函数
这个函数是获取设备的一些硬件信息之类的,如果此处有问题可能会导致后续挂载创建文件系统失败。
原来的代码是:

修改后的代码是:(SPI_FLASH1和SPI_FLASH2中处理过程一样,SECTOR_SIZE是扇区大小、SECTOR_COUNT是扇区数量,W25Q256扇区大小是4096,一共有8192个扇区。此处的扇区数量必须填写,开始本人漏掉了这个,后续创建文件系统时一直返回14号错误代码,通过一点一点的打印寻找,才发现在f_mkfs函数中调用disk_ioctl查询扇区数量时一直为0导致的)

3.4.8 添加get_fattime函数
这个函数源代码中未给出,直接编译会导致报错。所以需要手动添加,此函数是为了获取文件读写时间的,如果用了RTC实时时钟可以替换这里的年月日时分秒。

3.4.9 diskio.c完整代码
修改后的完整diskio.c文件如下:
#include "ff.h" /* Obtains integer types */
#include "diskio.h" /* Declarations of disk functions */
#include "spi.h"
#include "flash.h"
#include "delay.h"
#define SPI_FLASH1 0
#define SPI_FLASH2 1
#define PAGE_SIZE 256
#define SECTOR_SIZE 4096
#define SECTOR_COUNT 8192
DSTATUS disk_status(BYTE pdrv)
{
DSTATUS stat = STA_NOINIT;
switch (pdrv)
{
case SPI_FLASH1:
if (W25Q256_ReadID(FLASH1) == 0xEF18)
{
stat &= ~STA_NOINIT;
}
break;
case SPI_FLASH2:
if (W25Q256_ReadID(FLASH2) == 0xEF18)
{
stat &= ~STA_NOINIT;
}
break;
}
return stat;
}
DSTATUS disk_initialize(BYTE pdrv)
{
DSTATUS stat = STA_NOINIT;
switch (pdrv)
{
case SPI_FLASH1:
W25Q256_Init(FLASH1);
delay_us(200);
stat = disk_status(pdrv);
break;
case SPI_FLASH2:
W25Q256_Init(FLASH2);
delay_us(200);
stat = disk_status(pdrv);
break;
}
return stat;
}
// pdrv : Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive
// buff : Data buffer to store read data
// sector: Start sector in LBA
// count : Number of sectors to read
DRESULT disk_read(BYTE pdrv, BYTE *buff, LBA_t sector, UINT count)
{
DRESULT res = RES_PARERR;
switch (pdrv)
{
case SPI_FLASH1:
W25Q256_Read(FLASH1, buff, sector << 12, count << 12);
res = RES_OK;
break;
case SPI_FLASH2:
W25Q256_Read(FLASH2, buff, sector << 12, count << 12);
res = RES_OK;
break;
}
return res;
}
#if FF_FS_READONLY == 0
// pdrv : Physical drive nmuber to identify the drive
// buff : Data to be written
// sector : Start sector in LBA
// count : Number of sectors to write
DRESULT disk_write(BYTE pdrv, const BYTE *buff, LBA_t sector, UINT count)
{
DRESULT res = RES_PARERR;
switch (pdrv)
{
case SPI_FLASH1:
W25Q256_Write(FLASH1, (u8 *)buff, sector << 12, count << 12);
res = RES_OK;
break;
case SPI_FLASH2:
W25Q256_Write(FLASH2, (u8 *)buff, sector << 12, count << 12);
res = RES_OK;
break;
}
return res;
}
#endif
// pdrv : Physical drive nmuber
// cmd : Control code
// buff : Buffer to send/receive control data
DRESULT disk_ioctl(BYTE pdrv, BYTE cmd, void *buff)
{
DRESULT res = RES_PARERR;
switch (pdrv)
{
case SPI_FLASH1:
switch (cmd)
{
case CTRL_SYNC:
break;
case CTRL_TRIM:
break;
case GET_BLOCK_SIZE:
break;
case GET_SECTOR_SIZE:
*(DWORD*)buff = SECTOR_SIZE;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_COUNT:
*(DWORD*)buff = SECTOR_COUNT;
break;
default:
res = RES_PARERR;
break;
}
res = RES_OK;
case SPI_FLASH2:
switch (cmd)
{
case CTRL_SYNC:
break;
case CTRL_TRIM:
break;
case GET_BLOCK_SIZE:
break;
case GET_SECTOR_SIZE:
*(DWORD*)buff = SECTOR_SIZE;
break;
case GET_SECTOR_COUNT:
*(DWORD*)buff = SECTOR_COUNT;
break;
default:
res = RES_PARERR;
break;
}
res = RES_OK;
}
return res;
}
__weak DWORD get_fattime(void) // 获取时间
{
return ((DWORD)(2024-1980)<<25) // 设置年份为2024
| ((DWORD)1<<21) // 设置月份为1
| ((DWORD)1<<16) // 设置日期为1
| ((DWORD)1<<11) // 设置小时为1
| ((DWORD)1<<5) // 设置分钟为1
| ((DWORD)1<<1); // 设置秒数为1
}
3.5 修改ffconf.h
修改宏定义FF_USE_MKFS:(作用:创建文件系统函数,定义后才能创建文件系统)

修改宏定义FF_CODE_PAGE:(作用:文件语言,设置为简体中文)

修改宏定义FF_VOLUMES:(作用:硬件系统数量,我这挂了两个spi flash,所以是2)

修改宏定义FF_MIN_SS和FF_MAX_SS:(作用:配置扇区最小和最大空间,W25Q256的扇区大小是4096)

完整的ffconf.h文件如下:
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Configurations of FatFs Module
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FFCONF_DEF 5380 /* Revision ID */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Function Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_FS_READONLY 0
/* This option switches read-only configuration. (0:Read/Write or 1:Read-only)
/ Read-only configuration removes writing API functions, f_write(), f_sync(),
/ f_unlink(), f_mkdir(), f_chmod(), f_rename(), f_truncate(), f_getfree()
/ and optional writing functions as well. */
#define FF_FS_MINIMIZE 0
/* This option defines minimization level to remove some basic API functions.
/
/ 0: Basic functions are fully enabled.
/ 1: f_stat(), f_getfree(), f_unlink(), f_mkdir(), f_truncate() and f_rename()
/ are removed.
/ 2: f_opendir(), f_readdir() and f_closedir() are removed in addition to 1.
/ 3: f_lseek() function is removed in addition to 2. */
#define FF_USE_FIND 0
/* This option switches filtered directory read functions, f_findfirst() and
/ f_findnext(). (0:Disable, 1:Enable 2:Enable with matching altname[] too) */
#define FF_USE_MKFS 1
/* This option switches f_mkfs(). (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_FASTSEEK 0
/* This option switches fast seek feature. (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_EXPAND 0
/* This option switches f_expand(). (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_CHMOD 0
/* This option switches attribute control API functions, f_chmod() and f_utime().
/ (0:Disable or 1:Enable) Also FF_FS_READONLY needs to be 0 to enable this option. */
#define FF_USE_LABEL 0
/* This option switches volume label API functions, f_getlabel() and f_setlabel().
/ (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_FORWARD 0
/* This option switches f_forward(). (0:Disable or 1:Enable) */
#define FF_USE_STRFUNC 0
#define FF_PRINT_LLI 0
#define FF_PRINT_FLOAT 0
#define FF_STRF_ENCODE 3
/* FF_USE_STRFUNC switches the string API functions, f_gets(), f_putc(), f_puts()
/ and f_printf().
/
/ 0: Disable. FF_PRINT_LLI, FF_PRINT_FLOAT and FF_STRF_ENCODE have no effect.
/ 1: Enable without LF - CRLF conversion.
/ 2: Enable with LF - CRLF conversion.
/
/ FF_PRINT_LLI = 1 makes f_printf() support long long argument and FF_PRINT_FLOAT = 1/2
/ makes f_printf() support floating point argument. These features want C99 or later.
/ When FF_LFN_UNICODE >= 1 with LFN enabled, string API functions convert the character
/ encoding in it. FF_STRF_ENCODE selects assumption of character encoding ON THE FILE
/ to be read/written via those functions.
/
/ 0: ANSI/OEM in current CP
/ 1: Unicode in UTF-16LE
/ 2: Unicode in UTF-16BE
/ 3: Unicode in UTF-8
*/
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Locale and Namespace Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_CODE_PAGE 936
/* This option specifies the OEM code page to be used on the target system.
/ Incorrect code page setting can cause a file open failure.
/
/ 437 - U.S.
/ 720 - Arabic
/ 737 - Greek
/ 771 - KBL
/ 775 - Baltic
/ 850 - Latin 1
/ 852 - Latin 2
/ 855 - Cyrillic
/ 857 - Turkish
/ 860 - Portuguese
/ 861 - Icelandic
/ 862 - Hebrew
/ 863 - Canadian French
/ 864 - Arabic
/ 865 - Nordic
/ 866 - Russian
/ 869 - Greek 2
/ 932 - Japanese (DBCS)
/ 936 - Simplified Chinese (DBCS)
/ 949 - Korean (DBCS)
/ 950 - Traditional Chinese (DBCS)
/ 0 - Include all code pages above and configured by f_setcp()
*/
#define FF_USE_LFN 0
#define FF_MAX_LFN 255
/* The FF_USE_LFN switches the support for LFN (long file name).
/
/ 0: Disable LFN. FF_MAX_LFN has no effect.
/ 1: Enable LFN with static working buffer on the BSS. Always NOT thread-safe.
/ 2: Enable LFN with dynamic working buffer on the STACK.
/ 3: Enable LFN with dynamic working buffer on the HEAP.
/
/ To enable the LFN, ffunicode.c needs to be added to the project. The LFN feature
/ requiers certain internal working buffer occupies (FF_MAX_LFN + 1) * 2 bytes and
/ additional (FF_MAX_LFN + 44) / 15 * 32 bytes when exFAT is enabled.
/ The FF_MAX_LFN defines size of the working buffer in UTF-16 code unit and it can
/ be in range of 12 to 255. It is recommended to be set 255 to fully support the LFN
/ specification.
/ When use stack for the working buffer, take care on stack overflow. When use heap
/ memory for the working buffer, memory management functions, ff_memalloc() and
/ ff_memfree() exemplified in ffsystem.c, need to be added to the project. */
#define FF_LFN_UNICODE 0
/* This option switches the character encoding on the API when LFN is enabled.
/
/ 0: ANSI/OEM in current CP (TCHAR = char)
/ 1: Unicode in UTF-16 (TCHAR = WCHAR)
/ 2: Unicode in UTF-8 (TCHAR = char)
/ 3: Unicode in UTF-32 (TCHAR = DWORD)
/
/ Also behavior of string I/O functions will be affected by this option.
/ When LFN is not enabled, this option has no effect. */
#define FF_LFN_BUF 255
#define FF_SFN_BUF 12
/* This set of options defines size of file name members in the FILINFO structure
/ which is used to read out directory items. These values should be suffcient for
/ the file names to read. The maximum possible length of the read file name depends
/ on character encoding. When LFN is not enabled, these options have no effect. */
#define FF_FS_RPATH 0
/* This option configures support for relative path.
/
/ 0: Disable relative path and remove related API functions.
/ 1: Enable relative path. f_chdir() and f_chdrive() are available.
/ 2: f_getcwd() is available in addition to 1.
*/
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ Drive/Volume Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_VOLUMES 2
/* Number of volumes (logical drives) to be used. (1-10) */
#define FF_STR_VOLUME_ID 0
#define FF_VOLUME_STRS "RAM","NAND","CF","SD","SD2","USB","USB2","USB3"
/* FF_STR_VOLUME_ID switches support for volume ID in arbitrary strings.
/ When FF_STR_VOLUME_ID is set to 1 or 2, arbitrary strings can be used as drive
/ number in the path name. FF_VOLUME_STRS defines the volume ID strings for each
/ logical drive. Number of items must not be less than FF_VOLUMES. Valid
/ characters for the volume ID strings are A-Z, a-z and 0-9, however, they are
/ compared in case-insensitive. If FF_STR_VOLUME_ID >= 1 and FF_VOLUME_STRS is
/ not defined, a user defined volume string table is needed as:
/
/ const char* VolumeStr[FF_VOLUMES] = {"ram","flash","sd","usb",...
*/
#define FF_MULTI_PARTITION 0
/* This option switches support for multiple volumes on the physical drive.
/ By default (0), each logical drive number is bound to the same physical drive
/ number and only an FAT volume found on the physical drive will be mounted.
/ When this feature is enabled (1), each logical drive number can be bound to
/ arbitrary physical drive and partition listed in the VolToPart[]. Also f_fdisk()
/ will be available. */
#define FF_MIN_SS 4096
#define FF_MAX_SS 4096
/* This set of options configures the range of sector size to be supported. (512,
/ 1024, 2048 or 4096) Always set both 512 for most systems, generic memory card and
/ harddisk, but a larger value may be required for on-board flash memory and some
/ type of optical media. When FF_MAX_SS is larger than FF_MIN_SS, FatFs is
/ configured for variable sector size mode and disk_ioctl() needs to implement
/ GET_SECTOR_SIZE command. */
#define FF_LBA64 0
/* This option switches support for 64-bit LBA. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable the 64-bit LBA, also exFAT needs to be enabled. (FF_FS_EXFAT == 1) */
#define FF_MIN_GPT 0x10000000
/* Minimum number of sectors to switch GPT as partitioning format in f_mkfs() and
/ f_fdisk(). 2^32 sectors maximum. This option has no effect when FF_LBA64 == 0. */
#define FF_USE_TRIM 0
/* This option switches support for ATA-TRIM. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable this feature, also CTRL_TRIM command should be implemented to
/ the disk_ioctl(). */
/*---------------------------------------------------------------------------/
/ System Configurations
/---------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#define FF_FS_TINY 0
/* This option switches tiny buffer configuration. (0:Normal or 1:Tiny)
/ At the tiny configuration, size of file object (FIL) is shrinked FF_MAX_SS bytes.
/ Instead of private sector buffer eliminated from the file object, common sector
/ buffer in the filesystem object (FATFS) is used for the file data transfer. */
#define FF_FS_EXFAT 0
/* This option switches support for exFAT filesystem. (0:Disable or 1:Enable)
/ To enable exFAT, also LFN needs to be enabled. (FF_USE_LFN >= 1)
/ Note that enabling exFAT discards ANSI C (C89) compatibility. */
#define FF_FS_NORTC 0
#define FF_NORTC_MON 11
#define FF_NORTC_MDAY 1
#define FF_NORTC_YEAR 2024
/* The option FF_FS_NORTC switches timestamp feature. If the system does not have
/ an RTC or valid timestamp is not needed, set FF_FS_NORTC = 1 to disable the
/ timestamp feature. Every object modified by FatFs will have a fixed timestamp
/ defined by FF_NORTC_MON, FF_NORTC_MDAY and FF_NORTC_YEAR in local time.
/ To enable timestamp function (FF_FS_NORTC = 0), get_fattime() need to be added
/ to the project to read current time form real-time clock. FF_NORTC_MON,
/ FF_NORTC_MDAY and FF_NORTC_YEAR have no effect.
/ These options have no effect in read-only configuration (FF_FS_READONLY = 1). */
#define FF_FS_NOFSINFO 0
/* If you need to know correct free space on the FAT32 volume, set bit 0 of this
/ option, and f_getfree() at the first time after volume mount will force
/ a full FAT scan. Bit 1 controls the use of last allocated cluster number.
/
/ bit0=0: Use free cluster count in the FSINFO if available.
/ bit0=1: Do not trust free cluster count in the FSINFO.
/ bit1=0: Use last allocated cluster number in the FSINFO if available.
/ bit1=1: Do not trust last allocated cluster number in the FSINFO.
*/
#define FF_FS_LOCK 0
/* The option FF_FS_LOCK switches file lock function to control duplicated file open
/ and illegal operation to open objects. This option must be 0 when FF_FS_READONLY
/ is 1.
/
/ 0: Disable file lock function. To avoid volume corruption, application program
/ should avoid illegal open, remove and rename to the open objects.
/ >0: Enable file lock function. The value defines how many files/sub-directories
/ can be opened simultaneously under file lock control. Note that the file
/ lock control is independent of re-entrancy. */
#define FF_FS_REENTRANT 0
#define FF_FS_TIMEOUT 1000
/* The option FF_FS_REENTRANT switches the re-entrancy (thread safe) of the FatFs
/ module itself. Note that regardless of this option, file access to different
/ volume is always re-entrant and volume control functions, f_mount(), f_mkfs()
/ and f_fdisk(), are always not re-entrant. Only file/directory access to
/ the same volume is under control of this featuer.
/
/ 0: Disable re-entrancy. FF_FS_TIMEOUT have no effect.
/ 1: Enable re-entrancy. Also user provided synchronization handlers,
/ ff_mutex_create(), ff_mutex_delete(), ff_mutex_take() and ff_mutex_give(),
/ must be added to the project. Samples are available in ffsystem.c.
/
/ The FF_FS_TIMEOUT defines timeout period in unit of O/S time tick.
*/
/*--- End of configuration options ---*/
四、文件系统测试
在主函数中只需要包含ff.h文件即可,完整的主程序如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include "system.h"
#include "delay.h"
#include "uart.h"
#include "flash.h"
#include "ff.h"
// 文件系统变量
FATFS fs;
FIL fp;
FRESULT fres;
UINT fnum;
// 文件读写变量
BYTE buffer[4096] = {0};
BYTE textBuffer[] = "ABCDEFG";
uint8_t c[256] = {0};
int main(void)
{
HAL_Init();
SystemClock_Config();
Uart_Init(115200);
fres = f_mount(&fs, "1:", 1); // 挂载文件系统
if(fres == FR_NO_FILESYSTEM) // 检测是否存在文件系统
{
fres = f_mkfs("1:", NULL, buffer, 4096); // 创建文件系统
if(fres == FR_OK) // 判断是否创建成功
{
printf("FATFS has been mkf\n");
fres = f_mount(NULL, "1:", 0); // 卸载文件系统
fres = f_mount(&fs, "1:", 1); // 重新挂载文件系统
}
else // 创建失败
{
printf("FATFS mkf filed: %d\n", fres);
while(1) // 死循环
{
}
}
}
else if(fres != FR_OK) // 挂载失败
{
printf("mount ERROR:%d\n", fres);
while(1) // 死循环
{
}
}
else // 挂载成功
{
printf("mount OK\n");
}
fres = f_open(&fp, "1:ABC.txt", FA_CREATE_ALWAYS | FA_WRITE); // 创建文件
if(fres == FR_OK) // 判断是否创建成功
{
printf("File open is OK\n");
}
fres = f_write(&fp, "ABCDEFG", 7, &fnum); // 写入数据
if(fres == FR_OK) // 判断是否写入成功
{
printf("File write is OK\n");
}
else // 写入失败
{
printf("%d\n", fres);
}
f_close(&fp); // 关闭文件
if(fres == FR_OK) // 判断是否关闭成功
{
printf("File close is OK\n");
}
else // 关闭失败
{
printf("%d\n", fres);
}
fres = f_unmount("1:"); // 卸载文件系统
fres = f_mount(&fs,"1:",1); // 重新挂载文件系统
fres = f_open(&fp, "1:ABC.txt", FA_OPEN_EXISTING | FA_READ); // 打开文件
if(fres == FR_OK) // 判断是否打开成功
{
printf("File open is OK\n");
}
else // 打开失败
{
printf("%d\n", fres);
}
fres = f_read(&fp, c, 7, &fnum); // 读取文件内容
if(fres == FR_OK) // 判断是否读取成功
{
printf("File read is OK\n");
printf("%s\n", c);
}
else // 读取失败
{
printf("%d\n", fres);
}
f_close(&fp); // 关闭文件
fres = f_unmount("1:"); // 卸载文件系统
if(fres == FR_OK) // 判断是否卸载成功
{
printf("unmount OK\n");
}
while (1)
{
delay_ms(500);
}
}
测试结果:

完整工程链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1YCRDXtLZMiMOpGDCTqMhLQ?pwd=ccvg
提取码: ccvg



















