Spring 异步@Async注解用法 Spring @Async注解用法总结 Spring @Async基本用法示例
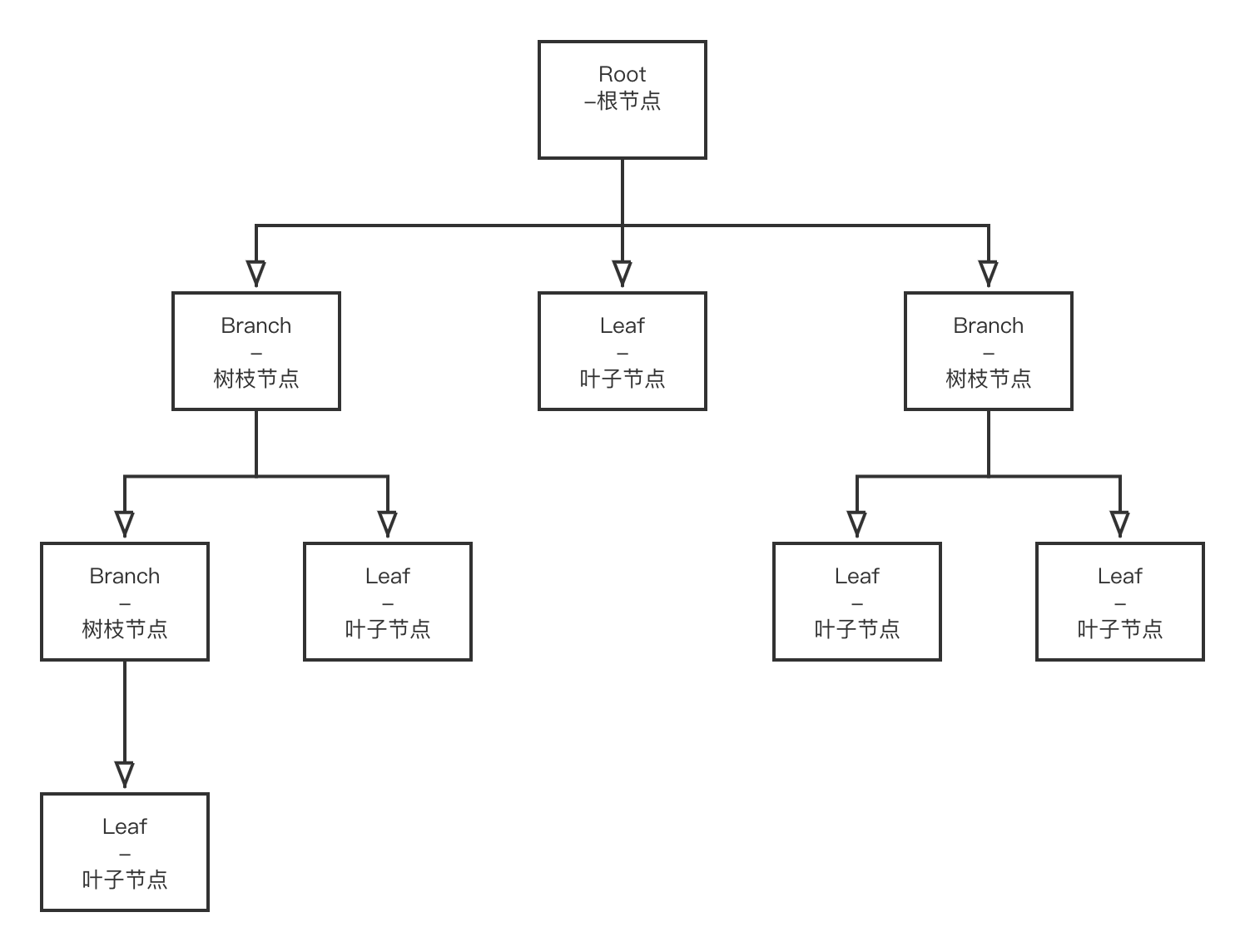
一、概述
在日常开发的工作中,经常会使用异步进行开发。Spring 提供一个简单的注解 @Async ,即可实现异步的开发,无需创建线程池,简单明了。 本文将整理 @Async 的常见用法,包括:基础入门,获取返回值,配置线程池,异常处理等。
@Async 注解实现原理,请自行查看源码,从:org.springframework.aop.interceptor.AsyncExecutionInterceptor 开始...
二、简单用法
1、Spring Boot 环境中,启动类上 使用 @EnableAsync , 即可启用 异步
2、在类上或方法上,使用 @Async 注解,标记该方法为异步,可以通过 打印线程池名称验证。
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootTouristApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTouristApplication.class, args);
}
@Lazy
@Autowired
private SpringBootTouristApplication application;
@Bean
ApplicationRunner run(){
ApplicationRunner run = (args)->{
application.sayHi();
};
return run;
}
@Async
public void sayHi(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=== async 异步");
}
}
2.1、上述代码输出结果
task-1=== async 异步3、@Async 注解,用在 类上,标记这个类方法都是异步的
@Service
@Async
public class MessageAsync {
public void sendMsg(long millis){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" sendMsg start ===");
try {
Thread.sleep(millis);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(MessageAsync.class.getName() + " sendMsg 方法运行中 。。。");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" sendMsg end ===");
}
/**
* @Description: 使用指定的线程池
* @return void
* @version v1.0
* @author wu
* @date 2022/9/13 22:39
*/
@Async("taskExecutor222")
public void sendMsg222(long millis){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" sendMsg222 start ===");
try {
Thread.sleep(millis);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(MessageAsync.class.getName() + " sendMsg222 方法运行中 。。。");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" sendMsg222 end ===");
}
}三、获取返回值
1、Spring 提供了统一的异步返回结果:AsyncResult ,需要注意的是:方法return的AsyncResult 对象,方法的返回需要用 Future 接收; 若使用 AsyncResult 作为返回值,会导致异常 :ClassCastException
org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.AsyncResult2、获取返回值,触发 ClassCastException
@Async
public AsyncResult<String> getResult(Long mill){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 携带返回值 AsyncResult FileAsync start ===");
try {
Thread.sleep(mill);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(FileAsync.class.getName() + " AsyncResult 方法运行中 。。。");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 携带返回值 AsyncResult FileAsync end ===");
String res = "AsyncResult 返回值,延迟"+mill+" ms";
return new AsyncResult<String>(res);
}3、正常获取返回值
@Async
public Future<String> getFuture(Long mill){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 携带返回值 Future FileAsync start ===");
try {
Thread.sleep(mill);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(FileAsync.class.getName() + " getFuture 方法运行中 。。。");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 方携带返回值 Future FileAsync end ===");
String res = "getFuture 返回值,延迟"+mill+" ms";
return new AsyncResult<String>(res);
}四、配置线程池
1、方法一:配置全局线程池
@Configuration
public class AsyncPoolConfig {
/**
* 核心线程数 (默认线程数)
*/
@Value("${pool.core-size:4}")
// @Value("${pool.core-size:1}")
private int corePoolSize;
/**
* 最大线程数
*/
@Value("${pool.max-size:8}")
// @Value("${pool.max-size:2}")
private int maxPoolSize;
/**
* 允许线程空闲时间 - 单位:秒
*/
@Value("${pool.keep-alive:60}")
private int keepAliveSeconds;
/**
* 缓冲队列数
*/
@Value("${pool.queue-capacity:5}")
private int queueCapacity;
/**
* 线程前缀名称
*/
@Value("${thread-name-prefix: @Async-线程池pool}")
private String threadNamePrefix;
//设置@Async的默认线程池
@Bean("taskExecutor")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
pool.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);//核心线程池数
pool.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize); // 最大线程数
pool.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);//队列容量,当核心线程数达到最大时,新任务会放在队列中排队等待执行
pool.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);//线程空闲时间
pool.setAllowCoreThreadTimeOut(false);//核心线程会一直存活,即使没有任务需要执行。(默认false)时,核心线程会超时关闭
pool.setThreadNamePrefix(threadNamePrefix);//线程前缀名称
// 线程池的拒绝策略 --- 继续执行
// pool.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// 线程池的拒绝策略 --- 抛出异常 (默认方式)
pool.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
// 初始化
// pool.initialize();
return pool;
}
}2、方法二:实现 AsyncConfigurer 接口 ,重写 getAsyncExecutor,配置指定线程池
@Configuration
public class AsyncConifg implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
// 配置指定的线程池
final ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
return executorService;
}
}3、当项目中有多个线程池时,可以通过 @Async 注解的 value属性,使用指定的线程池
// 使用 beanName为: taskExecutor222 线程池
@Async("taskExecutor222")
4、注意:方法一 和 方法二的 优先级问题, 没有进行测试。
五、异常处理
1、当异步执行的时候,遇到异常,该如何处理呢?
2、假设如下方法,执行出现异常:
@Async
public String exp(int a, String b){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ; exp start ===");
Object str = null ;
final boolean res = str.equals("");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ; exp end === res = "+res);
return "exp";
}2.1、输出结果如下:
task-2 ; exp start ===
[ERROR] org.springframework.aop.interceptor.SimpleAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler:39 : Unexpected exception occurred invoking async method: public java.lang.String com.runcode.springboottourist.async.ExpAsync.exp(int,java.lang.String)
java.lang.NullPointerException
...
2.2、注意:" task-2 ; exp end === res = " ,语句没有输出 ..
2.3、方法体内,增加 try-catch
@Async
public String expFix(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ; expFix start ===");
boolean res = false;
try {
Object str = null ;
res = str.equals("");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
/**
* try-catch 后:end 语句会正常输出.
*/
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ; expFix end === res = "+res);
return "expFix";
}3、全局异常处理,实现 AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler 接口,处理异常
@Configuration
public class AsyncExpConfig implements AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler {
@Override
public void handleUncaughtException(Throwable ex, Method method, Object... params) {
System.out.println("handleUncaughtException ===== start ======");
System.out.println("异常的方法是:"+ method);
System.out.println("exp detail info :"+ ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(ex));
System.out.println("参数 prams :"+ Arrays.toString(params));
System.out.println("handleUncaughtException ===== end ======");
}
}4、配置异常处理接口: 实现 AsyncConfigurer 接口 ,重写 getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler 方法
@Configuration
public class AsyncConifg implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Autowired
private AsyncExpConfig asyncExpConfig;
@Override
public AsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler getAsyncUncaughtExceptionHandler() {
return asyncExpConfig;
}
}5.1、 再次执行,上述代码,异常信息变成了:
task-2 ; exp start ===
handleUncaughtException ===== start ======
异常的方法是:public java.lang.String com.runcode.springboottourist.async.ExpAsync.exp(int,java.lang.String)
exp detail info :java.lang.NullPointerException
at com.runcode.springboottourist.async.ExpAsyn ...
参数 prams :[1, 22]
handleUncaughtException ===== end ====== 六、总结
1、本文相对详细的记录@Async 注解的常见用法,可以满足日常大部分的开发需求。
2、注意一点: 在同一个类中,是可以存在 异步方法和非异步方法的,要注意的是调用的方式 , 比如下面代码
@Service
public class AsyncTestService {
/**
* @Lazy : 解决循环依赖问题 circular reference
*/
@Lazy
@Autowired
private AsyncTestService asyncTestService;
public void sync(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ; sync method ..");
/**
* 该方法实际被 this.async(); 调用,this 没有被AOP代理增强,故 不会执行 @Async 异步方法
*/
async();
/**
* 该方法被 AOP增强后的方法调用,会执行 @Async 异步方法
*/
asyncTestService.async();
}
@Async
public void async() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" ; async 异步 method ..");
}
}2.1、输出结果如下:
main ; sync method ..
main ; async 异步 method ..
@Async-线程池pool2 ; async 异步 method ..
2.2、注意理解点: @Async是基于AOP实现的,普通的this调用,是没有被增强的,故而会导致方法调用无效; asyncTestService.async(); 方法调用,该类是AOP代理后增强 ... 可以通过 debug 观察 ...

参考资料:
Java 多线程 Runnable 与 Callable
@Lazy 注解作用
@Async 注解 实现原理 (没研究)

![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot企业人事管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7e54e9dfc48649b89645d3b12d0314bb.png)

![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计高校校园社交网络(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c6d9bdb5fd634ea183a7a710097e76dc.png)