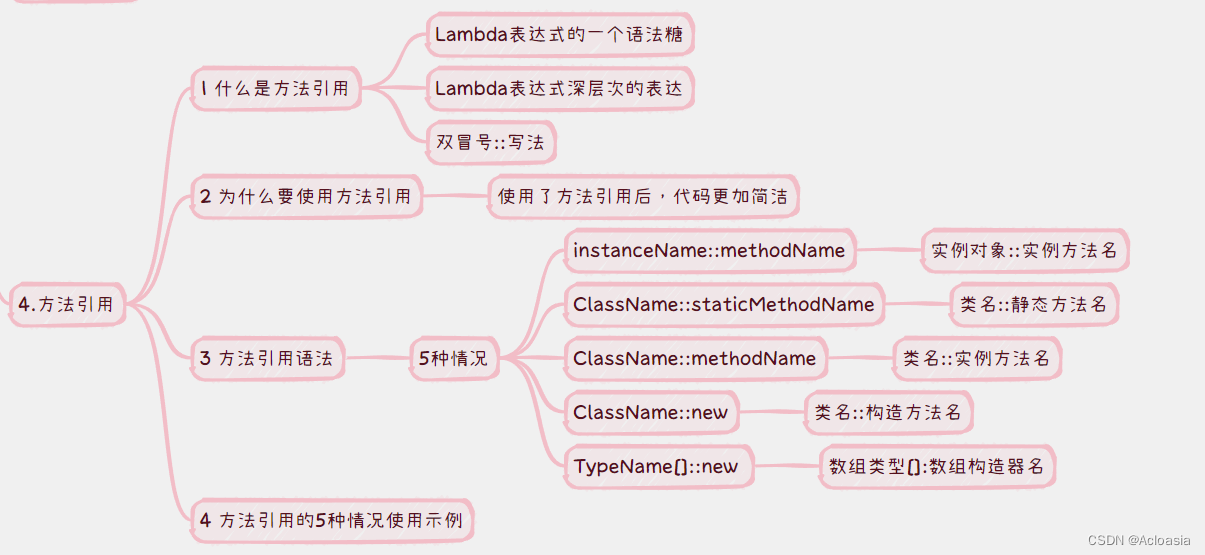
这个算法理解还是挺好理解的,就是到后面解决面积并问题的时候开始难理解了,看了半天,主要是还有其他的知识没理解就开始搞这个了。虽然最后还是直接懂了。
文章目录
- 扫描线算法的介绍
- 一维问题
- LintCode 391 数飞机
- 题目描述
- 解决
- letcode 218. 天际线问题
- 题目描述
- 题解
- 二维问题
- 洛谷 P5490 【模板】扫描线
- 题目描述
- 题目分析
扫描线算法的介绍
扫描线顾名思义也就是一条线进行扫描,一般从左到右,从下到上也是可以的。
算法适用于,前后时间的问题,一维区间重合的问题,然后还有最难的二维矩形面积重合问题。
总的来说就类似于需要一条线冲起来一样的。
一维问题
LintCode 391 数飞机
题目描述
给出飞机的起飞和降落时间的列表,用序列 interval 表示. 请计算出天上同时最多有多少架飞机?
样例
样例 1:
输入: [(1, 10), (2, 3), (5, 8), (4, 7)]
输出: 3
解释:
第一架飞机在1时刻起飞, 10时刻降落.
第二架飞机在2时刻起飞, 3时刻降落.
第三架飞机在5时刻起飞, 8时刻降落.
第四架飞机在4时刻起飞, 7时刻降落.
在5时刻到6时刻之间, 天空中有三架飞机.
样例 2:
输入: [(1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4)]
输出: 1
解释: 降落优先于起飞.
解决
以时间为线,扫描时刻。
我们可以以起飞设置为1.
落地设置为-1.
但是需要注意的是落地有优先权
public int countOfAirplanes(List<Interval> airplanes) {
// write your code here
int[][] arr = new int[airplanes.size() * 2][2];
for (int i = 0; i < airplanes.size(); i++) {
arr[2 * i] = new int[]{airplanes.get(i).start, 1};
arr[2 * i + 1] = new int[]{airplanes.get(i).end, -1};
}
Arrays.sort(arr, (o1, o2) -> o1[0] == o2[0] ? o1[1] - o2[1] : o1[0] - o2[0]);
int ans = 0,count = 0;
for (int[] ints : arr) {
if (ints[1] == 1)
count++;
else
count--;
ans = Math.max(ans,count);
}
return ans;
}
letcode 218. 天际线问题
题目描述

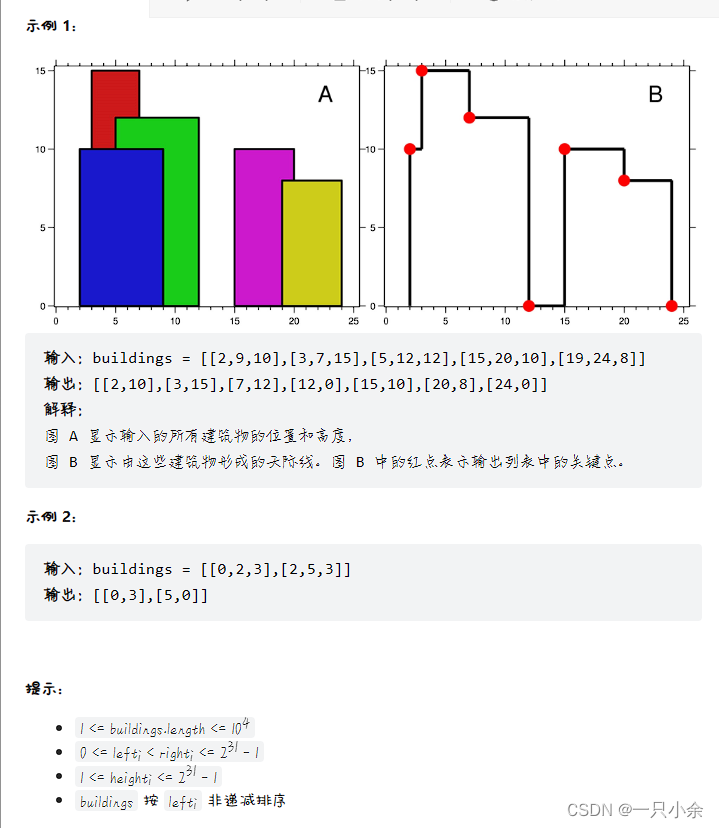
题解
这里提供的代码不是特别快。但是写起来舒服点。
还是老样子进行排序,然后入的高度设置为正,出设置为负。
我们每次只需要最高处的高度就可以了。所以用到pq。
pq的删除是一个线性
o
(
n
)
o(n)
o(n) 的删除,需要的时间比较长。
public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] buildings) {
ArrayList<Point> a = new ArrayList<>(buildings.length * 2 + 2);
for (int[] building : buildings) {
a.add(new Point(building[0], building[2]));
a.add(new Point(building[1], -building[2]));
}
a.sort((o1, o2) -> o1.x == o2.x ? o2.h - o1.h : o1.x - o2.x);
PriorityQueue<Integer> h = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparing(Integer::intValue).reversed());
h.add(0);
ArrayList<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int height = 0;
for (Point point : a) {
if (point.h > 0) {
h.offer(point.h);
} else {
h.remove(-point.h);
}
if (h.peek() != height) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(point.x, h.peek()));
}
height = h.peek();
}
return ans;
}
record Point(int x, int h) {}
二维问题
这个问题比较一维问题的难点就在于,除了对x的记录外,我们还需要y的记录。一维的最后一个题目上,y其实不需要记录下面,因为下一定是0.
而二维的矩阵上下y都需要记录,需要得到长度。
现在我们从一道模板题来分析
好像知道线段树会好理解,我搞完在去学。
洛谷 P5490 【模板】扫描线
题目描述
求
n
n
n 个四边平行于坐标轴的矩形的面积并。
输入格式
第一行一个正整数
n
n
n。
接下来 n n n 行每行四个非负整数 x 1 , y 1 , x 2 , y 2 x_1, y_1, x_2, y_2 x1,y1,x2,y2,表示一个矩形的四个端点坐标为 ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 1 , y 2 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) , ( x 2 , y 1 ) (x_1, y_1),(x_1, y_2),(x_2, y_2),(x_2, y_1) (x1,y1),(x1,y2),(x2,y2),(x2,y1)。
输出格式
一行一个正整数,表示 n n n 个矩形的并集覆盖的总面积。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
2
100 100 200 200
150 150 250 255
样例输出 #1
18000
提示
对于
20
%
20\%
20% 的数据,
1
≤
n
≤
1000
1 \le n \le 1000
1≤n≤1000。
对于
100
%
100\%
100% 的数据,
1
≤
n
≤
10
5
1 \le n \le {10}^5
1≤n≤105,
0
≤
x
1
<
x
2
≤
10
9
0 \le x_1 < x_2 \le {10}^9
0≤x1<x2≤109,
0
≤
y
1
<
y
2
≤
10
9
0 \le y_1 < y_2 \le {10}^9
0≤y1<y2≤109。
题目分析
这算是扫描线的一个经常算的题目了,计算矩形的面积。
对于下面这个图来说
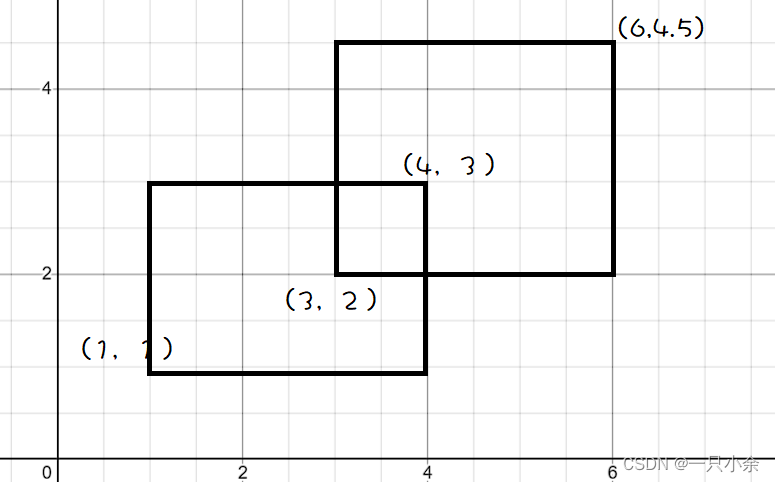
计算面积可以是
(
4
−
1
)
∗
(
3
−
1
)
+
(
6
−
3
)
∗
(
4.5
−
2
)
−
(
4
−
3
)
∗
(
3
−
2
)
(4-1)*(3-1)+(6-3)*(4.5-2) - (4-3)*(3-2)
(4−1)∗(3−1)+(6−3)∗(4.5−2)−(4−3)∗(3−2)
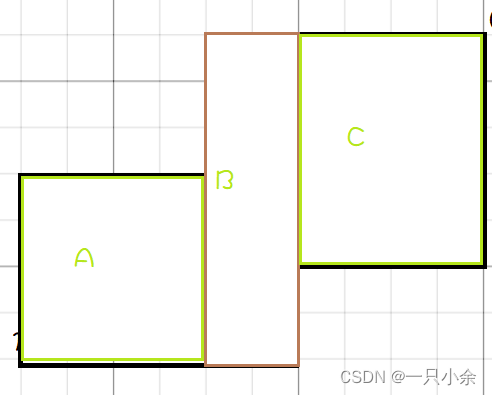
我们也可以拆分来计算
拆成abc3个部分来计算
面积就是
(
3
−
1
)
∗
(
3
−
1
)
+
(
4
−
3
)
∗
(
4.5
−
1
)
+
(
6
−
4
)
∗
(
4.5
−
2
)
(3-1)*(3-1)+(4-3)*(4.5-1)+(6-4)*(4.5-2)
(3−1)∗(3−1)+(4−3)∗(4.5−1)+(6−4)∗(4.5−2)
我们就可以像一维那样,从左到右,分为入边和出边来计算。
△
x
\triangle x
△x很好处理。但是高度就比较难处理了。
首先我想到的就是可以入边则加区间,出边则将区间减去。
每次都对区间来在进行一次区间计算高度。
但是这样复杂度比较高。
我们采取的是离散化来进行计算。
将y离散化,即下面这样的区间。
如果在区间则,入边则令所在区间+1,出边则-1
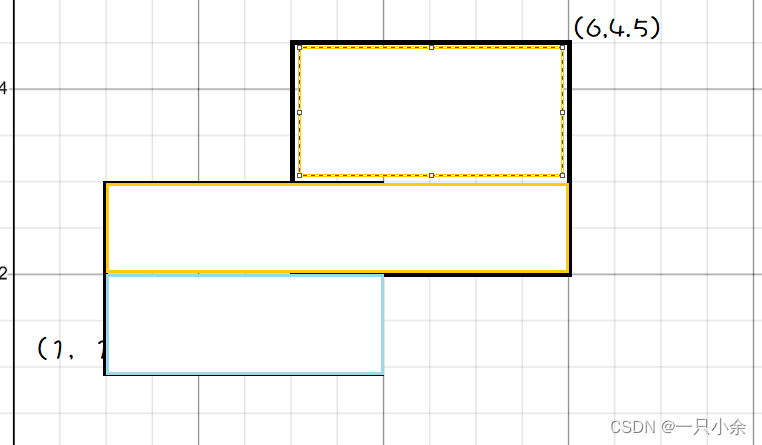
这个题的y离散后就是
[
1
,
2
,
3
,
4.5
]
[1,2,3,4.5]
[1,2,3,4.5]
进行模拟:
- 第一条入边为[1,3] 长度为2,宽度为2 s u m = 4 sum = 4 sum=4
- 第二条入边为[2,4] 长度为3.5 宽度为1 s u m = 7.5 sum = 7.5 sum=7.5
- 第三条出边为[1,3] 则剩下[3,4] 长度为2.5 宽度为2 s u m = 11.5 sum = 11.5 sum=11.5
接下来就是实现了:
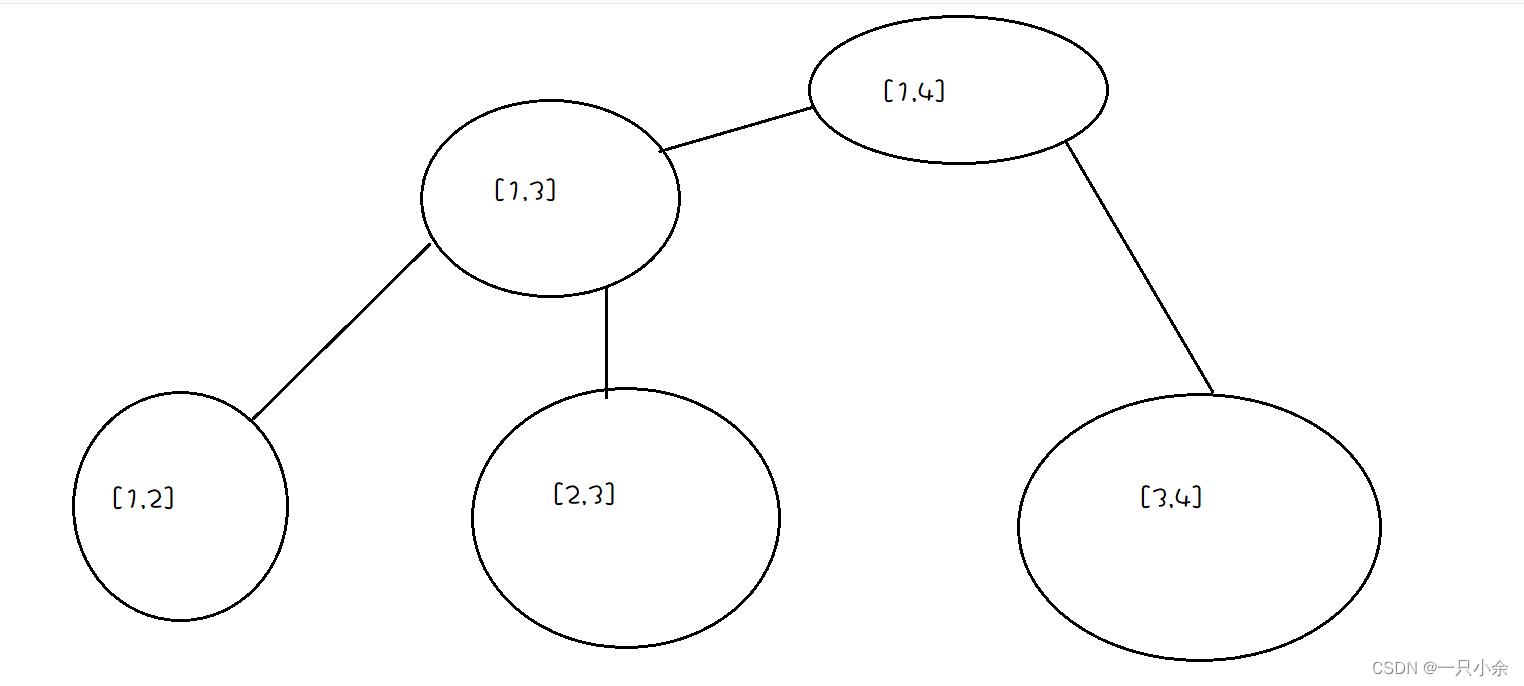
采用的是建树。
至于原因,我的理解是更快的求得长度。
如我想要获得
[
1
,
3
]
[1,3]
[1,3]就直接有想要
[
2
,
4
]
[2,4]
[2,4]就用
[
1
,
4
]
[1,4]
[1,4]减去
12
12
12
接下来就是代码了
先实现建树
树维护着
- 树的节点个数
- 访问的节点
- 每个节点对应的区间
- 区间所占用的长度
去重手写会更快,不过stream写的很爽。
本来还用set试试了,但是转化为Integer[]还行int[]太麻烦了。不如stream爽。
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.StreamTokenizer;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class test {
static final StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)));
public static int nextInt() throws IOException {
st.nextToken();
return (int) st.nval;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//初始化
int n = nextInt();
int size = n << 1;
Line[] lines = new Line[size + 1];
int[] yPos = new int[size];
// HashSet<Integer> yPos = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x1 = nextInt();
int y1 = nextInt();
int x2 = nextInt();
int y2 = nextInt();
int now = i << 1;
int next = now - 1;
lines[now] = new Line(y1, y2, x1, 1);
lines[next] = new Line(y1, y2, x2, -1);
yPos[now - 1] = y1;
yPos[next - 1] = y2;
}
// 离散化排序
yPos = Arrays.stream(yPos).distinct().sorted().toArray();
int len = yPos.length;
uniqueY = new int[len + 2];
System.arraycopy(yPos, 0, uniqueY, 1, len);
uniqueY[len + 1] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Arrays.sort(lines, 1, size + 1);
uniqueYCnt = len;
// duplicateRemoval(yPos, size);
// 线段树
SegmentTree tree = new SegmentTree(uniqueYCnt, uniqueY);
// 扫描线
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < size; i++) {
Line line = lines[i];
tree.update(line.y1, line.y2, line.weight);
ans += tree.getSum() * (lines[i + 1].x - line.x);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
//去重后的个数
static int uniqueYCnt;
//去重数组
static int[] uniqueY;
// 手写去重会更快
// static void duplicateRemoval(int[] arr, int len) {
// int[] array = Arrays.stream(arr).distinct().toArray();
// int last = uniqueY[1] = arr[1];
// uniqueYCnt = 1;
// for (int i = 2; i <= len; i++) {
// if (arr[i] == last)
// continue;
// last = uniqueY[++uniqueYCnt] = arr[i];
// }
// uniqueY[uniqueYCnt + 1] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// }
static class Line implements Comparable<Line> {
int y1;
int y2;
int x;
int weight;
public Line(int y1, int y2, int x, int weight) {
this.y1 = y1;
this.y2 = y2;
this.x = x;
this.weight = weight;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Line o) {
return x - o.x;
}
}
}
class SegmentTree {
private final long[] tree;// 线段树
private final int size;// 离散化后的长度
private final int[] mapping;// 离散化
private final int[] visitCount;// 访问次数
// 初始化
public SegmentTree(int size, int[] mapping) {
this.size = size;
this.mapping = mapping;
this.tree = new long[size * 10 + 1];
this.visitCount = new int[size * 10 + 1];
}
// 获取区间左边
private int updateL;
// 获取区间右边
private int updateR;
/**
* 获取区间和
*
* @param l 区间左边
* @param r 区间右边
* @param value 访问更新值 1 为访问 -1 为取消访问
*/
public void update(int l, int r, int value) {
updateL = l;
updateR = r;
getUpdate(1, size, 1, value);
}
/**
* 更新
*
* @param currentL 当前区间左边
* @param currentR 当前区间右边
* @param pos 当前节点
* @param value 访问更新值 1 为访问 -1 为取消访问
*/
private void getUpdate(int currentL, int currentR, int pos, int value) {
int leftValueMapping = mapping[currentL];
int rightValueMapping = mapping[currentR + 1];
// 不相交
if (rightValueMapping <= updateL || leftValueMapping >= updateR) {
return;
}
// 完全覆盖
if (updateL <= leftValueMapping && rightValueMapping <= updateR) {
visitCount[pos] += value;
} else {
// 递归子节点
int mid = (currentL + currentR) >> 1;
// 左子节点
getUpdate(currentL, mid, pos << 1, value);
// 右子节点
getUpdate(mid + 1, currentR, pos << 1 | 1, value);
}
if (visitCount[pos] > 0) {
// 访问次数大于0,说明这个区间被访问过
// 那么这个区间的值就是区间长度
tree[pos] = rightValueMapping - leftValueMapping;
} else {
int temp = pos << 1;
// 没有访问=子节点相加
tree[pos] = tree[temp] + tree[temp | 1];
}
}
// 获取区间和
public long getSum() {
return tree[1];
}
}