《力扣》138.复制带随机指针的链表
给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝。 深拷贝应该正好由 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random 指针也都应指向复制链表中的新节点,并使原链表和复制链表中的这些指针能够表示相同的链表状态。复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有 x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。
random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
解题思路
总结:题目叫我们深度拷贝链表,链表里包含一个随机生成的指针random,指向链表内其他结点,深度拷贝的过程中,新链表要还原随机生成的指针在原链表中指向的对应位置(新链表指向新链表对应的位置)
本题如果没有随即指针random会变得非常简单,难点在random的拷贝
(第一步)
- 我们可以将新链表插入到原链表中,新的第一个结点放在原链表的第一个结点后,新的第二个结点放在原的第二个结点后….(以此类推)
插入前
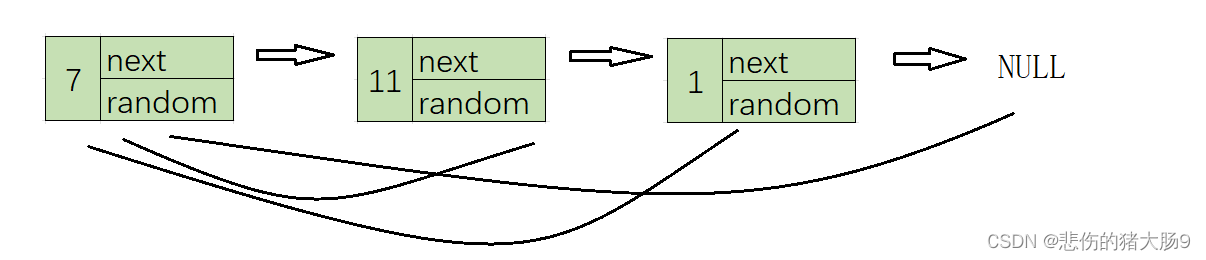
插入后

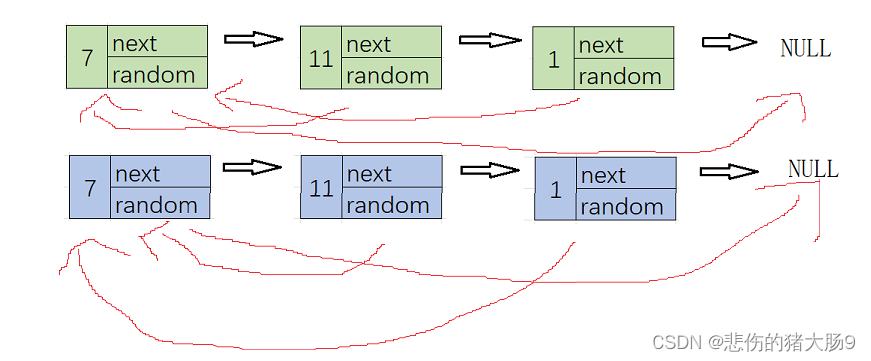
(第二步)由上图中可以了解到
- 原结点1的random指针指向原结点3,新结点1的random指针指向的是原结点3的next
- 原结点3的random指针指向原结点2,新结点3的random指针指向的是原结点2的next
(第三步)
- 将链表分开,并返回新的链表即可
代码实现⭐
优解
struct Node* BuyNode(int x) //创建新结点,初始化变量。
{
struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if(temp==NULL)
{
perror("malloc:");
}
struct Node* NewNode = temp;
NewNode->next = NULL;
NewNode->val = x;
NewNode->random = NULL;
return NewNode;
}
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
struct Node* cur = head;
struct Node* rethead = NULL;
struct Node* rettail = NULL;
while(cur) //将新链表插入到原链表中
{
struct Node* next = cur->next;
cur->next = BuyNode(cur->val);
cur->next->next = next;
cur = next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur) //将random进行对应的赋值
{
if(cur->random==NULL)
{
cur->next->random=NULL;
}
else
{
cur->next->random = cur->random->next;
}
cur = cur->next->next;
}
cur = head;
while(cur) //将链表分开
{
if(rettail==NULL)
{
rethead = rettail = cur->next;
}
else
{
rettail->next = cur->next;
rettail = rettail->next;
}
cur = cur->next->next;
}
return rethead;
}
暴力破解
就是每次都从头遍历记录random是原链表的第几个,然后遍历相同位数在新链表上。
struct Node* BuyNode(int x)
{
struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if(temp==NULL)
{
perror("malloc:");
}
struct Node* NewNode = temp;
NewNode->next = NULL;
NewNode->val = x;
NewNode->random = NULL;
return NewNode;
}
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
struct Node* Newhead = NULL;
struct Node* Newtail = NULL;
struct Node* phead = head;
while(phead)
{
if(Newtail==NULL)
{
Newtail = Newhead = BuyNode(phead->val);
}
else
{
Newtail->next = BuyNode(phead->val);
Newtail = Newtail->next;
}
phead = phead->next;
}
phead = head;
int count;
struct Node* newhead = Newhead;
while(phead)
{
count = 0;
struct Node* temp = phead->random;
if(temp==NULL)
{
newhead->random = NULL;
newhead = newhead->next;
phead = phead->next;
continue;
}
struct Node* cur = head;
while(cur)
{
if(temp!=cur)
{
cur = cur->next;
count++;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
cur = Newhead;
while(count--)
{
cur = cur->next;
}
newhead->random = cur;
newhead = newhead->next;
phead = phead->next;
}
return Newhead;
}
完结
创作不易,还请各位小伙伴多多点赞👍关注收藏⭐
![[羊城杯 2020]a_piece_of_java](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/414ba59cca7745009fd7bd1a645da217.png)
![win10安装pytorch全网最好用的教程[2023.5.7更新]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ecc0dfdbcece411d962218390663315e.png)