---- 整理自狄泰软件唐佐林老师课程
1. 类型识别
在面向对象中可能出现下面的情况:
- 基类指针指向子类对象
- 基类引用成为子类对象的别名
这个时候就会出现问题:(由于 赋值兼容性原则 )没法通过一个父类指针判断指向的是父类对象还是子类对象
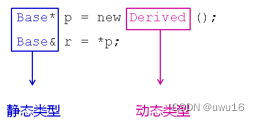
- 静态类型:变量(对象)自身的类型
- 动态类型:指针(引用)所指向对象的实际类型

基类指针是否可以强制类型转换为子类指针取决于动态类型
1.1 问题
C++中如何得到 动态类型 ?
1.2 解决方案:利用 多态
- 在基类中定义虚函数返回具体的类型信息
- 所有的派生类都必须实现类型相关的虚函数
- 每个类中的类型虚函数都需要不同的实现
1.3 编程实验:动态类型识别
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
virtual string type()
{
return "Base";
}
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
string type()
{
return "Derived";
}
void printf()
{
cout << "I'm a Derived." << endl;
}
};
class Child : public Base
{
public:
string type()
{
return "Child";
}
};
void test(Base* b)
{
/* 危险的转换方式 */
// Derived* d = static_cast<Derived*>(b);
if( b->type() == "Derived" )
{
Derived* d = static_cast<Derived*>(b);
d->printf();
}
// cout << dynamic_cast<Derived*>(b) << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
Base b;
Derived d;
Child c;
test(&b);
test(&d);
test(&c);
return 0;
}
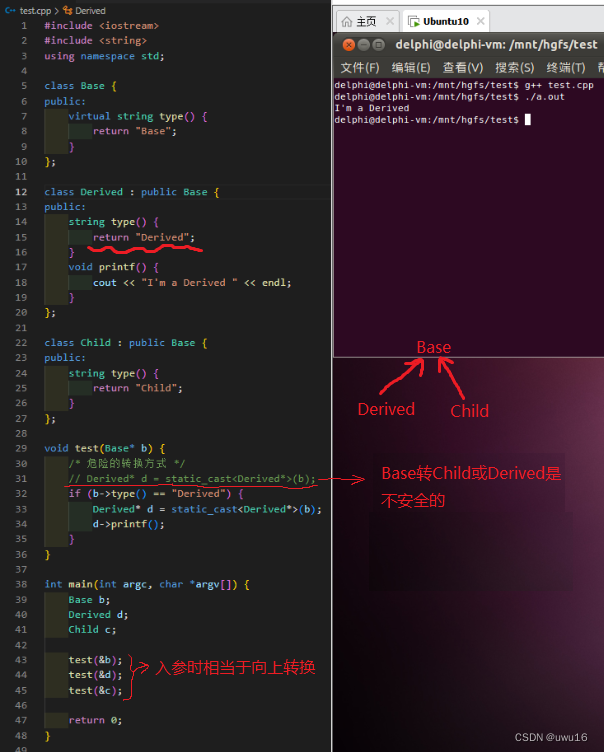
向上/向下转换可参看 55 - 经典问题解析四(动态内存分配&虚函数&继承中的强制类型转换)
1.4 多态解决方案的缺陷
- 必须从基类开始提供类型虚函数
- 所有的派生类都必须重写类型虚函数
- 每个派生类的类型名必须唯一
1.5 类型识别关键字
- C++提供了 typeid关键字 用于获取类型信息
- typeid关键字 返回对应参数的 类型信息
- typeid返回一个type_info类对象
- 当typeid的参数为NULL时将抛出异常
1.5.1 typeid关键字的使用
int i = 0;
const type_info& tiv = typeid(i);
const type_info& tii = typeid(int);
cout << (tiv == tii) << endl;
1.5.2 typeid的注意事项
- 当参数为 类型 时:返回静态类型信息
- 当参数为 变量 时:
- 不存在虚函数表 – 返回静态类型信息
- 存在虚函数表 – 返回动态类型信息
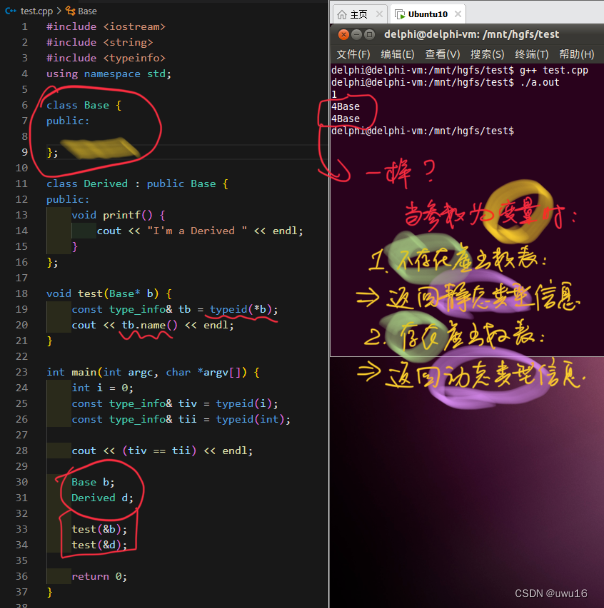
1.5.3 编程实验:typeid类型识别
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
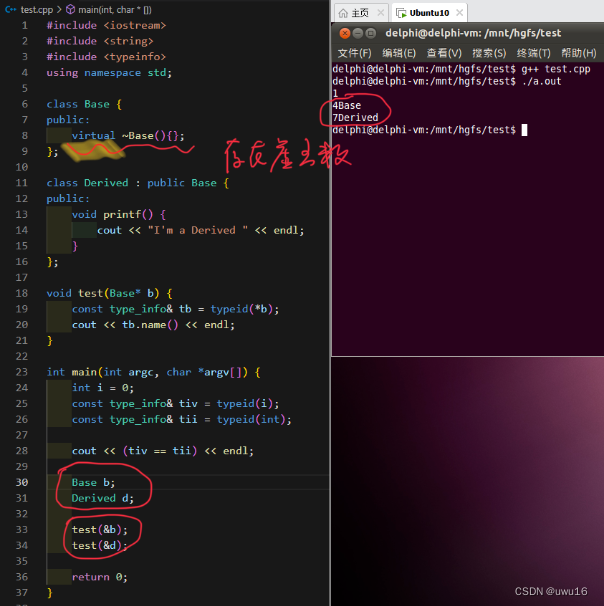
virtual ~Base()
{
}
};
class Derived : public Base
{
public:
void printf()
{
cout << "I'm a Derived." << endl;
}
};
void test(Base* b)
{
const type_info& tb = typeid(*b);
cout << tb.name() << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i = 0;
const type_info& tiv = typeid(i);
const type_info& tii = typeid(int);
cout << (tiv == tii) << endl;
Base b;
Derived d;
test(&b);
test(&d);
return 0;
}
2. 小结
- C++中有静态类型和动态类型的概念
- 利用多态能够实现对象的动态类型识别
- typeid是专用于 类型识别 的关键字
- typeid能够返回对象的动态类型信息




![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot基于Web的绿色环保网站](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e9dff6394d3f44e2a5bdbe541b45791d.png)

![[附源码]计算机毕业设计JAVA小型医院药品及门诊管理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d58f2445c9774006b40ec72620c662ef.png)