[C++ 基于Eigen库实现CRN前向推理]
第三部分:TransposedConv2d实现 (含dilation)
- 前言:(Eigen库使用记录)
- 第一部分:WavFile.class (实现读取wav/pcm,实现STFT)
- 第二部分:Conv2d实现
- 第三部分:TransposedConv2d实现 (mimo,padding,stride,dilation,kernel,outpadding)
- 第四部分:NonLinearity (Sigmoid,Tanh,ReLU,ELU,Softplus)
- 第五部分:LSTM
- GITHUB仓库
1. LSTM介绍
1.1 pytorch LSTM介绍
Lstm是RNN网络中最有趣的结构之一,不仅仅使得模型可以从长序列中学习,还创建了长短期记忆模块,模块中所记忆的数值在需要时可以得到更改。
-
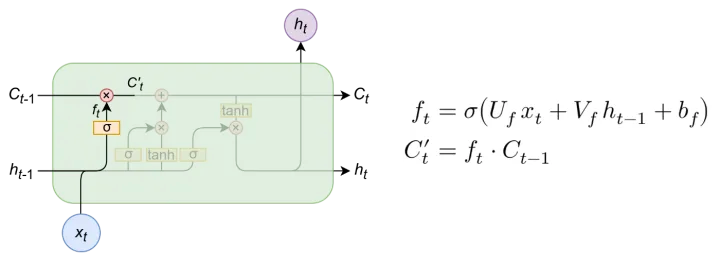
遗忘门
遗忘单元可以将输入信息和隐藏信息进行信息整合,并进行信息更替,更替步骤如右图公式,其中与乘上权重矩阵后,加上偏置项后,经过激活函数,此时输出值为位于[0,1]之间,并将上一个时间步的与激活函数输出值相乘,更新为
-
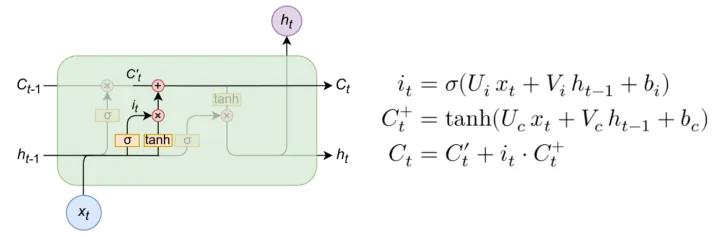
输入门
当有输入进入时,输入门会结合输入信息与隐藏信息进行整合,并对信息进行更替
过程与 过程类似,中间公式使用了tanh函数,可以将输出缩放到[-1,1]之间,再更新
-
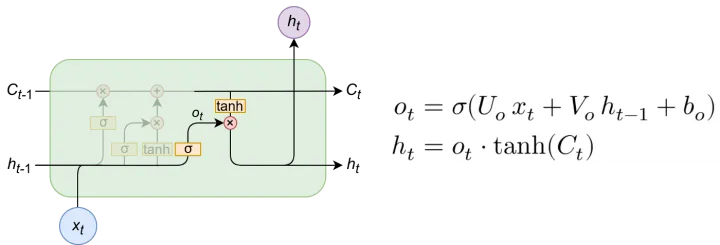
输出门
输出门也会对输出过程进行控制,与输入门不同的是,输出门使用tannh激活函数
1.2 LSTM递推公式
pytorch的lstm递推公式如下图所示。
在pytorch中,4个权重矩阵Wii,Wif,Wig,Wio被合并为一个权重矩阵Wih,Whh也类似,方便一步计算。

1.3 python实现手动lstm
可以根据公式简单的写出手动实现的版本
这是一个两层的lstm,w和b都写死了,就是固定两层的参数。hidden为1024.
def test_lstm(input, wih0, bih0, whh0, bhh0, wih1, bih1, whh1, bhh1):
# 手动模拟
B, T, F = input.shape
hidden_size = 1024
inp_pointer = input
for layer in range(2):
h_t, c_t = (torch.zeros(B, hidden_size).cuda(), torch.zeros(B, hidden_size).cuda())
output = torch.zeros(B, T, hidden_size).cuda()
batch, time, freq = output.shape
if layer == 0:
cur_w_ih = wih0
cur_w_hh = whh0
cur_b_ih = bih0
cur_b_hh = bhh0
else:
cur_w_ih = wih1
cur_w_hh = whh1
cur_b_ih = bih1
cur_b_hh = bhh1
for t in range(time):
x_t = inp_pointer[:, t, :]
gates = x_t @ cur_w_ih.T + cur_b_ih + h_t @ cur_w_hh.T + cur_b_hh
i_t, f_t, g_t, o_t = (
torch.sigmoid(gates[:, :hidden_size]), # input
torch.sigmoid(gates[:, hidden_size:hidden_size * 2]), # forget
torch.tanh(gates[:, hidden_size * 2:hidden_size * 3]),
torch.sigmoid(gates[:, hidden_size * 3:]), # output
)
c_t = f_t * c_t + i_t * g_t
h_t = o_t * torch.tanh(c_t)
output[:, t, :] = h_t
inp_pointer = output
return inp_pointer
另外,还实现了一个双向LSTM的版本,用了一个小样本进行测试,同样参数都是写死了。
def test_lstm():
input_size = 4
hidden_size = 6
num_layer = 2
bidirectional = True
direction = 2 if bidirectional else 1
input = torch.Tensor([[[[0.896227, 0.713551],
[0.605188, 0.0700275],
[0.827175, 0.186436]],
[[0.872269, 0.032015],
[0.259925, 0.517878],
[0.224867, 0.943635]]],
[[[0.290171, 0.0767354],
[0.251816, 0.31538],
[0.828251, 0.730255]],
[[0.24641, 0.757985],
[0.354927, 0.694123],
[0.990138, 0.946459]]]]).float().transpose(1, 2).reshape(2, 3, 4)
B, T, F = input.shape
lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=input_size, hidden_size=hidden_size, num_layers=num_layer, batch_first=True,
bidirectional=bidirectional)
state = OrderedDict()
state['weight_ih_l0'] = torch.ones([4 * hidden_size, input_size])
state['weight_hh_l0'] = torch.ones([4 * hidden_size, hidden_size]) * 2
state['bias_ih_l0'] = torch.zeros(4 * hidden_size) + 0.5
state['bias_hh_l0'] = torch.zeros(4 * hidden_size) + 1.0
state['weight_ih_l1'] = torch.ones([4 * hidden_size, hidden_size * direction]) * 2
state['weight_hh_l1'] = torch.ones([4 * hidden_size, hidden_size]) * 3
state['bias_ih_l1'] = torch.zeros(4 * hidden_size) + 0.5
state['bias_hh_l1'] = torch.zeros(4 * hidden_size) + 1.0
state['weight_ih_l0_reverse'] = torch.ones([4 * hidden_size, input_size])
state['weight_hh_l0_reverse'] = torch.ones([4 * hidden_size, hidden_size]) * 2
state['bias_ih_l0_reverse'] = torch.zeros(4 * hidden_size) + 0.5
state['bias_hh_l0_reverse'] = torch.zeros(4 * hidden_size) + 1.0
state['weight_ih_l1_reverse'] = torch.ones([4 * hidden_size, hidden_size * direction]) * 2
state['weight_hh_l1_reverse'] = torch.ones([4 * hidden_size, hidden_size]) * 3
state['bias_ih_l1_reverse'] = torch.zeros(4 * hidden_size) + 0.5
state['bias_hh_l1_reverse'] = torch.zeros(4 * hidden_size) + 1.0
lstm.load_state_dict(state, strict=False)
# 手动模拟
inp_pointer = input
for layer in range(num_layer):
h_t, c_t = (torch.zeros(B, hidden_size), torch.zeros(B, hidden_size))
h_t_reverse, c_t_reverse = (torch.zeros(B, hidden_size), torch.zeros(B, hidden_size))
output = torch.zeros(B, T, hidden_size)
output_reverse = torch.zeros(B, T, hidden_size)
batch, time, freq = output.shape
cur_w_ih = state['weight_ih_l{}'.format(layer)]
cur_w_ih_reverse = state['weight_ih_l{}_reverse'.format(layer)]
cur_w_hh = state['weight_hh_l{}'.format(layer)]
cur_w_hh_reverse = state['weight_hh_l{}_reverse'.format(layer)]
cur_b_ih = state['bias_ih_l{}'.format(layer)]
cur_b_ih_reverse = state['bias_ih_l{}_reverse'.format(layer)]
cur_b_hh = state['bias_hh_l{}'.format(layer)]
cur_b_hh_reverse = state['bias_hh_l{}_reverse'.format(layer)]
for t in range(time):
x_t = inp_pointer[:, t, :]
r_t = inp_pointer[:, time - t - 1, :]
gates = x_t @ cur_w_ih.T + cur_b_ih + h_t @ cur_w_hh.T + cur_b_hh
gates_r = r_t @ cur_w_ih_reverse.T + cur_b_ih_reverse + h_t_reverse @ cur_w_hh_reverse.T + cur_b_hh_reverse
i_t, f_t, g_t, o_t = (
torch.sigmoid(gates[:, :hidden_size]), # input
torch.sigmoid(gates[:, hidden_size:hidden_size * 2]), # forget
torch.tanh(gates[:, hidden_size * 2:hidden_size * 3]),
torch.sigmoid(gates[:, hidden_size * 3:]), # output
)
i_r, f_r, g_r, o_r = (
torch.sigmoid(gates_r[:, :hidden_size]), # input
torch.sigmoid(gates_r[:, hidden_size:hidden_size * 2]), # forget
torch.tanh(gates_r[:, hidden_size * 2:hidden_size * 3]),
torch.sigmoid(gates_r[:, hidden_size * 3:]), # output
)
c_t = f_t * c_t + i_t * g_t
c_t_reverse = f_r * c_t_reverse + i_r * g_r
h_t = o_t * torch.tanh(c_t)
h_t_reverse = o_r * torch.tanh(c_t_reverse)
output[:, t, :] = h_t
output_reverse[:, time - t - 1, :] = h_t_reverse
inp_pointer = torch.cat([output, output_reverse], dim=2)
print(inp_pointer.view(2, 3, 2, -1).transpose(1, 2))
th_out, (h, c) = lstm(input)
print(th_out)
2. 基于Eigen实现C++ 的LSTM推理
2.1 Layer_LSTM.h
//
// Created by 65181 on 2022/10/31.
//
#ifndef CRN_LAYER_LSTM_H
#define CRN_LAYER_LSTM_H
#include "Eigen"
#include "mat.h"
#include "Eigen/CXX11/Tensor"
class Layer_LSTM {
public:
Layer_LSTM();
Layer_LSTM(int64_t inp_size, int64_t hid_size, int64_t num_layer = 2, bool bidirectional = false);
void LoadState(MATFile *pmFile, const std::string &state_preffix);
void LoadTestState();
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> forward(Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> &input, std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &h_t,
std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &c_t);
private:
int64_t input_size;
int64_t hidden_size;
int64_t num_layers;
int64_t direction;
bool bidirectional;
std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> weight_ih, weight_hh;
std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> weight_ih_reverse, weight_hh_reverse;
std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> bias_ih, bias_hh;
std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> bias_ih_reverse, bias_hh_reverse;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> _load_mat(MATFile *pmFile, const std::string &state_name);
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> _uni_lstm(Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> &input, std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &h_t,
std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &c_t);
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> _bi_lstm(Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> &input, std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &h_t,
std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &c_t);
void print2(Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> input);
void print3(Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> input);
};
#endif //CRN_LAYER_LSTM_H
2.2 Layer_LSTM.cpp
//
// Created by 65181 on 2022/10/31.
//
#include "iostream"
#include "../include/Layer_LSTM.h"
using namespace std;
Layer_LSTM::Layer_LSTM() {
this->input_size = 64;
this->hidden_size = 64;
this->num_layers = 2;
this->direction = 1;
}
Layer_LSTM::Layer_LSTM(int64_t inp_size, int64_t hid_size, int64_t num_layer, bool bidirectional) {
this->input_size = inp_size;
this->hidden_size = hid_size;
this->num_layers = num_layer;
this->bidirectional = bidirectional;
this->direction = bidirectional ? 2 : 1;
}
void Layer_LSTM::LoadState(MATFile *pmFile, const std::string &state_preffix) {
for (int layer_idx = 0; layer_idx < this->num_layers; layer_idx++) {
std::string weight_ih_name = state_preffix + "_weight_ih_l" + std::to_string(layer_idx);
std::string bias_ih_name = state_preffix + "_bias_ih_l" + std::to_string(layer_idx);
std::string weight_hh_name = state_preffix + "_weight_hh_l" + std::to_string(layer_idx);
std::string bias_hh_name = state_preffix + "_bias_hh_l" + std::to_string(layer_idx);
this->weight_ih.push_back(_load_mat(pmFile, weight_ih_name));
this->bias_ih.push_back(_load_mat(pmFile, bias_ih_name));
this->weight_hh.push_back(_load_mat(pmFile, weight_hh_name));
this->bias_hh.push_back(_load_mat(pmFile, bias_hh_name));
if (this->bidirectional) {
std::string w_ih_reverse = state_preffix + "_weight_ih_l" + std::to_string(layer_idx) + "_reverse";
std::string b_ih_reverse = state_preffix + "_bias_ih_l" + std::to_string(layer_idx) + "_reverse";
std::string w_hh_reverse = state_preffix + "_weight_hh_l" + std::to_string(layer_idx) + "_reverse";
std::string b_hh_reverse = state_preffix + "_bias_hh_l" + std::to_string(layer_idx) + "_reverse";
this->weight_ih_reverse.push_back(_load_mat(pmFile, w_ih_reverse));
this->bias_ih_reverse.push_back(_load_mat(pmFile, b_ih_reverse));
this->weight_hh_reverse.push_back(_load_mat(pmFile, w_hh_reverse));
this->bias_hh_reverse.push_back(_load_mat(pmFile, b_hh_reverse));
}
}
}
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> Layer_LSTM::_load_mat(MATFile *pmFile, const std::string &state_name) {
mxArray *pa = matGetVariable(pmFile, state_name.c_str());
auto *values = (float_t *) mxGetData(pa);
long long dim1 = mxGetM(pa);
long long dim2 = mxGetN(pa);
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> matrix(dim1, dim2);
int idx = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dim2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < dim1; j++) {
matrix(j, i) = values[idx++];
}
}
return matrix;
}
void Layer_LSTM::LoadTestState() {
for (int layer = 0; layer < this->num_layers; layer++) {
int64_t _ih_DIM = layer == 0 ? this->input_size : this->hidden_size * this->direction;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> state_w_ih(this->hidden_size * 4, _ih_DIM);
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> state_w_hh(this->hidden_size * 4, this->hidden_size);
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> state_b_ih(1, this->hidden_size * 4);
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> state_b_hh(1, this->hidden_size * 4);
state_w_ih.setConstant(2);
state_w_hh.setConstant(2);
state_b_ih.setConstant(1.0);
state_b_hh.setConstant(1.0);
this->weight_ih.push_back(state_w_ih);
this->weight_hh.push_back(state_w_hh);
this->bias_ih.push_back(state_b_ih);
this->bias_hh.push_back(state_b_hh);
// Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> state_w_ih_reverse(this->hidden_size * 4, _ih_DIM);
// Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> state_w_hh_reverse(this->hidden_size * 4, this->hidden_size);
// Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> state_b_ih_reverse(1, this->hidden_size * 4);
// Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> state_b_hh_reverse(1, this->hidden_size * 4);
// state_w_ih_reverse.setConstant(layer + 1);
// state_w_hh_reverse.setConstant(layer + 2);
// state_b_ih_reverse.setConstant(0.5);
// state_b_hh_reverse.setConstant(1.0);
// this->weight_ih_reverse.push_back(state_w_ih_reverse);
// this->weight_hh_reverse.push_back(state_w_hh_reverse);
// this->bias_ih_reverse.push_back(state_b_ih_reverse);
// this->bias_hh_reverse.push_back(state_b_hh_reverse);
}
}
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> Layer_LSTM::forward(Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> &input,
std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &h_t,
std::vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &c_t) {
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> output;
if (this->bidirectional) {
output = this->_bi_lstm(input, h_t, c_t);
} else {
output = this->_uni_lstm(input, h_t, c_t);
}
return output;
}
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> Layer_LSTM::_uni_lstm(Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> &input,
vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &h_t,
vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &c_t) {
Eigen::Tensor<size_t, 3>::Dimensions dim_inp = input.dimensions();
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> out_pointer = input;
if (h_t.empty() || c_t.empty()) {
for (int idx_layer = 0; idx_layer < this->num_layers; idx_layer++) {
Eigen::Tensor<float, 2> ht_zeros(dim_inp[0], this->hidden_size);
Eigen::Tensor<float, 2> ct_zeros(dim_inp[0], this->hidden_size);
ht_zeros.setZero();
ct_zeros.setZero();
h_t.push_back(ht_zeros);
c_t.push_back(ct_zeros);
}
}
for (int idx_layer = 0; idx_layer < this->num_layers; idx_layer++) {
Eigen::Tensor<size_t, 3>::Dimensions dim_cur = out_pointer.dimensions();
int64_t N_BATCH = dim_cur[0], N_TIME = dim_cur[1], N_FREQ = dim_cur[2], N_HIDDEN = this->hidden_size;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_w_ih = this->weight_ih[idx_layer];
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_w_hh = this->weight_hh[idx_layer];
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_b_ih = this->bias_ih[idx_layer].broadcast(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{N_BATCH, 1});
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_b_hh = this->bias_hh[idx_layer].broadcast(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{N_BATCH, 1});
Eigen::Tensor<float, 2> &cur_ht = h_t[idx_layer];
Eigen::Tensor<float, 2> &cur_ct = c_t[idx_layer];
// print2(cur_w_ih);
// print2(cur_w_hh);
// print2(cur_b_ih);
// print2(cur_b_hh);
// print2(cur_ht);
// print2(cur_ct);
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> output(N_BATCH, N_TIME, N_HIDDEN);
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> X_t;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> gates;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> i_t, f_t, g_t, o_t;
Eigen::array<Eigen::IndexPair<int>, 1> product_dims = {Eigen::IndexPair<int>(1, 1)};
Eigen::array<int64_t, 2> gate_patch = Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{N_BATCH, N_HIDDEN};
for (int t = 0; t < N_TIME; t++) {
X_t = out_pointer.chip(t, 1);
// print2(X_t);
// print2(X_t.contract(cur_w_ih, product_dims) + cur_b_ih);
// print2(cur_ht.contract(cur_w_hh, product_dims) + cur_b_hh);
gates = X_t.contract(cur_w_ih, product_dims) + cur_b_ih + cur_ht.contract(cur_w_hh, product_dims) +
cur_b_hh;
// print2(gates);
i_t = gates.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 0}, gate_patch).sigmoid();
f_t = gates.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 1}, gate_patch).sigmoid();
g_t = gates.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 2}, gate_patch).tanh();
o_t = gates.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 3}, gate_patch).sigmoid();
// print2(i_t);
// print2(f_t);
// print2(g_t);
// print2(o_t);
cur_ct = f_t * cur_ct + i_t * g_t;
cur_ht = o_t * cur_ct.tanh();
// print2(cur_ct);
// print2(cur_ht);
output.chip(t, 1) = cur_ht;
}
out_pointer = output;
}
return out_pointer;
}
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> Layer_LSTM::_bi_lstm(Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> &input,
vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &h_t,
vector<Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2>> &c_t) {
Eigen::Tensor<size_t, 3>::Dimensions dim_inp = input.dimensions();
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> out_pointer = input;
if (h_t.empty() || c_t.empty()) {
for (int idx_layer = 0; idx_layer < this->num_layers * this->direction; idx_layer++) {
Eigen::Tensor<float, 2> ht_zeros(dim_inp[0], this->hidden_size);
Eigen::Tensor<float, 2> ct_zeros(dim_inp[0], this->hidden_size);
ht_zeros.setZero();
ct_zeros.setZero();
h_t.push_back(ht_zeros);
c_t.push_back(ct_zeros);
}
}
for (int idx_layer = 0; idx_layer < this->num_layers; idx_layer++) {
Eigen::Tensor<size_t, 3>::Dimensions dim_cur = out_pointer.dimensions();
int64_t N_BATCH = dim_cur[0], N_TIME = dim_cur[1], N_FREQ = dim_cur[2], N_HIDDEN = this->hidden_size;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_w_ih = this->weight_ih[idx_layer];
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_w_ih_reverse = this->weight_ih_reverse[idx_layer];
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_w_hh = this->weight_hh[idx_layer];
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_w_hh_reverse = this->weight_hh_reverse[idx_layer];
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_b_ih = this->bias_ih[idx_layer].broadcast(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{N_BATCH, 1});
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_b_ih_reverse = this->bias_ih_reverse[idx_layer].broadcast(
Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{N_BATCH, 1});
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_b_hh = this->bias_hh[idx_layer].broadcast(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{N_BATCH, 1});
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_b_hh_reverse = this->bias_hh_reverse[idx_layer].broadcast(
Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{N_BATCH, 1});
Eigen::Tensor<float, 2> &cur_ht = h_t[idx_layer * 2];
Eigen::Tensor<float, 2> &cur_ht_reverse = h_t[idx_layer * 2 + 1];
Eigen::Tensor<float, 2> &cur_ct = c_t[idx_layer * 2];
Eigen::Tensor<float, 2> &cur_ct_reverse = c_t[idx_layer * 2 + 1];
// cout << "cur_w_ih" << endl << cur_w_ih << endl;
// cout << "cur_w_hh" << endl << cur_w_hh << endl;
// cout << "cur_b_ih" << endl << cur_b_ih << endl;
// cout << "cur_b_hh" << endl << cur_b_hh << endl;
// cout << "cur_ht" << endl << cur_ht << endl;
// cout << "cur_ct" << endl << cur_ct << endl;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> output(N_BATCH, N_TIME, N_HIDDEN);
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> output_reverse(N_BATCH, N_TIME, N_HIDDEN);
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> X_t;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> X_t_reverse;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> gates;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> gates_reverse;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> i_t, f_t, g_t, o_t;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> i_t_reverse, f_t_reverse, g_t_reverse, o_t_reverse;
Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> cur_cat;
Eigen::array<Eigen::IndexPair<int>, 1> product_dims = {Eigen::IndexPair<int>(1, 1)};
Eigen::array<int64_t, 2> gate_patch = Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{N_BATCH, N_HIDDEN};
for (int t = 0; t < N_TIME; t++) {
X_t = out_pointer.chip(t, 1);
X_t_reverse = out_pointer.chip(N_TIME - t - 1, 1);
// cout << "X_t" << endl << X_t << endl;
// cout << "X_t_reverse" << endl << X_t_reverse << endl;
gates = X_t.contract(cur_w_ih, product_dims) + cur_b_ih + cur_ht.contract(cur_w_hh, product_dims) +
cur_b_hh;
gates_reverse = X_t_reverse.contract(cur_w_ih_reverse, product_dims) + cur_b_ih_reverse +
cur_ht_reverse.contract(cur_w_hh_reverse, product_dims) +
cur_b_hh_reverse;
i_t = gates.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 0}, gate_patch).sigmoid();
f_t = gates.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 1}, gate_patch).sigmoid();
g_t = gates.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 2}, gate_patch).tanh();
o_t = gates.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 3}, gate_patch).sigmoid();
i_t_reverse = gates_reverse.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 0}, gate_patch).sigmoid();
f_t_reverse = gates_reverse.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 1}, gate_patch).sigmoid();
g_t_reverse = gates_reverse.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 2}, gate_patch).tanh();
o_t_reverse = gates_reverse.slice(Eigen::array<int64_t, 2>{0, N_HIDDEN * 3}, gate_patch).sigmoid();
cur_ct = f_t * cur_ct + i_t * g_t;
cur_ht = o_t * cur_ct.tanh();
cur_ct_reverse = f_t_reverse * cur_ct_reverse + i_t_reverse * g_t_reverse;
cur_ht_reverse = o_t_reverse * cur_ct_reverse.tanh();
output.chip(t, 1) = cur_ht;
output_reverse.chip(N_TIME - t - 1, 1) = cur_ht_reverse;
}
out_pointer = output.concatenate(output_reverse, 2);
}
return out_pointer;
}
void Layer_LSTM::print2(Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 2> input) {
const Eigen::Tensor<size_t, 2>::Dimensions &dim_inp = input.dimensions();
std::cout << "Variable:" << std::endl;
// 0 0
std::cout << input(0, 0) << " " << input(0, 1) << " " << input(0, 2) << " ";
std::cout << input(0, dim_inp[1] - 3) << " " << input(0, dim_inp[1] - 2) << " "
<< input(0, dim_inp[1] - 1);
std::cout << std::endl;
// 0 -1
std::cout << input(dim_inp[0] - 1, 0) << " " << input(dim_inp[0] - 1, 1) << " "
<< input(dim_inp[0] - 1, 2) << " ";
std::cout << input(dim_inp[0] - 1, dim_inp[1] - 3) << " " << input(dim_inp[0] - 1, dim_inp[1] - 2)
<< " "
<< input(dim_inp[0] - 1, dim_inp[1] - 1);
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void Layer_LSTM::print3(Eigen::Tensor<float_t, 3> input) {
const Eigen::Tensor<size_t, 3>::Dimensions &dim_inp = input.dimensions();
std::cout << "Variable:" << std::endl;
// 0 0
std::cout << input(0, 0, 0) << " " << input(0, 0, 1) << " " << input(0, 0, 2) << " ";
std::cout << input(0, 0, dim_inp[2] - 3) << " " << input(0, 0, dim_inp[2] - 2) << " "
<< input(0, 0, dim_inp[2] - 1);
std::cout << std::endl;
// 0 -1
std::cout << input(0, dim_inp[1] - 1, 0) << " " << input(0, dim_inp[1] - 1, 1) << " "
<< input(0, dim_inp[1] - 1, 2) << " ";
std::cout << input(0, dim_inp[1] - 1, dim_inp[2] - 3) << " " << input(0, dim_inp[1] - 1, dim_inp[2] - 2)
<< " "
<< input(0, dim_inp[1] - 1, dim_inp[2] - 1);
std::cout << std::endl;
}
3.参考链接
[1] 实现LSTM-pytorch版