生产者消费者问题
问题描述
系统中有一组生产者进程和一组消费者进程,生产者进程每次生产一个产品放入缓冲区,消费者进程每次从缓冲区中取出一个产品并使用。生产者、消费者共享一个初始为空、大小为n的缓冲区
伪码描述
semaphore mutex = 1;//互斥信号量,实现对缓冲区的互斥访问
semaphore empty = n;//同步信号量,表示空闲缓冲区的数量
semaphore full = 0; //同步信号量,表示产品的数量,也即非空缓冲区的数量
producer () {
while (1) {
生产一个产品;
P(empty); //消耗一个空闲缓冲区
P(mutex); //实现互斥是在同一进程中进行一对PV操作
把产品放入缓冲区;
V(mutex);
V(full); //增加一个产品
}
}
consumer () {
while(1){
P(full); //消耗一个产品(非空闲缓冲区
P(mutex);
从缓冲区取出一个产品;
V(mutex);
V(empty); //增加一个空闲缓冲区
使用产品;
}
}
C语言代码实现
//producer-consumer.c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define NUM 5
volatile int arr[NUM] = {-1, - 1, -1, -1, -1}; //the shared buffer
volatile int wp; //write position
volatile int rp; //read position
sem_t empty;
sem_t full;
pthread_mutex_t lock;
void* producer(void* arg) {
while(1) {
int t = rand() % 100;
sem_wait(&empty);
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
arr[wp] = t;
wp = (wp + 1) % NUM;
printf("\033[32mproducer %ld: t = %d\033[0m\n", (long)arg, t);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
sem_post(&full);
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
void* consumer(void* arg) {
while(1) {
int t = 0;
sem_wait(&full);
pthread_mutex_lock(&lock);
t = arr[rp];
arr[rp] = -1;
rp = (rp + 1) % NUM;
printf("\033[31mconsumer %ld: t = %d\033[0m\n", (long)arg, t);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lock);
sem_post(&empty);
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
sem_init(&empty, 0, NUM);
sem_init(&full, 0, 0);
pthread_mutex_init(&lock, NULL);
srand(time(NULL));
wp = rp = 0;
pthread_t tid[8];
long i = 0;
for(; i < 4; ++i) { //4 producers
pthread_create(tid + i, NULL, producer, (void*)i);
}
for(; i < 8; ++i) { //4 consumers
pthread_create(tid + i, NULL, consumer, (void*)i);
}
for(i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
sem_destroy(&empty);
sem_destroy(&full);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
return 0;
}
读者写者问题
问题描述
有读者和写者两组并发进程,共享一个文件,当两个或两个以上的读进程同时访问共享数据时不会产生副作用,但若某个写进程和其他进程(读进程或写进程)同时访问共享数据时则可能导致数据不一致的错误。因此要求:
- 允许多个读者可以同时对文件执行读操作
- 只允许一个写者往文件中写信息
- 任一写者在完成写操作之前不允许其他读者或写者工作
- 写者执行写操作前,应让已有的读者和写者全部退出
借助POSIX线程库提供的读写锁,这个问题很容易用代码实现(当然采用信号量也是可以实现的)
C语言代码实现
//reader-writer.c
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int n = 0;
pthread_rwlock_t rwlock;
void* reader(void* arg) {
while (1) {
int t = 0;
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock);
t = n;
printf("\033[32mreader %ld: n = %d\033[0m\n", (long)arg, n);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
void* writer(void* arg) {
while (1) {
int t = rand() % 100000;
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);
n = t;
printf("\033[31mwriter %ld: n = %d\033[0m\n", (long)arg, n);
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
sleep(1);
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
pthread_t tid[8];
pthread_rwlock_init(&rwlock, NULL);
srand(time(NULL));
long i = 0;
for (; i < 6; ++i) { // 6 readers
pthread_create(tid + i, NULL, reader, (void*)i);
}
for (; i < 8; ++i) { // 2 writers
pthread_create(tid + i, NULL, writer, (void*)i);
}
for (i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&rwlock);
return 0;
}
哲学家进餐问题
问题描述
一张圆桌上坐着 5 名哲学家,桌子上每两个哲学家之间摆了一根筷子,桌子的中间是一碗米饭,如图所示:
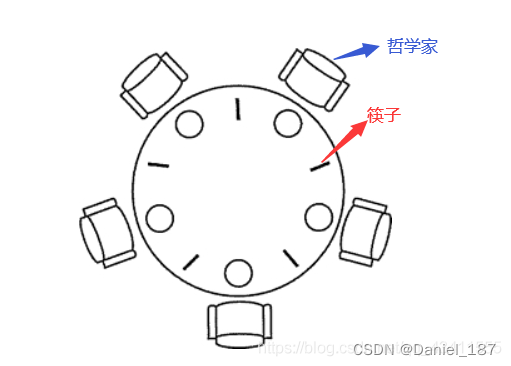
哲学家们倾注毕生精力用于思考和进餐,哲学家在思考时,并不影响他人。只有当哲学家饥饿的时候,才试图拿起左、右两根筷子(一根一根拿起)。如果筷子已在他人手上,则需等待。饥饿的哲学家只有同时拿到了两根筷子才可以开始进餐,当进餐完毕后,放下筷子继续思考
伪码实现
首先看一种会导致死锁的native实现:
sem chopstick[5]={1,1,1,1,1}//5根筷子
Pi()
{
while(1)
{
P(chopstick[i]);//取左边筷子
P(chopstick[(i+1)%5]);//取右边筷子
eat;//吃饭
V(chopstick[i]);//放左边筷子
V(chopstick[(i+1)%5]);//放右边筷子
think;//思考
}
}
一种导致死锁的情况是:当5位哲学家都执行了P(chopstick[i]);,那么他们就会因为都拿不起右边的筷子而死锁
解决死锁的方式有3种:
- 最多允许四个哲学家同时进餐
- 仅当一个哲学家左右两边的筷子都可用时才允许他抓起筷子,破坏请求条件
- 对哲学家顺序编号,要求奇数号哲学家先抓左边的筷子,然后再抓他右边的筷子,而偶数号哲学家刚好相反,破坏循环等待
对应的伪码实现分别为:
- 最多允许四个哲学家同时进餐:
sem cho[5]={1,1,1,1,1}//5根筷子
sem count = 4;//设置一个count最多有四个哲学家可以进来
void pi(int i)
{
while(1)
{
P(count);//请求进入房间进餐,获取资源,当count为0的时候,不能允许哲学家再进来了,阻塞
P(cho[i]);//请求左手边的筷子
P(cho[(i+1)%5]);//请求右手边的筷子
eat();
V(cho[i]); //释放左手边的筷子
V(cho[(i+1)%5]);//释放右手边的筷子
V(count);//退出房间释放资源
}
}
- 仅当一个哲学家左右两边的筷子都可用时才允许他抓起筷子,也就是两只筷子必须同时拿起:
sem cho[5]={1,1,1,1,1}//5根筷子
sem mutex=1;//允许拿筷子
void pi(int i)
{
while(1)
{
P(mutex);//允许拿筷子,同一时刻只允许一个哲学家获取
P(cho[i]);//请求左手边的筷子
P(cho[(i+1)%5]);//请求右手边的筷子
V(mutex);//拿完筷子,释放资源
eat();
V(cho[i]); //释放左手边的筷子
V(cho[(i+1)%5]);//释放右手边的筷子
}
}
- 对哲学家顺序编号,要求奇数号哲学家先抓左边的筷子,然后再抓他右边的筷子,而偶数号哲学家刚好相反:
sem cho[5]={1,1,1,1,1}//5根筷子
void pi(int i)
{
while(1)
{
if(i%2==0)//偶数哲学家,先右后左
{
P(cho[(i+1)%5]);//请求右手边的筷子
P(cho[i]);//请求左手边的筷子
eat();
V(cho[(i+1)%5]);//释放右手边的筷子
V(cho[i]); //释放左手边的筷子
}
else//奇数哲学家,先左后右
{
P(cho[i]);//请求左手边的筷子
P(cho[(i+1)%5]);//请求右手边的筷子
eat();
V(cho[i]); //释放左手边的筷子
V(cho[(i+1)%5]);//释放右手边的筷子
}
}
}
C语言代码实现
- 最多允许4个哲学家同时进餐:
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
sem_t chopsticks[5];
sem_t max_dining_num;
void* philosopher(void* arg) {
long i = (long)arg;
while (1) {
sem_wait(&max_dining_num);
sem_wait(&chopsticks[i]);
sem_wait(&chopsticks[(i + 1) % 5]);
printf("philosopher %ld: eating\n", i);
printf("philosopher %ld: finished\n", i);
sem_post(&chopsticks[(i + 1) % 5]);
sem_post(&chopsticks[i]);
sem_post(&max_dining_num);
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
long i = 0;
for (; i < 5; ++i) {
sem_init(chopsticks + i, 0, 1);
}
sem_init(&max_dining_num, 0, 4);
pthread_t tid[5];
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
pthread_create(tid + i, NULL, philosopher, (void*)i);
}
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
for(i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
sem_destroy(&chopsticks[i]);
}
sem_destroy(&max_dining_num);
return 0;
}
- 强制哲学家必须同时拿起左右两只筷子:
//dining-philosophers-2.c
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
sem_t chopsticks[5];
pthread_mutex_t pickup_chopsticks; //enable pickup chopsticks
void* philosopher(void* arg) {
long i = (long)arg;
while (1) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&pickup_chopsticks);
sem_wait(&chopsticks[i]);
sem_wait(&chopsticks[(i + 1) % 5]);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&pickup_chopsticks);
printf("philosopher %ld: eating\n", i);
printf("philosopher %ld: finished\n", i);
sem_post(&chopsticks[(i + 1) % 5]);
sem_post(&chopsticks[i]);
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
long i = 0;
for (; i < 5; ++i) {
sem_init(chopsticks + i, 0, 1);
}
pthread_mutex_init(&pickup_chopsticks, NULL);
pthread_t tid[5];
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
pthread_create(tid + i, NULL, philosopher, (void*)i);
}
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
for(i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
sem_destroy(&chopsticks[i]);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&pickup_chopsticks);
return 0;
}
- 奇数号哲学家先拿左手边的筷子,偶数号哲学家先拿右手边的筷子:
//dining-philosophers-3.c
#include <errno.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <semaphore.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
sem_t chopsticks[5];
void* philosopher(void* arg) {
long i = (long)arg;
while (1) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
sem_wait(&chopsticks[i]);
sem_wait(&chopsticks[(i + 1) % 5]);
printf("philosopher %ld: eating\n", i);
printf("philosopher %ld: finished\n", i);
sem_post(&chopsticks[(i + 1) % 5]);
sem_post(&chopsticks[i]);
} else {
sem_wait(&chopsticks[(i + 1) % 5]);
sem_wait(&chopsticks[i]);
printf("philosopher %ld: eating\n", i);
printf("philosopher %ld: finished\n", i);
sem_post(&chopsticks[i]);
sem_post(&chopsticks[(i + 1) % 5]);
}
}
return 0;
}
int main() {
long i = 0;
for (; i < 5; ++i) {
sem_init(chopsticks + i, 0, 1);
}
pthread_t tid[5];
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
pthread_create(tid + i, NULL, philosopher, (void*)i);
}
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
for (i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
sem_destroy(&chopsticks[i]);
}
return 0;
}