1、find()
find() 用于找出第一个符合条件的数组成员。它的参数是一个回调函数,所有数组成员依次执行该回调函数,直到找出第一个返回值为true的成员,然后返回该成员。如果没有符合条件的成员,则返回undefined。
find()方法的回调函数可以接受三个参数,依次为当前的值、当前的位置和原数组。
例 a:
我们有一个包含名称 age 和 id 属性的用户对象列表,如下所示:
let users = [{id:1, name: 'John', age: 22 }, {id:2, name: 'Tom',age: 22 }, {id:3, name: 'Balaji', age: 24 }];
查找到第一个年龄为 22 的用户
console.log(users.find(user => user.age === 22));
//console
//{ id: 1, name: 'John', age:22}
例 b:
寻找数组中第一个素数
function isPrime(element, index, array) {
let start = 2;
while (start <= Math.sqrt(element)) {
if (element % start++ < 1) {
return false;
}
}
return element > 1;
}
console.log([4, 6, 8, 12].find(isPrime)); // undefined,未找到
console.log([4, 5, 8, 12].find(isPrime)); // 5
- findIndex()
findIndex()方法与find()方法的用法非常类似,返回第一个符合条件的数组成员的位置,如果所有成员都不符合条件,则返回-1。
[1, 2, 5, -1, 9].findIndex((n) => n < 0)
//返回符合条件的值的位置(索引)
// 3
- filter()
filter()方法创建一个包含所有通过测试函数的元素的新数组。如果没有元素满足测试函数,则返回一个空数组。
例:
过滤年龄为 22 岁的用户
console.log(users.filter(user => user.age === 22));
//console
//[{ id: 1, name: 'John', age:22},{ id: 2, name: 'Tom', age:22}]
filter()回调函数
var arr = ['A', 'B', 'C'];
var r = arr.filter(function (element, index, self) {
console.log(element); // 依次打印'A', 'B', 'C'
console.log(index); // 依次打印0, 1, 2
console.log(self); // self就是变量arr
return true;
});
- some()
some 为数组中的每一个元素执行一次 callback 函数,直到找到一个使得 callback 返回一个“真值”(即可转换为布尔值 true 的值)。如果找到了这样一个值,some 将会立即返回 true。
例子:检测在数组中是否有大于10的元素。
var a = [11,50,40,3,5,80,90,4]
function some(item,index,array){
console.log(item);
return item>10
}
a.some(some);
//11
//true
- every()
every()方法测试一个数组内的所有元素是否都能通过指定函数的测试。它返回一个布尔值。
const isBelowThreshold = (currentValue) => currentValue < 40;
const array1 = [1, 30, 39, 29, 10, 13];
console.log(array1.every(isBelowThreshold));
// Expected output: true
- forEach()
forEach() 方法用于调用数组的每个元素,并将元素传递给回调函数。
例子:
a. 列出数组中的每一项:
注意: forEach() 对于空数组是不会执行回调函数的。
var fruits = ["apple", "orange", "cherry"];
fruits.forEach(myFunction);
function myFunction(item, index) {
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML += index + ":" + item + "<br>";
}
b. 对于数组中的每个元素:将值更新为原始值的 10 倍:
var numbers = [65, 44, 12, 4];
numbers.forEach(myFunction)
function myFunction(item, index, arr) {
arr[index] = item * 10;
}
c. forEach() 的 continue 与 break
forEach() 本身是不支持的 continue 与 break 语句的,我们可以通过 some 和 every 来实现。
使用 return 语句实现 continue 关键字的效果:
continue 实现
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
arr.forEach(function (item) {
if (item === 3) {
return;
}
console.log(item);
});
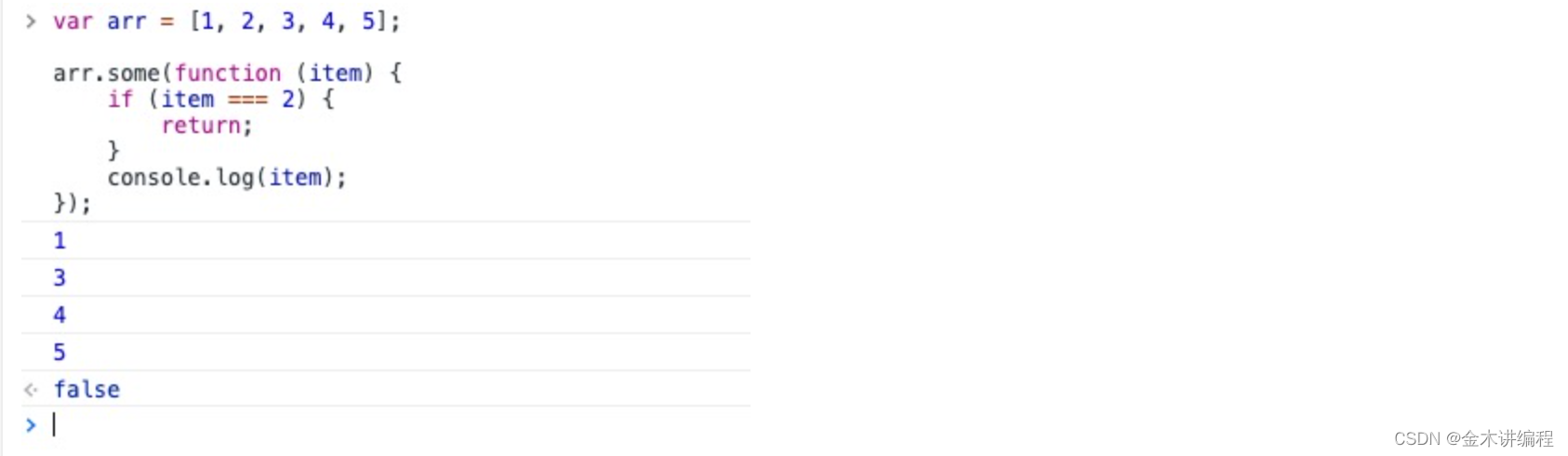
通过some实现
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
arr.some(function (item) {
if (item === 2) {
return; // 不能为 return false
}
console.log(item);
});
break 实现
var arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
arr.every(function (item) {
console.log(item);
return item !== 3;
});

- map()
map() 方法返回一个新数组,数组中的元素为原始数组元素调用函数处理后的值。
map() 方法按照原始数组元素顺序依次处理元素。
注意:map() 不会对空数组进行检测。
注意:map() 不会改变原始数组。
const array1 = [1, 4, 9, 16];
// Pass a function to map
const map1 = array1.map(x => x * 2);
console.log(map1);
// Expected output: Array [2, 8, 18, 32]`