1、通信接口
• 通信的目的:将一个设备的数据传送到另一个设备,扩展硬件系统
• 通信协议:制定通信的规则,通信双方按照协议规则进行数据收发
异步:需要双方约定一个频率
2、 硬件电路
• 简单双向串口通信有两根通信线(发送端 TX 和接收端 RX )
• TX 与 RX 要交叉连接
• 当只需单向的数据传输时,可以只接一根通信线
• 当电平标准不一致时,需要加电平转换芯片
两个设备之间的GND一定要接在一起,但是VCC可以各自接
3、电平标准
• TTL 电平: +3.3V 或 +5V 表示 1 , 0V 表示 0
• RS232 电平: -3~-15V 表示 1 , +3~+15V 表示 0
• RS485 电平:两线压差 +2~+6V 表示 1 , -2~-6V 表示 0 (差分信号)
4、串口参数及时序
• 波特率:串口通信的速率
速率的参数就是波特率,波特率就是每秒传输码元的个数,单位是码元/s(baud)
比特率:每秒传输的比特数,单位是bit/s,或者是bps
在二进制的情况下,一个码元及时一个bit,此时波特率等于比特率
• 起始位:标志一个数据帧的开始,固定为低电平
• 数据位:数据帧的有效载荷, 1 为高电平, 0 为低电平,低位先行
• 校验位:用于数据验证,根据数据位计算得来
• 停止位:用于数据帧间隔,固定为高电平
字节装载在数据帧中,数据帧由起始位、数据位、停止位组成
数据位有8个,代表一个字节的8位置,可以在最右边加一个奇偶校验位,则数据位总共是9位。接收方在接收数据后,会验证数据位和校验位
若规定发送的波特率是1000bps,表示1s要发1000位,每一位的时间就是1ms,发送方每隔1ms发送一位,接收方每隔1ms接受一位,决定了每隔多久发送一位
空闲状态下,起始位为高电平,起始位给低电平,使其产生下降沿,表示数据帧要开始
字节装载在数据帧中,数据帧由起始位、数据位、停止位组成
数据位有8个,代表一个字节的8位置,可以在最右边加一个奇偶校验位,则数据位总共是9位。接收方在接收数据后,会验证数据位和校验位
若规定发送的波特率是1000bps,表示1s要发1000位,每一位的时间就是1ms,发送方每隔1ms发送一位,接收方每隔1ms接受一位,决定了每隔多久发送一位
空闲状态下,起始位为高电平,起始位给低电平,使其产生下降沿,表示数据帧要开始
5、USART简介
• USART: 通用同步 / 异步收发器
• USART 是 STM32 内部集成的硬件外设,可根据数据寄存器的一个字节数据自动生成数据帧时序,从 TX 引脚发送出去,也可自动接收 RX 引脚的数据帧时序,拼接为一个字节数据,存放在数据寄存器里.
• 自带波特率(一般设置为9600/115200)发生器,最高达 4.5Mbits/s
• 可配置数据位长度( 8/9 )、停止位长度( 0.5/1/1.5/2 )
• 可选校验位(无校验 / 奇校验 / 偶校验)
• 支持同步模式、硬件流控制、 DMA 、智能卡、 IrDA 、 LIN
同步模式:多了个时钟CLK的输出
• STM32F103C8T6 USART 资源: USART1(APB2总线上的设备) 、 USART2(APB1)、 USART3(APB1)
6、USART工作
(1)写操作
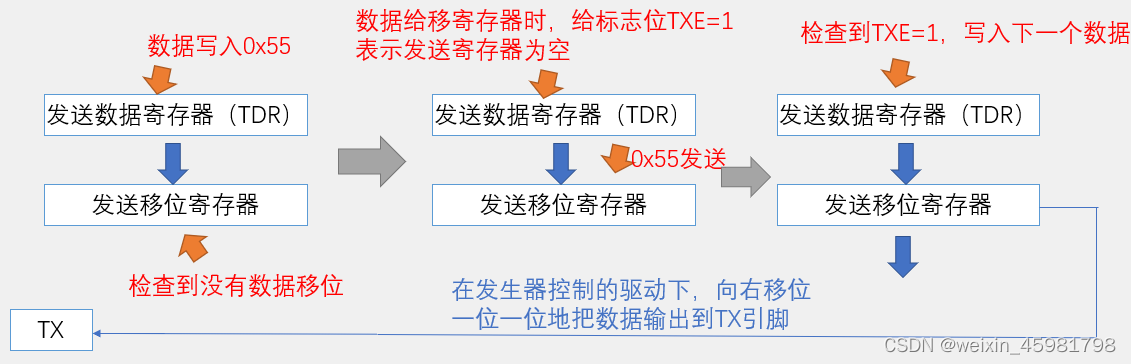
当数据移位完成后,数据会立刻自动从TDR发送移位寄存器
TDR和移位寄存器的双重缓存,保证在连续发送数据时,数据帧之间不会有空闲,提高了工作效率
(2)读操作
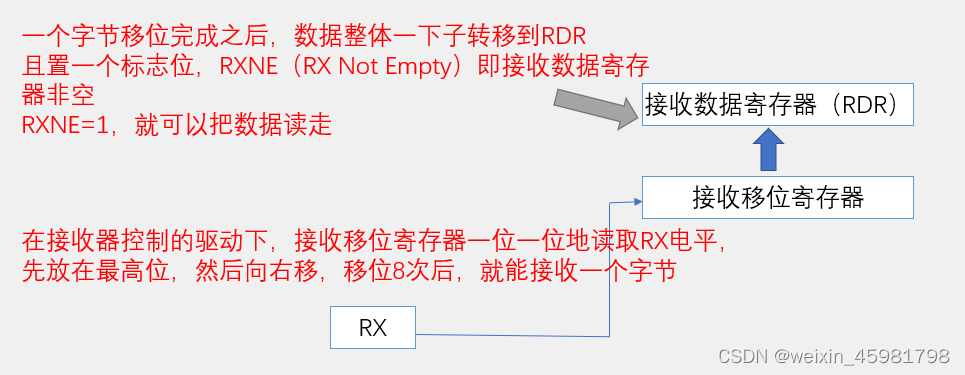
因为串口协议规定是低位先行,所以接收移位寄存器时从高位往低位方向移动
(3)帧头和帧尾的添加和除由电路自动执行
(4)硬件数据控制流
A向B发送数据,当A一直发,B处理不过来;
若无硬件控制流,B只能抛弃新数据或者覆盖元数据;
有硬件控制流,硬件电路上会多出一条线,B没准备好置高电平,准备好置低电平;
A收到B的反馈决定数据发送,防止因为B处理慢而导致数据丢失。
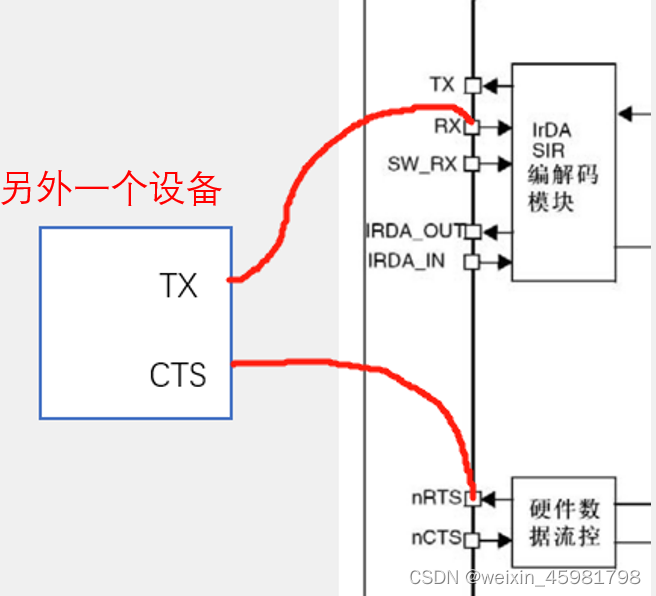
能接收的时候,RTS就置低电平,请求对方发送,对方的CTS接收到后,就可以一直发
处理不过来时,RTS就置高电平,对方的CTS接收到后,就会暂停发送
7、USART基本结构
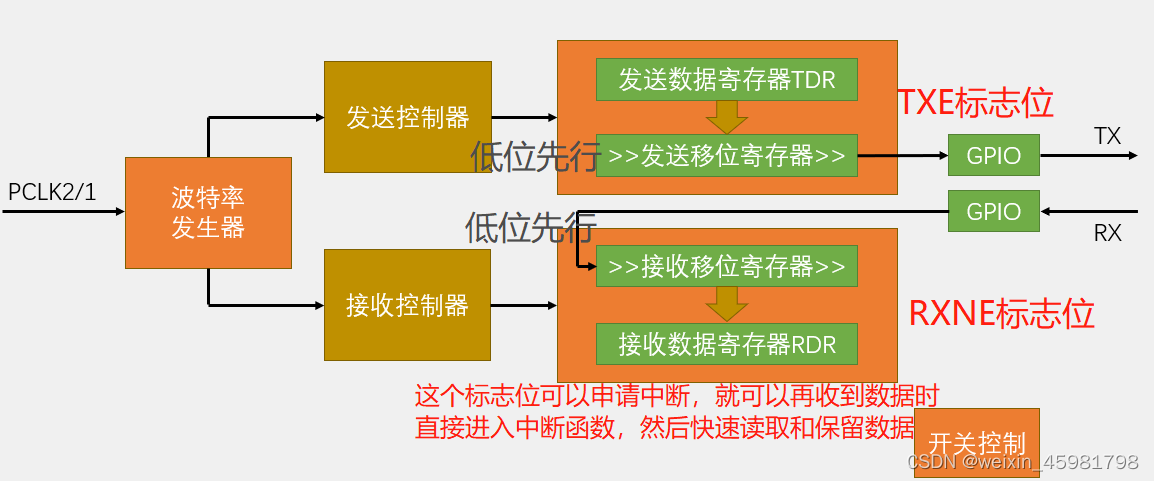
8、数据帧
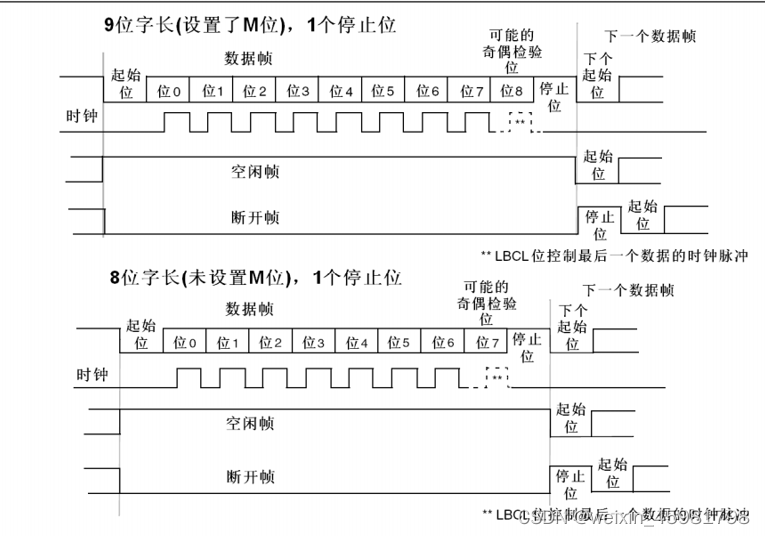
有8位字长和9位字长,分别可以选择有校验和无校验
9位建议有校验,8位建议无校验
停止位有0.5,1,1.5,2,建于选择1位
9、USART串口发送
1.连线图
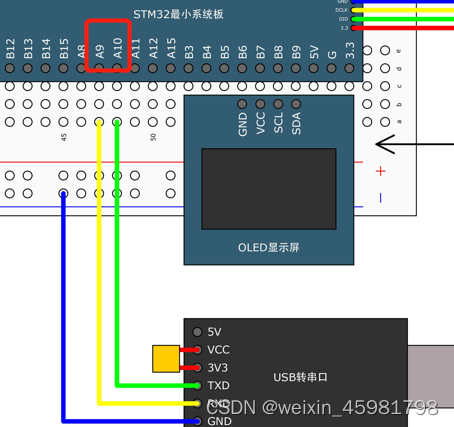

要交叉连接,所以RX接TX
2、printf函数的移植方法
使用printf之前,先打开工程选项
再serial.c中,添加#include <stdio.h>,再在文件中重写fputc函数
int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
{
Serial_SendByte(ch);
return ch;
}fputc是printf函数的底层,printf在打印的时候,就是不断调用fputc函数一个个打印的,现在把fputc函数重定向到了串口,则printf自然就输出到串口
在serial.h文件中要包含头文件
#include <stdio.h>
这种方法printf只能有一个,若重定向到串口1了,则串口2不能使用
若多个串口都想用printf,则使用sprintf,sprintf可以把格式化字符输出到一个字符串中
3、serial.c
#include "stm32f10x.h" // Device header
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
void Serial_Init(void)
{
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_USART1, ENABLE);
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
//TX引脚是USART外设控制的输出引脚,所以要选复用推挽输出
//RX引脚是USART外设数据输入脚,所以要选择输入模式
//一根线只能有一个输出,可以有多个输入,故输入脚,外设和GPIO都可以用
//一般RX配置是浮空输入或者上拉输入,因为串口波形空闲状态是高电平,故不选择下拉输入
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP;//复用推挽输出,数据只需要数据发送
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_9;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
USART_InitTypeDef USART_InitStructure;
USART_InitStructure.USART_BaudRate = 9600;//9600波特率
USART_InitStructure.USART_HardwareFlowControl = USART_HardwareFlowControl_None;//硬件流控制
USART_InitStructure.USART_Mode = USART_Mode_Tx;
USART_InitStructure.USART_Parity = USART_Parity_No;//无校验
USART_InitStructure.USART_StopBits = USART_StopBits_1;//1位停止位
USART_InitStructure.USART_WordLength = USART_WordLength_8b;//8位字长
USART_Init(USART1, &USART_InitStructure);
USART_Cmd(USART1, ENABLE);
}
void Serial_SendByte(uint8_t Byte)
{
USART_SendData(USART1, Byte);//发送数据
while (USART_GetFlagStatus(USART1, USART_FLAG_TXE) == RESET);
}
void Serial_SendArray(uint8_t *Array, uint16_t Length)
{
uint16_t i;
for (i = 0; i < Length; i ++)
{
Serial_SendByte(Array[i]);
}
}
void Serial_SendString(char *String)
{
uint8_t i;
for (i = 0; String[i] != '\0'; i ++)
{
Serial_SendByte(String[i]);
}
}
uint32_t Serial_Pow(uint32_t X, uint32_t Y)
{
uint32_t Result = 1;
while (Y --)
{
Result *= X;
}
return Result;
}
//传输12345,相当于12345/10000%10=1,12345/1000%10=2
void Serial_SendNumber(uint32_t Number, uint8_t Length)
{
uint8_t i;
for (i = 0; i < Length; i ++)
{
Serial_SendByte(Number / Serial_Pow(10, Length - i - 1) % 10 + '0');
}
}
int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
{
Serial_SendByte(ch);//改发送给串口
return ch;
}
//用来接收后面的可变参数列表
void Serial_Printf(char *format, ...)
{
char String[100];
va_list arg;
va_start(arg, format);
vsprintf(String, format, arg);
va_end(arg);
Serial_SendString(String);
}4、main.c
#include "stm32f10x.h" // Device header
#include "Delay.h"
#include "OLED.h"
#include "Serial.h"
int main(void)
{
OLED_Init();
Serial_Init();
Serial_SendByte(0x41);//发送字节
uint8_t MyArray[] = {0x42, 0x43, 0x44, 0x45};
Serial_SendArray(MyArray, 4);//发送数组
Serial_SendString("\r\nNum1=");//发送字符串
Serial_SendNumber(111, 3);//发送n位数字
printf("\r\nNum2=%d", 222);
char String[100];
sprintf(String, "\r\nNum3=%d", 333);
Serial_SendString(String);
Serial_Printf("\r\nNum4=%d", 444);
Serial_Printf("\r\n");
while (1)
{
}
}5、解决直接写汉字,编译器报错
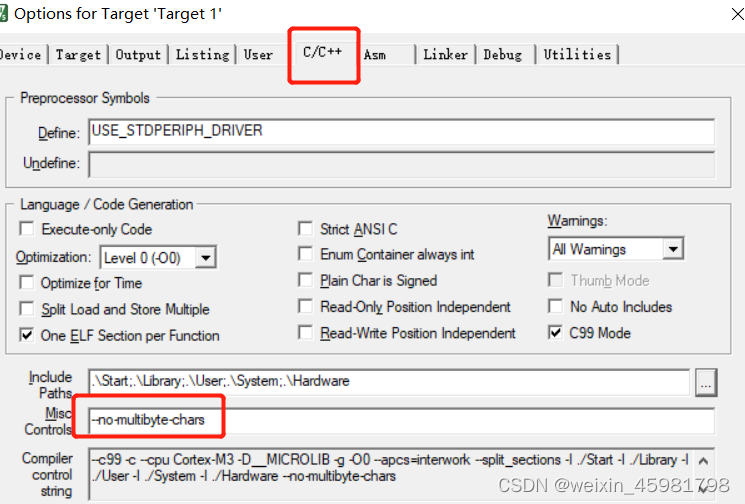
--no-multibyte-chars
Serial_Printf("你好,世界");便可以在显示屏中显示汉字
10 、USART串口发送和接收
1、查询实现
查询流程:在主函数里不断判断那RXNE标志位,如果置1,说明接收到数据了
再调用ReceiveData读取DR寄存器的值即可
while(1)
{
if (USART_GetFlagStatus(USART1,USART_FLAG_RXNE) == RET )
{
//DR完成读操作后会自动清零,故需要手动清0
RxData = USART_ReceiveData(USART1);
OLED_ShowHexNum(1 , 1 , RxData , 2);
}
}在串口调试助手中,发送AF,就会在单片机的显示屏上显示AF
2、中断实现
(1)在Serial.c中添加的代码
uint8_t Serial_RxData;
uint8_t Serial_RxFlag;
在初始化的函数中:
//写入中断的代码
USART_ITConfig(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE, ENABLE);//开启RXNE标志位到中断的输出
//以下是配置NVIC
NVIC_PriorityGroupConfig(NVIC_PriorityGroup_2);//先分组
NVIC_InitTypeDef NVIC_InitStructure;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannel = USART1_IRQn;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelCmd = ENABLE;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelPreemptionPriority = 1;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelSubPriority = 1;
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStructure);
USART_Cmd(USART1, ENABLE);//使能
uint8_t Serial_GetRxFlag(void)//读后自动清除的功能
{
if (Serial_RxFlag == 1)
{
Serial_RxFlag = 0;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
uint8_t Serial_GetRxData(void)
{
return Serial_RxData;
}
void USART1_IRQHandler(void)
{
if (USART_GetITStatus(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE) == SET)//判断标志位
{
//在中断中对数据进行转存
Serial_RxData = USART_ReceiveData(USART1);//先读取模块的变量里
Serial_RxFlag = 1;
//如果读取DR,就自动清除,如果没有读取DR,就要手动清除
USART_ClearITPendingBit(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE);//清除标志位
}
}(2)主函数中调用
while (1)
{
if (Serial_GetRxFlag() == 1)
{
RxData = Serial_GetRxData();
Serial_SendByte(RxData);//把接收到的数据回传给电脑
OLED_ShowHexNum(1, 8, RxData, 2);//显示在显示屏上
}
}(3)思路
当RXNE=1时,也就是电脑串口小助手有数据传递给开发板时,进入中断
获取电脑上的数据,并手动清零,将获取到的数据用函数封装起来
在主函数中调用函数,将获取到的值显示在电脑上和显示屏中
(4)完整的Serial.c代码
#include "stm32f10x.h" // Device header
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
uint8_t Serial_RxData;
uint8_t Serial_RxFlag;
void Serial_Init(void)
{
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_USART1, ENABLE);
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA, ENABLE);
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP;//复用推挽输出
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_9;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IPU;//上拉输入模式
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_10;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure);
USART_InitTypeDef USART_InitStructure;
USART_InitStructure.USART_BaudRate = 9600;
USART_InitStructure.USART_HardwareFlowControl = USART_HardwareFlowControl_None;
USART_InitStructure.USART_Mode = USART_Mode_Tx | USART_Mode_Rx;//接收+发送
USART_InitStructure.USART_Parity = USART_Parity_No;
USART_InitStructure.USART_StopBits = USART_StopBits_1;
USART_InitStructure.USART_WordLength = USART_WordLength_8b;
USART_Init(USART1, &USART_InitStructure);
//写入中断的代码
USART_ITConfig(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE, ENABLE);//开启RXNE标志位到中断的输出
//以下是配置NVIC
NVIC_PriorityGroupConfig(NVIC_PriorityGroup_2);//先分组
NVIC_InitTypeDef NVIC_InitStructure;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannel = USART1_IRQn;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelCmd = ENABLE;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelPreemptionPriority = 1;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelSubPriority = 1;
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStructure);
USART_Cmd(USART1, ENABLE);//使能
}
void Serial_SendByte(uint8_t Byte)
{
USART_SendData(USART1, Byte);
while (USART_GetFlagStatus(USART1, USART_FLAG_TXE) == RESET);
}
void Serial_SendArray(uint8_t *Array, uint16_t Length)
{
uint16_t i;
for (i = 0; i < Length; i ++)
{
Serial_SendByte(Array[i]);
}
}
void Serial_SendString(char *String)
{
uint8_t i;
for (i = 0; String[i] != '\0'; i ++)
{
Serial_SendByte(String[i]);
}
}
uint32_t Serial_Pow(uint32_t X, uint32_t Y)
{
uint32_t Result = 1;
while (Y --)
{
Result *= X;
}
return Result;
}
void Serial_SendNumber(uint32_t Number, uint8_t Length)
{
uint8_t i;
for (i = 0; i < Length; i ++)
{
Serial_SendByte(Number / Serial_Pow(10, Length - i - 1) % 10 + '0');
}
}
int fputc(int ch, FILE *f)
{
Serial_SendByte(ch);
return ch;
}
void Serial_Printf(char *format, ...)
{
char String[100];
va_list arg;
va_start(arg, format);
vsprintf(String, format, arg);
va_end(arg);
Serial_SendString(String);
}
uint8_t Serial_GetRxFlag(void)//读后自动清除的功能
{
if (Serial_RxFlag == 1)
{
Serial_RxFlag = 0;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
uint8_t Serial_GetRxData(void)
{
return Serial_RxData;
}
void USART1_IRQHandler(void)
{
if (USART_GetITStatus(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE) == SET)//判断标志位
{
//在中断中对数据进行转存
Serial_RxData = USART_ReceiveData(USART1);//先读取模块的变量里
Serial_RxFlag = 1;
//如果读取DR,就自动清除,如果没有读取DR,就要手动清除
USART_ClearITPendingBit(USART1, USART_IT_RXNE);//清除标志位
}
}(5)mian.c
#include "stm32f10x.h" // Device header
#include "Delay.h"
#include "OLED.h"
#include "Serial.h"
uint8_t RxData;
int main(void)
{
OLED_Init();
OLED_ShowString(1, 1, "RxData:");
Serial_Init();
while (1)
{
if (Serial_GetRxFlag() == 1)
{
RxData = Serial_GetRxData();
Serial_SendByte(RxData);//把接收到的数据回传给电脑
OLED_ShowHexNum(1, 8, RxData, 2);//显示在显示屏上
}
}
}