有些时候给出毫秒值来让我们计算时间该怎么办。
文章目录
- 介绍
- [蓝桥杯 2021 省 B] 时间显示
- 题目描述
- 代码
- 蓝桥杯–航班时间
介绍
将毫秒值直接转成日期的有
- new Date(毫秒)
- Instant.ofEpochMilli(毫秒)
- Instant.ofEpochSecond(秒)
- Instant.ofEpochSecond(秒,纳秒)
建议用instant
instant可以转换为ZonedDateTime而ZonedDateTime的功能是非常强大的。
date虽然也可以转换为instant但是底层调用的是ofEpochSecond的方法所以就没有必要用date了
[蓝桥杯 2021 省 B] 时间显示
题目描述
小蓝要和朋友合作开发一个时间显示的网站。在服务器上,朋友已经获取了当前的时间,用一个整数表示,值为从 1970 年 1 月 1 日 00:00:00 到当前时刻经过的毫秒数。
现在,小蓝要在客户端显示出这个时间。小蓝不用显示出年月日,只需要 显示出时分秒即可,毫秒也不用显示,直接舍去即可。
给定一个用整数表示的时间,请将这个时间对应的时分秒输出。
输入格式
输入一行包含一个整数,表示时间。
输出格式
输出时分秒表示的当前时间, 格式形如
H
H
:
M
M
:
S
S
\mathrm{HH}: \mathrm{MM}: \mathrm{SS}
HH:MM:SS, 其中
H
H
\mathrm{HH}
HH 表示时, 值 为
0
0
0 到
23
,
M
M
23, \mathrm{MM}
23,MM 表示分。值为
0
0
0 到
59
59
59。
S
S
\mathrm{SS}
SS 表示秒, 值为
0
0
0 到
59
59
59。时、分、秒不足两位时补前导 0 。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
46800999
样例输出 #1
13:00:00
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
1618708103123
样例输出 #2
01:08:23
提示
对于所有评测用例, 给定的时间为不超过 1 0 18 10^{18} 1018 的正整数。
蓝桥杯 2021 第一轮省赛 B 组 F 题。
代码
import java.io.*;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class Main {
static final PrintWriter print = new PrintWriter(System.out);
// 更快的输入输出
static final StreamTokenizer st = new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)));
public static long nextLong() throws IOException {
st.nextToken();
return (long) st.nval;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long time = nextLong();
System.out.println(Instant.ofEpochMilli(time).atZone(ZoneId.of("GMT")).format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("HH:mm:ss")));
print.flush();
}
}
蓝桥杯–航班时间
这个题目在实例1介绍过了
在洛谷刷的时候只能jdk8.然后发现编译失败了。原来蓝桥杯平台还高些。这些平台怎么还在jdk8啊。
下面是代码,具体逻辑没有改变,只改变了使用秒转换为时间的过程。下面有更加深入的了解
import java.io.*;
import java.time.*;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class Main {
static final BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//在此输入您的代码...
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String[] s = br.readLine().split(" ");
String[] s2 = br.readLine().split(" ");
long t = (getTime(s).getSeconds() + getTime(s2).getSeconds())/2;
ZonedDateTime time = Instant.ofEpochSecond(t).atZone(ZoneId.of("GMT"));
System.out.printf("%02d:%02d:%02d\n",time.getHour(),time.getMinute(),time.getSecond());
}
}
public static Duration getTime(String[] s){
String d = "2019-01-01 ";
LocalDateTime time1 = LocalDateTime.parse(d+s[0], DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
LocalDateTime time2 = LocalDateTime.parse(d+s[1], DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"));
if (s.length > 2){
time2 = time2.plusDays((int) s[2].charAt(2));
}
return Duration.between(time1, time2);
}
}
我就在想能不能直接用instant做了。
首先就是如果pase字符串。
看见instant有pase的方法。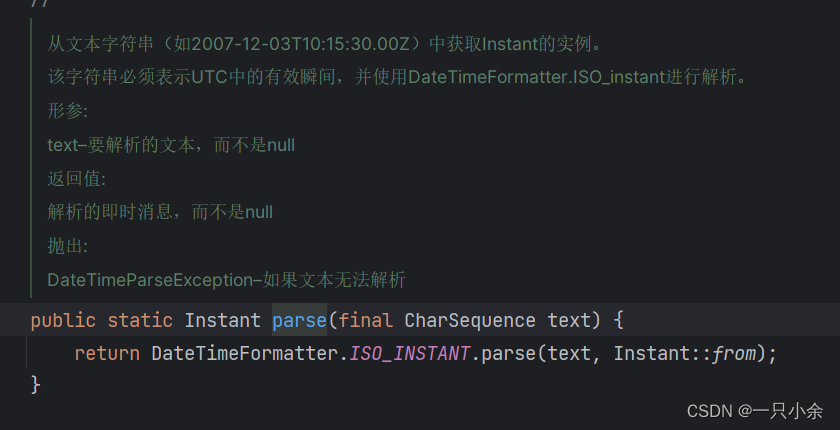
这样速度快了一丢丢,也减少了点类的使用。
public static long getTime(String[] s) {
String d = "2019-01-01T%s.00Z";
Instant t1 = Instant.parse(String.format(d, s[0]));
Instant t2 = Instant.parse(String.format(d, s[1]));
if (s.length > 2) {
t2 = t2.plus((int) s[2].charAt(2), ChronoUnit.DAYS);
}
return t2.getEpochSecond() - t1.getEpochSecond();
}