前言
本文主要描述在c++中应用Eigen进行矩阵(向量)的表示运算,以及Eigen库的下载和配置。
一. Eigen库介绍、下载及配置
Eigen是C++中可以用来调用并进行矩阵计算的一个库,里面封装了一些类,需要的头文件和功能如下:
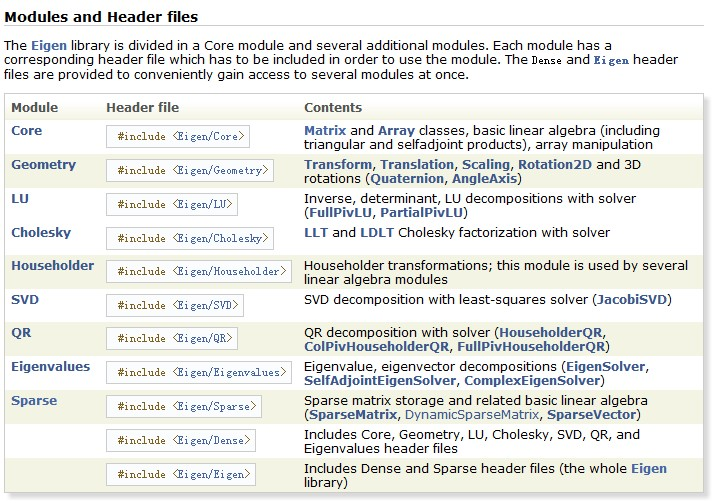
有关Eigen的详细介绍可以查看其官网主页:http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/dox/index.html
- 下载
Eigen的下载地址如下:http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/index.php?title=Main_Page#Download
在网页右上方选择选择不同版本及格式的压缩包,我这里选择的最新(2023.4.24)发布版本3.4.0的zip文件,点击直接进行下载。 - 配置
(1)将下载的压缩包进行解压;
----------------在VS中配置------------------
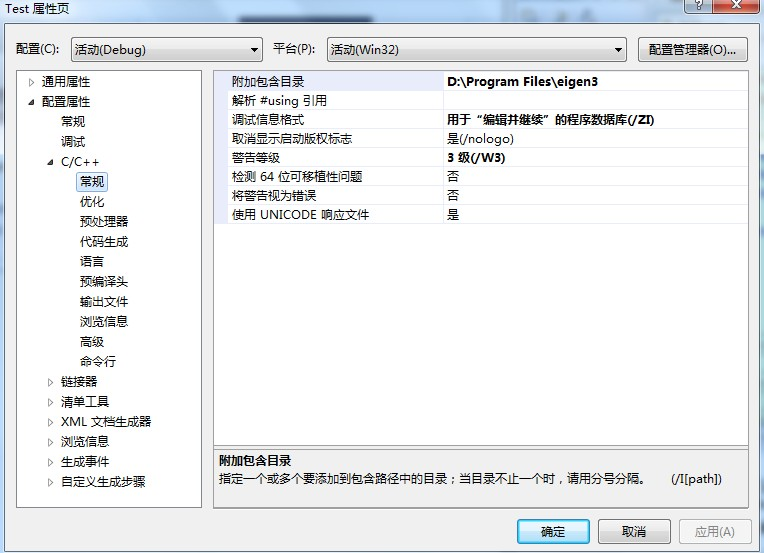
右键 项目属性—》配置属性—》C/C++—》常规—》附加包含目录(对话框右边),在对应条款右侧的编辑框中添加解压的Eigen文件夹完整地址目录即可。(如引用下图)
----------------在QT中配置------------------
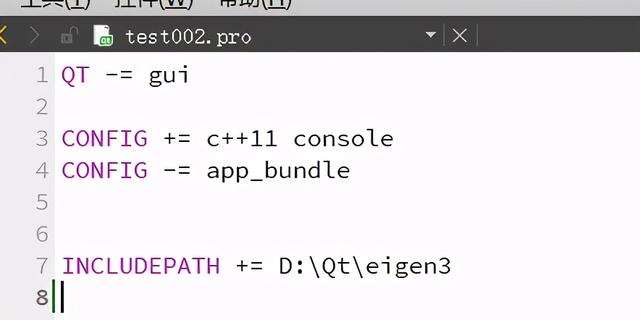
在QT creator中新建控制台应用项目,在define bulid system中选择qmake,下一步选择MinGW构建套件。完成项目创建后,在项目下的pro文件中添加:INCLUDEPATH += D:\Program Files\eigen3,如下图:
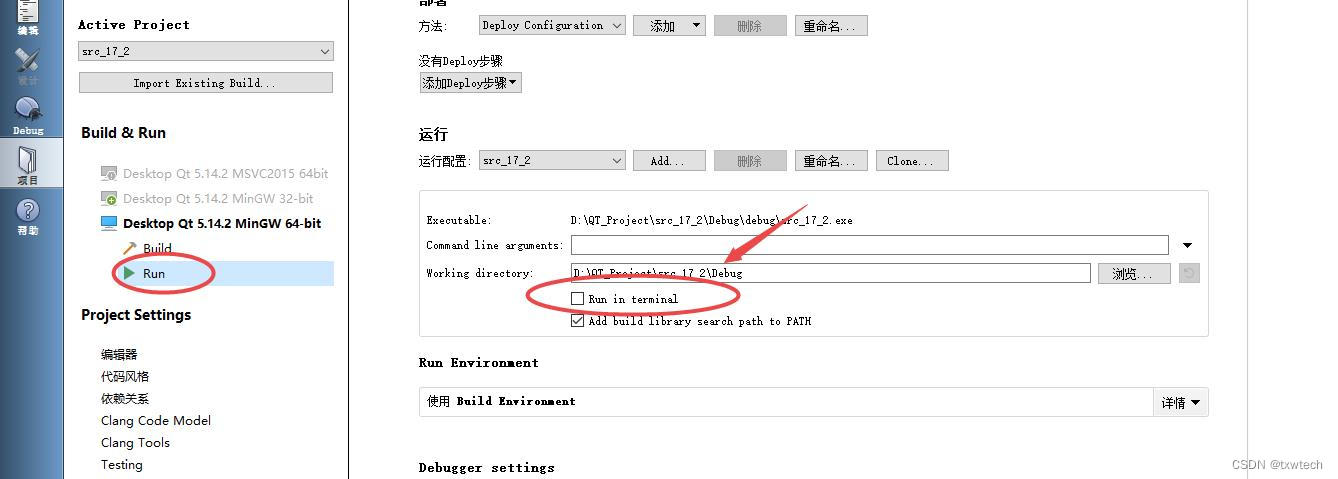
PS:要在命令窗口中显示结果,需要设置:左侧菜单栏项目–》运行–》勾选在终端运行 即可。
二. 使用
(1)Eigen库的引用–一个栗子
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
//typedef Eigen::MatrixXd Matrix;
//typedef Eigen::VectorXd Vector;
using namespace Eigen;
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
// Matrix m(3,3);
MatrixXd m(3,3);
m<<1,2,3,
4,5,6,
7,8,9;
// Vector v(3);
VectorXd v(3);
v<<1,2,3;
Vector3d w(11,22,33);
// cout<<"m*v=\n"<<m*v<<endl;
// cout<<m.block(0,0,2,2)<<endl; //取子块
// cout<<m.block<2,2>(0,0)<<endl; // 与上等价
// cout<<m.row(2)<<endl; //取第2行
// m.row(2)<<11,12,13; //第2行赋值
// cout<<m.row(2)<<endl;
// MatrixXd mm;
// mm=m;
// cout<<mm<<endl;
Eigen::Matrix<int, 3, 4> mat1;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, Dynamic> mat2;
Eigen::Matrix2cd mat3;
return a.exec();
}
(2)矩阵的定义
矩阵模板函数中一共包含六个模板参数,前三个是比较常用的,分别表示矩阵元素的类型、行数、列数。在矩阵定义的时候可以使用 Dynamic 来表示行或者列数未知。
template<typename _Scalar, int _Rows, int _Cols, int _Options, int _MaxRows, int _MaxCols>
class Eigen::Matrix< _Scalar, _Rows, _Cols, _Options, _MaxRows, _MaxCols >
Eigen::Matrix<int, 3, 4> mat1; // 3x4 的 int 类型的矩阵 mat1
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, Dynamic> mat2; // 3x? 的 double 类型的矩阵 mat2
Eigen::Matrix<float, Dynamic, 4> mat3; // ?x4 的 float 类型的矩阵 mat3
Eigen::Matrix<long, Dynamic, Dynamic> mat4; // ?x? 的 long 类型的矩阵 mat4
在 Eigen 中 typedef 了很多矩阵的类型,通常命名为 Matrix 前缀加一个长度为 1∼4的字符串 S 的命名——MatrixS。其中 S 可以用来判断该矩阵类型,数字 n 表示 n ∗ n,n 的范围是2∼4,字母 d、f、i、c 表示 double、float、int、complex,另外 X 表示行或者列数未知的矩阵。
typedef Matrix<std::complex<double>, 2, 2> Eigen::Matrix2cd; // 2x2 的 cd 类型的矩阵
typedef Matrix<double, 2, 2> Eigen::Matrix2d; // 2x2 的 d 类型的矩阵
typedef Matrix<std::complex<double>, 2, Dynamic> Eigen::Matrix2Xcd; // 2x? 的 cd 类型的矩阵
typedef Matrix<std::complex<float>, Dynamic, 2> Eigen::MatrixX2cf; // ?x2 的 cf 类型的矩阵
typedef Matrix<std::complex<double>, Dynamic, Dynamic> Eigen::MatrixXcd;// ?x? 的 cd 类型的矩阵
typedef Matrix<int, Dynamic, Dynamic> Eigen::MatrixXi; // ?x? 的 i 类型的矩阵
- 说明1 :行/列优先。Eigen库中的矩阵默认存储是列优先的,和matlab很相似,而在C++中的存储方式是行优先,如果为了不搞混,可以使用矩阵模板中的第四个参数(默认是 ColMajor),关于行/列优先可参考https://blog.csdn.net/shenck1992/article/details/50041777
Matrix<int, 5, 6, RowMajor> matRow; // 行优先的 5x6 的 int 类型矩阵
- 说明2:静/动态矩阵。动态矩阵是Eigen 中可以用 Dynamic 表示行或者列数未知,如果定义一个矩阵时并不能确定矩阵的大小,只有在运行时才可以确定大小进行动态分配,而静态矩阵是在定义时便明确给定了行数以及列数,在编译时就可以分配好内存。
MatrixXd m = MatrixXd::Random(3,3);
Matrix3d m = Matrix3d::Random();
MatrixXd表示任意大小的元素类型为double的矩阵变量,其大小在运行时被赋值后才能知道;MatrixXd::Random(3,3)表示产生一个元素类型为double的33的临时矩阵对象。
Matrix3d表示元素类型为double大小为33的矩阵变量,其大小在编译时就知道。
(3)矩阵访问/赋值
======================矩阵元素、块访问,矩阵赋值===================
x = mat(a, b); // 获取到矩阵 mat 的 a 行 b 列的元素并赋值给 x
mat(b, a) = x; // 将 x 赋值给矩阵 mat 的 b 行 a 列
mat1 = mat2; // 将矩阵 mat2 赋值(拷贝)给矩阵 mat1
mat = mat1.block(i, j, p, q); // 从矩阵 mat1 的 i 行 j 列开始获取一个 p 行 q 列的子矩阵
mat = mat1.block<p, q>(i, j); // 从矩阵 mat1 的 i 行 j 列开始获取一个 p 行 q 列的子矩阵(动态矩阵)
mat = mat1.row(i); // 获取 mat1 的第 i 行
mat = mat1.col(j); // 获取 mat1 的第 j 列
Matrix3f m;
m << 1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9;
std::cout << m;
mat.fill(n); // 将 mat 的所有元素均赋值为 n
看如下例子:
MatrixXd m(2, 2); //MatrixXd表示是任意尺寸的矩阵ixj, m(2,2)代表一个2x2的方块矩阵
m(0, 0) = 3; //代表矩阵元素a11
m(1, 0) = 2.5; //a21
m(0, 1) = -1; //a12
m(1, 1) = m(1, 0) + m(0, 1);//a22=a21+a12
cout << "m="<<endl<<m << endl;//输出矩阵m
cout << "m(2)="<<m(2) << endl; //这里注意,这里的二维数组是列优先,m(2)取得是第二列第一行的数
输出结果:

(4)矩阵计算
//=====================================加减法=============================================
Matrix2d a;//这里直接定义的a是个2*2的方阵
a << 1, 2,
3, 4;
MatrixXd b(2, 2);
b << 2, 3,
1, 4;
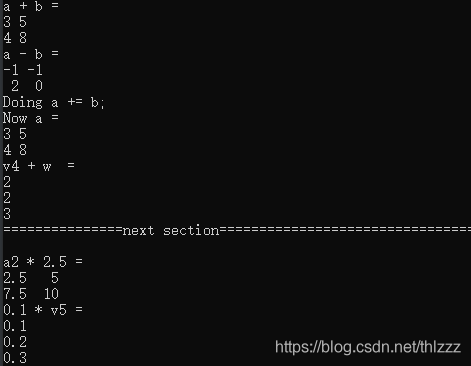
cout << "a + b =\n" << a + b << endl;//矩阵加法
cout << "a - b =\n" << a - b << endl;//矩阵减法
cout << "Doing a += b;" << endl;
a += b;//a = a + b,同时重新赋值a
cout << "Now a =\n" << a << endl;
Vector3d v4(1, 2, 3);
Vector3d w(1, 0, 0);
cout << "v4 + w =\n" << w + v4 << endl;//向量加减法
cout << "===============next section===============================================" << endl << endl;
//=================================矩阵数乘===============================================
Matrix2d a2;
a2 << 1, 2,
3, 4;
Vector3d v5(1, 2, 3);
cout << "a2 * 2.5 =\n" << a2 * 2.5 << endl;//矩阵数乘
cout << "0.1 * v5 =\n" << 0.1 * v5 << endl;//向量数乘
//====================================矩阵/向量乘法========================================
Matrix2d m4;
m4 << 1, 2,
3, 4;
Vector2d u6(-1, 1), v6(2, 0);
cout << "Here is m4*m4:\n" << m4 * m4 << endl;//矩阵-矩阵
cout << "Here is m4*u6:\n" << m4 * u6 << endl;//矩阵-向量
cout << "Here is u6^T*m4:\n" << u6.transpose()*m4 << endl;//向量-矩阵
cout << "Here is u6^T*v6:\n" << u6.transpose()*v6 << endl;//向量-向量
cout << "Here is u6*v6^T:\n" << u6 * v6.transpose() << endl;//向量-向量
cout << "===============next section===============================================" << endl << endl;

//==============================转置,共轭,伴随以及逆矩阵=======================================
MatrixXcf a3 = MatrixXcf::Random(2, 2);//定义2-by-2随机矩阵
cout << "Here is the matrix a3\n" << a3 << endl;//矩阵a3
cout << "Here is the matrix a3^T\n" << a3.transpose() << endl;//a3的转置
cout << "Here is the matrix a3^H\n" << a3.conjugate() << endl;//a3的共轭
cout << "Here is the adjoint of a3\n" <<a3.adjoint( << endl;//a3的伴随矩阵
cout << "Here is the matrix a3^{-1}\n" << a3.inverse() << endl;//a3的逆
cout << "===============next section===============================================" << endl << endl;
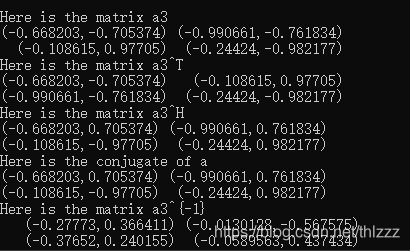
ps:伴随矩阵图片结果有问题,请自动忽略。
//=====================================点乘/叉乘============================================
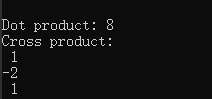
Vector3d v7(1, 2, 3);
Vector3d w7(0, 1, 2);
cout << "Dot product: " << v7.dot(w7) << endl;//向量点乘
cout << "Cross product:\n" << v7.cross(w7) << endl;//向量叉乘
cout << "===============next section===============================================" << endl << endl;
//==================================== 其他功能==============================================
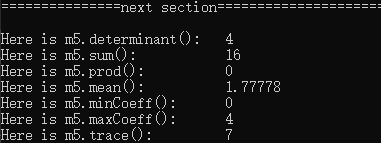
Matrix3d m5;
m5 << 1, 2, 3,
1, 2, 1,
0, 2, 4;
cout << "Here is m5.determinant(): " << m5.determinant() << endl;// 行列式
cout << "Here is m5.sum(): " << m5.sum() << endl;//所有元素之和
cout << "Here is m5.prod(): " << m5.prod() << endl;//所有元素之积
cout << "Here is m5.mean(): " << m5.mean() << endl;//元素的平均数
cout << "Here is m5.minCoeff(): " << m5.minCoeff() << endl;//最小元素
cout << "Here is m5.maxCoeff(): " << m5.maxCoeff() << endl;//最大元素
cout << "Here is m5.trace(): " << m5.trace() << endl;//迹(对角元素之和)
cout << "===============next section===============================================" << endl << endl;
当前矩阵的行数、列数、大小可以通过rows(),cols()和size()来获取,上面用“=”改变矩阵大小的方式除此之外,对于动态矩阵可以通过resize()函数来动态修改矩阵的大小.
需注意:
(1) 固定大小的矩阵是不能使用resize()来修改矩阵的大小;
(2) resize()函数会析构掉原来的数据,因此调用resize()函数之后将不能保证元素的值不改变。
//==================================== 矩阵改变大小============================================
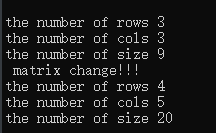
MatrixXd m6(3,3);
cout << " the number of rows " << m6.rows() << endl;
cout << " the number of cols " << m6.cols() << endl;
cout << " the number of size " << m6.size() << endl;
m6.resize(4, 5);
cout << "matrix change!!!" << endl;
cout << " the number of rows " << m6.rows() << endl;
cout << " the number of cols " << m6.cols() << endl;
cout << " the number of size " << m6.size() << endl;
参考资料
- http://www.360doc.com/content/20/1230/15/277688_954383797.shtml
- https://blog.csdn.net/thlzzz/article/details/110451022
- https://blog.csdn.net/txwtech/article/details/126090883